Spring框架第一篇之Spring的第一个程序
一、下载Spring的jar包
通过http://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/地址下载最新的Spring的zip包,当然,如果你是在使用maven工程的话,可以不用下载Zip包,可以直接在maven工程的pom.xml文件中添加Spring的依赖即可。
二、创建工程导入jar包
第一篇的内容记录一些入门知识点,所以只需要导入几个必要的基础包则可,这里项目只导入Spring的以下几个包:
spring-core-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-beans-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-context-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar
除此之外,还需要导入两个日志jar包:
log4j-1.2.15.jar
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar
三、创建测试工程
整个工程目录如下图所示:
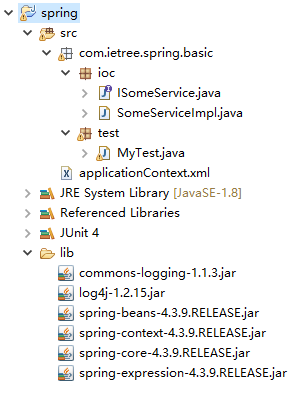
3.1 编写ISomeService接口类
package com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc; /** * 接口类 * * @author Root */ public interface ISomeService { void doSomeThing(); }
3.2 编写SomeServiceImpl类,实现ISomeService
package com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc; /** * 实现类 * * @author Root */ public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService { public SomeServiceImpl() { System.out.println("执行无参构造器,创建SomeServiceImpl对象"); } @Override public void doSomeThing() { System.out.println("执行doSomeThing()方法..."); } }
3.3 编写applicationContext.xml配置文件
其中xml中的schema配置可以直接从Spring官方文档中复制(spring-framework-4.3.9.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html\xsd-configuration.html)
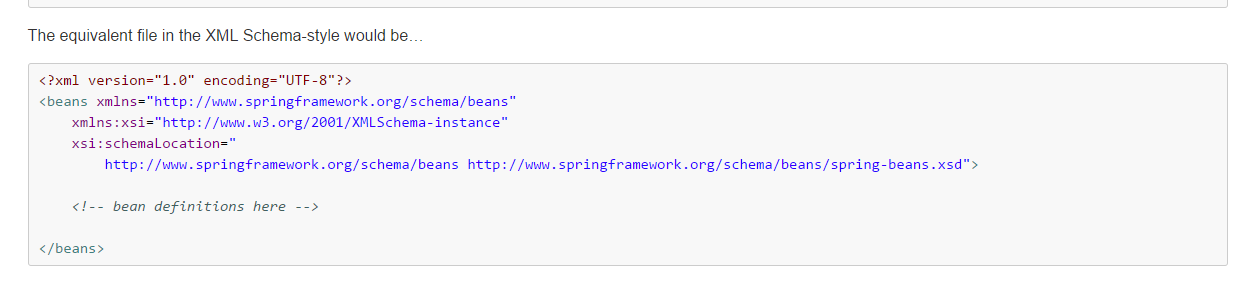
所以将schema复制之后需要配置对应的bean,这里的id可以随便命名,只需要对应需要创建的类即可,之后需要根据配置的bean的id值来获取对象,不要再通过最早的那种通过new Object()的方式获取了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 注册Service 这里相当于容器做了SomeServiceImpl myService = new SomeServiceImpl(); --> <bean id="myService" class="com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc.SomeServiceImpl"/> </beans>
以上步骤配置完成之后,Spring的环境就算简单搭建完成了,现在来测试一下。
四、获取对象的几种方式
1、通过new Object();方式获取对象
@Test public void test01() { ISomeService service = new SomeServiceImpl(); service.doSomeThing(); }
2、通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象加载Spring的配置文件,采用getBean的方式获取对象
@Test public void test02() { // 创建容器对象,加载Spring配置文件 // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext会从类路径下查找配置文件 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
3、通过FileSystemXmlApplicationContext对象加载Spring的配置文件,采用getBean的方式获取对象
@Test public void test03() { // FileSystemXmlApplicationContext会从项目的根下查找配置文件,或者从当前系统的D盘根目录下查找配置文件 ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
4、通过BeanFactory对象加载Spring的配置文件,采用getBean的方式获取对象
// ApplicationContext与BeanFactory容器的区别: // 1)ApplicationContext容器在进行初始化时,会将其中的所有Bean(对象)进行创建。 // 缺点:占用系统资源(内存、CPU等) // 优点:响应速度快 // 2)BeanFactory容器中的对象,在容器初始化时并不会被创建,而是在真正获取该对象时才被创建。 // 缺点:响应速度慢 // 优点:不多占用系统资源(内存、CPU等) @Test public void test04() { // 创建容器对象,加载Spring配置文件 BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml")); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) bf.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
五、获取对象的源码分析
点击ApplicationContext按 CTRL + T 可以看到下图,ApplicationContext对象实际上是一个接口,它有ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext两种实现方式。
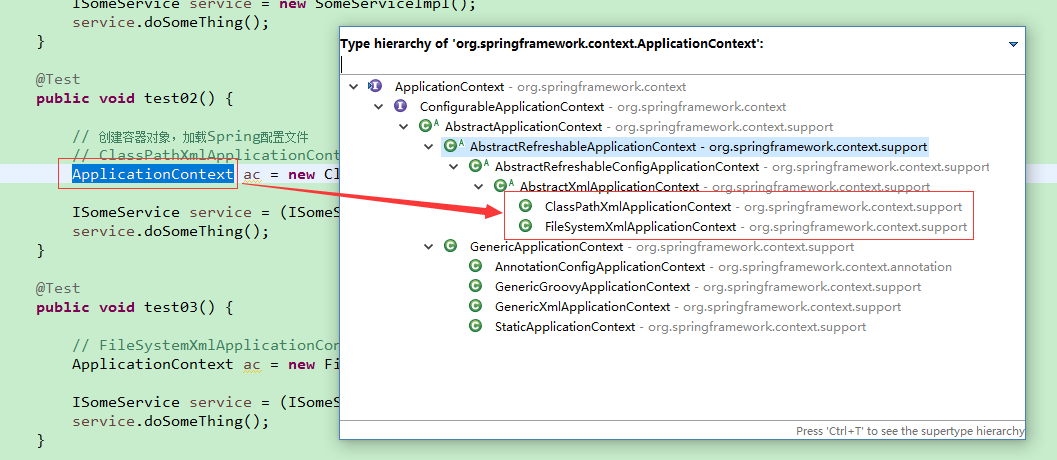
1、首先进入ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象,可以看到有很多的构造方法,实际上只要将applicationContext.xml配置文件放在项目中的src目录下,使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的任何一种构造方法都可以获取到容器。
比如:
@Test public void test02() { // 创建容器对象,加载Spring配置文件 // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext会从类路径下查找配置文件 @SuppressWarnings("resource") ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"applicationContext.xml"}, true, null); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
使用快捷键CTRL + O 可以查看类结构,下图是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象结构图:
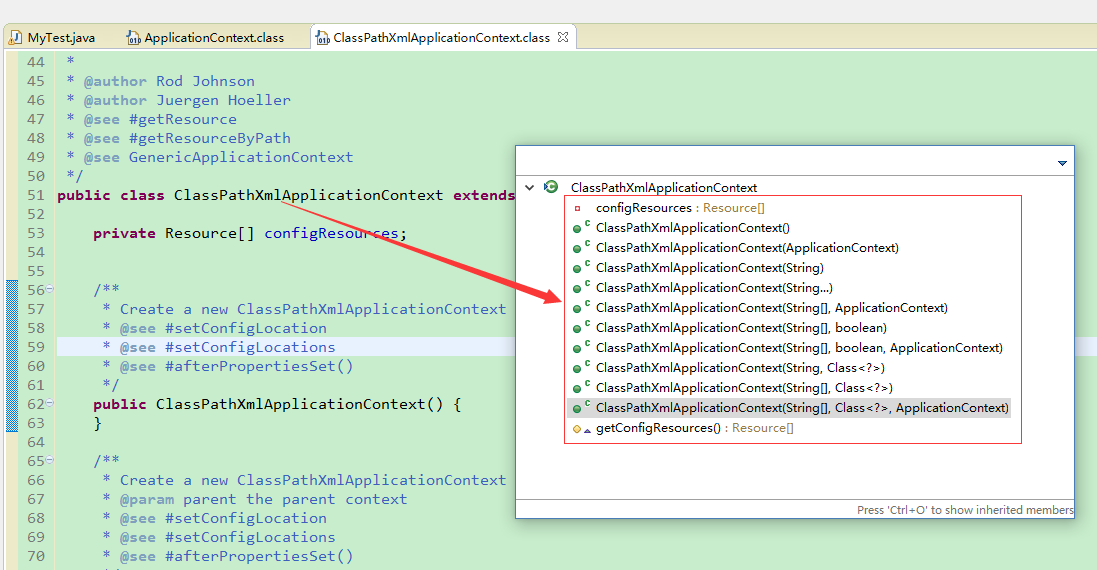
2、之后再进入FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类查看类结构:
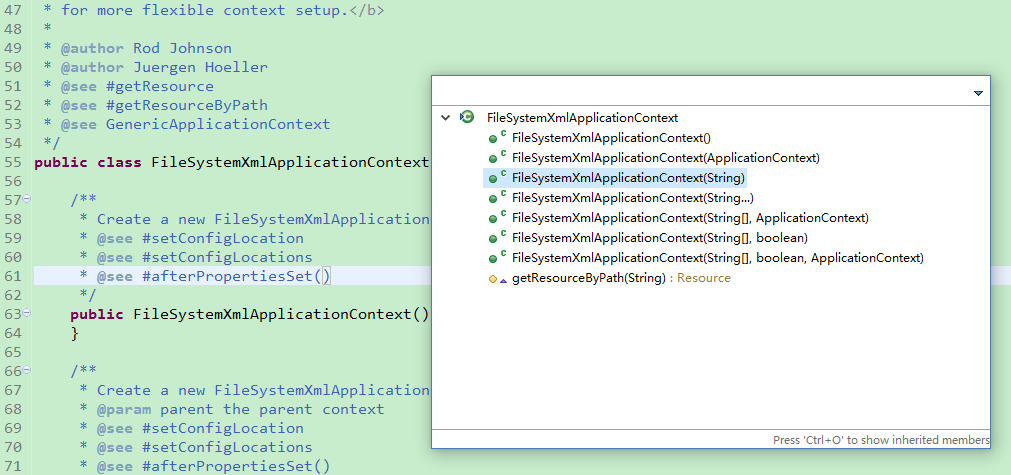
实际上会发现这两个类非常相似,不同的是,在使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类时,applicationContext.xml配置文件只能放在项目的src目录下,而在使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext类时,只需要将类放在项目的根目录下,
或者放在当前系统指定的盘符下,程序都可以加载到容器。因为 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext首先会从项目的根下查找配置文件,或者从当前系统的盘盘符根目录下查找配置文件。
3、看看使用 BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));方式实现的原理:
首先进入ApplicationContext接口会发现这个接口实际继承了很多的其他类,其中有HierarchicalBeanFactory类,
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
进入HierarchicalBeanFactory接口,可以看到还有XmlBeanFactory的实现方式:

所以使用 XmlBeanFactory的构造函数也能够实现获取容器对象
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException { this(resource, null); }



