LeetCode 987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
题目:
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
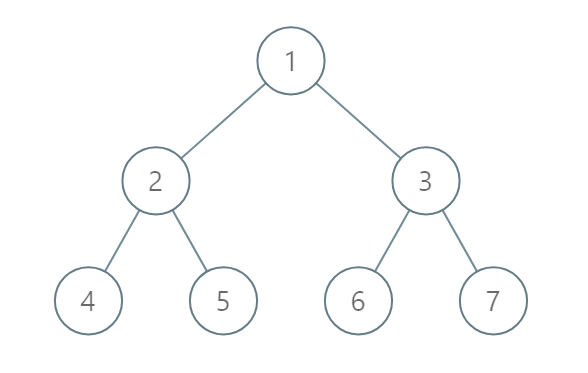
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
题解:
For vertical order, we need a HashMap to maintain key as column.
When there is same column, they should be put into same value collection.
Here is one more extra constraint, that is to for same column and same row, have smaller value come first.
Thus when coming out the HashMap, sort the values first based on row, then based on value.
Time Complexity: O(n + logn*loglogn). n is the number of nodes. Thus the longest list is the height of tree m = logn. sort takes O(mlogm).
Space: O(n).
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { 18 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); 19 if(root == null){ 20 return res; 21 } 22 23 HashMap<Integer, List<Pair>> hm = new HashMap<>(); 24 int min = 0; 25 int max = 0; 26 LinkedList<Pair> que = new LinkedList<>(); 27 que.add(new Pair(0, 0, root)); 28 while(!que.isEmpty()){ 29 Pair cur = que.poll(); 30 min = Math.min(min, cur.y); 31 max = Math.max(max, cur.y); 32 hm.putIfAbsent(cur.y, new ArrayList<Pair>()); 33 hm.get(cur.y).add(cur); 34 35 if(cur.node.left != null){ 36 que.add(new Pair(cur.x - 1, cur.y - 1, cur.node.left)); 37 } 38 39 if(cur.node.right != null){ 40 que.add(new Pair(cur.x - 1, cur.y + 1, cur.node.right)); 41 } 42 } 43 44 for(int i = min; i <= max; i++){ 45 List<Pair> item = hm.get(i); 46 Collections.sort(item, (a, b) -> a.x == b.x ? a.node.val - b.node.val : b.x - a.x); 47 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 48 for(Pair p : item){ 49 list.add(p.node.val); 50 } 51 52 res.add(list); 53 } 54 55 return res; 56 } 57 } 58 59 class Pair{ 60 int x; 61 int y; 62 TreeNode node; 63 public Pair(int x, int y, TreeNode node){ 64 this.x = x; 65 this.y = y; 66 this.node = node; 67 } 68 }
AC Python:
1 # Definition for a binary tree node. 2 # class TreeNode: 3 # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): 4 # self.val = val 5 # self.left = left 6 # self.right = right 7 class Solution: 8 def verticalTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]: 9 if not root: 10 return [] 11 hm = {} 12 que = deque([(0, 0, root)]) 13 minCol, maxCol = 0, 0 14 while que: 15 x, y, node = que.popleft() 16 if y not in hm: 17 hm[y] = [] 18 hm[y].append((x, node.val)) 19 minCol = min(minCol, y) 20 maxCol = max(maxCol, y) 21 if node.left: 22 que.append((x + 1, y - 1, node.left)) 23 if node.right: 24 que.append((x + 1, y + 1, node.right)) 25 res = [] 26 for y in range(minCol, maxCol + 1): 27 res.append([val for x, val in sorted(hm[y], key = lambda k: (k[0], k[1]))]) 28 return res


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号