8.11 树论+分块
P3320 [SDOI2015] 寻宝游戏
题意相当于是让你动态维护一个点集的最小生成树的边权和
一个结论:如果我们让所有节点按照
这里钦定
考虑证明:连通后的子树 每条边在
得到结论之后 我们可以用
否则我们减去上面的柿子即可
不开
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define endl '\n'
#define inl inline
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define lson ls,l,mid
#define rson rs,mid+1,r
#define eb emplace_back
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define int long long
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
char buf[1<<24] , *p1 , *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
// #define getchar() cin.get();
int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit(ch) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while ( isdigit(ch) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar(); }
return x * f ;
}
int n , m , vis[N] , dis[N] , ans;
int dep[N] , fa[N] , sz[N] , son[N];
int pos[N] , timer , rev[N] , top[N];
set<int> s;
set<int> :: iterator it;
vector<pii> e[N];
inl void add ( int u , int v , int w ) { e[u].eb(v,w); }
struct LCA
{
void dfs1 ( int u , int f )
{
dep[u] = dep[fa[u] = f] + 1 , sz[u] = 1;
for ( auto [v,w] : e[u] )
if ( v ^ f )
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
dfs1 ( v , u );
sz[u] += sz[v];
if ( sz[son[u]] < sz[v] ) son[u] = v;
}
}
void dfs2 ( int u , int tp )
{
top[u] = tp , pos[u] = ++timer , rev[timer] = u;
if ( son[u] ) dfs2 ( son[u] , tp );
for ( auto [v,w] : e[u] ) if ( v ^ fa[u] && v ^ son[u] ) dfs2 ( v , v );
}
int lca ( int u , int v )
{
while ( top[u] != top[v] )
{
if ( dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]] ) swap ( u , v );
u = fa[top[u]];
}
if ( dep[u] < dep[v] ) swap ( u , v );
return v;
}
}L;
inl int diss ( int u , int v ) { return dis[u] + dis[v] - 2 * dis[L.lca(u,v)]; }
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr) , cout.tie(nullptr);
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 , u , v , w ; i < n ; i ++ ) u = read() , v = read() , w = read() , add ( u , v , w ) , add ( v , u , w );
L.dfs1 ( 1 , 0 ) , L.dfs2 ( 1 , 1 );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ )
{
int x = pos[read()];
if ( !vis[x] ) s.insert(x);
int y = rev[ ( it = s.lower_bound(x) ) == s.begin() ? *--s.end() : *--it ];
int z = rev[ ( it = s.upper_bound(x) ) == s.end() ? *s.begin() : *it ];
int d = diss ( y , rev[x] ) + diss ( rev[x] , z ) - diss ( y , z );
if ( vis[x] ) s.erase(x);
if ( vis[x] ) vis[x] ^= 1 , ans -= d;
else vis[x] ^= 1 , ans += d;
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
P5597 【XR-4】复读
很巧妙的一道题 借用题解中的图:
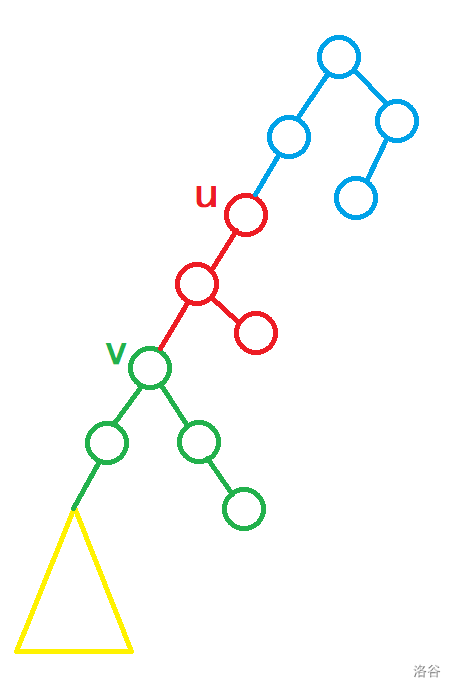
设置运行第一次指令后 机器人走到的点为
因为机器人在根节点运行指令的时候不会跑到根节点上面 所以当机器人在
所以我们的第一次指令必须将
我们将
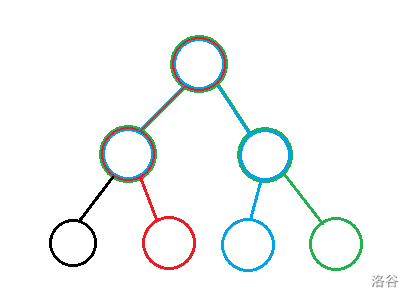
除了根到黑点的路径只需要走一遍 别的路径都需要两遍 这样可以算出指令的长度
那么我们
建新树时也搜索 需要同时保存在原树上的位置和在新树上的位置
如果原树的结点在新树上没有 新建新树结点即可
如果在新树上走到了黑点(
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define endl '\n'
#define inl inline
#define eb emplace_back
const int N = 2e3 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
char buf[1<<24] , *p1 , *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
// #define getchar() cin.get();
int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit(ch) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while ( isdigit(ch) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar(); }
return x * f ;
}
int n , m , rt , tot , totnew , black , blacknew , ans = inf;
struct node { int ls , rs; } t[N] , tnew[N];
void in ( int &u )
{
char ch = cin.get() - '0';
u = ++tot;
if ( ch & 1 ) in ( t[u].ls );
if ( ch & 2 ) in ( t[u].rs );
}
void dfs2 ( int u , int v )
{
if ( u == black || v == blacknew ) { blacknew = v , v = 1; }
if ( t[u].ls )
{
if ( !tnew[v].ls ) tnew[v].ls = ++ totnew;
dfs2 ( t[u].ls , tnew[v].ls );
}
if ( t[u].rs )
{
if ( !tnew[v].rs ) tnew[v].rs = ++ totnew;
dfs2 ( t[u].rs , tnew[v].rs );
}
}
void dfs1 ( int u , int dep )
{
black = u , blacknew = 0;
memset ( tnew , 0 , sizeof tnew );
dfs2 ( 1 , totnew = 1 );
ans = min ( ans , ( totnew - 1 ) * 2 - dep );
if ( t[u].ls ) dfs1 ( t[u].ls , dep + 1 );
if ( t[u].rs ) dfs1 ( t[u].rs , dep + 1 );
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr) , cout.tie(nullptr);
in(rt);
dfs1 ( 1 , 0 );
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
P4168 [Violet] 蒲公英
暴力出奇迹!正解代码留坑()
需要注意的是正常用
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define endl '\n'
#define inl inline
#define eb emplace_back
const int N = 4e4 + 5;
char buf[1<<24] , *p1 , *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
// #define getchar() cin.get();
int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit(ch) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while ( isdigit(ch) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar(); }
return x * f ;
}
int n , m , a[N] , b[N] , lsh[N] , lstans , l , r;
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) lsh[i] = a[i] = read();
sort ( lsh + 1 , lsh + n + 1 );
int sz = unique ( lsh + 1 , lsh + n + 1 ) - lsh - 1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) a[i] = lower_bound ( lsh + 1 , lsh + sz + 1 , a[i] ) - lsh;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= m ; ++ i )
{
l = ( read() + lstans - 1 ) % n + 1 , r = ( read() + lstans - 1 ) % n + 1;
if ( l > r ) swap ( l , r );
for ( int j = l ; j <= r ; ++ j ) ++ b[a[j]];
int ans = 0;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= sz ; ++ j ) if ( b[ans] < b[j] ) ans = j;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= sz ; ++ j ) b[j] = 0;
cout << ( lstans = lsh[ans] ) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
看到
我们可以开两个数组:
对于统计 如果两端的差值小于等于
否则为整块中的众数和散块中的众数的整体统计 我们先将所有的散块加入
答案先设置为整块中的众数 每次枚举散块中的一个数 将
调了一上午 最大的错误
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define endl '\n'
#define inl inline
#define eb emplace_back
const int N = 4e4 + 5;
const int sqrtn = 2e2 + 5;
char buf[1<<24] , *p1 , *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
// #define getchar() cin.get();
int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit(ch) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while ( isdigit(ch) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar(); }
return x * f ;
}
int n , m , a[N] , bel[N] , ll[N] , rr[N] , block , tot , lstans , l , r , cnt[N] , s[sqrtn][N] , f[sqrtn][sqrtn];
vector<int> lsh;
void LSH()
{
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) a[i] = read() , lsh.eb(a[i]);
sort ( lsh.begin() , lsh.end() );
lsh.erase ( unique ( lsh.begin() , lsh.end() ) , lsh.end() );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) a[i] = lower_bound ( lsh.begin() , lsh.end() , a[i] ) - lsh.begin() + 1;
}
void upd ( int x , int y ) { for ( int i = x ; i <= y ; i ++ ) ++ cnt[a[i]]; }
void clear ( int x , int y ) { for ( int i = x ; i <= y ; i ++ ) cnt[a[i]] = 0; }
void init()
{
block = (int)sqrt(n) , tot = n / block;
if ( n % block ) tot ++;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) bel[i] = ( i - 1 ) / block + 1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++ ) ll[i] = ( i - 1 ) * block + 1 , rr[i] = i * block; rr[tot] = n;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++ )
{
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) s[i][a[j]] = s[i-1][a[j]];
for ( int j = ll[i] ; j <= rr[i] ; j ++ ) ++ s[i][a[j]];
}
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++ )
for ( int j = i ; j <= tot ; j ++ )
{
int maxx = f[i][j-1];
for ( int k = ll[j] ; k <= rr[j] ; k ++ )
if ( s[j][a[k]] - s[i-1][a[k]] > s[j][maxx] - s[i-1][maxx] || s[j][a[k]] - s[i-1][a[k]] == s[j][maxx] - s[i-1][maxx] && a[k] < maxx ) maxx = a[k];
f[i][j] = maxx;
}
}
int query ( int x , int y )
{
int xx = bel[x] , yy = bel[y] , maxx = 0;
if ( yy - xx <= 1 )
{
upd ( x , y );
for ( int i = x ; i <= y ; i ++ ) if ( cnt[a[i]] > cnt[maxx] || cnt[a[i]] == cnt[maxx] && a[i] < maxx ) maxx = a[i];
clear ( x , y );
return lsh[maxx-1];
}
upd ( x , rr[xx] ) , upd ( ll[yy] , y );
maxx = f[xx+1][yy-1];
for ( int i = x , tmp , pre ; i <= rr[xx] ; i ++ )
{
pre = cnt[maxx] + s[yy-1][maxx] - s[xx][maxx] , tmp = cnt[a[i]] + s[yy-1][a[i]] - s[xx][a[i]];
if ( tmp > pre || tmp == pre && a[i] < maxx ) maxx = a[i];
}
for ( int i = ll[yy] , tmp , pre ; i <= y ; i ++ )
{
pre = cnt[maxx] + s[yy-1][maxx] - s[xx][maxx] , tmp = cnt[a[i]] + s[yy-1][a[i]] - s[xx][a[i]];
if ( tmp > pre || tmp == pre && a[i] < maxx ) maxx = a[i];
}
clear ( x , rr[xx] ) , clear ( ll[yy] , y );
return lsh[maxx-1];
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , m = read();
LSH() , init();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ )
{
l = ( read() + lstans - 1 ) % n + 1 , r = ( read() + lstans - 1 ) % n + 1;
if ( l > r ) swap ( l , r );
cout << ( lstans = query ( l , r ) ) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
P2801 教主的魔法
第三遍写了......
注意
注意
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define endl '\n'
#define inl inline
#define eb emplace_back
#define int long long
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
char buf[1<<24] , *p1 , *p2;
#define getchar() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#define getchar() cin.get();
int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit(ch) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while ( isdigit(ch) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar(); }
return x * f ;
}
int n , q , block , a[N] , b[N] , l[N] , r[N] , bel[N] , tot;
int add[N];
void init()
{
block = (int)sqrt(n) , tot = n / block;
if ( n % block ) tot ++;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++ ) l[i] = ( i - 1 ) * block + 1 , r[i] = i * block;
r[tot] = n;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) bel[i] = ( i - 1 ) / block + 1 , b[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++ ) sort ( b + l[i] , b + r[i] + 1 );
}
void reset ( int x )
{
for ( int i = l[x] ; i <= r[x] ; i ++ ) b[i] = a[i];
sort ( b + l[x] , b + r[x] + 1 );
}
void upd ( int x , int y , int w )
{
int xx = bel[x] , yy = bel[y];
if ( xx == yy )
{
for ( int i = x ; i <= y ; i ++ ) a[i] += w;
reset(xx); return;
}
for ( int i = x ; i <= r[xx] ; i ++ ) a[i] += w;
for ( int i = l[yy] ; i <= y ; i ++ ) a[i] += w;
reset(xx) , reset(yy);
for ( int i = xx + 1 ; i <= yy - 1 ; i ++ ) add[i] += w;
}
int query ( int x , int y , int w )
{
int xx = bel[x] , yy = bel[y] , res = 0;
if ( xx == yy )
{
for ( int i = x ; i <= y ; i ++ ) res += ( a[i] + add[xx] >= w );
return res;
}
for ( int i = x ; i <= r[xx] ; i ++ ) res += ( a[i] + add[xx] >= w );
for ( int i = l[yy] ; i <= y ; i ++ ) res += ( a[i] + add[yy] >= w );
for ( int i = xx + 1 ; i <= yy - 1 ; i ++ ) res += r[i] - ( lower_bound ( b + l[i] , b + r[i] + 1 , w - add[i] ) - b - 1 );
return res;
}
char ch;
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr) , cout.tie(nullptr);
n = read() , q = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) a[i] = read();
init();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= q ; i ++ )
{
cin >> ch;
int l = read() , r = read() , w = read();
if ( ch == 'M' ) upd ( l , r , w );
else cout << query ( l , r , w ) << endl;
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!