YbtOJ 「基础算法」 第5章 广度搜索
广搜
A. 【例题1】走迷宫图
[题目描述]
现在有一个
[输入格式]
第一行一个正整数
接下来
最后一行四个整数
[输出格式]
仅有一个数,表示答案。
[算法分析]
广搜裸题 注意check的时候要判断障碍
[代码实现]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define inl inline
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int dx[5] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 };
const int dy[5] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 };
inl int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar (); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar (); }
return x * f;
}
int n , sx , sy , tx , ty , vis[N][N] , dep[N][N];
struct node { int x , y; };
char ch;
int check ( int x , int y ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= n && !vis[x][y]; }
void bfs()
{
queue <node> q;
q.push ( (node) { sx , sy } );
dep[sx][sy] = 0 , vis[sx][sy] = 1;
while ( !q.empty() )
{
int x = q.front().x , y = q.front().y; q.pop();
if ( x == tx && y == ty ) { printf ( "%d" , dep[x][y] ); return; }
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i ++ )
{
int xx = x + dx[i] , yy = y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( xx , yy ) ) continue;
dep[xx][yy] = dep[x][y] + 1;
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push ( (node) { xx , yy } );
}
}
}
signed main ()
{
n = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
cin >> ch , vis[i][j] = ch - '0';
sx = read() , sy = read() , tx = read() , ty = read();
bfs();
return 0;
}
B. 【例题2】山峰山谷
[题目描述]
给定一个
定义山峰山谷如下:
均由地图上的一个联通块组成。
所有方格高度都相同。
周围的方格(即不属于山峰或山谷但与山峰或山谷相邻的格子)高度均大于山谷的高度,或小于山峰的高度。
求地图内山峰和山谷的数量。特别的,如果整个地图方格的高度均相同,则整个地图即是一个山谷,也是一个山峰.
[输入格式]
第一行一个正整数
接下来
[输出格式]
输出一行两个整数,分别表示山峰和山谷的数量。
[算法分析]
对于每一个联通块进行一次广搜并标记
如果搜到了边界 如果这个边界值大于联通块值 那么这个联通块不可能是山峰 山谷也同理
最后输出山峰联通块个数和山谷联通块个数即可
[代码实现]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define inl inline
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int dx[9] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 , 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };
const int dy[9] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 , -1 , 1 , -1 , 1 };
inl int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar (); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar (); }
return x * f;
}
int n , sx , sy , tx , ty , w[N][N] , vis[N][N] , not_up , not_down , cnt_up , cnt_down;
inl int check ( int x , int y ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= n; }
void bfs ( int sxx , int syy , int val )
{
not_up = 0 , not_down = 0;
queue < pii > q;
q.push ( make_pair ( sxx , syy ) );
vis[sxx][syy] = 1;
while ( !q.empty() )
{
int x = q.front().fi , y = q.front().se; q.pop();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 8 ; i ++ )
{
int xx = x + dx[i] , yy = y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( xx , yy ) ) continue;
if ( !vis[xx][yy] && val == w[xx][yy] )
{
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push ( make_pair(xx,yy) );
}
if ( w[xx][yy] > val ) not_up = 1;
if ( w[xx][yy] < val ) not_down = 1;
}
}
if ( !not_up ) cnt_up ++;
if ( !not_down ) cnt_down ++;
}
signed main ()
{
n = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
cin >> w[i][j];
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
if ( !vis[i][j] ) bfs(i,j,w[i][j]);
printf ( "%d %d" , cnt_up , cnt_down );
return 0;
}
C. 【例题3】荆轲刺秦
[题目描述]
时隔数年,刺客荆轲再次来到咸阳宫,试图刺杀嬴政。
咸阳宫的地图可以描述为一个
- 起点,也就是荆轲的所在点,在地图中用字符
S代表。 - 终点,也就是嬴政的所在点,在地图中用字符
T代表。 - 卫兵,在地图中用一个正整数
- 空地,在地图中用字符
.代表。
荆轲的正常移动方式为每秒向八连通的任意方向前进一格。如下图,中间的点为荆轲当前所在点,每一秒,他可以走向其余的八个点。
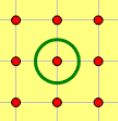
需要注意的是,正常移动时,荆轲不能踏进任何一个有卫兵或者卫兵能观察到的格子。当然,他也不能走出咸阳宫,也就是说,无论何时,荆轲的坐标
荆轲还有两种技能:隐身和瞬移。
- 隐身:下一秒荆轲进入隐身状态,卫兵观察不到荆轲,荆轲可以进入卫兵的观察范围内,但仍然不能进入卫兵所在的格子。注意这个状态只能维持一秒。
- 瞬移:荆轲下一秒移动的距离改为
在本题中,两种技能可以同时使用,而且不考虑冷却时间,即一次用完可以立即用下一次,两种技能都分别有使用次数限制,你也可以不用完所有次数。
现在给出咸阳城的地图,请计算荆轲到达秦王所在点所需的最短时间。此外,在所用时间相同情况下,荆轲希望使用的两种技能总次数尽可能少;在所用时间与技能次数相同情况下,荆轲希望使用的隐身次数尽可能少。
[输入格式]
第一行五个整数
接下来 S、T、. 或者一个正整数
[输出格式]
若荆轲无法到达秦王所在点,则输出一行一个
否则输出一行三个整数
[算法分析]
首先考虑如何处理士兵能观察到的范围(例:k=3)
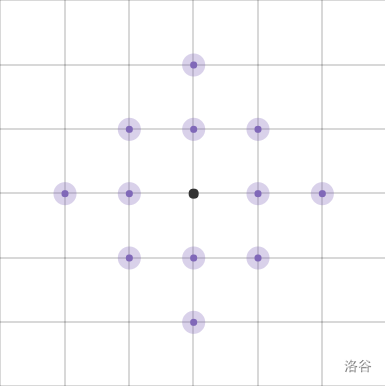
那么考虑差分 对于每一行来说 菱形的最左点位置加一 菱形的最右点+1的位置减一
每次bfs中四种情况:
- 不隐形不瞬移
- 隐形不瞬移
- 瞬移不隐形
- 隐形又瞬移
设一个四元组
[代码实现]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define inl inline
using namespace std;
const int N = 355;
const int inf = 233333333;
const int dx[9] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 , 0 , 1 , -1 , -1 , 1 };
const int dy[9] = { 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 , 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };
inl int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar (); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar (); }
return x * f;
}
int c1 , c2 , n , m , d , mp[N][N] , tag[N][N];
int sx , sy , tx , ty;
bool vis[N][N][20][20],look[N][N];//vis是走没走过(xy坐标,隐形,瞬移),look是能不能看到
string s;
struct qwq
{
int x , y , yx , sy , s;
//x,y——对应的坐标
//s——走到这一步的步数
//yx——隐形使用次数
//sy——瞬移使用次数
}ans;
void lookaround ( int x , int y , int k )
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i <= k ; i ++ )
{
tag[min(x+i,n)][max(y-(k-i),1)] ++;
tag[min(x+i,n)][min(y+(k-i),m)+1] --;
tag[max(x-i,1)][max(y-(k-i),1)] ++;
tag[max(x-i,1)][min(y+(k-i),m)+1] --;
}//(k-i)是另一个坐标的曼哈顿步数
}
qwq minn ( qwq x , qwq y )
{
if ( x.s != y.s ) return x.s < y.s ? x : y;
if ( x.yx + x.sy != y.yx + y.sy ) return x.yx + x.sy < y.yx + y.sy ? x : y;
return x.yx < y.yx ? x : y;
}
int check ( int x , int y ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m && mp[x][y] <= 0; }
queue <qwq> q;
void bfs()
{
q.push ( (qwq) { sx , sy , 0 , 0 , 0 } );
vis[sx][sy][0][0] = 1;
while ( !q.empty() )
{
qwq tmp = q.front(); q.pop();
if ( tmp.s > ans.s ) continue;
if ( tmp.x == tx && tmp.y == ty )
{ ans = minn ( ans , tmp ); continue; }
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 8 ; i ++ )//瞬移
{
int xx = tmp.x + dx[i] , yy = tmp.y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( xx , yy ) ) continue;
if ( look[xx][yy] )
{
if ( vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx+1][tmp.sy] || tmp.yx + 1 > c1 ) continue;
vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx+1][tmp.sy] = 1;
q.push ( (qwq) { xx , yy , tmp.yx + 1 , tmp.sy , tmp.s + 1 } );
}
else
{
if ( vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx][tmp.sy] ) continue;
vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx][tmp.sy] = 1;
q.push ( (qwq) { xx , yy , tmp.yx , tmp.sy , tmp.s + 1 } );
}
}
if ( tmp.sy + 1 > c2 ) continue;//瞬移用不了了
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i ++ )//不瞬移
{
int xx = tmp.x + dx[i] * d , yy = tmp.y + dy[i] * d;
if ( !check ( xx , yy ) ) continue;
if ( look[xx][yy] )
{
if ( vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx+1][tmp.sy+1] || tmp.yx + 1 > c1 ) continue;
vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx+1][tmp.sy+1] = 1;
q.push ( (qwq) { xx , yy , tmp.yx + 1 , tmp.sy + 1 , tmp.s + 1 } );
}
else
{
if ( vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx][tmp.sy+1] ) continue;
vis[xx][yy][tmp.yx][tmp.sy+1] = 1;
q.push ( (qwq) { xx , yy , tmp.yx , tmp.sy + 1 , tmp.s + 1 } );
}
}
}
}
int main ()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &c1, &c2, &d);
ans = { 0 , 0 , inf , inf , inf };
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ )
{
cin >> s;
if ( s[0] == 'S' ) sx = i , sy = j , mp[i][j] = -1;
else if ( s[0] == 'T' ) tx = i , ty = j , mp[i][j] = -2;
else if ( s[0] == '.' ) mp[i][j] = 0;
else
{
int x = 0;
for ( int p = 0 ; p < s.size() ; p ++ ) x = x * 10 + ( s[p] - '0' );
mp[i][j] = x;
lookaround ( i , j , x - 1 );
}
}
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
int sum = 0;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ )
{
sum += tag[i][j];
if ( sum > 0 ) look[i][j] = 1;
}
}
bfs();
if ( ans.s == inf ) printf ( "-1" );
else printf ( "%d %d %d" , ans.s , ans.yx , ans.sy );
return 0;
}
D. 【例题4】电路维修
[题目描述]
有一种正方形的电路原件,在它的两组相对顶点中,有一组会用导线连接起来,另一组则不会。
有 这样的原件,你想将其排成
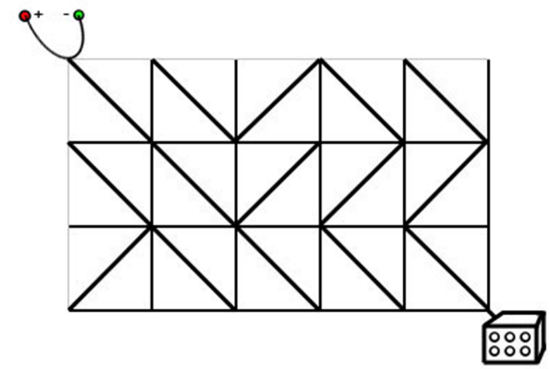
试求:至少要旋转多少个正方形元件才能让电源与灯泡联通,若无解则输出 NO SOLUTION。
[输入格式]
有多组测试数据。
一行为测试数据组数,以下每组测试数据描述为:
一行有两个整数
接下来的\ 或 /,表示正方形元件上导线的连接方向。
[输出格式]
每组测试数据输出描述:
输出共一行,若有解则输出一个整数,表示至少要旋转多少个正方形元件才能让电源与灯泡联通;若无解则输出 NO SOLUTION。
[算法分析]
数组大小!!!!!!!wssb
考虑dijkstra最短路 将每一个题中给定的的路径边权设置为0 将每一个需要旋转才能到达的边设置为1 建立双向边 那么跑最短路即可
[代码实现]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define inl inline
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mkp make_pair
#define pii pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
const int M = 500 + 5;
const int N = M * M + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inl int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar (); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar (); }
return x * f;
}
int n , m , tot , mark[M][M];
char s[M][M];
struct node { int to , nxt , w; } e[N<<4];
int head[N] , cnt;
void add ( int u , int v , int w ) { e[++cnt] = { v , head[u] , w } , head[u] = cnt; }
int dis[N];
priority_queue < pii , vector<pii> , greater<pii> > q;
void dij ( int s )
{
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= (m+1) * (n+1); i ++ ) dis[i] = inf;
dis[s] = 0;
q.push ( mkp ( 0 , s ) );
while ( !q.empty() )
{
int u = q.top().se , f = q.top().fi; q.pop();
if ( f != dis[u] ) continue;
for ( int i = head[u] ; i ; i = e[i].nxt )
{
int v = e[i].to;
if ( dis[v] > dis[u] + e[i].w )
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + e[i].w;
q.push ( mkp(dis[v],v) );
}
}
}
}
void init()
{
memset ( head , 0 , sizeof ( head ) );
cnt = tot = 0;
}
signed main ()
{
int T = read();
while ( T -- )
{
init();
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n + 1 ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m + 1 ; j ++ )
mark[i][j] = ++tot;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ )
{
cin >> s[i][j];
if ( s[i][j] == '/' )
{
add ( mark[i][j] , mark[i+1][j+1] , 1 );
add ( mark[i+1][j+1] , mark[i][j] , 1 );
add ( mark[i+1][j] , mark[i][j+1] , 0 );
add ( mark[i][j+1] , mark[i+1][j] , 0 );
}
else
{
add ( mark[i][j] , mark[i+1][j+1] , 0 );
add ( mark[i+1][j+1] , mark[i][j] , 0 );
add ( mark[i+1][j] , mark[i][j+1] , 1 );
add ( mark[i][j+1] , mark[i+1][j] , 1 );
}
}
dij ( mark[1][1] );
if ( dis[mark[n+1][m+1]] == inf ) printf ( "NO SOLUTION\n" );
else printf ( "%d\n" , dis[mark[n+1][m+1]] );
}
return 0;
}
E. 【例题5】逃离噩梦
[题目描述]
给定一张
字符 . 表示道路,字符 X 表示墙,字符 M 表示男孩的位置,字符 G 表示女孩的位置,字符 Z 表示鬼的位置。
男孩每秒可以移动
每个鬼占据的区域每秒可以向四周扩张
注意:每一秒鬼会先扩展,扩展完毕后男孩和女孩才可以移动。
求在不进入鬼的占领区的前提下,男孩和女孩能否回合,若能回合,求出最短会和时间。
[输入格式]
第一行包含整数
每组测试用例第一行包含两个整数
接下来
注意:地图中一定有且仅有
[输出格式]
每个测试用例输出一个整数
如果无法会合则输出 -1。
每个结果占一行。
[算法分析]
每一次枚举男孩和女孩 更新此时队列中男女的所有点(这时候的队列中男女所有点就是这一个时刻 男女分别能到达什么地方 将扩展后的路径记录)
一旦男/女走到了路径重合处 那么返回time
要看清check的是xx还是t.x 并要注意清零cnt
[代码实现]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define inl inline
const int N = 810;
const int dx[5] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 };
const int dy[5] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 };
inl int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = getchar (); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = getchar (); }
return x * f;
}
struct point {
int x, y;
}b,g,gui[3];
int n , m , cnt , mp[N][N];
char ch;
bool check ( int x , int y , int tim )
{
if ( x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x > n || y > m || mp[x][y] == -1 ) return false;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 2 ; i ++ ) if ( abs ( x - gui[i].x ) + abs ( y - gui[i].y ) <= tim * 2 ) return false;
return true;
}
int bfs()
{
queue < point > boy , girl;
boy.push(b) , girl.push(g);
for ( int timer = 1 ; !boy.empty() || !girl.empty() ; timer ++ )
{
for ( int stp = 1 ; stp <= 3 ; stp ++ )//三步 每一步把上一步能走到的点拿出来处理
{
for ( int j = 1 , len = boy.size() ; j <= len ; j ++ )
{
point t = boy.front(); boy.pop();
if ( !check ( t.x , t.y , timer ) ) continue;
for ( int k = 1 ; k <= 4 ; k ++ )
{
int xx = t.x + dx[k] , yy = t.y + dy[k];
if ( !check ( xx , yy , timer ) ) continue;
if ( mp[xx][yy] == 1 ) return timer;
if ( mp[xx][yy] == 0 ) { mp[xx][yy] = 2; boy.push ( (point) { xx , yy } ); }
}
}
}
//一步即可
for ( int j = 1 , len = girl.size() ; j <= len ; j ++ )
{
point t = girl.front(); girl.pop();
if ( !check ( t.x , t.y , timer ) ) continue;
for ( int k = 1 ; k <= 4 ; k ++ )
{
int xx = t.x + dx[k] , yy = t.y + dy[k];
if ( !check ( xx , yy , timer ) ) continue;
if ( mp[xx][yy] == 2 ) return timer;
if ( mp[xx][yy] == 0 ) { mp[xx][yy] = 1; girl.push ( (point) { xx , yy } ); }
}
}
}
return -1;
}
void init()
{
memset ( mp , 0 , sizeof mp );
cnt = 0;
}
signed main ()
{
int T = read();
while ( T -- )
{
init();
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ )
{
cin >> ch;
if ( ch == 'X' ) mp[i][j] = -1;
if ( ch == 'Z' ) mp[i][j] = -1 , gui[++cnt] = (point){i,j};
if ( ch == 'G' ) mp[i][j] = 1 , g = (point) { i , j };//女1男2
if ( ch == 'M' ) mp[i][j] = 2 , b = (point) { i , j };
}
printf ( "%d\n" , bfs() );
}
return 0;
}
F. 1.最小权值
考虑二分这个最小权值 二分的下界就是第
每次以二分的最小权值作为界限 如果第一行所有点都无法到达第
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , m , l = -inf , r = -inf , a[N][N] , head = 1 , tail = 0;
int vis[N][N];
int check ( int x , int y , int val ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m && a[x][y] <= val && !vis[x][y]; }
struct node { int x , y; } q[10000000];
int dx[5] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 };
int dy[5] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 };
int bfs ( int x )
{
head = 1 , tail = 0;
memset ( vis , 0 , sizeof vis );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ ) if ( a[1][i] <= x ) q[++tail] = (node){ 1 , i } , vis[1][i] = 1;
while ( head <= tail )
{
node u = q[head++];
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i ++ )
{
int tx = u.x + dx[i] , ty = u.y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( tx , ty , x ) ) continue;
if ( tx == n ) return 1;
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
q[++tail] = (node){ tx , ty };
}
}
return 0;
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ ) a[i][j] = read() , r = max ( r , a[i][j] );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) l = max ( l , a[n][i] );
while ( l <= r )
{
if ( bfs(mid) ) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
return 0;
}
G. 2.射击问题
每次移动龙就需要重新打标记 显然是不明智的 所以我们在每一组询问开始的时候标记猎物可以被打到的地方 再移动龙到标记点上 记录最小步数
坑点:一定不要将龙和猎物的坐标看反了!!!!!!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int dx[] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };
const int dy[] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 };
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , m , mp[N][N] , stx , sty , edx , edy , vis[N][N] , dep[N][N] , mark[N][N];
struct node { int x , y; } q[10000000];
int check ( int x , int y ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m && !mp[x][y] && !vis[x][y]; }
void mk ()
{
mark[stx][sty] = 1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 8 ; i ++ )
{
int x = stx , y = sty;
while ( check ( x + dx[i] , y + dy[i] ) ) x += dx[i] , y += dy[i] , mark[x][y] = 1;
}
}
int bfs ()
{
int head = 1 , tail = 0;
vis[edx][edy] = 1;
q[++tail] = (node) { edx , edy };
while ( head <= tail )
{
node u = q[head++];
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i ++ )
{
int tx = u.x + dx[i] , ty = u.y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( tx , ty ) || vis[tx][ty] ) continue;
dep[tx][ty] = dep[u.x][u.y] + 1 , vis[tx][ty] = 1;
if ( mark[tx][ty] ) return dep[tx][ty];
q[++tail] = (node) { tx , ty };
}
}
return -1;
}
char ch;
void init()
{
memset ( dep , 0 , sizeof dep );
memset ( vis , 0 , sizeof vis );
memset ( mark , 0 , sizeof mark );
}
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++ )
{
cin >> ch;
if ( ch == 'X' ) mp[i][j] = 1;
}
while ( 1 )
{
init();
cin >> stx >> sty >> edx >> edy;//猎物是st 龙是ed
if ( !stx && !sty && !edx && !edy ) break;
mk();
if ( mark[edx][edy] ) { cout << 0 << endl; continue; }
int res = bfs();
if ( res == -1 ) cout << "Impossible!" << endl;
else cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
H. 3.追捕小狗
每次模拟人先扩展 狗再扩展 如果人的当前步数已经扩展完了 那么判断是否到达狗的位置
狗的转圈可以用取模来实现
麻了 cin90分 scanf100分
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int dx[] = { -1 , 0 , 1 , 0 };
const int dy[] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , m , mp[N][N] , vis[N][N] , timer , st;
struct node { int x , y; } q[10000000] , p , d;
int check ( int x , int y ) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= n && !mp[x][y]; }
int bfs ()
{
int head = 1 , tail = 0;
q[++tail] = p;
vis[p.x][p.y] = 1;
while ( head <= tail )
{
int sz = tail - head + 1;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= sz ; i ++ )
{
node u = q[head++];
int x = u.x , y = u.y;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++ )
{
int tx = x + dx[i] , ty = y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( tx , ty ) || vis[tx][ty] ) continue;
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
q[++tail] = (node) { tx , ty };
}
}
if ( vis[d.x][d.y] ) return timer;
int tx = d.x + dx[st] , ty = d.y + dy[st] , cnt = 0;
while ( !check ( tx , ty ) )
{
st = ( st + 1 ) % 4;
tx = d.x + dx[st] , ty = d.y + dy[st];
cnt ++;
if ( cnt > 3 ) return -1;
}
d = (node) { tx , ty };
++ timer;
}
return -1;
}
char g[N][N];
signed main ()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) scanf ( "%s" , g[i] + 1 );
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ )
{
// cin >> g[i][j];//用cin的话会90分????????不李姐
if ( g[i][j] == '*' ) mp[i][j] = 1;
if ( g[i][j] == 'F' ) p.x = i , p.y = j;
if ( g[i][j] == 'J' ) d.x = i , d.y = j;
}
int res = bfs();
if ( res == -1 ) cout << "No solution." << endl;
else cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
I. 4.渡过河流
我们可以从地图边界开始bfs 每次遇到不同的地形就说明需要一个竹筏来过渡 可以预处理出所有点的答案并批量回答询问
注意:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e3 + 5;
const int dx[] = { 0 , 1 , -1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , -1 , -1 };
const int dy[] = { 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 , 1 , -1 };
int read ()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1;
char ch = cin.get();
while ( !isdigit ( ch ) ) { if ( ch == '-' ) f = -1; ch = cin.get(); }
while ( isdigit ( ch ) ) { x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 ); ch = cin.get(); }
return x * f;
}
int n , m , mp[N][N] , head = 1 , tail = 0 , color , col[N][N];
struct node { int x , y; } q[100000000];
int check ( int x , int y ) { return 0 <= x && x <= n && 0 <= y && y <= n && !col[x][y]; }
void dfs ( int x , int y )
{
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 8 ; i ++ )
{
int tx = x + dx[i] , ty = y + dy[i];
if ( !check ( tx , ty ) ) continue;
if ( mp[tx][ty] == mp[x][y] )
{
col[tx][ty] = col[x][y];
dfs ( tx , ty );
}
else
{
col[tx][ty] = col[x][y] + 1;
q[++tail] = (node) { tx , ty };
}
}
}
void bfs ()
{
head = 1 , tail = 0;
q[++tail] = (node) { 0 , 0 };
col[0][0] = 1;
while ( head <= tail )
{
node u = q[head++];
int x = u.x , y = u.y;
dfs ( x , y );
}
}
char ch;
signed main ()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0) , cout.tie(0);
n = read() , m = read();
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) cin >> ch , mp[i][j] = ch - '0';
n += 1;
bfs();
while ( m -- )
{
int i = read() , j = read();
cout << ( col[i][j] - 1 ) / 2 << ' ';
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!