吴恩达机器学习第一章作业:线性回归,TASK2 多变量线性回归(python实现)
TASK2 多变量线性回归
由于是多变量线性回归,所以数据不一定可视化,就比如这个例子:
第一列是房屋的面积x1,第二列是房屋的房间数量x2,第三列是房屋的售价y,由公式可以这么写:
x1————x2————(f)————y
也就是x1和x2都对y有影响,道理和单变量线性回归类似:
1、先进行多变量的归一化,让数据显得不是那么庞大:
path = 'D:\python学习\吴恩达机器学习\ex1data2.txt' data = pd.read_csv(path,names = ['feets','bedrooms','price']) data = (data-data.mean())/data.std()##已经处理完数据,进行了归一化操作了
这里解释一下data.mean()是data的平均数,data.std()是data的方差,归一化的公式为:
x.归一化 =( x-x.mean )/x.std
2、照例写出cost的函数
def computecost(x,y,theta): h_x = x*theta.T temp = np.power((h_x-y),2) J_theta = np.sum(temp)/(2*len(x)) return J_theta
3、写出梯度下降的函数
def gradientdiscent(x,y,theta,epoch,alpha): temp = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) cost = np.zeros(epoch) for i in range(epoch): temp = theta-(alpha/len(x))*(x*theta.T-y).T*x theta = temp cost[i] = computecost(x,y,theta) return theta,cost
以上两个函数和单变量线性回归基本上一样
4、计算一下theta未跟新时的cost值
data.insert(0,'ones',1) col = data.shape[1] x = data.iloc[:,0:col-1] y = data.iloc[:,col-1:col] x = np.matrix(x.values) y = np.matrix(y.values) theta = np.matrix([0,0,0])
计算出来cost = 0.48936
已经很小了,但是这是归一化之后的cost,原来的cost应该还是非常大,所以要进行梯度下降来跟新theta,使cost变小
5、跟新theta
epoch = 1000 alpha = 0.01 theta,cost = gradientdiscent(x,y,theta,epoch,alpha)##算出来theta和cost了
6、绘制cost曲线图
fig,m = plt.subplots(figsize =(6,6) ) m.plot(np.arange(epoch),cost,'blue') m.set_xlabel('iters') m.set_ylabel('cost') plt.show()
cost的曲线图如下图所示:
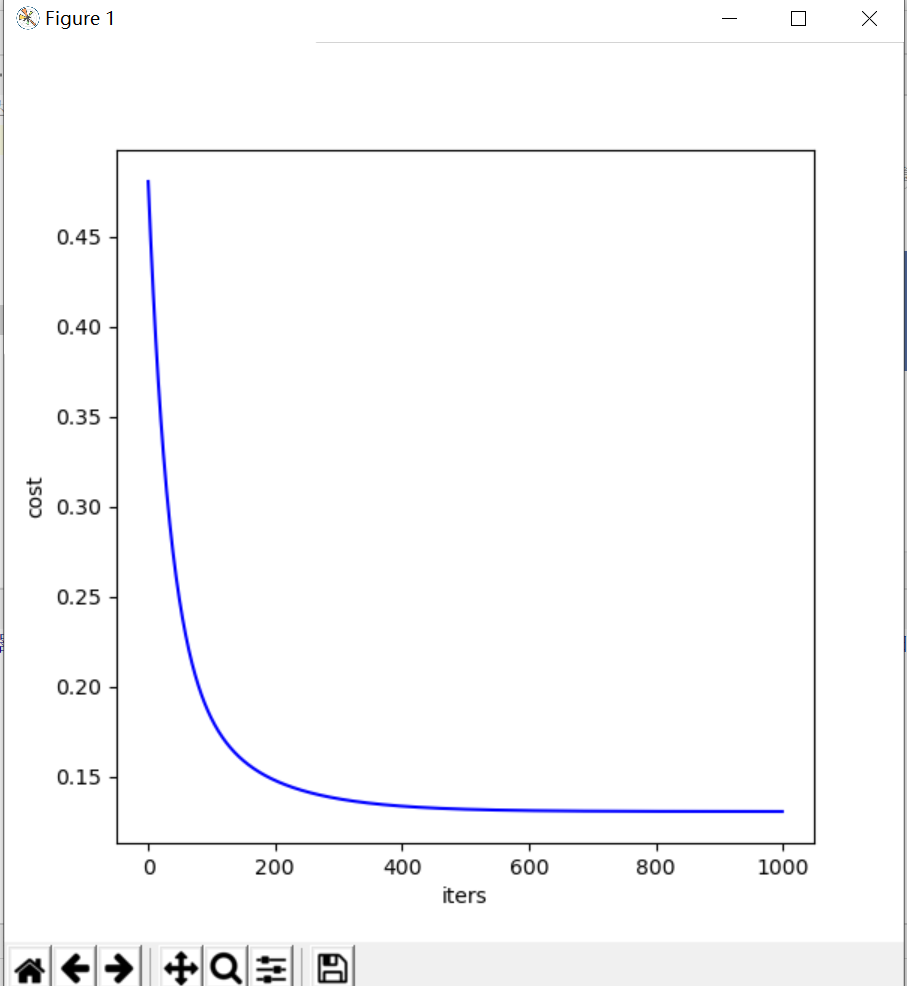
可以看出,跟新到300次之后cost已经基本稳定在0.13附近,还是比较小的。
完整代码如下:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt path = 'D:\python学习\吴恩达机器学习\ex1data2.txt' data = pd.read_csv(path,names = ['feets','bedrooms','price']) data = (data-data.mean())/data.std()##已经处理完数据,进行了归一化操作了 #写代价函数了 def computecost(x,y,theta): h_x = x*theta.T temp = np.power((h_x-y),2) J_theta = np.sum(temp)/(2*len(x)) return J_theta data.insert(0,'ones',1) col = data.shape[1] x = data.iloc[:,0:col-1] y = data.iloc[:,col-1:col] x = np.matrix(x.values) y = np.matrix(y.values) theta = np.matrix([0,0,0]) ##算出来costfunction为0.4893617021276595 #接下来算gradientdiscent了,来跟新theta def gradientdiscent(x,y,theta,epoch,alpha): temp = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) cost = np.zeros(epoch) for i in range(epoch): temp = theta-(alpha/len(x))*(x*theta.T-y).T*x theta = temp cost[i] = computecost(x,y,theta) return theta,cost epoch = 1000 alpha = 0.01 theta,cost = gradientdiscent(x,y,theta,epoch,alpha)##算出来theta和cost了 ##下面开始绘制cost的下降梯度 fig,m = plt.subplots(figsize =(6,6) ) m.plot(np.arange(epoch),cost,'blue') m.set_xlabel('iters') m.set_ylabel('cost') plt.show()

