[JDK1.8]LinkedHashMap源码浅析
引言
上篇我们了解了JDK1.7中LinkedHashMap的源码,这篇文章试着分析一下JDK1.8中LinkedHashMap的源码(由于1.8HashMap做了优化,所以作为其子类的LinkedHashMap自然也做了一些修改.基于1.8的HashMap源码分析在之前的文章已经有了,不多阐述)
在每次插入数据,或者访问、修改数据时,都会增加节点(插入时)或调整链表的节点顺序。
LinkedHashMap的成员变量
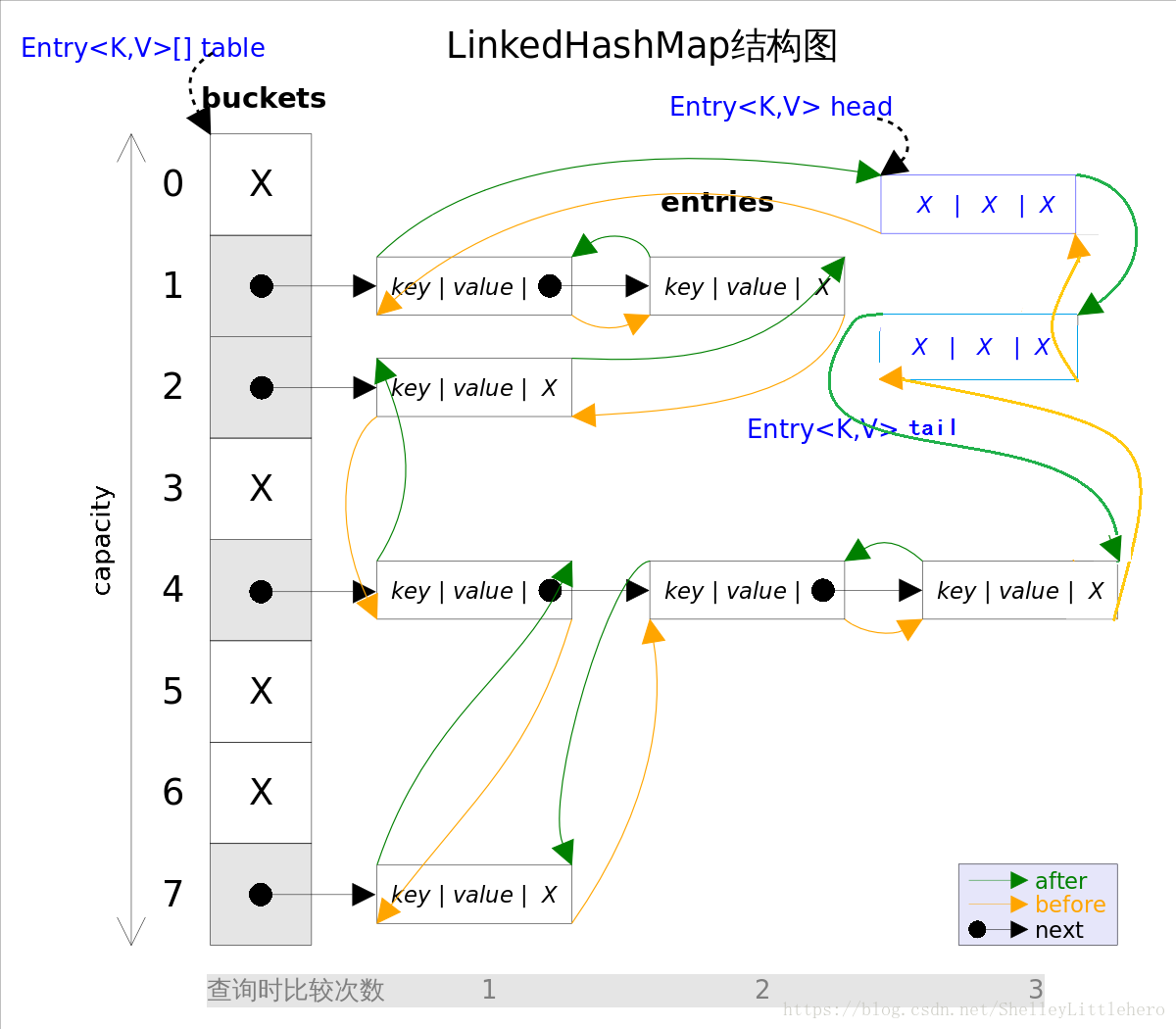
区别于1.7中的成员变量标志位置只有一个header节点;
JDK1.8中有一个head和一个tail节点;
JDK1.7
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
private final boolean accessOrder;
JDK1.8
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
// 用于指向双向链表的头部, 双向链表头节点(最老)
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
//用于指向双向链表的尾部,双向列表尾节点(最新)
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* 用来指定LinkedHashMap的迭代顺序,
* true则表示按照基于访问的顺序来排列,意思就是最近使用的entry,放在链表的最末尾
* false则表示按照插入顺序来
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
构造函数
1.8
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt>
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
1.8的构造函数和1.7的构造函数有差异的在接收map的构造函数;
1.7
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
accessOrder = false;
}
super(m)调用hashMap的构造函数进行初始化:
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
inflateTable(threshold);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
putAllForCreate(m)内部循环调用putForCreate(K key, V value)
private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
int hash = null == key ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
/**
* Look for preexisting entry for key. This will never happen for
* clone or deserialize. It will only happen for construction if the
* input Map is a sorted map whose ordering is inconsistent w/ equals.
*/
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
}
//如果没有存在的key对应的Entry,那么新建Entry
createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
1.8
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
/**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
//evict false when initially constructing this map, else true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
//调用putVal函数
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
Entry
LinkedHashMap 1.8中的Entry和1.7中的区别不大,都是Map.Entry<K,V>的实现
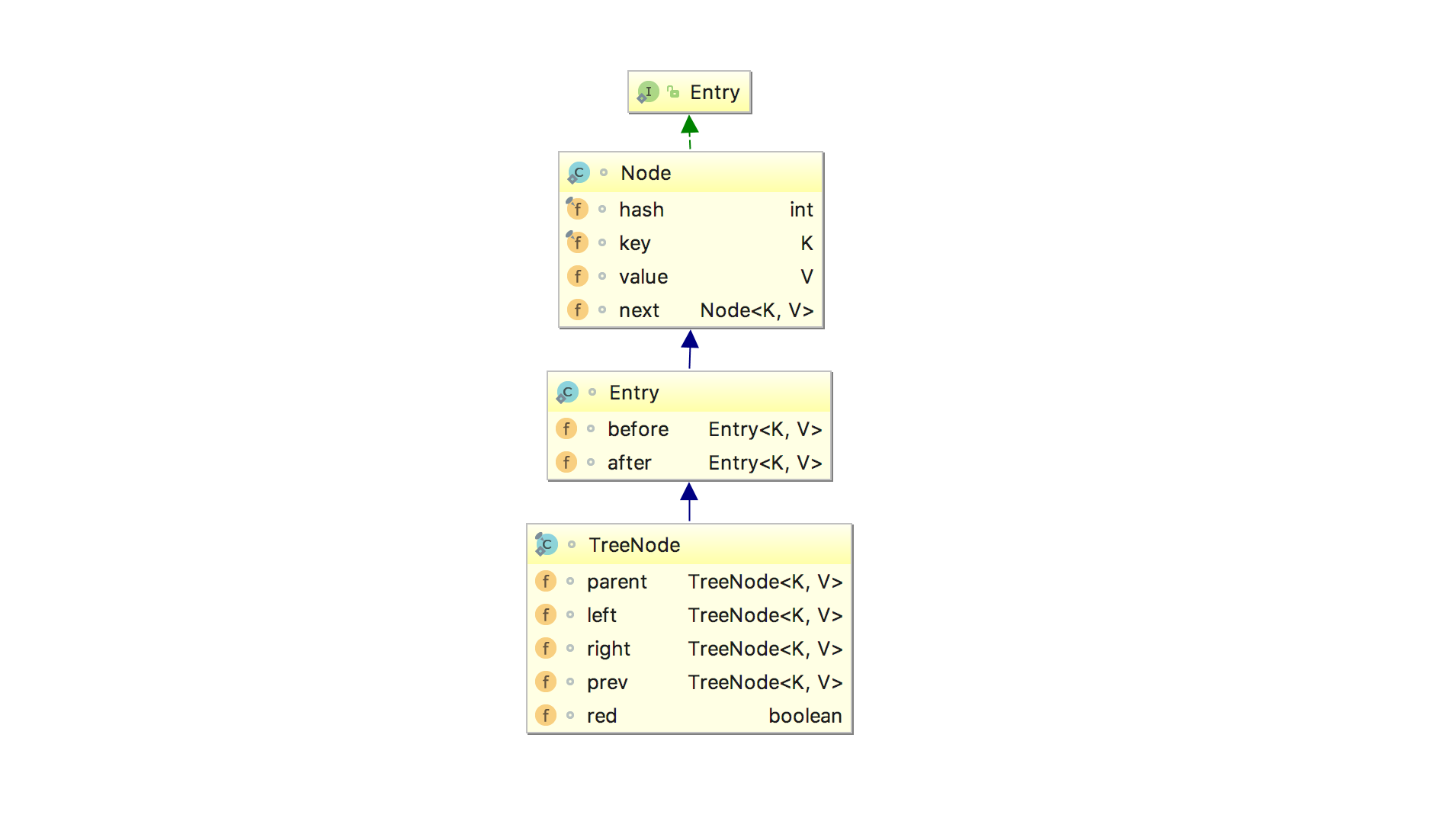
同样的:
Entry里面的属性:
1、K key
2、V value
3、Entry<K, V> next
4、int hash
5、Entry<K, V> before
6、Entry<K, V> after
其中前面四个,也就是红色部分是从HashMap.Entry中继承过来的;后面两个,也就是蓝色部分是LinkedHashMap独有的。不要搞错了next和before、After,next是用于维护HashMap指定table位置上连接的Entry的顺序的,before、After是用于维护Entry插入的先后顺序的。
1.8中LinkedHashMap结构如下图:
有head和tail节点;
put
LinkedHashMap的没有自己的put方法的实现,而是使用父类HashMap的put方法:
在正常新增之后,调用afterNodeAccess(e)和 afterNodeInsertion(evict)让LinkedHashMap自己做后续处理
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//存放元素的table桶不存在,则对table数组进行初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//用来存放目标hash值得节点不存在,新建
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//hash相同,key值相同
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//是否是二叉树节点,如是放入二叉树中
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//树化
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
//回调函数,新节点插入之后回调 , 根据evict 和 判断是否需要删除最老插入的节点。
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
//LinkedHashMap 默认返回false 则不删除节点
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
//LinkedHashMap 默认返回false 则不删除节点。 返回true 代表要删除最早的节点。通常构建一个LruCache会在达到Cache的上限是返回true
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
HashMap专门预留给LinkedHashMap的afterNodeAccess() afterNodeInsertion() afterNodeRemoval() 方法。
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
remove
LinkedHashMap也没有重写remove()方法,它使用的是HashMap的remove方法。
以remove(Object key)为例:
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
如果movable参数是false,在删除节点时,不移动其他节点;
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
// p 是待删除节点的前置节点
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
//如果哈希表不为空,则根据hash值算出的index下是否有节点。
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//node是待删除节点
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//如果链表头的就是需要删除的节点
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;//将待删除节点引用赋给node
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {//否则循环遍历 找到待删除节点,赋值给node
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//如果有待删除节点node, 且 matchValue为false,或者值也相等
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)//如果node == p,说明是链表头是待删除节点
tab[index] = node.next;
else//否则待删除节点在表中间
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;//修改modCount
--size;//修改size
afterNodeRemoval(node);//LinkedHashMap回调函数
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
//在删除节点e时,同步将e从双向链表上删除
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//待删除节点 p 的前置后置节点都置空
p.before = p.after = null;
//如果前置节点是null,则现在的头结点应该是后置节点a
if (b == null)
head = a;
else//否则将前置节点b的后置节点指向a
b.after = a;
//同理如果后置节点时null ,则尾节点应是b
if (a == null)
tail = b;
else//否则更新后置节点a的前置节点为b
a.before = b;
}
get 查
LinkedHashMap重写了get()和getOrDefault()方法:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)//accessOrder 为true时(按访问顺序排序)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return defaultValue;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
Node为HashMap的节点类;
而LinkedHashMap的Entry为其子类;
//此函数执行的效果就是将最近使用的Node,放在链表的最末尾
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
//仅当按照LRU原则且e不在最末尾,才执行修改链表,将e移到链表最末尾的操作
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
//将e赋值临时节点p, b是e的前一个节点, a是e的后一个节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//设置p的后一个节点为null,因为执行后p在链表末尾,after肯定为null
p.after = null;
//p前一个节点不存在,情况一
if (b == null) // ①
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
//p的后一个节点不存在,情况二
else // ②
last = b;
//情况三
if (last == null) // ③
head = p;
//正常情况,将p设置为尾节点的准备工作,p的前一个节点为原先的last,last的after为p
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
//将p设置为将p设置为尾节点
tail = p;
// 修改计数器+1
++modCount;
}
}
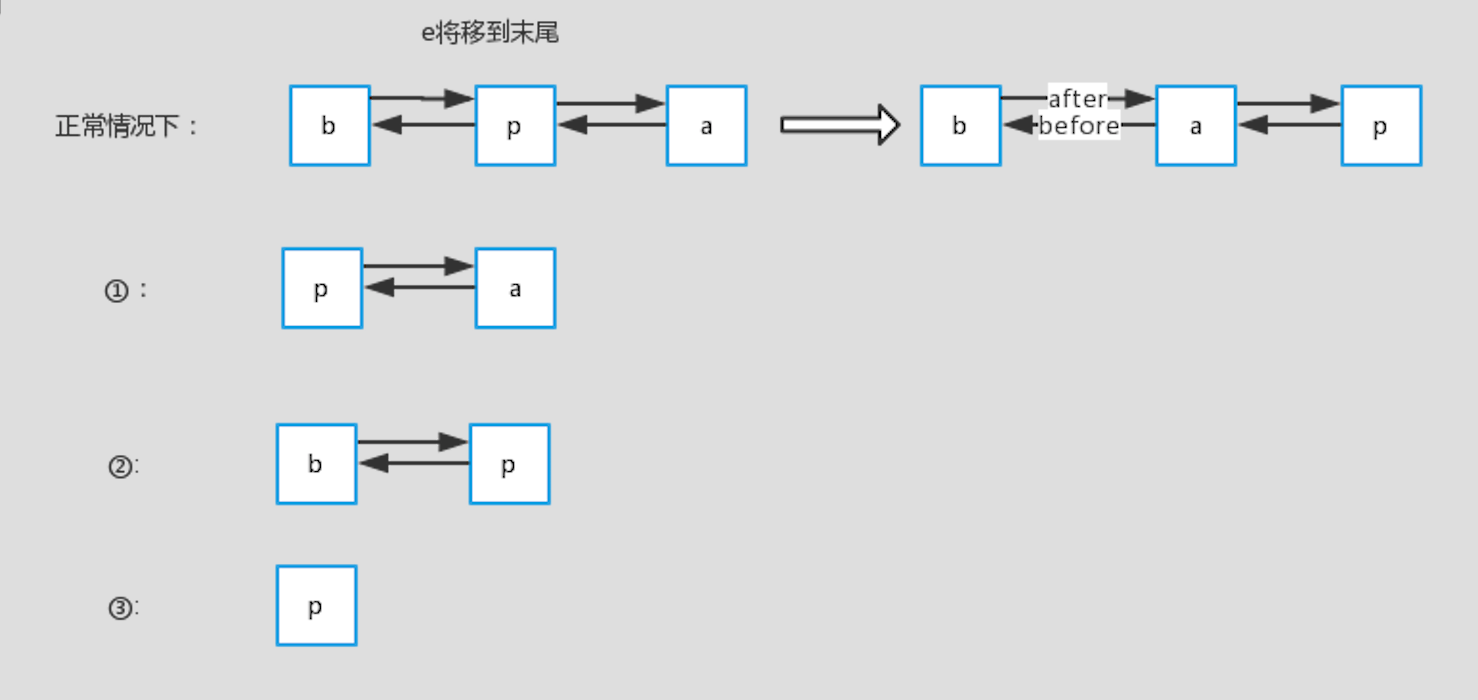
下面来简单说明一下:
正常情况下:查询的p在链表中间,那么将p设置到末尾后,它原先的前节点b和后节点a就变成了前后节点。
情况一:p为头部,前一个节点b不存在,那么考虑到p要放到最后面,则设置p的后一个节点a为head
情况二:p为尾部,后一个节点a不存在,那么考虑到统一操作,设置last为b
情况三:p为链表里的第一个节点,head=p
containsKey
LinkedHashMap使用HashMap的containsKey方法:
之所以不去重写的原因在于:
hashMap中containsKey调用了getNode方法,它直接根据key计算出hash值,找到这个key的哈希桶,只需遍历这个哈希桶中有没有这个key。如果重写去遍历keySet效率无法再有提高.
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
containsValue
LinkedHashMap重写了containsValue方法;更为高效,而高效来源于其双端链表结构,而HashMap的查找就需要先遍历数组,在table[i]的基础上遍历链表(或树);
LinkedHashMap:
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
V v = e.value;
if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
HashMap:
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((v = e.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
遍历
LinkedHashMap的迭代器为遍历节点提供了自己的实现——LinkedHashIterator,对于Key、Value、Entry的3个迭代器,都继承自它。
final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().getKey(); }
}
final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
abstract class LinkedHashIterator {
//下一个节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> next;
//当前节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> current;
int expectedModCount;
LinkedHashIterator() {
//初始化时,next 为 LinkedHashMap内部维护的双向链表的表头
next = head;
//记录当前modCount,以满足fail-fast
expectedModCount = modCount;
//当前节点为null
current = null;
}
//判断是否还有next
public final boolean hasNext() {
//就是判断next是否为null,默认next是head 表头
return next != null;
}
//nextNode() 就是迭代器里的next()方法 。
//该方法的实现可以看出,迭代LinkedHashMap,就是从内部维护的双链表的表头开始循环输出。
final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
//记录要返回的e。
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
//判断fail-fast
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
//如果要返回的节点是null,异常
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//更新当前节点为e
current = e;
//更新下一个节点是e的后置节点
next = e.after;
//返回e
return e;
}
//删除方法 最终还是调用了HashMap的removeNode方法
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
LRUCache
见:https://blog.csdn.net/ShelleyLittlehero/article/details/82954474