YbtOJ 「数学基础」 第2章 质数和约数
质数和约数
线性筛
void getprime ( int lim )
{
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= lim ; i ++ )
{
if ( !isntprime[i] ) prime[++cnt] = i;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= cnt && i * prime[j] <= lim ; j ++ )
{
isntprime[i*prime[j]] = 1;
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
}
算术基本定理
正整数\(n\)可以唯一分解成有限个质数的乘积\(n=p_1^{c_1}+p_2^{c_2}+\dots +p_m^{c_m}\) 其中\(c_i\)都是正整数
算术基本定理的推论
正整数\(n\)的正约数个数:\((c_1 + 1) * (c_2 + 1) * ... * (c_m + 1) = \prod_{i=1}^{m}(c_i + 1)\) 其中加的\(1\)表示质数\(p_i\)的\(0\)次方
最大公约数和最小公倍数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gcd ( int a , int b )
{
if ( a % b == 0 ) return b;
else return gcd ( b , a % b );
}
int main()
{
int a , b;
scanf ( "%d%d" , &a , &b );
printf ( "%d\n" , gcd ( a , b ) );//最大公约数
printf ( "%d\n" , a * b / gcd ( a , b ) ); //最小公倍数
return 0;
}
A. 【例题 1】线性筛素数
线性筛板子题
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e8 + 5;
#define endl '\n'
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , q;
int prime[N] , isntprime[N] , cnt;
void getprime ( int lim )
{
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= lim ; i ++ )
{
if ( !isntprime[i] ) prime[++cnt] = i;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= cnt && i * prime[j] <= lim ; j ++ )
{
isntprime[i*prime[j]] = 1;
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , q = read(); getprime(n);
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= q ; i ++ ) cout << prime[read()] << endl;
return 0;
}
B. 【例题2】质数距离
显然对于任意一个合数\(n\) 它一定有一个不超过\(\sqrt n\)的质因子 所以对于一个质数\(p\) \(i*p\)就是一个合数 所以我们可以预先处理出\([2,\sqrt R]\)的的所有质数
再通过这些质数去筛出\([L,R]\)之间的所有合数 而区间内没有被筛到的就是质数
注意循环条件需要严格保证 \(j*prime[i]\)覆盖了\([l,r]\)区间内的所有值 如果直接\(l/prime[i]\)的话 有可能会下取整 导致\(j\)的下界变大 覆盖范围变大导致出错
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e7 + 5;
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , q;
int prime[N] , isntprime[N] , cnt;
void getprime ( int lim )
{
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= lim ; i ++ )
{
if ( !isntprime[i] ) prime[++cnt] = i;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= cnt && i * prime[j] <= lim ; j ++ )
{
isntprime[i*prime[j]] = 1;
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
}
int l , r , num[N] , cntt;
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
getprime((int)sqrt(2147483647));
while ( cin >> l >> r )
{
memset ( isntprime , 0 , sizeof isntprime );
cntt = 0;
if ( l == 1 ) l ++;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= cnt ; i ++ )
for ( int j = ( l - 1 ) / prime[i] + 1 ; j <= r / prime[i] ; j ++ )
if ( j > 1 ) isntprime[j*prime[i]-l] = 1;
for ( int i = l ; i <= r ; i ++ ) if ( !isntprime[i-l] ) num[++cntt] = i;
if ( cntt < 2 ) cout << "There are no adjacent primes." << endl;
else
{
int maxx1 = num[1] , maxx2 = num[2] , maxx = num[2] - num[1];
int minn1 = num[1] , minn2 = num[2] , minn = num[2] - num[1];
for ( int i = 3 ; i <= cntt ; i ++ )
{
if ( num[i] - num[i-1] > maxx ) maxx = num[i] - num[i-1] , maxx1 = num[i-1] , maxx2 = num[i];
if ( num[i] - num[i-1] < minn ) minn = num[i] - num[i-1] , minn1 = num[i-1] , minn2 = num[i];
}
cout << minn1 << ',' << minn2 << " are closest, " << maxx1 << ',' << maxx2 << " are most distant." << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. 【例题3】不定方程
\(y=\frac {xn!} {x-n!}\) 那么我们设\(t=x-n!\) 那么\(x=t+n!\) 得到\(y=n!+\frac{{(n!)}^2}{t}\)
因为\(n\)和\(y\)都是整数 所以\(t\)一定是\({(n!)}^2\)的约数
我们知道对于一个合数\(n\)的约数个数是\(\prod_{i=1}^m (c_i+1)\)
那么\(n^2\)的约数个数就是\(\prod_{i=1}^m (c_i*2+1)\) (因为去掉了\(n*n\)计算了两次的情况)
解的个数就是\(t\)的个数
那么对于阶乘来说 \(c\)的求法如下
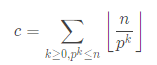
所有质数都是\(n!\)的质因子 那么这个质数的一次方 二次方或者多次方(在n的范围内)的出现次数之和就是质数\(prime[i]\)的出现次数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
const int N = 1e8 + 1;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , cnt , prime[5800001];
bool isntprime[N];
void getprime ( int lim )
{
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= lim ; i ++ )
{
if ( !isntprime[i] ) prime[++cnt] = i;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= cnt && i * prime[j] <= lim ; j ++ )
{
isntprime[i*prime[j]] = 1;
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
}
int c[N];
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read(); getprime(n);
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= cnt ; i ++ )
for ( int j = prime[i] ; j <= n ; j *= prime[i] )
c[i] += n / j , c[i] %= mod;
int ans = 1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= cnt ; i ++ ) ans = ( ans * ( c[i] * 2 + 1 ) ) % mod;
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
D. 【例题4】反素数
性质1:\(1-N\)中任何的不同质因子都不会超过\(10\)个,且所有质因子的指数总和不超过\(30\)。
证明:\(2^{31}\)就爆\(int\)了 而且前十个质数乘积已经超过了\(int\)的上限
性质2:正整数唯一分解定理中的质数底都是连续的 指数都是单调递减的
证明:根据正整数唯一分解定理 我们如果确定了一个\(c[i]\)(正整数分解的指数)集合 那么这个数的约数个数就确定了 是\(\prod_{i=1}^n(c[i]+1)\)
我们要将这些指数分配到一些质数上 所以取前\(n\)个最小的质数并将这里的约数从大到小排列 就可以构造出一个最小的质数
\(dfs\)中四个数为: 当前数大小 当前到了第几个质数 当前的约数个数和 上一个的次数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int pri[] = {0,2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31};
int n , k , ans , best;
void dfs ( int val , int pos , int cnt , int lim )
{
if ( pos > 11 ) return;
if ( cnt > best || ( cnt == best && val < ans ) ) ans = val , best = cnt;
for ( int i = 0 ; i <= lim ; i ++ )//取等原因:先dfs后更新权值 有可能最后lim没更新
{
if ( val > n ) break;
dfs ( val , pos + 1 , cnt * ( i + 1 ) , i );
val *= pri[pos];
}
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read();
dfs ( 1 , 1 , 1 , 30 );
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
E. 【例题5】余数之和
整除分块模板题 我们对于\(\lfloor \frac n i \rfloor\)最多只有\(2\sqrt n\)种取值
我们分情况讨论:
当 \(i>n\)时 只有一种取值0
当 \(0<i<\sqrt n\) 最多只有\(\sqrt n\)种取值
当 \(\sqrt n \le i \le n\)时 最多有\(\sqrt n\)种取值
所以最多分成\(2\sqrt n\)块(加一无所谓)
对于本题 \(ans=\sum_{i=1}^n k \% i\)
首先知道\(k\% i\)可以表示为\(k-i*\lfloor \frac k i \rfloor\)
所以\(ans=\sum_{i=1}^n k-i*\lfloor \frac k i \rfloor=n\times k -\sum_{i=1}^n i*\lfloor \frac k i \rfloor\)
每个段的段长:\(r-l+1\) 每个段的区间和:\((l+r)/2\)
对于\(/2\)的下取整问题:如果区间左右端点相加为偶数 例如\(3+5\) \(4+6\)则区间长度必为奇数 如果相加为奇数 区间长度必为偶数 那么\(/2\)后不会造成下取整的答案损失
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
const int N = 1e7 + 5;
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , k , ans;
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , k = read();
ans = n * k;
for ( int l = 1 , r ; l <= n ; l = r + 1 )
{
if ( k / l != 0 ) r = min ( k / ( k / l ) , n );
else r = n;
ans -= ( l + r ) * ( k / l ) * ( r - l + 1 ) / 2;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}

