随机生成数组函数+nth-element函数
这几天做了几道随机生成数组的题,且需要用nth-elemeng函数,并且都是北航出的多校题……
首先我们先贴一下随机生成数组函数的代码:

1 unsigned x = A, y = B, z = C; 2 unsigned rng61() { 3 unsigned t; 4 x ^= x << 16; 5 x ^= x >> 5; 6 x ^= x << 1; 7 t = x; 8 x = y; 9 y = z; 10 z = t ^ x ^ y; 11 return z; 12 }
这个函数的原理原谅我不太懂,就不多说了-_-||。
接下来来谈一下stl中的一个nth_element函数,这个函数对于一个数组、容器(我们就用最普通的数组a来进行讨论),假设我们需要求这个数组中的第k个元素,那么我们只需nth_element(a,a+k,a+n)(下标从0开始),那么a中第k小的数将会出现在第k个位置,且能够保证前k-1个元素都比它小,后面的元素都比它大(但是这两堆数是无序的),复杂度为O(n),该函数的一般用法为:nth_element(开始位置,所求位置,结束位置)。stl是个神奇的东西,里面还有max_element,min_element函数,具体用法请点击链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/Dillonh/p/9042456.html。
顺便贴一下这几天做的两道题:
第一道为昨天牛客多校的J题Heritage of skywalkert,题目链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/144/J
题目:
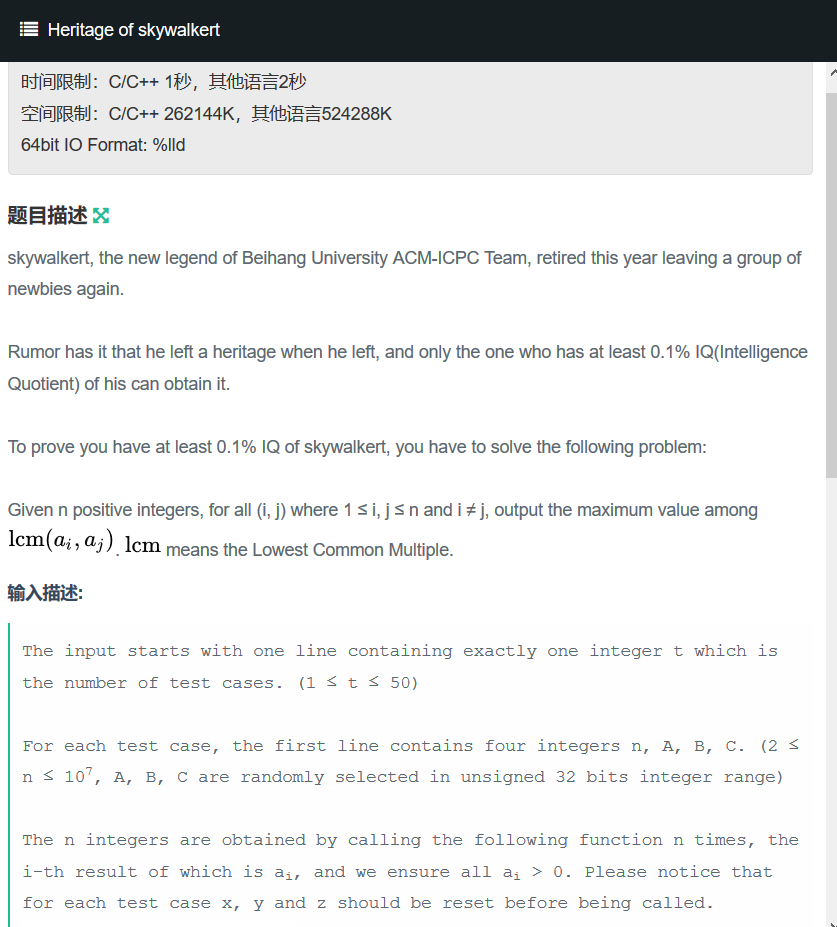


题意:用随机生成数组函数生成n个数,求这n个数中两两的lcm(最小公倍数)的最大值,n的范围为2e6.
思路:虽说要n个,但是我们只需要取出100个最大的即可,因为据证明两个数互质的概率为 (具体证明请自行百度),所以我们只需将这100个数求次lcm即可。
(具体证明请自行百度),所以我们只需将这100个数求次lcm即可。
代码实现如下:

1 #include <set> 2 #include <map> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <stack> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <bitset> 7 #include <cstdio> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <cstdlib> 11 #include <cstring> 12 #include <iostream> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 using namespace std; 15 16 typedef long long ll; 17 typedef pair<ll, ll> pll; 18 typedef pair<ll, int> pli; 19 typedef pair<int, ll> pil;; 20 typedef pair<int, int> pii; 21 typedef unsigned long long ull; 22 23 #define lson i<<1 24 #define rson i<<1|1 25 #define bug printf("*********\n"); 26 #define FIN freopen("D://code//in.txt", "r", stdin); 27 #define debug(x) cout<<"["<<x<<"]" <<endl; 28 #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0); 29 30 const double eps = 1e-8; 31 const int mod = 10007; 32 const int maxn = 1e7 + 7; 33 const double pi = acos(-1); 34 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 35 const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 36 37 int tt, n; 38 unsigned int x, y, z; 39 ull num[maxn]; 40 41 unsigned int tang() { 42 unsigned t; 43 x ^= x << 16; 44 x ^= x >> 5; 45 x ^= x << 1; 46 t = x; 47 x = y; 48 y = z; 49 z = t ^ x ^ y; 50 return z; 51 } 52 53 ull gcd(ull a, ull b) { 54 return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); 55 } 56 57 int main() { 58 //FIN; 59 scanf("%d", &tt); 60 int icase = 0; 61 while(tt--) { 62 scanf("%d%u%u%u", &n, &x, &y, &z); 63 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 64 num[i] = tang(); 65 } 66 ull mx = 0; 67 if(n > 101) { 68 int tmp = n - 100; 69 nth_element(num, num + tmp, num + n); 70 for(int i = tmp; i < n; i++) { 71 for(int j = tmp; j < n; j++) { 72 ull tt = num[i] / gcd(num[i], num[j]) * num[j]; 73 mx = mx > tt ? mx : tt; 74 } 75 } 76 } else { 77 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 78 for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 79 ull tt = num[i] / gcd(num[i], num[j]) * num[j]; 80 mx = mx > tt ? mx : tt; 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 printf("Case #%d: %llu\n", ++icase, mx); 85 } 86 return 0; 87 }
第二题是2017年杭电多校的题目,Hints of sd0061(HDU6040:
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6040
题目:
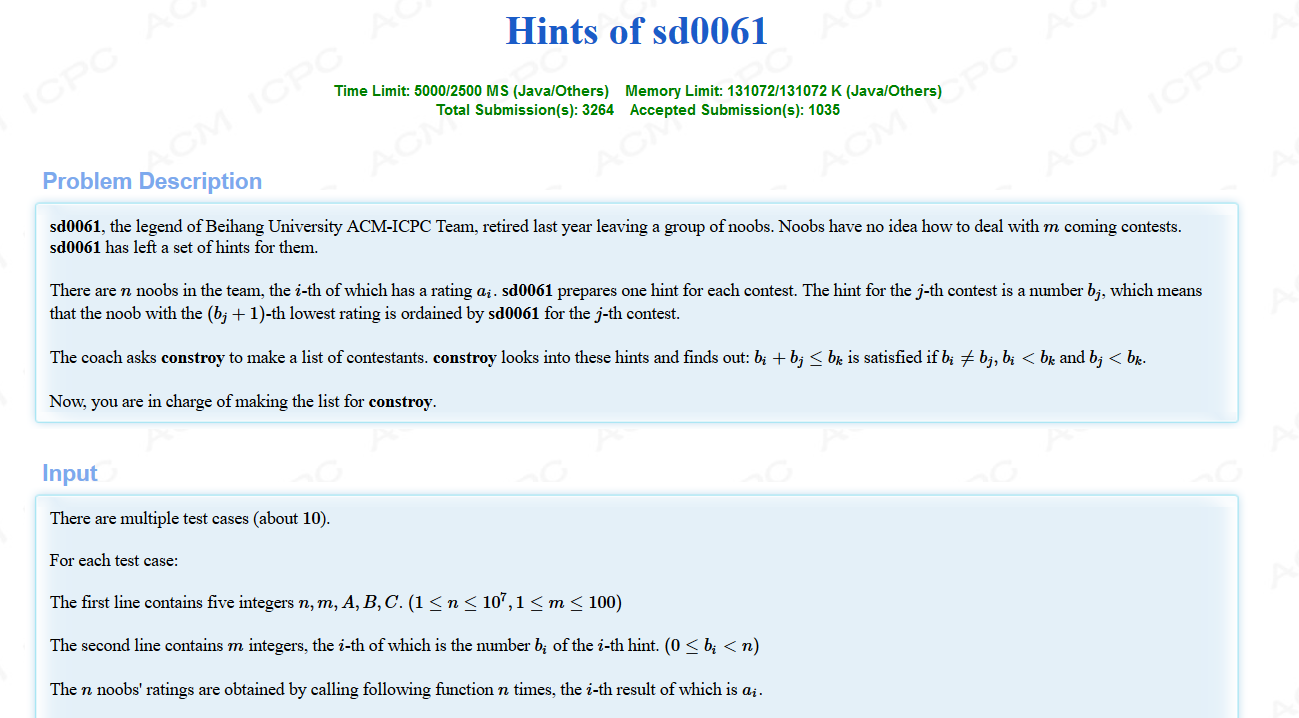

题意:用随机生成数组函数生成n个数,且求出第bi+1位的数,n的范围为1e7。
思路:这题照样需要借助nth_element函数,但是由于n太大,再加上要求m个数,复杂度妥妥地T,所以我们要想点优化,我们知道nth_element的复杂度是与所求范围来决定的,且nth_element函数会将大于某个数小于某个数分开,那么我们可以借助先求出排在后面的数,再求排在前面的数,逐步将范围缩小,从而缩小范围。
代码实现如下:

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 const int maxn = 1e7 + 7; 6 7 int n, m; 8 pair<int, int> b[105]; 9 unsigned a[maxn], num[maxn]; 10 unsigned x, y, z; 11 12 unsigned rng61() { 13 unsigned t; 14 x ^= x << 16; 15 x ^= x >> 5; 16 x ^= x << 1; 17 t = x; 18 x = y; 19 y = z; 20 z = t ^ x ^ y; 21 return z; 22 } 23 24 int main() { 25 int icase = 0; 26 while(~scanf("%d", &n)) { 27 scanf("%d%u%u%u", &m, &x, &y, &z); 28 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { 29 scanf("%d", &b[i].first); 30 b[i].second = i; 31 } 32 sort(b, b + m); 33 b[m].first = n; 34 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 35 a[i] = rng61(); 36 } 37 printf("Case #%d:", ++icase); 38 for(int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 39 nth_element(a, a + b[i].first, a + b[i+1].first); 40 num[b[i].second] = a[b[i].first]; 41 } 42 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { 43 printf(" %u", num[i]); 44 } 45 printf("\n"); 46 } 47 return 0; 48 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号