Vijos P1448 校门外的树【多解,线段树,树状数组,括号序列法+暴力优化】
校门外的树
描述
校门外有很多树,有苹果树,香蕉树,有会扔石头的,有可以吃掉补充体力的……
如今学校决定在某个时刻在某一段种上一种树,保证任一时刻不会出现两段相同种类的树,现有两个操作:
K=1,K=1,读入l、r表示在区间[l,r]中种上一种树,每次操作种的树的种类都不同
K=2,读入l,r表示询问l~r之间能见到多少种树
(l,r>0)
格式
输入格式
第一行n,m表示道路总长为n,共有m个操作
接下来m行为m个操作
输出格式
对于每个k=2输出一个答案
样例1
样例输入1
5 4
1 1 3
2 2 5
1 2 4
2 3 5样例输出1
1
2限制
1s
提示
范围:20%的数据保证,n,m<=100
60%的数据保证,n <=1000,m<=50000
100%的数据保证,n,m<=50000
来源
dejiyu@CSC WorkGroup
分析:这题目从上午九点写到下午四点,历经七个小时的磨难,只为给大家提供最优质的方法!
这道题我用了三种方法去解决!
第一种:线段树【时间花费最长,也最伤脑的写法】,做法是将[a,b]种上一种树,这个修改操作影响的询问满足,
询问区间与[a,b]有交,转化为统计总修改数-与某询问交为空集的修改数
对于一个修改操作[l,r],与它为空集的询问[a,b]满足a∈[1,l-1]或者b∈[r+1,n]
用两棵线段树维护,修改[l,r],将第一棵的[1,l-1]区间+1,第二棵[r+1,n]区间+1
询问[a,b],答案为之前的修改数-(第一棵单点询问b+第二棵单点询问a)
代码中线段树结点的l,r其实就是两棵线段树。。。标记永久化
下面给出线段树的代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=500050; 4 int n,m; 5 inline int read() 6 { 7 int x=0,f=1; 8 char ch=getchar(); 9 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') 10 { 11 if(ch=='-') 12 f=-1; 13 ch=getchar(); 14 } 15 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') 16 { 17 x=x*10+ch-'0'; 18 ch=getchar(); 19 } 20 return x*f; 21 } 22 inline void write(int x) 23 { 24 if(x<0) 25 { 26 putchar('-'); 27 x=-x; 28 } 29 if(x>9) 30 { 31 write(x/10); 32 } 33 putchar(x%10+'0'); 34 } 35 struct Tree 36 { 37 int l,r; 38 int left,right; 39 }tree[N<<3]; 40 inline void buildtree(int x,int y,int pos) 41 { 42 tree[pos].left=x; 43 tree[pos].right=y; 44 if(x==y) 45 { 46 return; 47 } 48 int mid=(x+y)/2; 49 buildtree(x,mid,pos*2); 50 buildtree(mid+1,y,pos*2+1); 51 } 52 inline void insertl(int x,int y,int pos) 53 { 54 int l=tree[pos].left; 55 int r=tree[pos].right; 56 if(l==x&&r==y) 57 { 58 tree[pos].l++; 59 return; 60 } 61 int mid=(l+r)/2; 62 if(y<=mid) 63 insertl(x,y,pos*2); 64 else if(x>mid) 65 insertl(x,y,pos*2+1); 66 else 67 { 68 insertl(x,mid,pos*2); 69 insertl(mid+1,y,pos*2+1); 70 } 71 } 72 inline void insertr(int x,int y,int pos) 73 { 74 int l=tree[pos].left; 75 int r=tree[pos].right; 76 if(l==x&&r==y) 77 { 78 tree[pos].r++; 79 return; 80 } 81 int mid=(l+r)/2; 82 if(y<=mid) 83 insertr(x,y,pos*2); 84 else if(x>mid) 85 insertr(x,y,pos*2+1); 86 else 87 { 88 insertr(x,mid,pos*2); 89 insertr(mid+1,y,pos*2+1); 90 } 91 } 92 inline int askl(int k,int x) 93 { 94 int l=tree[k].left; 95 int r=tree[k].right; 96 if(l==r) 97 return tree[k].l; 98 int mid=(l+r)/2; 99 if(x<=mid) 100 return tree[k].l+askl(k*2,x); 101 else return tree[k].l+askl(k*2+1,x); 102 } 103 inline int askr(int k,int x) 104 { 105 int l=tree[k].left; 106 int r=tree[k].right; 107 if(l==r) 108 return tree[k].r; 109 int mid=(l+r)/2; 110 if(x<=mid) 111 return tree[k].r+askr(k*2,x); 112 else return tree[k].r+askr(k*2+1,x); 113 } 114 int main() 115 { 116 n=read(); 117 m=read(); 118 int tot=0; 119 buildtree(0,n,1); 120 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 121 { 122 int t,a,b; 123 cin>>t>>a>>b; 124 if(t==1) 125 { 126 insertl(0,a-1,1); 127 insertr(b+1,n,1); 128 tot++; 129 } 130 else 131 { 132 int ans=askr(1,a)+askl(1,b); 133 write(tot-ans); 134 cout<<endl; 135 } 136 } 137 return 0; 138 }
第二种写法:树状数组
做法:这题是一条条线段,所以我们可以用线段树之类的东东来实现,然后感觉树状数组写起来简单一点所以就打了
开两个数组来存一个是开始的点的数量,一个是结束的 ,然后随便搞一下,最后输出就可以了
下面给出树状数组写法:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=50050; 4 int l[N],r[N]; 5 int n,m; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int x=0,f=1; 9 char ch=getchar(); 10 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') 11 { 12 if(ch=='-') 13 f=-1; 14 ch=getchar(); 15 } 16 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') 17 { 18 x=x*10+ch-'0'; 19 ch=getchar(); 20 } 21 return x*f; 22 } 23 inline void write(int x) 24 { 25 if(x<0) 26 { 27 putchar('-'); 28 x=-x; 29 } 30 if(x>9) 31 { 32 write(x/10); 33 } 34 putchar(x%10+'0'); 35 } 36 int lowbit(int x) 37 { 38 return x&-x; 39 } 40 void add(int x,int d,int c[]) 41 { 42 while(x<=n) 43 { 44 c[x]+=d; 45 x+=lowbit(x); 46 } 47 } 48 int sum(int x,int c[]) 49 { 50 int s=0; 51 while(x>0) 52 { 53 s+=c[x]; 54 x-=lowbit(x); 55 } 56 return s; 57 } 58 int main() 59 { 60 int k,x,y; 61 n=read(); 62 m=read(); 63 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 64 { 65 cin>>k>>x>>y; 66 if(k==1) 67 { 68 add(x,1,l); 69 add(y,1,r); 70 } 71 else 72 { 73 write(sum(y,l)-sum(x-1,r)); 74 cout<<endl; 75 } 76 } 77 return 0; 78 }
第三种方法:括号序列法【简称括号法】
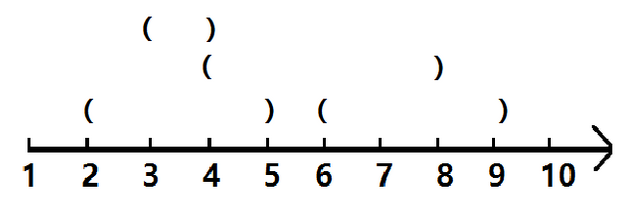
以上就是括号序列的过程。简单的说,就是更新区间[a,b]时,点a记录左括号数,点b记录右括号数,查询区间[a,b]时,即为b之前(包括b)的左括号数-a之前的右括号数。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=50050; 4 int l[N],r[N]; 5 int n,m; 6 inline int read() 7 { 8 int x=0,f=1; 9 char ch=getchar(); 10 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') 11 { 12 if(ch=='-') 13 f=-1; 14 ch=getchar(); 15 } 16 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') 17 { 18 x=x*10+ch-'0'; 19 ch=getchar(); 20 } 21 return x*f; 22 } 23 inline void write(int x) 24 { 25 if(x<0) 26 { 27 putchar('-'); 28 x=-x; 29 } 30 if(x>9) 31 { 32 write(x/10); 33 } 34 putchar(x%10+'0'); 35 } 36 int main() 37 { 38 int k,x,y; 39 n=read(); 40 m=read(); 41 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 42 { 43 cin>>k>>x>>y; 44 if(k==1) 45 { 46 for(int j=x;j<=n;j+=j&-j) 47 l[j]++; 48 for(int j=y;j<=n;j+=j&-j) 49 r[j]++; 50 } 51 else 52 { 53 int ans=0; 54 for(int j=y;j;j-=j&-j) 55 ans+=l[j]; 56 for(int j=x-1;j;j-=j&-j) 57 ans-=r[j]; 58 write(ans); 59 cout<<endl; 60 } 61 } 62 return 0; 63 }
作 者:Angel_Kitty
出 处:https://www.cnblogs.com/ECJTUACM-873284962/
关于作者:阿里云ACE,目前主要研究方向是Web安全漏洞以及反序列化。如有问题或建议,请多多赐教!
版权声明:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。
特此声明:所有评论和私信都会在第一时间回复。也欢迎园子的大大们指正错误,共同进步。或者直接私信我
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是作者坚持原创和持续写作的最大动力!
欢迎大家关注我的微信公众号IT老实人(IThonest),如果您觉得文章对您有很大的帮助,您可以考虑赏博主一杯咖啡以资鼓励,您的肯定将是我最大的动力。thx.

我的公众号是IT老实人(IThonest),一个有故事的公众号,欢迎大家来这里讨论,共同进步,不断学习才能不断进步。扫下面的二维码或者收藏下面的二维码关注吧(长按下面的二维码图片、并选择识别图中的二维码),个人QQ和微信的二维码也已给出,扫描下面👇的二维码一起来讨论吧!!!

欢迎大家关注我的Github,一些文章的备份和平常做的一些项目会存放在这里。

















【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述