Task1-机器学习算法基础
·损失函数:单一样本预测错误程度————越小越好
·代价函数:全部样本集的平均误差
目标函数:代价函数、正则化函数,最终优化者
设定目标函数的原因:代价函数可以度量全部样本集的平均误差。模型过大,预测测试集会出现过拟合。
练习
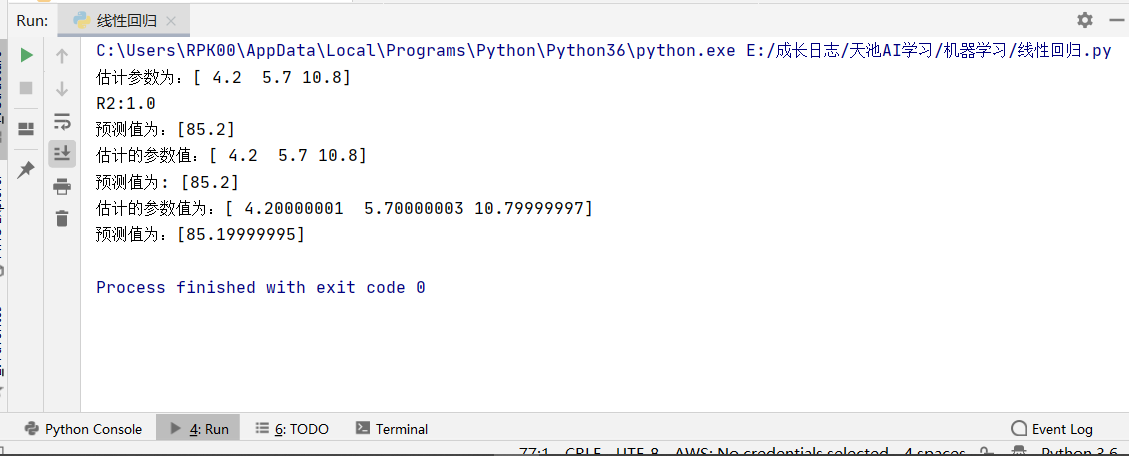
1 #os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1" 2 #生成数据 3 import numpy as np 4 #生成随机数 5 np.random.seed(1234) 6 x = np.random.rand(500,3) 7 #构建映射关系时,模拟真实的数据待预测值,映射关系为:y=4.2+5.7*x1+10.8*x2,可自行设置值进行尝试 8 y = x.dot(np.array([4.2,5.7,10.8])) 9 #lr = sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=1) 10 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression 11 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 12 #% matplotlib inline 13 #sklearn模型 14 #调用模型 15 lr = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True) 16 #训练模型 17 lr.fit(x,y) 18 print("估计参数为:%s" %(lr.coef_)) 19 #计算R平方 20 print('R2:%s' %(lr.score(x,y))) 21 #任意设定变量,预测目标值 22 x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1) 23 y_hat = lr.predict(x_test) 24 print("预测值为:%s" %(y_hat)) 25 #=========================== 26 #========================== 27 #最小二乘法矩阵模型 28 class LR_LS(): 29 def __init__(self): 30 self.w = None 31 def fit(self, X, y): 32 # 最小二乘法矩阵求解 33 #============================= show me your code ======================= 34 self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y) 35 #============================= show me your code ======================= 36 def predict(self, X): 37 # 用已经拟合的参数值预测新自变量 38 #============================= show me your code ======================= 39 y_pred = X.dot(self.w) 40 #============================= show me your code ======================= 41 return y_pred 42 43 if __name__ == "__main__": 44 lr_ls = LR_LS() 45 lr_ls.fit(x,y) 46 print("估计的参数值:%s" %(lr_ls.w)) 47 x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1) 48 print("预测值为: %s" %(lr_ls.predict(x_test))) 49 50 #梯度下降模型 51 class LR_GD(): 52 def __init__(self): 53 self.w = None 54 def fit(self,X,y,alpha=0.02,loss = 1e-10): # 设定步长为0.002,判断是否收敛的条件为1e-10 55 y = y.reshape(-1,1) #重塑y值的维度以便矩阵运算 56 [m,d] = np.shape(X) #自变量的维度 57 self.w = np.zeros((d)) #将参数的初始值定为0 58 tol = 1e5 59 #============================= show me your code ======================= 60 while tol > loss: 61 h_f = X.dot(self.w).reshape(-1,1) 62 theta = self.w + alpha*np.mean(X*(y - h_f),axis=0) #计算迭代的参数值 63 tol = np.sum(np.abs(theta - self.w)) 64 self.w = theta 65 #============================= show me your code ======================= 66 def predict(self, X): 67 # 用已经拟合的参数值预测新自变量 68 y_pred = X.dot(self.w) 69 return y_pred 70 71 if __name__ == "__main__": 72 lr_gd = LR_GD() 73 lr_gd.fit(x,y) 74 print("估计的参数值为:%s" %(lr_gd.w)) 75 x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1) 76 print("预测值为:%s" %(lr_gd.predict(x_test)))
#os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1"
#生成数据
import numpy as np
#生成随机数
np.random.seed(1234)
x = np.random.rand(500,3)
#构建映射关系时,模拟真实的数据待预测值,映射关系为:y=4.2+5.7*x1+10.8*x2,可自行设置值进行尝试
y = x.dot(np.array([4.2,5.7,10.8]))
#lr = sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=1)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#% matplotlib inline
#sklearn模型
#调用模型
lr = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
#训练模型
lr.fit(x,y)
print("估计参数为:%s" %(lr.coef_))
#计算R平方
print('R2:%s' %(lr.score(x,y)))
#任意设定变量,预测目标值
x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1)
y_hat = lr.predict(x_test)
print("预测值为:%s" %(y_hat))
#===========================
#==========================
#最小二乘法矩阵模型
class LR_LS():
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
def fit(self, X, y):
# 最小二乘法矩阵求解
#============================= show me your code =======================
self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
#============================= show me your code =======================
def predict(self, X):
# 用已经拟合的参数值预测新自变量
#============================= show me your code =======================
y_pred = X.dot(self.w)
#============================= show me your code =======================
return y_pred
if __name__ == "__main__":
lr_ls = LR_LS()
lr_ls.fit(x,y)
print("估计的参数值:%s" %(lr_ls.w))
x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1)
print("预测值为: %s" %(lr_ls.predict(x_test)))
#梯度下降模型
class LR_GD():
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
def fit(self,X,y,alpha=0.02,loss = 1e-10): # 设定步长为0.002,判断是否收敛的条件为1e-10
y = y.reshape(-1,1) #重塑y值的维度以便矩阵运算
[m,d] = np.shape(X) #自变量的维度
self.w = np.zeros((d)) #将参数的初始值定为0
tol = 1e5
#============================= show me your code =======================
while tol > loss:
h_f = X.dot(self.w).reshape(-1,1)
theta = self.w + alpha*np.mean(X*(y - h_f),axis=0) #计算迭代的参数值
tol = np.sum(np.abs(theta - self.w))
self.w = theta
#============================= show me your code =======================
def predict(self, X):
# 用已经拟合的参数值预测新自变量
y_pred = X.dot(self.w)
return y_pred
if __name__ == "__main__":
lr_gd = LR_GD()
lr_gd.fit(x,y)
print("估计的参数值为:%s" %(lr_gd.w))
x_test = np.array([2,4,5]).reshape(1,-1)
print("预测值为:%s" %(lr_gd.predict(x_test)))

