LeetCode 1110. Delete Nodes And Return Forest
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-nodes-and-return-forest/
题目:
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
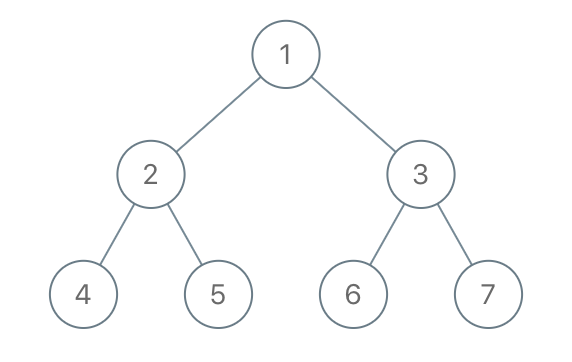
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
题解:
For DFS state, we need current node, to_delete set and List<TreeNode> res.
The return should be TreeNode.
It uses divide and conquer, which is bottom-up DFS.
Comes to the bottom leaf node, if it is null, return null.
otherwise, check if the current node is to be deleted.
If yes, then its children need to be added to res.
Time Complexity: O(n). n is tree size.
Space: O(logn + m) m = to_delete.length.
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public List<TreeNode> delNodes(TreeNode root, int[] to_delete) { 12 List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); 13 HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<>(); 14 for(int n : to_delete){ 15 hs.add(n); 16 } 17 18 root = dfs(root, hs, res); 19 if(root != null){ 20 res.add(root); 21 } 22 23 return res; 24 } 25 26 private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root, HashSet<Integer> hs, List<TreeNode> res){ 27 if(root == null){ 28 return root; 29 } 30 31 root.left = dfs(root.left, hs, res); 32 root.right = dfs(root.right, hs, res); 33 if(hs.contains(root.val)){ 34 if(root.left != null){ 35 res.add(root.left); 36 } 37 38 if(root.right != null){ 39 res.add(root.right); 40 } 41 42 return null; 43 } 44 45 return root; 46 } 47 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号