Java 8 新特性 Stream 和 Lambda函数
什么是 Stream?
Stream(流)是一个来自数据源的元素队列并支持聚合操作
生成流
在 Java 8 中, 集合接口有两个方法来生成流:
-
stream() − 为集合创建串行流。
-
parallelStream() − 为集合创建并行流。
1、使用parallelStream方法可以得到一个并行流,并行流底层使用的是Fork/Join框架,对于一些计算量比较大的任务,使用并行流可能极大的提升效率。
流的操作
当把一个数据结构包装成 Stream 后,就要开始对里面的元素进行各类操作了。常见的操作可以归类如下。
- Intermediate:
map (mapToInt, flatMap 等)、 filter、 distinct、 sorted、 peek、 limit、 skip、 parallel、 sequential、 unordered
- Terminal:
forEach、 forEachOrdered、 toArray、 reduce、 collect、 min、 max、 count、 anyMatch、 allMatch、 noneMatch、 findFirst、 findAny、 iterator
- Short-circuiting:
anyMatch、 allMatch、 noneMatch、 findFirst、 findAny、 limit
Stream的主要方法:
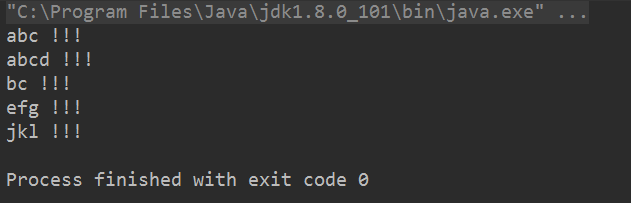
1.将strings正序输出并去重去空,并在每个元素的结尾加"!!!":
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd", "", "jkl", "bc");
strings.stream()
.filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()) // 过滤空字符串
.distinct() // 去重
.sorted() // 正序输出
.map(s -> s + " !!! ") // 将每一个元素加上"!!!"后,再映射到其相对应的位置
.forEach(System.out::println); // 循环遍历输出
运行结果如下:
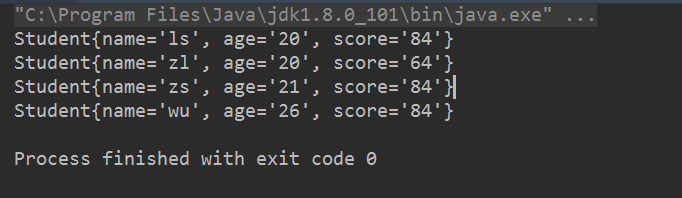
2.按学生年龄正序,成绩倒序输出
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Student("zs", 21, 84)); list.add(new Student("ls", 20, 84)); list.add(new Student("wu", 26, 84)); list.add(new Student("zl", 20, 64)); list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge).reversed() .thenComparing(Student::getScore).reversed()) .forEach(System.out::println);
3.Collectors(点击进入)
Collectors 类实现了很多归约操作,例如将流转换成集合和聚合元素。Collectors 可用于返回列表或字符串:
常见方法: Collectors(toList()、toSet()、toCollection()、joining()、partitioningBy()、collectingAndT)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号