Asp.Net构架(Http请求处理流程)
Http请求处理流程概述
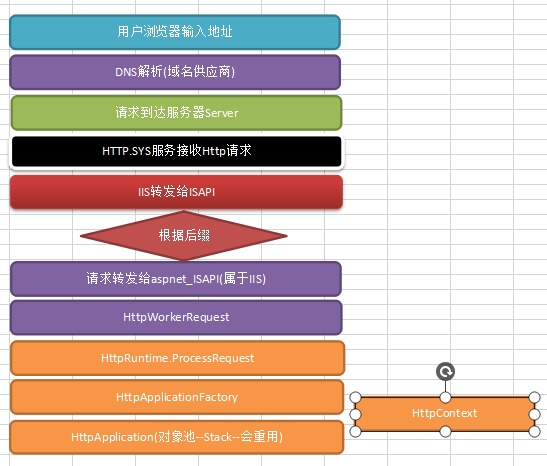
当用户在浏览器输入一个URL地址后,浏览器会发送一个请求到服务器。这时候在服务器上第一个负责处理请求的是IIS。然后IIS再根据请求的URL扩展名将请求分发给不同的ISAPI处理,然后,IIS 接收返回的数据流,并重新返还给 HTTP.SYS,最后,HTTP.SYS 再将这些数据返回给客户端浏览器。
ISAPI
ISAPI是一个底层的WIN32 API,开发者可以使用这些接口深入到IIS,让IIS支持各种其他处理程序。ISAPI是一个桥接口,通常用于高层次的工具与IIS之间的接驳。例如Windows下的Apache与Tomcat就是构建于ISAPI之上。ISAPI是自定义Web请求处理中第一个IIS入口点。
能够处理各种后缀名的应用程序,通常被称为ISAPI应用程序(NOTE:Internet Server Application Programe Interface,互联网服务器应用程序接口)。虽然这 ISAPI 听上去还挺气派,也算是“应用程序”呢,但仔细看看它的全称就明白了:它实际上只是一个接口,起到一个代理的作用,它的主要工作是映射所请求的页面(文件) 和与此后缀名相对应的实际的处理程序。
Http请求刚刚到达服务器的时候
IIS依赖一个叫做 HTTP.SYS 的内置驱动程序来监听来自外部的 HTTP请求。在操作系统启动的时候,IIS首先在HTTP.SYS中注册自己的虚拟路径。
实际上相当于告诉HTTP.SYS哪些URL是可以访问的,哪些是不可以访问的。为什么你访问不存在的文件会出现 404 错误呢?就是在这一步确定的。
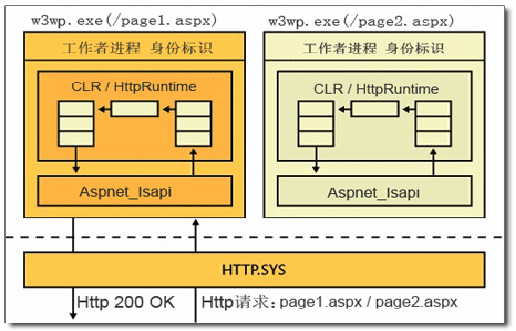
如果请求的是一个可访问的URL,HTTP.SYS会将这个请求交给 IIS 工作者进程。
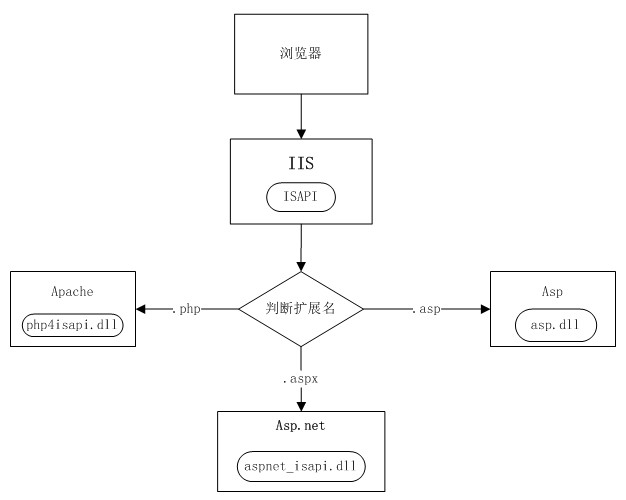
当服务器接收到一个 Http请求的时候,IIS 如何去处理这个请求,依据什么去处理呢?―― 根据文件的后缀名。对于html页面,txt文件,jpeg和gif图像的请求,IIS就自己处理了,当发现请求是Asp.net的资源时(如.aspx,.asmx,*.ashx),请求将传递到ASP.NET ISAPI扩展aspnet_isapi.dll。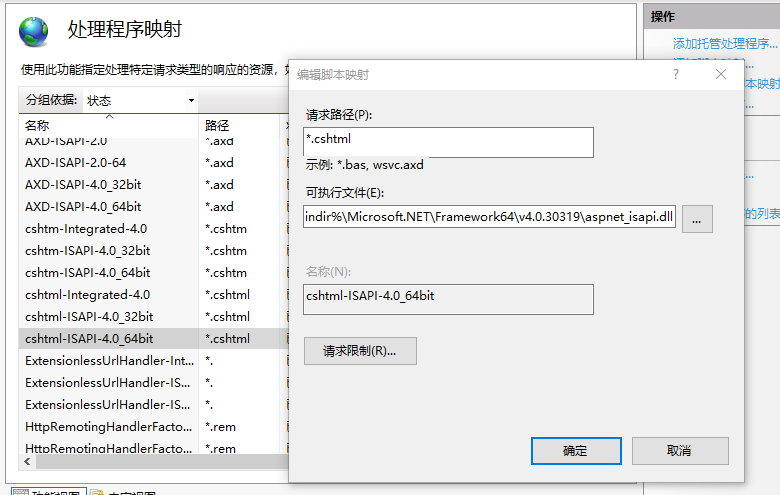
服务器获取所请求的页面的后缀名以后,接下来会在服务器端寻找可以处理这类后缀名的应用程序,如果IIS找不到可以处理此类文件的应用程序,并且这个文件也没有受到服务器端的保护(NOTE:一个受保护的例子就是 cs文件,一个不受保护的例子就是js脚本),那么IIS将直接把这个文件返还给客户端。
aspnet_isapi.dll可以处理多种资源类型,包括Web服务和HTTP处理程序调用等。
除了以外,ISAPI 还做一些其他的工作:
- 从HTTP.SYS中获取当前的Httq请求信息,并且将这些信息保存到 HttpWorkerRequest 类中。
- 在相互隔离的应用程序域AppDomain中加载HttpRuntime。
- 调用 HttpRuntime的ProcessRequest方法。
IIS与aspnet_isapi的处理逻辑:
- 当请求到达时,IIS检查资源类型并调用aspnet_isapi扩展。如果启用了默认的进程模型。aspnet_isapi会将请求排队。并将请求分配给辅助进程、所有的请求数据都是通过异步I/O发送。
- 收到请求后,ASP.NET辅助进程将通知aspnet_isapi,它将为请求服务(建立管道)。
- 在辅助进程的上下文中执行请求。有时,辅助进程可能需要回调aspnet_isapi以完成请求,也就是需要说枚举服务器变量。这种情况下,辅助进程将使用同步管道,因为这样可以保持请求处理的逻辑顺序。
- 完成后,响应被发送到打开了异步管道的aspnet_isapi。如果aspnet_isapi检测到辅助进程已取消,它将自动终止请求并释放所有相关的IIS资源。
宿主环境(Hosting)与管道(Pipeline)
从本质上讲,Asp.Net 主要是由一系列的类组成,这些类的主要目的就是将Http请求转变为对客户端的响应。
当 Web.config文件的内容发生改变 或者 .aspx文件发生变动的时候,为了能够卸载运行在同一个进程中的应用程序(NOTE:卸载也是为了重新加载),Http请求被分放在相互隔离的应用程序域中(应用程序域就是 AppDomain)。

- Asp.net处理管道的第一步是创建HttpWorkerRequest对象,它包含于当前请求有关的所有信息。
- HttpWorkerRequest把请求传递给HttpRuntime类的静态ProcessRequest方法。HttpRuntime首先要做的事是创建HttpContext对象,并用HttpWorkerRequest进行初始化。
/// <devdoc>
/// <para><SPAN>The method that drives
/// all ASP.NET web processing execution.</SPAN></para>
/// </devdoc>
[AspNetHostingPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Level = AspNetHostingPermissionLevel.Medium)]
public static void ProcessRequest(HttpWorkerRequest wr) {
if (wr == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("wr");
if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) {//判断是否为集成管道
throw new PlatformNotSupportedException(SR.GetString(SR.Method_Not_Supported_By_Iis_Integrated_Mode, "HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest"));
}
ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr);
}
internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr) {
RequestQueue rq = _theRuntime._requestQueue;
wr.UpdateInitialCounters();
if (rq != null) // could be null before first request
wr = rq.GetRequestToExecute(wr);
if (wr != null) {
CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr);
wr.ResetStartTime();
ProcessRequestNow(wr);
}
}
private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) {
// Count active requests
Interlocked.Increment(ref _activeRequestCount);
if (_disposingHttpRuntime) {//当请求数量超出程序处理速度,服务器返回503,服务器繁忙的响应
// Dev11 333176: An appdomain is unloaded before all requests are served, resulting in System.AppDomainUnloadedException during isapi completion callback
//
// HttpRuntim.Dispose could have already finished on a different thread when we had no active requests
// In this case we are about to start or already started unloading the appdomain so we will reject the request the safest way possible
try {
wr.SendStatus(503, "Server Too Busy");
wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(HttpWorkerRequest.HeaderContentType, "text/html; charset=utf-8");
byte[] body = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Server Too Busy</body></html>");
wr.SendResponseFromMemory(body, body.Length);
// this will flush synchronously because of HttpRuntime.ShutdownInProgress
wr.FlushResponse(true);
wr.EndOfRequest();
} finally {
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _activeRequestCount);
}
return;
}
// Construct the Context on HttpWorkerRequest, hook everything together
HttpContext context;
try {
context = new HttpContext(wr, false /* initResponseWriter */);
}
catch {//HttpContext 组装错误,返回400错误
try {
// If we fail to create the context for any reason, send back a 400 to make sure
// the request is correctly closed (relates to VSUQFE3962)
wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request");
wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(HttpWorkerRequest.HeaderContentType, "text/html; charset=utf-8");
byte[] body = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>");
wr.SendResponseFromMemory(body, body.Length);
wr.FlushResponse(true);
wr.EndOfRequest();
return;
} finally {
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _activeRequestCount);
}
}
wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(_asyncEndOfSendCallback, context);
HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount();
try {
// First request initialization
try {
EnsureFirstRequestInit(context);
}
catch {
// If we are handling a DEBUG request, ignore the FirstRequestInit exception.
// This allows the HttpDebugHandler to execute, and lets the debugger attach to
// the process (VSWhidbey 358135)
if (!context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) {
throw;
}
}
// Init response writer (after we have config in first request init)
// no need for impersonation as it is handled in config system
context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
// Get application instance
IHttpHandler app = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context);
if (app == null)
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_create_app_object));
if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(EtwTraceLevel.Verbose, EtwTraceFlags.Infrastructure)) EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, context.WorkerRequest, app.GetType().FullName, "Start");
if (app is IHttpAsyncHandler) {
// asynchronous handler
IHttpAsyncHandler asyncHandler = (IHttpAsyncHandler)app;
context.AsyncAppHandler = asyncHandler;
asyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(context, _handlerCompletionCallback, context);
}
else {
// synchronous handler
app.ProcessRequest(context);
FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
context.Response.InitResponseWriter();
FinishRequest(wr, context, e);
}
}
- 当Http请求进入 Asp.Net Runtime以后,它的管道由托管模块(NOTE:Managed Modules)和处理程序(NOTE:Handlers)组成,并且由管道来处理这个 Http请求。
- 创建了HttpContext实例之后,HttpRuntime类就通过调用HttpApplicationFactory的静态GetApplicationInstance()方法,为该应用程序请求HttpApplication派生类的一个示例。GetApplicationInstance()方法要么创建一个HttpApplication类的一个新实例,要么从应用程序对象池中取出一个实例。
internal static IHttpHandler GetApplicationInstance(HttpContext context) {
if (_customApplication != null)
return _customApplication;
// Check to see if it's a debug auto-attach request
if (context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest)
return new HttpDebugHandler();
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited();
_theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context);
return _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context);
}
private void EnsureInited() {
if (!_inited) {
lock (this) {
if (!_inited) {
Init();
_inited = true;
}
}
}
}
//
// Initialization on first request
//
private void Init() {
if (_customApplication != null)
return;
try {
try {
_appFilename = GetApplicationFile();//获取global.asax 地址
CompileApplication();//编译应用程序
}
finally {
// Always set up global.asax file change notification, even if compilation
// failed. This way, if the problem is fixed, the appdomain will be restarted.
SetupChangesMonitor();//启动变化监控
}
}
catch { // Protect against exception filters
throw;
}
}
//
// Application instance management
//
private HttpApplication GetNormalApplicationInstance(HttpContext context) {
HttpApplication app = null;
if (!_freeList.TryTake(out app)) {
// If ran out of instances, create a new one
app = (HttpApplication)HttpRuntime.CreateNonPublicInstance(_theApplicationType);
using (new ApplicationImpersonationContext()) {
app.InitInternal(context, _state, _eventHandlerMethods);
}
}
if (AppSettings.UseTaskFriendlySynchronizationContext) {
// When this HttpApplication instance is no longer in use, recycle it.
app.ApplicationInstanceConsumersCounter = new CountdownTask(1); // representing required call to HttpApplication.ReleaseAppInstance
app.ApplicationInstanceConsumersCounter.Task.ContinueWith((_, o) => RecycleApplicationInstance((HttpApplication)o), app, TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously);
}
return app;
}
- 在创建完成HttpApplication实例之后,就对它进行初始化,并在初始化期间分配应用程序定义的所
有模块。模块式实现IHttpModule接口的类,作用就是为了实现那经典的19个标准处理事件。
private void CompileApplication() {
// Get the Application Type and AppState from the global file
_theApplicationType = BuildManager.GetGlobalAsaxType();
BuildResultCompiledGlobalAsaxType result = BuildManager.GetGlobalAsaxBuildResult();
if (result != null) {
// Even if global.asax was already compiled, we need to get the collections
// of application and session objects, since they are not persisted when
// global.asax is compiled. Ideally, they would be, but since <object> tags
// are only there for ASP compat, it's not worth the trouble.
// Note that we only do this is the rare case where we know global.asax contains
// <object> tags, to avoid always paying the price (VSWhidbey 453101)
if (result.HasAppOrSessionObjects) {
GetAppStateByParsingGlobalAsax();
}
// Remember file dependencies
_fileDependencies = result.VirtualPathDependencies;
}
if (_state == null) {
_state = new HttpApplicationState();
}
// Prepare to hookup event handlers via reflection
ReflectOnApplicationType();
}
private void ReflectOnApplicationType() {//这个方法为应用程序注册事件
ArrayList handlers = new ArrayList();
MethodInfo[] methods;
Debug.Trace("PipelineRuntime", "ReflectOnApplicationType");
// get this class methods
methods = _theApplicationType.GetMethods(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static);
foreach (MethodInfo m in methods) {
if (ReflectOnMethodInfoIfItLooksLikeEventHandler(m))
handlers.Add(m);
}
// get base class private methods (GetMethods would not return those)
Type baseType = _theApplicationType.BaseType;
if (baseType != null && baseType != typeof(HttpApplication)) {
methods = baseType.GetMethods(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static);
foreach (MethodInfo m in methods) {
if (m.IsPrivate && ReflectOnMethodInfoIfItLooksLikeEventHandler(m))
handlers.Add(m);
}
}
// remember as an array
_eventHandlerMethods = new MethodInfo[handlers.Count];
for (int i = 0; i < _eventHandlerMethods.Length; i++)
_eventHandlerMethods[i] = (MethodInfo)handlers[i];
}
private bool ReflectOnMethodInfoIfItLooksLikeEventHandler(MethodInfo m) {
if (m.ReturnType != typeof(void))
return false;
// has to have either no args or two args (object, eventargs)
ParameterInfo[] parameters = m.GetParameters();
switch (parameters.Length) {
case 0:
// ok
break;
case 2:
// param 0 must be object
if (parameters[0].ParameterType != typeof(System.Object))
return false;
// param 1 must be eventargs
if (parameters[1].ParameterType != typeof(System.EventArgs) &&
!parameters[1].ParameterType.IsSubclassOf(typeof(System.EventArgs)))
return false;
// ok
break;
default:
return false;
}
// check the name (has to have _ not as first or last char)
String name = m.Name;
int j = name.IndexOf('_');
if (j <= 0 || j > name.Length-1)
return false;
// special pseudo-events
if (StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Application_OnStart") ||
StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Application_Start")) {
_onStartMethod = m;
_onStartParamCount = parameters.Length;
}
else if (StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Application_OnEnd") ||
StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Application_End")) {
_onEndMethod = m;
_onEndParamCount = parameters.Length;
}
else if (StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Session_OnEnd") ||
StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "Session_End")) {
_sessionOnEndMethod = m;
_sessionOnEndParamCount = parameters.Length;
}
return true;
}
private void EnsureAppStartCalled(HttpContext context) {
if (!_appOnStartCalled) {
lock (this) {
if (!_appOnStartCalled) {
using (new DisposableHttpContextWrapper(context)) {
// impersonation could be required (UNC share or app credentials)
WebBaseEvent.RaiseSystemEvent(this, WebEventCodes.ApplicationStart);
// fire outside of impersonation as HttpApplication logic takes
// care of impersonation by itself
FireApplicationOnStart(context);
}
_appOnStartCalled = true;
}
}
}
}
//
// Application on_start
//
private void FireApplicationOnStart(HttpContext context) {
if (_onStartMethod != null) {
HttpApplication app = GetSpecialApplicationInstance();
app.ProcessSpecialRequest(
context,
_onStartMethod,
_onStartParamCount,
this,
EventArgs.Empty,
null);//执行前面注册的启动事件_onStartMethod
RecycleSpecialApplicationInstance(app);
}
}
private HttpApplication GetSpecialApplicationInstance() {
return GetSpecialApplicationInstance(IntPtr.Zero, null);
}
private HttpApplication GetSpecialApplicationInstance(IntPtr appContext, HttpContext context) {
HttpApplication app = null;
if (!_specialFreeList.TryTake(out app)) {
//
// Put the context on the thread, to make it available to anyone calling
// HttpContext.Current from the HttpApplication constructor or module Init
//
using (new DisposableHttpContextWrapper(context)) {
// If ran out of instances, create a new one
app = (HttpApplication)HttpRuntime.CreateNonPublicInstance(_theApplicationType);
using (new ApplicationImpersonationContext()) {
app.InitSpecial(_state, _eventHandlerMethods, appContext, context);
}
}
}
return app;
}
- 在创建了模块之后,HttpRuntime类通过调用它的BeginProcessRequest方法,要求最新检索到的HttpApplication类对当前请求提供服务。然后,为当前请求找到合适的处理程序工厂。
创建处理程序,传递当前HttpContext,一旦ProcessRequest方法返回,请求完成。
本文参考文档
- .NET Framework源码:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/download.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/kissdodog/p/3527379.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/kissdodog/p/3527871.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2007/09/04/880967.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2007/09/15/894124.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2007/11/25/971878.html
作者:德乌姆列特
本博客所有文章仅用于学习、研究和交流目的,欢迎非商业性质转载。
博主的文章没有高度、深度和广度,只是凑字数。由于博主的水平不高,不足和错误之处在所难免,希望大家能够批评指出。
博主是利用读书、参考、引用、抄袭、复制和粘贴等多种方式打造成自己的文章,请原谅博主成为一个无耻的文档搬运工!

