数据结构和算法(5)-二叉树
4.4 二叉树抽象数据类型及其实现
4.4.1 二叉树 ADT
二叉树ADT支持的基本操作:
| 操作方法 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| getElement(): | 返回存放当前节点处的对象 输入:无 输出:对象 |
| setElement(e): | 将对象 e 存入当前节点,并返回其中此前所存的内容 输入:一个对象 输出:对象 |
| getParent(): | 返getParent(): 返回当前节点的父节点 输入:无 输出:树节点 |
| getElement(): | 返回存放当前节点处的对象 输入:无 输出:对象 |
| getLChild(): | 返回当前节点的左孩子 输入:无 输出:二叉树节点 |
| getRChild(): | 返回当前节点的右孩子 输入:无 输出:二叉树节点 |
4.4.2 二叉树类的 Java 接口
public interface BinTree {
//返回树根
public BinTreePosition getRoot();
//判断是否树空
public boolean isEmpty();
//返回树的规模(即树根的后代数目)
public int getSize();
//返回树(根)的高度
public int getHeight();
//前序遍历
public Iterator elementsPreorder();
//中序遍历
public Iterator elementsInorder();
//后序遍历
public Iterator elementsPostorder();
//层次遍历
public Iterator elementsLevelorder();
}
BinTreePosition 接口:
public interface BinTreePosition extends Position {
// 判断是否有父亲(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasParent();
// 返回当前节点的父节点
public BinTreePosition getParent();
// 设置当前节点的父节点
public void setParent(BinTreePosition p);
// 判断是否为叶子
public boolean isLeaf();
// 判断是否为左孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean isLChild();
// 判断是否有左孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasLChild();
// 返回当前节点的左孩子
public BinTreePosition getLChild();
// 设置当前节点的左孩子(注意: this.lChild和c.parent都不一定为空)
public void setLChild(BinTreePosition c);
// 判断是否为右孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean isRChild();
// 判断是否有右孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasRChild();
// 返回当前节点的右孩子
public BinTreePosition getRChild();
// 设置当前节点的右孩子(注意: this.rChild和c.parent都不一定为空)
public void setRChild(BinTreePosition c);
// 返回当前节点后代元素的数目
public int getSize();
// 在孩子发生变化后,更新当前节点及其祖先的规模
public void updateSize();
// 返回当前节点的高度
public int getHeight();
// 在孩子发生变化后,更新当前节点及其祖先的高度
public void updateHeight();
// 返回当前节点的深度
public int getDepth();
// 在父亲发生变化后,更新当前节点及其后代的深度
public void updateDepth();
// 按照中序遍历的次序,找到当前节点的直接前驱
public BinTreePosition getPrev();
// 按照中序遍历的次序,找到当前节点的直接后继
public BinTreePosition getSucc();
// 断绝当前节点与其父亲的父子关系
// 返回当前节点
public BinTreePosition secede();
// 将节点c作为当前节点的左孩子
public BinTreePosition attachL(BinTreePosition c);
// 将节点c作为当前节点的右孩子
public BinTreePosition attachR(BinTreePosition c);
// 前序遍历
public Iterator elementsPreorder();
// 中序遍历
public Iterator elementsInorder();
// 后序遍历
public Iterator elementsPostorder();
// 层次遍历
public Iterator elementsLevelorder();
}
4.4.3 二叉树类的实现
public class BinTreeNode implements BinTreePosition {
protected Object element;// 该节点中存放的对象
protected BinTreePosition parent;// 父亲
protected BinTreePosition lChild;// 左孩子
protected BinTreePosition rChild;// 右孩子
protected int size;// 后代数目
protected int height;// 高度
protected int depth;// 深度
/**************************** 构造方法 ****************************/
public BinTreeNode() {
this(null, null, true, null, null);
}
public BinTreeNode(Object e, // 节点内容
BinTreePosition p, // 父节点
boolean asLChild, // 是否作为父节点的左孩子
BinTreePosition l, // 左孩子
BinTreePosition r)// 右孩子
{
size = 1;
height = depth = 0;
parent = lChild = rChild = null;// 初始化
element = e;// 存放的对象
// 建立与父亲的关系
if (null != p)
if (asLChild)
p.attachL(this);
else
p.attachR(this);
// 建立与孩子的关系
if (null != l)
attachL(l);
if (null != r)
attachR(r);
}
/**************************** Position接口方法 ********************************/
// 返回当前节点中存放的对象
public Object getElem() {
return element;
}
// 将对象obj存入当前节点,并返回此前的内容
public Object setElem(Object obj) {
Object bak = element;
element = obj;
return bak;
}
/**************************** BinTreePosition接口方法 *************************/
// 判断是否有父亲(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasParent() {
return null != parent;
}
// 返回当前节点的父节点
public BinTreePosition getParent() {
return parent;
}
// 设置当前节点的父节点
public void setParent(BinTreePosition p) {
parent = p;
}
// 判断是否为叶子
public boolean isLeaf() {
return !hasLChild() && !hasRChild();
}
// 判断是否为左孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
// 若当前节点有父亲,而且是左孩子,则返回true;否则,返回false
public boolean isLChild() {
return (hasParent() && this == getParent().getLChild()) ? true : false;
}
// 判断是否有左孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasLChild() {
return null != lChild;
}
// 返回当前节点的左孩子
public BinTreePosition getLChild() {
return lChild;
}
// 设置当前节点的左孩子(注意: this.lChild和c.parent都不一定为空)
public void setLChild(BinTreePosition c) {
lChild = c;
}
// 判断是否为右孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
// 若当前节点有父亲,而且是右孩子,则返回true;否则,返回false
public boolean isRChild() {
return (hasParent() && this == getParent().getRChild()) ? true : false;
}
// 判断是否有右孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasRChild() {
return null != rChild;
}
// 返回当前节点的右孩子
public BinTreePosition getRChild() {
return rChild;
}
// 设置当前节点的右孩子(注意: this.rChild和c.parent都不一定为空)
public void setRChild(BinTreePosition c) {
rChild = c;
}
// 返回当前节点后代元素的数目
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 在孩子发生变化后,更新当前节点及其祖先的规模
public void updateSize() {
size = 1;// 当前节点
if (hasLChild())
size += getLChild().getSize();// 左子树的规模
if (hasRChild())
size += getRChild().getSize();// 右子树的规模
if (hasParent())
getParent().updateSize();// 递归更新各个真祖先的规模记录
}
// 返回当前节点的高度
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
// 在孩子发生变化后,更新当前节点及其祖先的高度
public void updateHeight() {
height = 0;// 先假设没有左、右孩子
if (hasLChild())
height = Math.max(height, 1 + getLChild().getHeight());// 左孩子
if (hasRChild())
height = Math.max(height, 1 + getRChild().getHeight());// 右孩子
if (hasParent())
getParent().updateHeight();// 递归更新各个真祖先的高度记录
}
// 返回当前节点的深度
public int getDepth() {
return depth;
}
// 在父亲发生变化后,更新当前节点及其后代的深度
public void updateDepth() {
depth = hasParent() ? 1 + getParent().getDepth() : 0;// 当前节点
if (hasLChild())
getLChild().updateDepth();// 沿孩子引用逐层向下,
if (hasRChild())
getRChild().updateDepth();// 递归地更新所有后代的深度记录
}
// 按照中序遍历的次序,找到当前节点的直接前驱
public BinTreePosition getPrev() {
// 若左子树非空,则其中的最大者即为当前节点的直接前驱
if (hasLChild())
return findMaxDescendant(getLChild());
// 至此,当前节点没有左孩子
if (isRChild())
return getParent();// 若当前节点是右孩子,则父亲即为其直接前驱
// 至此,当前节点没有左孩子,而且是左孩子
BinTreePosition v = this;// 从当前节点出发
while (v.isLChild())
v = v.getParent();// 沿左孩子链一直上升
// 至此, v或者没有父亲,或者是父亲的右孩子
return v.getParent();
}
// 按照中序遍历的次序,找到当前节点的直接后继
public BinTreePosition getSucc() {
// 若右子树非空,则其中的最小者即为当前节点的直接后继
if (hasRChild())
return findMinDescendant(getRChild());
// 至此,当前节点没有右孩子
if (isLChild())
return getParent();// 若当前节点是左孩子,则父亲即为其直接后继
// 至此,当前节点没有右孩子,而且是右孩子
BinTreePosition v = this;// 从当前节点出发
while (v.isRChild())
v = v.getParent();// 沿右孩子链一直上升
// 至此, v或者没有父亲,或者是父亲的左孩子
return v.getParent();
}
// 断绝当前节点与其父亲的父子关系
// 返回当前节点
public BinTreePosition secede() {
if (null != parent) {
if (isLChild())
parent.setLChild(null);// 切断父亲指向当前节点的引用
else
parent.setRChild(null);
parent.updateSize();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的规模
parent.updateHeight();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的高度
parent = null;// 切断当前节点指向原父亲的引用
updateDepth();// 更新节点及其后代节点的深度
}
return this;// 返回当前节点
}
// 将节点c作为当前节点的左孩子
public BinTreePosition attachL(BinTreePosition c) {
if (hasLChild())
getLChild().secede();// 摘除当前节点原先的左孩子
if (null != c) {
c.secede();// c脱离原父亲
lChild = c;
c.setParent(this);// 确立新的父子关系
updateSize();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的规模
updateHeight();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的高度
c.updateDepth();// 更新c及其后代节点的深度
}
return this;
}
// 将节点c作为当前节点的右孩子
public BinTreePosition attachR(BinTreePosition c) {
if (hasRChild())
getRChild().secede();// 摘除当前节点原先的右孩子
if (null != c) {
c.secede();// c脱离原父亲
rChild = c;
c.setParent(this);// 确立新的父子关系
updateSize();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的规模
updateHeight();// 更新当前节点及其祖先的高度
c.updateDepth();// 更新c及其后代节点的深度
}
return this;
}
// 前序遍历
public Iterator elementsPreorder() {
List list = new List_DLNode();
preorder(list, this);
return list.elements();
}
// 中序遍历
public Iterator elementsInorder() {
List list = new List_DLNode();
inorder(list, this);
return list.elements();
}
// 后序遍历
public Iterator elementsPostorder() {
List list = new List_DLNode();
postorder(list, this);
return list.elements();
}
// 层次遍历
public Iterator elementsLevelorder() {
List list = new List_DLNode();
levelorder(list, this);
return list.elements();
}
/**************************** 辅助方法 ****************************/
// 在v的后代中,找出最小者
protected static BinTreePosition findMinDescendant(BinTreePosition v) {
if (null != v)
while (v.hasLChild())
v = v.getLChild();// 从v出发,沿左孩子链一直下降
// 至此, v或者为空,或者没有左孩子
return v;
}
// 在v的后代中,找出最大者
protected static BinTreePosition findMaxDescendant(BinTreePosition v) {
if (null != v)
while (v.hasRChild())
v = v.getRChild();// 从v出发,沿右孩子链一直下降
// 至此, v或者为空,或者没有右孩子
return v;
}
// 前序遍历以v为根节的(子)树
protected static void preorder(List list, BinTreePosition v) {
if (null == v)
return;// 递归基:空树
list.insertLast(v);// 访问v
preorder(list, v.getLChild());// 遍历左子树
preorder(list, v.getRChild());// 遍历右子树
}
// 中序遍历以v为根节的(子)树
protected static void inorder(List list, BinTreePosition v) {
if (null == v)
return;// 递归基:空树
inorder(list, v.getLChild());// 遍历左子树
list.insertLast(v);// 访问v
inorder(list, v.getRChild());// 遍历右子树
}
// 后序遍历以v为根节的(子)树
protected static void postorder(List list, BinTreePosition v) {
if (null == v)
return;// 递归基:空树
postorder(list, v.getLChild());// 遍历左子树
postorder(list, v.getRChild());// 遍历右子树
list.insertLast(v);// 访问v
}
// 层次遍历以v为根节的(子)树
protected static void levelorder(List list, BinTreePosition v) {
Queue_List Q = new Queue_List();// 空队
Q.enqueue(v);// 根节点入队
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
BinTreePosition u = (BinTreePosition) Q.dequeue();// 出队
list.insertLast(u);// 访问v
if (u.hasLChild())
Q.enqueue(u.getLChild());
if (u.hasRChild())
Q.enqueue(u.getRChild());
}
}
}
二叉树类的实现
public class BinTree_LinkedList implements BinTree {
protected BinTreePosition root;// 根节点
/**************************** 构造函数 ****************************/
public BinTree_LinkedList() {
this(null);
}
public BinTree_LinkedList(BinTreePosition r) {
root = r;
}
/**************************** BinaryTree接口方法 ****************************/
// 返回树根
public BinTreePosition getRoot() {
return root;
}
// 判断是否树空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return null == root;
}
// 返回树的规模(即树根的后代数目)
public int getSize() {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : root.getSize();
}
// 返回树(根)的高度
public int getHeight() {
return isEmpty() ? -1 : root.getHeight();
}
// 前序遍历
public Iterator elementsPreorder() {
return root.elementsPreorder();
}
// 中序遍历
public Iterator elementsInorder() {
return root.elementsInorder();
}
// 后序遍历
public Iterator elementsPostorder() {
return root.elementsPostorder();
}
// 层次遍历
public Iterator elementsLevelorder() {
return root.elementsLevelorder();
}
}
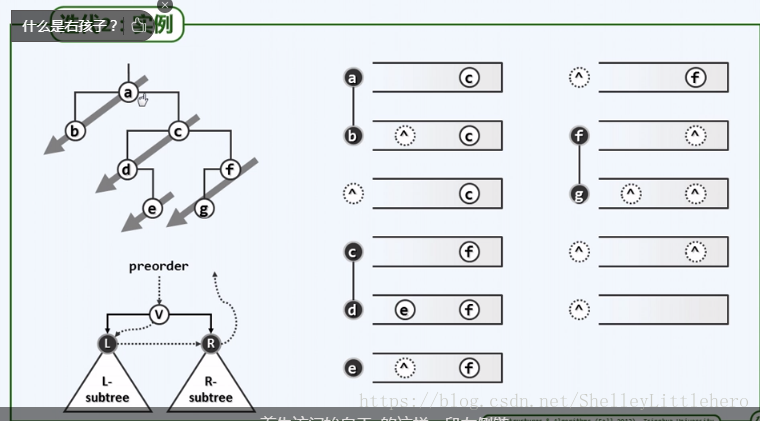
以先序遍历为例展示
4.5 二叉树的基本算法
4.5.1 getSize()、 getHeight()和 getDepth()
/返回当前节点后代元素的数目,即以当前节点为根的子树的规模
public int getSize() {
int size = 1;//当前节点也是自己的后代
TreeLinkedList subtree = firstChild;//从长子开始
while (null != subtree) {//依次
size += subtree.getSize();//累加
subtree = subtree.getNextSibling();//所有孩子的后代数目
}
return size;//即可得到当前节点的后代总数
}
//返回当前节点的高度
public int getHeight() {
int height = -1;
TreeLinkedList subtree = firstChild;//从长子开始
while (null != subtree) {//依次
height = Math.max(height, subtree.getHeight());//在所有孩子中取最大高度
subtree = subtree.getNextSibling();
}
return height+1;//即可得到当前节点的高度
}
//返回当前节点的深度
public int getDepth() {
int depth = 0;
TreeLinkedList p = parent;//从父亲开始
while (null != p) {//依次
depth++; p = p.getParent();//访问各个真祖先
}
return depth;//真祖先的数目,即为当前节点的深度
}
4.5.2 updateSize()
算法: updateSize(v)
输入:二叉树中任一节点v
输出:更新v的后代规模记录
{
令size(v) = 1 + size(lc) + size(rc);//由观察结论四.13
若v的父亲p存在,则调用updateSize(p),递归地更新父亲的规模记录;//尾递归,可改写为迭代形式
}
4.5.3 updateHeight()
算法: updateHeight(v)
输入:二叉树中任一节点v
输出:更新v的高度记录
{
height(v) = 0;//先假设没有左、右孩子
若v有左孩子lc,则令: height(v) = Max(height(v), 1 + height(lc));
若v有右孩子lc,则令: height(v) = Max(height(v), 1 + height(rc));
若v的父亲p存在,则调用updateHeight(p),递归地更新父亲的高度记录;
}
4.5.4 updateDepth()
算法: updateDepth(v)
输入:二叉树中任一节点v
输出:更新v的深度记录
{
若v的父亲节点p存在,则令depth(v) = depth(p)+1;
否则,令depth(v) = 0;
若v的左孩子lc存在,则调用updateDepth(lc);//沿孩子引用逐层向下,
若v的右孩子rc存在,则调用updateDepth(rc);//递归地更新所有后代的深度记录
}
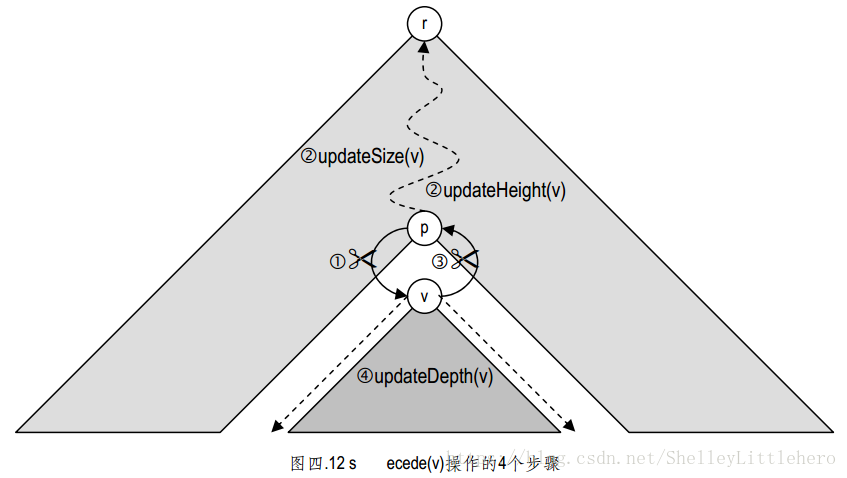
4.5.5 secede()
secede方法的功能是, 将以某一节点为根的子树从母树中分离出来:
算法: secede(v)
输入:二叉树中任一节点v
输出:将以v为根的子树丛母树中分离出来
{
若v有父亲 {
c 切断父亲指向v的引用;
d 调用updateSize(v)和updateHeight(v),更新v及其祖先的规模记录和高度记录;
e 切断v指向父亲的引用;
f 调用updateDepth(v),更新v及其后代的深度记录;
}
}
secede(v)算法的运行时间为 O(depth(v)+ size(v)+1)
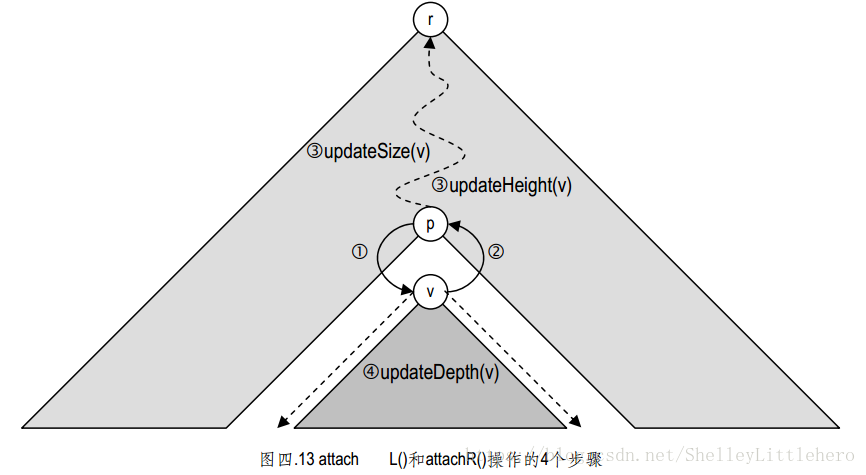
4.5.6 attachL()和 attachR()
这一对方法的功能是,将节点c作为左或右孩子与节点v联接起来;
算法: attachL(p, c)
输入:两个二叉树节点p与c
输出:将c作为左孩子,与p联接起来
{
b 若p已经有左孩子lc,则首先调用secede(lc)将其摘除;
b 调用secede(c),使c及其后代脱离原属母树;
cd 设置相应的引用,在p和c之间建立父子关系;
e 调用updateSize(p)和updateHeight(p),更新节点p及其祖先的规模和高度;
f 调用updateDepth(c),更新c及其后代节点的深度;
}
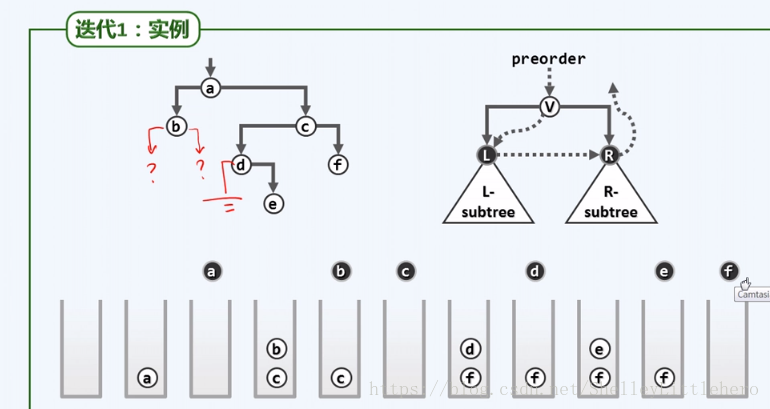
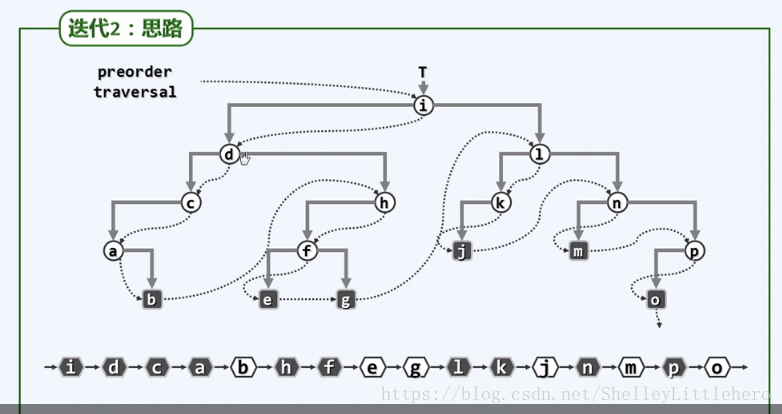
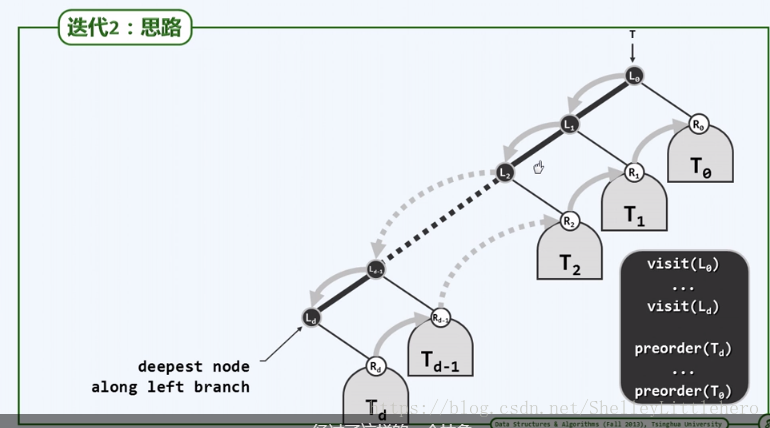
4.5.7 二叉树的遍历
二叉树中序遍历的过程
算法: InorderTraversal(v)
输入:二叉树节点v
输出: v所有后代的中序遍历序列
{
if (null != v) {//设lc、 rc分别为v的左、右孩子
调用InorderTraversal(lc)对v的左子树做中序遍历;
访问并输出v;
调用InorderTraversal(rc)对v的右子树做中序遍历;
}
}
4.6 完全二叉树的 Java 实现
4.6.1 完全二叉树类的 Java 接口
/*
* 完全二叉树接口
*/
public interface ComplBinTree extends BinTree {
//生成并返回一个存放e的外部节点,该节点成为新的末节点
public BinTreePosition addLast(Object e);
//删除末节点,并返回其中存放的内容
public Object delLast();
//返回按照层次遍历编号为i的节点的位置, 0 <= i < size()
public BinTreePosition posOfNode(int i);
}
4.6.2 基于向量的实现
在完全二叉树中,
c 若节点 v 有左孩子,则 i(lchild(v)) = 2 ×i(v) + 1;
d 若节点 v 有右孩子,则 i(rchild(v)) = 2 ×i(v) + 2;
e 若节点 v 有父节点,则 i(parent(v)) = ⎣(i(v) - 1)/2⎦ = ⎡(i(v)/2⎤ - 1。
d基于可扩充向量来实现完全二叉树,则就分摊复杂度而言,每次 addLast()和
delLast()操作都可以在 O(1)时间内完成。
完全二叉树节点类的 Java 实现
/*
* 基于秩实现的完全二叉树节点
*/
public class ComplBinTreeNode_Rank extends BinTreeNode implements BinTreePosition {
private Vector T;//所属的树
private int rank;//在所属树中的秩
private Object element;//存放的对象
//构造函数
public ComplBinTreeNode_Rank (Vector t, Object obj) {
element = obj;
T = t;
rank = T.getSize();
T.insertAtRank(rank, this);
}
//返回当前节点中存放的对象
public Object getElem()
{ return element; }
//将对象obj存入当前节点,并返回此前的内容
public Object setElem(Object obj)
{ Object bak = element; element = obj; return bak; }
//判断是否有父亲(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasParent()
{ return (0 != rank) ? true : false; }
//返回当前节点的父节点
public BinTreePosition getParent()
{ return hasParent() ? (BinTreePosition) T.getAtRank((rank-1)/2) : null; }
//判断是否有左孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasLChild()
{ return (1+rank*2 < T.getSize()) ? true : false; }
//返回当前节点的左孩子
public BinTreePosition getLChild()
{ return hasLChild() ? (BinTreePosition) (T.getAtRank(1+rank*2)) : null; }
//判断是否有右孩子(为使代码描述简洁)
public boolean hasRChild()
{ return (2+rank*2 < T.getSize()) ? true : false; }
//返回当前节点的右孩子
public BinTreePosition getRChild()
{ return hasRChild() ? (BinTreePosition) (T.getAtRank(2+rank*2)) : null; }
//返回当前节点后代元素的数目
public int getSize() {
int size = 1;
if (hasLChild()) size += getLChild().getSize();
if (hasRChild()) size += getRChild().getSize();
return size;
}
//返回当前节点的高度
public int getHeight() {
int hL = hasLChild() ? getLChild().getHeight() : -1;
int hR = hasRChild() ? getRChild().getHeight() : -1;
return 1 + Math.max(hL, hR);
}
//返回当前节点的深度
public int getDepth() {
return hasParent() ? 1+getParent().getDepth() : 0;
}
}
完全二叉树类的 Java 实现
/*
* 基于向量实现的完全二叉树
*/
public class ComplBinTree_Vector extends BinTree_LinkedList implements ComplBinTree {
private Vector T;//向量
//构造方法:默认的空树
public ComplBinTree_Vector()
{ T = new Vector_ExtArray(); root = null; }
//构造方法:按照给定的节点序列,批量式建立完全二叉树
public ComplBinTree_Vector(Sequence s)
{ this(); if (null !=s) while (!s.isEmpty()) addLast(s.removeFirst()); }
/*---------- BinaryTree接口中各方法的实现 ----------*/
//返回树根(重写)
public BinTreePosition getRoot()
{ return T.isEmpty() ? null : posOfNode(0); }
//判断是否树空(重写)
public boolean isEmpty()
{ return T.isEmpty(); }
//返回树的规模(重写)
public int getSize()
{ return T.getSize(); }
//返回树(根)的高度(重写)
public int getHeight()
{return isEmpty() ? -1 : getRoot().getHeight(); }
/*---------- ComplBinTree接口中各方法的实现 ----------*/
//生成并返回一个存放e的外部节点,该节点成为新的末节点
public BinTreePosition addLast(Object e) {
BinTreePosition node = new ComplBinTreeNode_Rank(T, e);
root = (BinTreePosition) T.getAtRank(0);
return node;
}
//删除末节点,并返回其中存放的内容
public Object delLast() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;//若树(堆)已空,无法删除
if (1 == getSize()) root = null;//若删除最后一个节点,则树空
return T.removeAtRank(T.getSize()-1);
}
//返回按照层次遍历编号为i的节点的位置, 0 <= i < size()
public BinTreePosition posOfNode(int i) {
return (BinTreePosition)T.getAtRank(i);
}
}
来源于:Java数据结构,邓俊辉