hot tea.
\(\rm I\) 解析几何临时例题
Problem I 【非对称韦达】
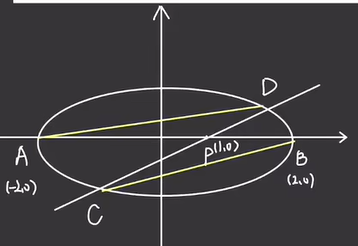
【Description】已知椭圆 \(\dfrac{x^2}4+y^2=1\),其长轴上两定点为 \(A(-2, 0), B(2, 0)\)。过 \(P(1, 0)\) 作直线交椭圆于 \(C, D\) 两点,证明:\(k_{AD}\cdot k_{BC}\) 为定值。
椭圆的第三定义:\(k_{PA}\cdot k_{PB}=e^2-1\)
貌似可以 参与运算??
【Solution】
网上给了 n 中解法,自己发现可以先设 \(\ell_{AD}, \ell_{BC}\) 的斜率为 \(k_1, k_2\),然后用 \(k_1, k_2\) 表示 \(x_D, y_D, x_C, y_C\),由 \(C, D, P\) 共线得 \(\dfrac{y_D}{x_D-1}=\dfrac{y_C}{x_C-1}\),带入并因式分解得到 \((4k_1k_2+1)(3k_1-k_2)=0\)。前者为椭圆的第三定义,那么取后者 \(\dfrac{k_1}{k_2}=\dfrac13\)。
Problem II 【齐次化-平移】
【Description】已知椭圆 \(\dfrac{x^2}{6}+\dfrac{y^2}{3}=1\),其上有定点 \(A(2, 1)\)。过 \(A\) 引两条互相垂直的直线 \(\ell_{AM}, \ell_{AN}\) 交椭圆于 \(M, N\)。过 \(A\) 作 \(\ell_{AD}\perp \ell_{MN}\) 交 \(\ell_{MN}\) 于 \(D\)。证明有定点 \(Q\) 满足 \(|DQ|\) 为定值。
【Solution】本题是齐次化 - 平移例题。
将坐标系原点平移至 \(A\)。设 \(\ell_{MN}:mx+ny=0\)。带入使用齐次化惯用手段得到 \(m+n+\dfrac34=0\),解出过的定点是什么。
但是我们可以这样做:因为 \(D\) 在一个圆上,而从 \(D\) 出发已经有两条垂直的直线,那么就是说如果能在这两条直线上分别找两个定点,就可以构出斜边中线(可以证明这是充要的)。所以我们要做的就是找出 \(\ell_{MN}\) 过哪一个定点 \(P\),构出 \(\Delta ADP\) 的斜边中线。
设其过的定点为 \(P(x_0, y_0)\),并设 \(\ell_{MN}:y=k(x-x_0)+y_0\)。那么我们将 \(\ell_{MN}\) 与椭圆联立。根据 \(\ell_{AM}\perp\ell_{AN}\) 列式 \(\dfrac{y_M-1}{x_M-2}\cdot\dfrac{y_N-1}{x_N-2}=-1\),发现该式对称,那么利用韦达定理算出 \(x_M+x_N, x_Mx_N, y_M+y_N, y_My_N\) 关于主元 \(k\) 和参数 \(x_0, y_0\) 的式子,得到 \((9x_0^2-24x_0+12)k^2+(-18x_0y_0+24y_0+6x_0)k+9y_0^2-6y_0-3=0\)。该式子可看成关于 \(k\) 的二次方程,对于任意 \(k\) 都有上式成立,则 \(\begin{cases}9x_0^2-24x_0+12=0\\-18x_0y_0+24y_0+6x_0\\9y_0^2-6y_0-3\end{cases}\)。解得 \(P(1, 2)\)(舍)或 \(P(\dfrac23, -\dfrac13)\)。故 \(Q(\dfrac43, \dfrac13)\)。
Problem III ?
【Description】椭圆 \(\dfrac{x^2}{4}+\dfrac{y^2}{3}=1\)。椭圆上一点 \(P\),过 \(P\) 作椭圆的切线交直线 \(x=4\) 与 \(Q\)。证明存在一定点 \(D\),满足 \(\ell_{PD}\perp\ell_{QD}\)。
Problem IV ???
过椭圆外一点 \(P\) 引椭圆的两条割线 \(\ell_{AC}, \ell_{BD}\),且 \(\ell_{OP}\) 过弦 \(AB\) 的中点。求证:\(\ell_{AB}\parallel\ell_{CD}\)。
\(\rm II\)
- T1
- \(\cos(A+2B)+\cos A=\sin2B\)
- 求 \(\min\{\dfrac{4a^2+5b^2}{c^2}\}\)
- T2
- 锐角 \(\Delta ABC\),\(\cos2B-\cos2A=4(\cos C-\cos^3C)\)
- 求 \(\dfrac ab+\dfrac{b^2}{c^2}\) 取值范围
- T3
- 锐角 \(\Delta ABC\),角 \(A, B, C\) 的对边依次为 \(a, b, c\),满足 \(2S_{\Delta ABC}=a^2-(b-c)^2\)。求 \(\dfrac{4b^2-12bc+17c^2}{4b^2-12bc+13c^2}\) 的取值范围。
- 答案:\((\dfrac{281}{181}, 2]\)
三角
- 化边或化角?
- 看证什么?
- 证角就化角,因为边证不了角
- 如果考虑化边(转为 \(a, b, c\) 的式子)那么就基本上就是用正弦、余弦等等。
- 看证什么?
- 代数化简
- 原则:多倍化同倍,异名化同名,往待证的方向化简(如果没有直接的待证那么就当是要得到一个强力的角度关系)
- 和差化积:一堆复杂的角的和差的同名三角函数加减,像 \(\cos(A+2B)+\cos A=\sin 2B\)
- 一个 trick:题目中给了角或边可以将值带入调节次数。
\(\rm III\ \overrightarrow{\boldsymbol{Derivative}}\)
\(\it 50\ {Problems}\)
Problem 1
Description
\(f(x)=\ln x+\dfrac ax\)
- 若不等式 \(f(x)\ge\dfrac{2-e}{x}+a\) 对于 \(x>0\) 恒成立,求 \(a\) 范围。
Solution
必要性探路:取 \(x=1\) 和 \(x=e\),得到 \(a\le 2\)。
求导,\(f'(x)=\dfrac 1x-\dfrac{e-2+a}{x^2}\),极值点 \(x_0=e-2+a\)。带入 \(f(x_0)\ge0\) 求解即可。
Problem 2
Description
证明:对 \(\forall a\in(0, 1)\),存在 \(b>0\) 使得 \(ae^b=a+b\),且 \(2\ln a+b<0\)。
Solution
画图,得到大致图像,确定方程有唯一合法解。
利用方程消元,\(a=\dfrac{b}{e^b-1}\),\(b\) 为原方程的零点,取值范围为 \((0, +\infin)\),问题转化为证明 \(2\ln\dfrac{b}{e^b-1}+b<0\),即证 \(\forall x>0, x^2e^x<(e^x-1)^2\)。
写出函数 \(g(x)=e^{2x}-(2+x^2)e^x+1\),\(g'(x)=2e^{2x}-(x^2+2x+2)e^x=2e^x(e^x-\dfrac12x^2-x-1)\),经典不等式放缩得 \(g'(x)>0\),带入端点原式得证。
Problem 3
Description
\(f(x)=e^x\ln(x+1)\),证明:对 \(\forall x, t\in (0, +\infin)\),有 \(f(x+y)>f(x)+f(y)\)。
Solution
思路:选取主元,证明不等式大于零(显然构造的函数是单调的)
令 \(x<m\),构造 \(g(x)=f(x+m)-f(x)\),则 \(g(x)=e^x\cdot (e^m\cdot\ln(x+m+1)-\ln(x+1))\),即证 \((e^m\cdot \ln(x+m-1)-\ln(x+1))\),即政 \(h(x)=e^m\cdot\ln(x+m-1)-\ln(x+1)\)。
求导,\(h'(x)=\dfrac{e^m}{x+m+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\),易证 \(h'(x)>0\)。得证。
Problem 4
Description
同 Problem 3
Solution
Problem 5
Description
证明:\(e^x\ln x-1+\dfrac{2e^{x-1}}{x}>0\)
Solution
直接求导,发现零点没法弄,带入了几个点发现都取不到等去,于是考虑是不是没卡死的不等式,考虑放缩。
初步化简:即证 \(\ln x+\dfrac{2}{ex}>e^{-x}\)
画图,发现的确没卡死,那么考虑“隔离折线”。但是不好操作。
变一下,即证 \(x\ln x>\dfrac{x}{e^x}-\dfrac{2}{e}\),隔离直线 \(y=-\dfrac{1}{e}\)。
一般在隔离直线的时候,函数的凹凸性得考虑一下。
放缩解法:
\(\ln x-\dfrac{1}{e^x}+\dfrac{2}{ex}\quad\overset{e^x\ge ex}{\longrightarrow}\quad\ge\ln x-\dfrac{1}{ex}+\dfrac{2}{ex}=\ln x+\dfrac1{ex}>0\)
\(\Large\star\) Problem 6
Description
证明:对 \(\forall x>1\) 有 \(e^x-x^4+3x^3\ln x-x^2\ge 0\)
Solution
\(e^t-t\ge 1\ge \dfrac1x\)
得证。
Problem 7
Description
证明:\(a\le 1\) 时有 \(xe^x-ax\ge \ln x+1\)
Solution
\(xe^x-ax\ge xe^x-x\)
即证 \(xe^x-x+\ln x-1\ge 0\)
同构,\(xe^x-\ln(xe^x)\ge 1\longrightarrow t-\ln t\ge 1\) 得证。
Problem 8
Description
证明:对 \(\forall a\ge 1\) 有 \(ae^x-x-a> x\ln x-\sin x\)
Solution
放缩参数,只需证明 \(a=1\) 时成立即可。
即证 \(e^x-x-1-x\ln x>-\sin x\)
设 \(f(x)=e^x-1-x-x\ln x\),求导,\(f'(x)=e^x-2-\ln x=0\),\(f''(x)=e^x-\dfrac1x\)。设 \(f''(x)=0\) 的根为 \(x_0\),则 \(x_0e^{x_0}=1\),对 \(f'(x_0)\) 的式子进行替换,\(f'(x_0)=\dfrac1{x_0}-2+x_0\ge 0\),即 \(f'(x)\ge 0\),\(f(x)\) 单增。
隔离折线,只需证明 \(x\in(0, \pi]\) 时 \(e^x-x-1-x\ln x>0>-\sin x\),\(x\in(\pi, +\infin)\) 时 \(e^x-x-1-x\ln x>1>-\sin x\) 即可。
得证。
Problem 9
Description
证明:\(\dfrac{1-\ln x}{e^x}+2x^2-\dfrac1x<2\) 在 \(x\in(0, 1)\) 恒成立。
Solution
一眼 · 丁真,鉴定为:
\(\dfrac{1-\ln x}{e^x}+2x^2-\dfrac1x<1-(\ln x+\dfrac1x)+2x^2\)
\(x\in(0, 1)\to\begin{cases} \ln x+\dfrac1x> 1\\ 2x^2< 2 \end{cases}\)
得证。
Problem 16
Description
\(f(x)=e^{x+1}+ax+a\)
- 若 \(x\ge 0\) 时,\(f(x-1)+\ln(x+1)\ge 1\),求 \(a\) 取值范围。
Solution
\(g(x)=e^x+ax+\ln(x+1)-1\),\(g'(x)=e^x+a+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)。
端点效应,带入 \(x=0\),\(g(0)=0\),则 \(g'(0)\ge 0\),解得 \(a\ge -2\)。
若 \(a\ge -2\),则 \(g'(x)=e^x+a+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\ge 0\)。带入 \(x=0\) 得 \(g(0)=0\)。
答案为 \(a\ge -2\)。
Problem 1
Description
\(f(x)=(x-1)\ln x-a(x+1)\) 有两个零点 \(x_1, x_2\)。
- 求 \(a\) 的范围。(答案:\(a>0\))
- 证明 \(\dfrac1{\ln x_1-a}+\dfrac1{\ln x_2-a}>0\)
tag:极值点偏移、预处理变形
Solution
\(\begin{cases} (x_1-1)\ln x_1=a(x_1+1)\\ (x_2-1)\ln x_2=a(x_2+1) \end{cases}\to\begin{cases} \ln x_1=a\cdot\dfrac{x_1+1}{x_1-1}\\ \ln x_2=a\cdot\dfrac{x_2+1}{x_2-1} \end{cases}\)
\(\dfrac1{\ln x_1-a}+\dfrac1{\ln x_2-a}=\dfrac{x_1-1}{2a}+\dfrac{x_2-1}{2a}>0\to x_1+x_2>2\)
这样子代?
Problem 2
Description
\(f(x)=ae^{x-1}-\ln x+\ln a\)
- 若 \(f(x)\ge 1\),求 \(a\) 取值范围。
Solution
- 同构。
- \(e^{x+\ln a-1}+x+\ln a-1\ge e^{\ln x}+\ln x\)
- 普通
- \(f'(x)=0\),解得 \(x=x_0\),满足 \(ae^{x-1}=\dfrac1x\)
- 然后把 \(a\) 代成 \(x_0\),发现刚好代完了。
- 于是 \(f(x_0)\) 与 \(a\) 脱离了关系,直接求即可。
- 还有。
Problem 3
Description
证明 \(\sum\limits_{k=1}^n\dfrac1{\sqrt{k^2+k}}>\ln(n+1)\)
Solution
首先常规数列不等式的套路,转化为证 \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x^2+x}}>\ln(x+1)-\ln x\)
这怎么证?????????????
瞎几把想ing
看一下均值不等式 \(\sqrt{ab}<\dfrac{b-a}{\ln b-\ln a}\)?
我去!做出来了!
还没看其他方法。
Problem 4
Description
\(f(x)=x-\dfrac12\sin x-\dfrac m2\ln x+1\)
- 若存在 \(x_1, x_2\in(0, +\infin)\),且 \(x_1\not=x_2\),\(f(x_1)=f(x_2)\),证明:\(x_1x_2<m^2\)
Solution
这个东西取小于号和小于等于号有什么猫腻?
首先尝试极值点偏移,但是发现 \(m\) 根本不是极值点!
那然后呢?不能用极值点的构造对称,那么要证明不等式成立,说明很可能并不是要取到等(卡死),而是能够放缩,而且正好三角函数基本是放缩。
于是只能模仿代数消元,先写关系式:
\(\begin{cases}x_1-\dfrac12\sin x_1-\dfrac m2\ln x_1+1=T\\x_2-\dfrac12\sin x_2-\dfrac m2\ln x_2+1=T\end{cases}\)
\(x_2-x_1-\dfrac12(\sin x_2-\sin x_1)=\dfrac m2(\ln x_2-\ln x_1)\)
运用三角函数放缩 \(x>\sin x\) 得 \(\dfrac m2(\ln x_2-\ln x_1)=x_2-x_1-\dfrac12(\sin x_2-\sin x_1)>\dfrac12(x_2-x_1)\),然后对数均值不等式悬而击之。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
signed main() {
}
Problem 4
Description
\(f(x)=ax-\ln x\),关于 \(x\) 的方程 \(f(x)=0\) 有两个不相等的实数根 \(x_1, x_2\),其中 \(x_1<x_2\)。
- 求实数 \(a\) 的取值范围。
- 设 \(k\) 为常数,当 \(a\) 变化时,若 \(x_1^kx_2\) 有最小值 \(e^e\),求常数 \(k\) 的值。
Solution
一眼看过去,式子极其丑陋,那么考虑列出方程组作代换,凑 \(x_1^k\) 出来。
\(\begin{cases} kax_1=\ln x_1^k\\ ax_2=\ln x_2 \end{cases}\)
于是 \(a(kx_1+x_2)=\ln x_1^kx_2\ge e\)
消去 \(a\),得到 \(a=\dfrac{\ln x_2-\ln x_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
带入,齐次化,设 \(t=\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}\),得到 \(\ln t\cdot\dfrac{t+k}{t-1}\ge e\)
那么问题转化为:已知定义域为 \((1, +\infin)\) 的函数 \(f(t)=\ln t\cdot\dfrac{t+k}{t-1}\) 最小值为 \(e\),求 \(k\).
啊???
答案:\(k=e^2-2e\)
Problem 5
Description
\(f(x)=e^x-x, g(x)=x-\ln x\)
- 证明存在一条直线 \(y=b\),使得该直线与 \(f(x)\) 和 \(g(x)\) 的图像共有三个交点,且交点的横坐标呈等差数列。
Solution
这不来一手同构?
画个图,发现 \(y=b\) 必然交在 \(f(x)\) 和 \(g(x)\) 的交点处。
大概判断一下零点的大小关系,得 \(x_1<0<x_2<1<x_3\)
然后同构大显身手!\(e^{x_1}-x_1=b, e^{x_2}-x_2=b, x_2-\ln x_2=b\)
那么得 \(e^{x_1}-\ln e^{x_1}=b\),所以 \(e^{x_1}=x_2\) 或 \(x_3\)。由根的所在值域得 \(e^{x_1}=x_2\)。同理 \(\ln x_3=x_2\)。
即证 \(e^{x_2}+\ln x_2=2x_2\)。结合前面的式子易证。
Problem 6
Description
已知 \(\begin{cases}a\ln x_1=2x_1-3\\a\ln x_2=2x_2-3\end{cases}\),求当 \(x_2\over x_1\) 最小时 \(a\) 的值。
Solution
先消元得到 \(\dfrac{\ln x_1}{2x_1-3}=\dfrac{\ln x_2}{2x_2-3}\),然后设 \(x_2=t\cdot x_1\),带入尝试各种操作看能不能分离,发现可以,完结。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号