LeetCode 430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list/description/
题目:
You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example:
Input:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
Output:
1-2-3-7-8-11-12-9-10-4-5-6-NULL
Explanation for the above example:
Given the following multilevel doubly linked list:
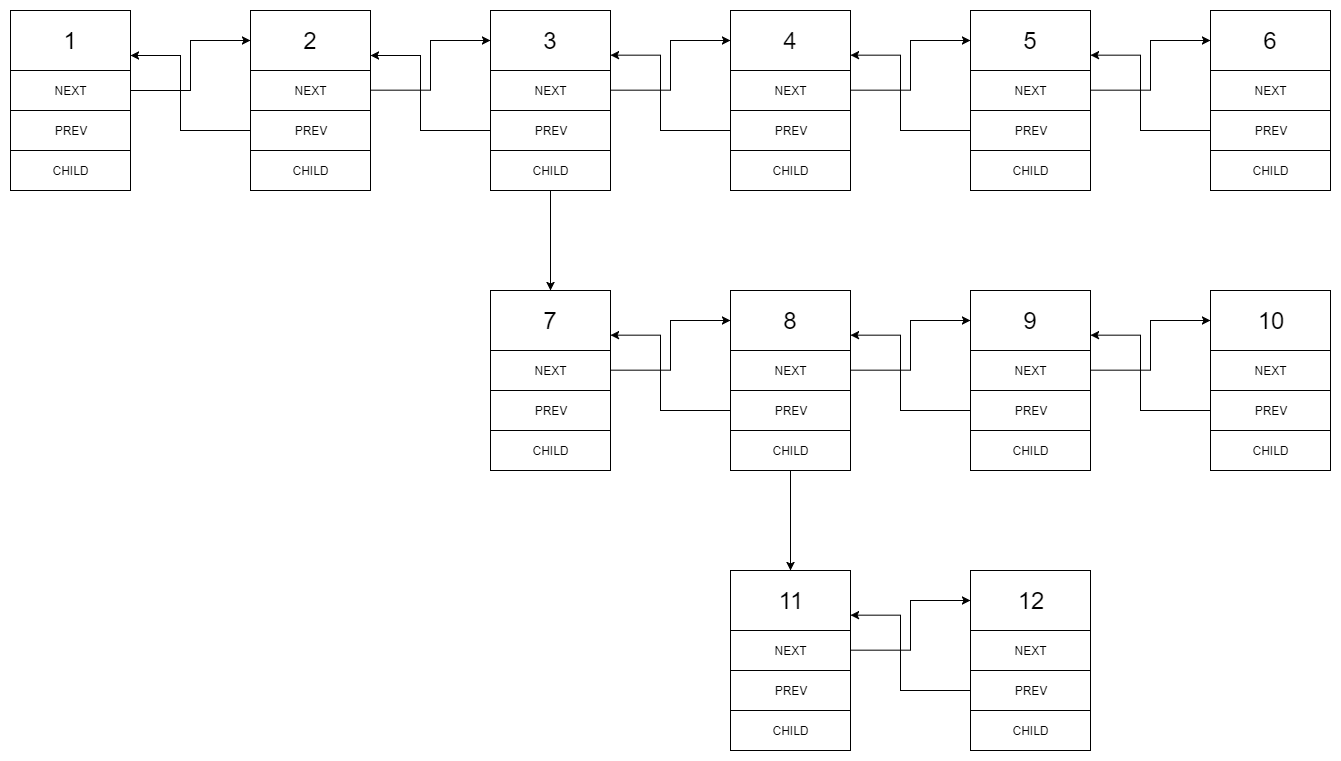
We should return the following flattened doubly linked list:

题解:
如果当前点cur 没有child, 直接跳到cur.next 进行下次计算.
如果cur 有child, 目标是把cur.child这个level提到cur这个level上. 至于cur.child 这个level上有没有点有child 先不管.
做法就是cur.child 一直只按next找到tail, 然后这一节插在cur 和 cur.next之间, cur再跳到更新的cur.next上.
Note: cur.next could be null. So it needs to check if cur.next != null, then cur.next.prev = childTail.
Time Complexity: O(n). n是所有点的个数, 每个点只走过constant次数.
Space: O(1).
AC Java:
1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 public int val; 5 public Node prev; 6 public Node next; 7 public Node child; 8 9 public Node() {} 10 11 public Node(int _val,Node _prev,Node _next,Node _child) { 12 val = _val; 13 prev = _prev; 14 next = _next; 15 child = _child; 16 } 17 }; 18 */ 19 class Solution { 20 public Node flatten(Node head) { 21 if(head == null){ 22 return head; 23 } 24 25 Node cur = head; 26 while(cur != null){ 27 if(cur.child == null){ 28 cur = cur.next; 29 continue; 30 } 31 32 Node child = cur.child; 33 Node childTail = child; 34 while(childTail.next != null){ 35 childTail = childTail.next; 36 } 37 38 cur.child = null; 39 child.prev = cur; 40 childTail.next = cur.next; 41 if(cur.next != null){ 42 cur.next.prev = childTail; 43 } 44 cur.next = child; 45 cur = cur.next; 46 } 47 48 return head; 49 } 50 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号