TensorFlow教程——Bi-LSTM+CRF进行序列标注(代码浅析)
https://blog.csdn.net/guolindonggld/article/details/79044574
Bi-LSTM
使用TensorFlow构建Bi-LSTM时经常是下面的代码:
cell_fw = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(num_units=100)
cell_bw = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(num_units=100)
(outputs, output_states) = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(cell_fw, cell_bw, inputs,
sequence_length=300)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
首先下面是我画的Bi-LSTM示意图:
其实LSTM使用起来很简单,就是输入一排的向量,然后输出一排的向量。构建时只要设定两个超参数:num_units和sequence_length。
LSTMCell
tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(
num_units,
use_peepholes=False,
cell_clip=None,
initializer=None,
num_proj=None,
proj_clip=None,
num_unit_shards=None,
num_proj_shards=None,
forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True,
activation=None,
reuse=None
)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
上面的LSTM Cell只有一个超参数需要设定,num_units,即输出向量的维度。
bidirectional_dynamic_rnn()
(outputs, output_states) = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
cell_fw,
cell_bw,
inputs,
sequence_length=None,
initial_state_fw=None,
initial_state_bw=None,
dtype=None,
parallel_iterations=None,
swap_memory=False,
time_major=False,
scope=None
)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
这个函数唯一需要设定的超参数就是序列长度sequence_length。
输入:
inputs的shape通常是[batch_size, sequence_length, dim_embedding]。
输出:
outputs是一个(output_fw, output_bw)元组,output_fw和output_bw的shape都是[batch_size, sequence_length, num_units]
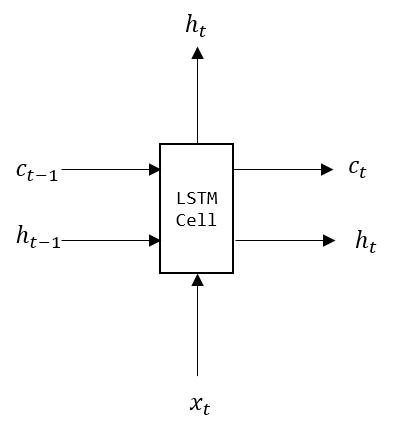
output_states是一个(output_state_fw, output_state_bw) 元组,分别是前向和后向最后一个Cell的Output,output_state_fw和output_state_bw的类型都是LSTMStateTuple,这个类有两个属性c和h,分别表示Memory Cell和Hidden State,如下图:
CRF
对于序列标注问题,通常会在LSTM的输出后接一个CRF层:将LSTM的输出通过线性变换得到维度为[batch_size, max_seq_len, num_tags]的张量,这个张量再作为一元势函数(Unary Potentials)输入到CRF层。

# 将两个LSTM的输出合并
output_fw, output_bw = outputs
output = tf.concat([output_fw, output_bw], axis=-1)
# 变换矩阵,可训练参数
W = tf.get_variable("W", [2 * num_units, num_tags])
# 线性变换
matricized_output = tf.reshape(output, [-1, 2 * num_units])
matricized_unary_scores = tf.matmul(matricized_output , W)
unary_scores = tf.reshape(matricized_unary_scores, [batch_size, max_seq_len, num_tags])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
损失函数
# Loss函数
log_likelihood, transition_params = tf.contrib.crf.crf_log_likelihood(unary_scores, tags, sequence_lengths)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(-log_likelihood)- 1
- 2
- 3
其中
tags:维度为[batch_size, max_seq_len]的矩阵,也就是Golden标签,注意这里的标签都是以索引方式表示的。
sequence_lengths:维度为[batch_size]的向量,记录了每个序列的长度。
log_likelihood:维度为[batch_size]的向量,每个元素代表每个给定序列的Log-Likelihood。
transition_params :维度为[num_tags, num_tags]的转移矩阵。注意这里的转移矩阵不像传统的HMM概率转移矩阵那样要求每个元素非负且每一行的和为1,这里的每个元素取值范围是实数(正负都可以)。
解码
decode_tags, best_score = tf.contrib.crf.crf_decode(unary_scores, transition_params, sequence_lengths)- 1
其中
decode_tags:维度为[batch_size, max_seq_len]的矩阵,包含最高分的标签序列。
best_score :维度为[batch_size]的向量,包含最高分数。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号