springboot 使用redis和lettuce原理
springboot使用redis
简介
在Spring Boot中,要访问Redis,可以直接引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis依赖,它实际上是Spring Data的一个子项目——Spring Data Redis,主要用到了这几个组件:
- Lettuce:一个基于Netty的高性能Redis客户端;
- RedisTemplate:一个类似于JdbcTemplate的接口,用于简化Redis的操作
客户端配置
首要任务便是,连接客户端,获取连接句柄。spring提供了RedisConnection来标识一个连接,使用RedisConnectionFactory来创建连接。
方法一: yml配置,默认为Lettuce

1 spring: 2 redis: 3 # Redis数据库索引(默认为0) 4 database: 0 5 # Redis服务器地址 6 host: 127.0.0.1 7 # Redis服务器连接端口 8 port: 6379 9 # 连接超时时间(毫秒) 10 timeout: 5000
方法二:bean注入

1 @Bean 2 public LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() { 3 return new LettuceConnectionFactory(new RedisStandaloneConfiguration("127.0.0.1", 6379)); 4 } 5 6 @Bean 7 public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() { 8 return new JedisConnectionFactory(new RedisStandaloneConfiguration("127.0.0.1", 6379)); 9 }
工具类
RedisTemplate属于org.springframework.data.redis.core,是redis模块的核心,支持多种特性并对redis操作进行了高度抽象。
操作
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface | Description |
|
Key Type Operations |
|
|
|
Redis geospatial operations, such as |
|
|
Redis hash operations |
|
|
Redis HyperLogLog operations, such as |
|
|
Redis list operations |
|
|
Redis set operations |
|
|
Redis string (or value) operations |
|
|
Redis zset (or sorted set) operations |
|
Key Bound Operations |
|
|
|
Redis key bound geospatial operations |
|
|
Redis hash key bound operations |
|
|
Redis key bound operations |
|
|
Redis list key bound operations |
|
|
Redis set key bound operations |
|
|
Redis string (or value) key bound operations |
|
|
Redis zset (or sorted set) key bound operations |
使用无太大区别 :
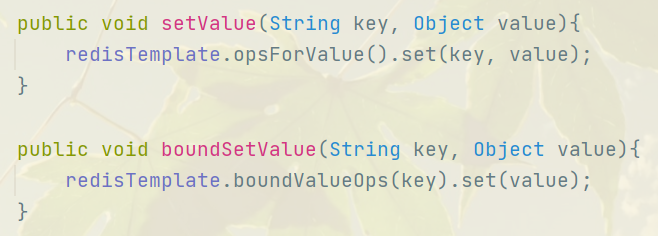

1 // 地理缓存 2 public void testGeoSpatial(){//reids 3.2版本之后支持 3 String citys = "citys"; 4 String chengdu = "chengdu"; 5 String beijing = "beijing"; 6 String chongqing = "beijing"; 7 String luzhou = "beijing"; 8 GeoOperations<String, String> geoOperations = redisTemplate.opsForGeo(); 9 geoOperations.add(citys,new RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>(chengdu,new Point(104,30))); 10 geoOperations.add(citys,new Point(116,40),beijing); 11 geoOperations.add(citys,new Point(106,29),chongqing); 12 geoOperations.add(citys,new Point(105,25),luzhou); 13 14 System.out.println(geoOperations.position(citys, "chengdu"));//获取成都经纬度 15 System.out.println(geoOperations.distance(citys, chengdu, beijing));//获取两地距离 16 17 Point center = new Point(104,30);//定义中心点 18 Distance radius = new Distance(800, Metrics.KILOMETERS);//定义范围 19 Circle within = new Circle(center, radius); 20 //返回范围内的城市 21 System.out.println(geoOperations.radius(citys, within)); 22 //根据距离排序,返回最近的两个 23 RedisGeoCommands.GeoRadiusCommandArgs args = RedisGeoCommands.GeoRadiusCommandArgs. 24 newGeoRadiusArgs().includeDistance().limit(2).sortAscending(); 25 System.out.println(geoOperations.radius(citys, within, args)); 26 27 } 28 29 // 计数缓存 30 void hyperLogLogTest() { 31 HyperLogLogOperations hyperLogLogOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog(); 32 // 添加元素 33 Long add = hyperLogLogOperations.add("20220628:uv", "ip1", "ip2", "ip3"); 34 System.out.println("add : " + add); 35 36 hyperLogLogOperations.add("20220629:uv", "ip1", "ip2", "ip3", "ip4", "ip5"); 37 hyperLogLogOperations.add("20220630:uv", "ip2", "ip4", "ip5", "ip6", "ip7", "ip8"); 38 39 // 获取元素基数 40 Long size = hyperLogLogOperations.size("20220628:uv", "20220629:uv"); 41 System.out.println("size : " + size); 42 43 // 合并多个元素 44 Long result = hyperLogLogOperations.union("unionResult", "20220628:uv", "20220629:uv", "20220630:uv"); 45 System.out.println("result : " + result); 46 Long unionResult = hyperLogLogOperations.size("unionResult"); 47 System.out.println("unionResult : " + unionResult); 48 }
序列化
RedisTemplate是基于java的序列化器进行操作。
序列化器
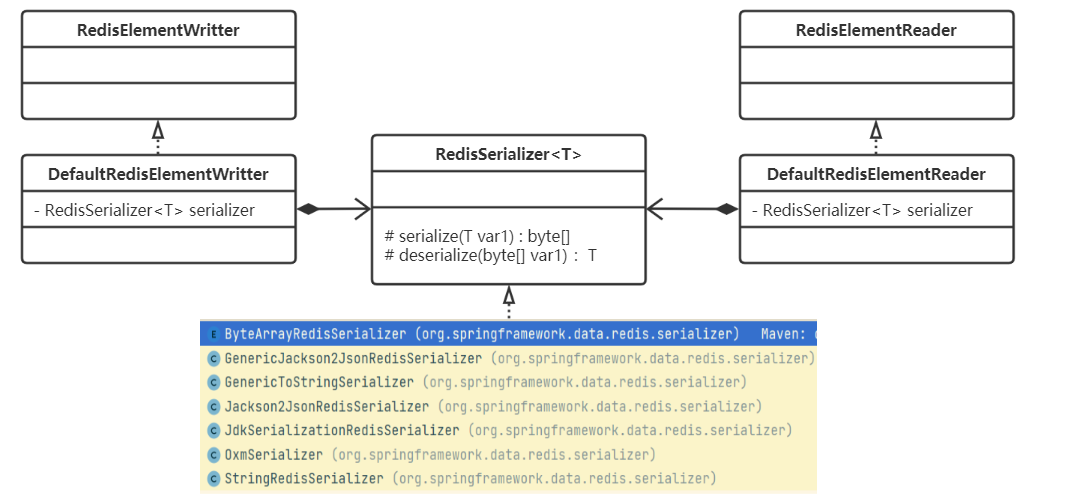
RedisTemplate与StringRedisTemplate的区别
- 两者的关系是StringRedisTemplate继承RedisTemplate。

- RedisTemplate默认使用JDK序列化策略,StringRedisTemplate默认使用String序列化策略。建议使用key为string,value为json。
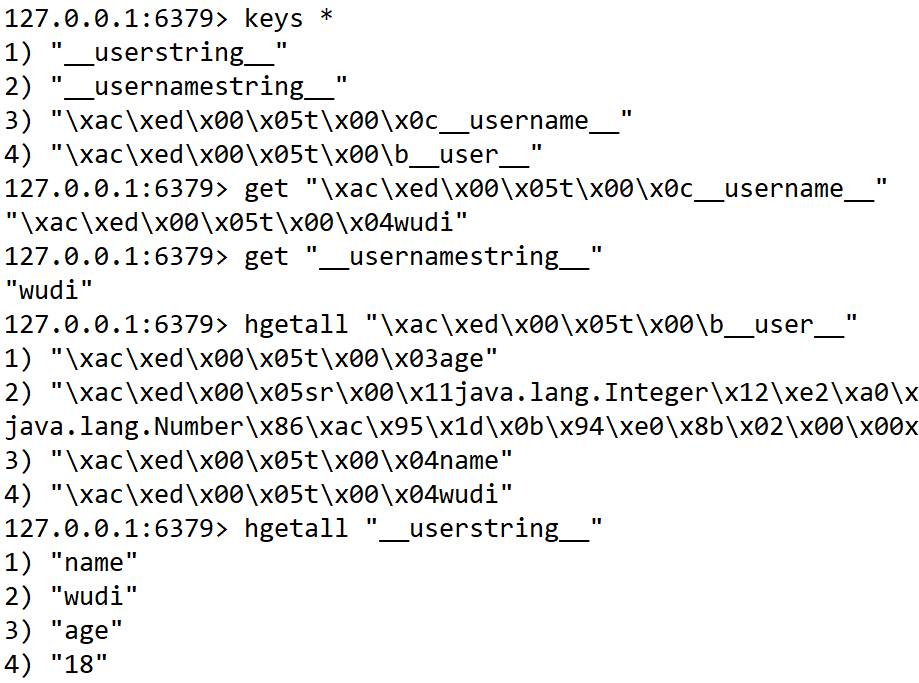
 通过bean注入生成redistemplate
通过bean注入生成redistemplate1 @Bean 2 public RedisTemplate<String, Object> template(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { 3 // 创建RedisTemplate<String, Object>对象 4 RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); 5 // 配置连接工厂 6 template.setConnectionFactory(factory); 7 // 定义Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer序列化对象 8 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jacksonSeial = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class); 9 ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); 10 // 指定要序列化的域,field,get和set,以及修饰符范围,ANY是都有包括private和public 11 om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); 12 // 指定序列化输入的类型,类必须是非final修饰的,final修饰的类,比如String,Integer等会报异常 13 om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); 14 jacksonSeial.setObjectMapper(om); 15 StringRedisSerializer stringSerial = new StringRedisSerializer(); 16 // redis key 序列化方式使用stringSerial 17 template.setKeySerializer(stringSerial); 18 // redis value 序列化方式使用jackson 19 template.setValueSerializer(jacksonSeial); 20 // redis hash key 序列化方式使用stringSerial 21 template.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerial); 22 // redis hash value 序列化方式使用jackson 23 template.setHashValueSerializer(jacksonSeial); 24 // 默认序列化器 , 给cache用 25 template.setDefaultSerializer(stringSerial); 26 // tmplate实现了InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet接口,注入bean需要手动调用 27 template.afterPropertiesSet(); 28 return template; 29 } 30 31 // 设置默认值 32 public void afterPropertiesSet() { 33 super.afterPropertiesSet(); 34 boolean defaultUsed = false; 35 // 默认使用jdk序列化 36 if (this.defaultSerializer == null) { 37 this.defaultSerializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : this.getClass().getClassLoader()); 38 } 39 40 if (this.enableDefaultSerializer) { 41 if (this.keySerializer == null) { 42 this.keySerializer = this.defaultSerializer; 43 defaultUsed = true; 44 } 45 46 if (this.valueSerializer == null) { 47 this.valueSerializer = this.defaultSerializer; 48 defaultUsed = true; 49 } 50 51 if (this.hashKeySerializer == null) { 52 this.hashKeySerializer = this.defaultSerializer; 53 defaultUsed = true; 54 } 55 56 if (this.hashValueSerializer == null) { 57 this.hashValueSerializer = this.defaultSerializer; 58 defaultUsed = true; 59 } 60 } 61 62 if (this.enableDefaultSerializer && defaultUsed) { 63 Assert.notNull(this.defaultSerializer, "default serializer null and not all serializers initialized"); 64 } 65 66 if (this.scriptExecutor == null) { 67 this.scriptExecutor = new DefaultScriptExecutor(this); 68 } 69 70 this.initialized = true; 71 }
lettuce 原理及参数说明调优
概念
Lettuce是一个高性能redis客户端,底层基于netty框架来管理连接,天然是非阻塞和线程安全的。
netty框架
Netty是 一个异步的,事件驱动的网络应用程序框架。
特点
- IO 线程模型:Netty的io线程模型采取了reactor主从模型,拥有很好的处理高并发的能力。
- 内存零拷贝:尽量减少不必要的内存拷贝,实现了更高效率的传输。
- 内存池设计:申请的内存可以重用,主要指直接内存。内部实现是用一颗二叉查找树管理内存分配情况。
- 串形化处理读写:避免使用锁带来的性能开销。
- 高性能序列化协议:支持 protobuf 等高性能序列化协议
reactor模型
其实就是对io多路复用(select/epoll)的一种应用。
特点
- 基于
I/O复用模型:多个连接共用一个阻塞对象,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象等待,无需阻塞等待所有连接。当某个连接有新的数据可以处理时, 操作系统通知应用程序,线程从阻塞状态返回,开始进行业务处理。Reactor对应的叫法: 1. 反应器模式 2. 分发者模式(Dispatcher) 3. 通知者模式(notifier),我更倾向于叫分发者模式。 - 基于线程池复用线程资源:不必再为每个连接创建线程,将连接完成后的业务处理任务分配给线程进行处理,一个线程可以处理多个连接的业务。

netty模型

模型说明:
- Netty将Selector以及Selector相关的事件及任务封装了NioEventLoop,这样BossGroup就可以通过管理NioEventLoop去管理各个Selector。
- 同时,Netty模型中主要存在两个大的线程池组BossGroup和WorkerGroup,用于管理主Reactor线程和从Reactor线程。
- Netty抽象出两组线程池,BossGroup专门负责接收客户端的连接,WorkerGroup专门负责网络的读写
- BossGroup和WorkerGroup类型的本质都是NioEventLoopGroup类型。
- NioEventLoopGroup相当于一个线程管理器(类似于ExecutorServevice),它下面维护很多个NioEventLoop线程。
- 在初始化这两个Group线程组时,默认会在每个Group中生成CPU*2个NioEventLoop线程
- 当n个连接来了,Group默认会按照连接请求的顺序分别将这些连接分给各个NioEventLoop去处理。
- 同时Group还负责管理EventLoop的生命周期。
- NioEventLoop表示一个不断循环的执行处理任务的线程
- 它维护了一个线程和任务队列。
- 每个NioEventLoop都包含一个Selector,用于监听绑定在它上面的socket通讯。
- 每个NioEventLoop相当于Selector,负责处理多个Channel上的事件
- 每增加一个请求连接,NioEventLoopGroup就将这个请求依次分发给它下面的NioEventLoop处理。
- 每个Boss NioEventLoop循环执行的步骤有3步:
- 轮询accept事件
- 处理accept事件,与client建立连接,生成NioSocketChannel,并将其注册到某个Worker NioEventLoop的selector上。
- 处理任务队列到任务,即runAllTasks
- 每个Worker NioEventLoop循环执行的步骤:
- 轮询read,write事件
- 处理I/O事件,即read,write事件,在对应的NioSocketChannel中进行处理
- 处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks
- 每个 Worker NioEventLoop处理业务时,会使用pipeline(管道)<数据结构为双向链表>,pipeline中维护了一个ChannelHandlerContext链表,而ChannelHandlerContext则保存了Channel相关的所有上下文信息,同时关联一个ChannelHandler对象。如图所示,Channel和pipeline一一对应,ChannelHandler和ChannelHandlerContext一一对应 由此可见每个worker上面通过pipeline管理多个socket的io操作。

- ChannelHandler 是一个接口,负责处理或拦截I/O操作,并将其转发到Pipeline中的下一个处理
Handler进行处理。 - 异步ChannelFuture,表示 Channel 中异步 I/O 操作的结果,在 Netty 中所有的 I/O 操作都是异步的,I/O 的调用会直接返回,调用者并不能立刻获得结果,但是可以通过 ChannelFuture 来获取 I/O 操作的处理状态。
 连接池配置
连接池配置redis: lettuce: pool: #最大连接数 max-active: 50 #最大阻塞等待时间 max-wait: 5000 #连接池中最大空闲连接 max-idle: 10 #连接池中最小空闲连接 min-idle: 5 #eviction线程调度时间间隔 time-between-eviction-runs: 1
 构造过程
构造过程// springboot实例化bean入口 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean({RedisConnectionFactory.class}) LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(ObjectProvider<LettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers, ClientResources clientResources) throws UnknownHostException { // 获取LettuceClientConfiguration配置 LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfig = this.getLettuceClientConfiguration(builderCustomizers, clientResources, this.getProperties().getLettuce().getPool()); // 构造LettuceConnectionFactory return this.createLettuceConnectionFactory(clientConfig); } // 初始化的过程会判断是单点模式/集群模式/哨兵模式,来初始化连接工厂 private LettuceConnectionFactory createLettuceConnectionFactory(LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfiguration) { if (this.getSentinelConfig() != null) { return new LettuceConnectionFactory(this.getSentinelConfig(), clientConfiguration); } else { return this.getClusterConfiguration() != nul l ? new LettuceConnectionFactory(this.getClusterConfiguration(), clientConfiguration) : new LettuceConnectionFactory(this.getStandaloneConfig(), clientConfiguration); } } // LettuceConnectionFactory构造 public LettuceConnectionFactory(RedisStandaloneConfiguration standaloneConfig, LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfig) { this(clientConfig); Assert.notNull(standaloneConfig, "RedisStandaloneConfiguration must not be null!"); this.standaloneConfig = standaloneConfig; this.configuration = this.standaloneConfig; } // InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet public void afterPropertiesSet() { this.client = this.createClient(); // lettuce默认提供了两种实现:有pool配置为LettucePoolingConnectionProvider 没有则为StandaloneConnectionProvider this.connectionProvider = this.createConnectionProvider(this.client, LettuceConnection.CODEC); this.reactiveConnectionProvider = this.createConnectionProvider(this.client, LettuceReactiveRedisConnection.CODEC); // ... }
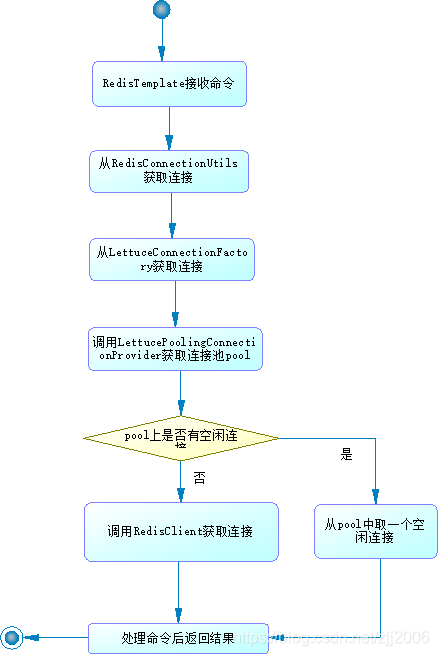
1 /** 2 * 从调用链看实现: redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key) 3 */ 4 1.RedisTemplate.execute() 5 public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean pipeline) { 6 // .. 7 RedisConnection conn = RedisConnectionUtils.getConnection(factory); 8 // .. 9 T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose); 10 // .. 11 finally { 12 RedisConnectionUtils.releaseConnection(conn, factory, this.enableTransactionSupport); 13 } 14 15 } 16 17 2.获取连接类 18 LettuceConnectionFactory.getConnection() 19 // 工厂生成连接类 20 public RedisConnection getConnection() { 21 // getSharedConnection() 实例化了一个连接 22 LettuceConnection connection = this.doCreateLettuceConnection(this.getSharedConnection(), this.connectionProvider, this.getTimeout(), this.getDatabase()); 23 connection.setConvertPipelineAndTxResults(this.convertPipelineAndTxResults); 24 return connection; 25 } 26 27 3.连接类执行 28 3.1 DefaultedRedisConnection.get() // RedisConnection爷爷类 29 3.2 LettuceStringCommands.get() 30 public byte[] get(byte[] key) { 31 // ... 最终执行命令类调用,会触发dispatcher的转发,将请求转为为命令类发送给服务器,服务器解析命令调用对应的命令处理参数,最后服务器最后会写会到命令输出区。 32 return (byte[])this.getConnection().get(key); 33 } 34 3.3 获取连接 35 LettuceConnection.getConnection() 36 protected RedisClusterCommands<byte[], byte[]> getConnection() { 37 if (this.isQueueing()) { 38 return this.getDedicatedConnection(); 39 } else { 40 // 获取共享连接 41 if (this.asyncSharedConn != null) { 42 if (this.asyncSharedConn instanceof StatefulRedisConnection) { 43 return ((StatefulRedisConnection)this.asyncSharedConn).sync(); 44 } 45 46 if (this.asyncSharedConn instanceof StatefulRedisClusterConnection) { 47 return ((StatefulRedisClusterConnection)this.asyncSharedConn).sync(); 48 } 49 } 50 // 从客户端获取, 并设置共享连接 51 return this.getDedicatedConnection(); 52 } 53 } 54 // 获取Command类,提供api调用redis操作 55 RedisClusterCommands<byte[], byte[]> getDedicatedConnection() { 56 StatefulConnection<byte[], byte[]> connection = this.getOrCreateDedicatedConnection(); // 根据支持器获取StatefulRedisConnection 57 if (connection instanceof StatefulRedisConnection) { 58 return ((StatefulRedisConnection)connection).sync(); // StatefulRedisConnection提供Command类来执行命令 59 } else if (connection instanceof StatefulRedisClusterConnection) { 60 return ((StatefulRedisClusterConnection)connection).sync(); 61 } else { 62 throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("%s is not a supported connection type.", connection.getClass().getName())); 63 } 64 } 65 3.4 根据支持器获取真正的连接 66 // StandaloneConnectionProvider 67 Lpublic <T extends StatefulConnection<?, ?>> T getConnection(Class<T> connectionType) { 68 // .. 69 return this.client.connect(this.codec); 70 // .. 71 } 72 // 最底层就是基于netty的接口调用了 73 RedisClient.connect() 74 private void initializeChannelAsync0(ConnectionBuilder connectionBuilder, CompletableFuture<Channel> channelReadyFuture, 75 SocketAddress redisAddress) { 76 77 logger.debug("Connecting to Redis at {}", redisAddress); 78 79 80 Bootstrap redisBootstrap = connectionBuilder.bootstrap(); 81 82 RedisChannelInitializer initializer = connectionBuilder.build(); 83 redisBootstrap.handler(initializer); 84 85 clientResources.nettyCustomizer().afterBootstrapInitialized(redisBootstrap); 86 CompletableFuture<Boolean> initFuture = initializer.channelInitialized(); 87 ChannelFuture connectFuture = redisBootstrap.connect(redisAddress); 88 //省略部分代码 89 } 90 // LettucePoolingConnectionProvider 91 public <T extends StatefulConnection<?, ?>> T getConnection(Class<T> connectionType) { 92 // 初次调用会创建线程池 93 GenericObjectPool pool = (GenericObjectPool)this.pools.computeIfAbsent(connectionType, (poolType) -> { 94 return ConnectionPoolSupport.createGenericObjectPool(() -> { 95 return this.connectionProvider.getConnection(connectionType); //创建连接的回调函数, 其实就是调用上方StandaloneConnectionProvider.getConnection 96 }, this.poolConfig, false); 97 }); 98 99 try { 100 // 从池子里获取一个连接 101 StatefulConnection<?, ?> connection = (StatefulConnection)pool.borrowObject(); 102 this.poolRef.put(connection, pool); 103 return (StatefulConnection)connectionType.cast(connection); 104 } catch (Exception var4) { 105 throw new PoolException("Could not get a resource from the pool", var4); 106 } 107 } 108 3.5 获取一个连接 109 public T borrowObject(long borrowMaxWaitMillis) throws Exception { 110 // ... 111 112 PooledObject<T> p = null; 113 boolean blockWhenExhausted = this.getBlockWhenExhausted(); 114 long waitTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 115 116 while(p == null) { 117 boolean create = false; 118 // 从闲置获取连接 119 p = (PooledObject)this.idleObjects.pollFirst(); 120 if (p == null) { 121 // 获取不到则创建,调用的是传入的回调函数 122 p = this.create(); 123 if (p != null) { 124 create = true; 125 } 126 } 127 } 128 // .. 129 return p.getObject(); 130 } 131 3.6 释放连接 132 public void returnObject(T obj) { 133 //... 134 int maxIdleSave = this.getMaxIdle(); 135 if (this.isClosed() || maxIdleSave > -1 && maxIdleSave <= this.idleObjects.size()) { 136 try { 137 this.destroy(p); 138 } catch (Exception var12) { 139 this.swallowException(var12); 140 } 141 142 try { 143 this.ensureIdle(1, false); 144 } catch (Exception var11) { 145 this.swallowException(var11); 146 } 147 } else { 148 if (this.getLifo()) { 149 this.idleObjects.addFirst(p); 150 } else { 151 this.idleObjects.addLast(p); 152 } 153 154 if (this.isClosed()) { 155 this.clear(); 156 } 157 } 158 }
调用链流程:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)