Struts入门(三)深入Struts用法讲解
- 访问Servlet API
- Action搜索顺序
- 动态方法调用
- 指定多个配置文件
- 默认Action
- Struts 后缀
- 接收参数
- 处理结果类型
1.访问Servlet API
首先我们了解什么是Servlet API
httpRequest、httpResponse、servletContext
3个api对应jsp面向对象:request、response、application
servlet中可以直接调用servlet api
struts2 Action中execute没有任何参数,也就是不存在servlet api
Struts2框架底层是基本Servlet的,所以我们肯定要去访问Servlet API,而且开发Web应用不去访问Servlet API也是不可能的,
所以我们Struts2框架提供了我们去访问Servlet API的方法;
struts2 提供了3种方式访问servlet api:
①:使用ServletActionContext访问Servlet API; ActionContext类
②:使用ActionContext访问ServletAPI; ServletActionCotext类
③:使用一些接口 如 ServletRequestAwa...; 实现***Aware接口
2.Action搜索顺序
我们来看一个路径:
我们这里新建一个student.action 没有命名空间那么我们访问的路径就是
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/student.action
那么我们改成下面的路径
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/path1/path2/path3/student.action
在浏览器中访问也能访问到正确的页面
因此我们可以看出访问的顺序是从文件的上级 也就是最后一级包开始找
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/path1/path2/path3/student.action
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/path1/path2/student.action
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/path1/student.action
http://localhost:8080/ProjectName(项目的名字)/student.action
从path3 一直到path1都找不到 最后在根目录下找到 如果找不到就会报错了
这就是action的搜索顺序!
3.动态方法调用
在.net MVC中 我们在Controller中创建一个一个方法 只要在页面中指定相应的mvc路径 我们视图的一个url就能请求得到
在struts中 我们则需要手工进行配置 指定页面和后台方法的匹配
这里的动态方法调用就是为了解决一个Action对应多个请求得处理。以免Action太多(像指定method属性的配置方式 )
动态调用有三种方式 这里指定method属性和感叹号方式(不推荐使用)不再说明 我们来说下常用的通配符方式:
首先在struts.xml配置我们的参数

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd" > <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="HelloWorld2" class="com.HelloWorldAction"> <result>/result.jsp</result> </action> <!-- name 代表我们的action名也就是url里面的名字 class是指定我们的后台类文件 method {1} 与name中的*对应 --> <action name="helloworld_*" method="{1}" class="com.HelloWorldAction"> <result >/result.jsp</result> <result name="add" >/add.jsp</result> <result name="update" >/update.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
这里我们需要创建三个jsp文件 默认路径的result.jsp 还有add方法的add.jsp update方法的update.jsp


页面里面我们都用一句话简单区分 这样 启动Debug as Server 然后在浏览器中访问就可以对应到相应的路径了

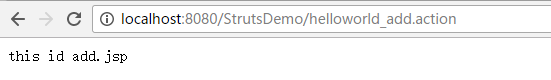
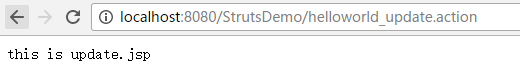
这里struts.xml文件result标签值都改成{1}.jsp 一样的道理 这里可以随意加参数进行配置
4.指定多个配置文件
如果项目比较大 则需要比较多的配置 我们在入门(二)文件中看到注释可以用include来包含多个配置文件
<include file="***.xml"> </include> <constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"> </constant>
ps: 1.被include的标签一定要符合struts的dtd规范。也就是说被include的xml文件的内部格式要符合struts的xml文件规范(跟struts.xml一摸一样)。 2.xml文件的编码格式要相同,如果是utf-8,那么都是utf-8。
5.默认Action
默认action是为了改善用户体验,当用户输入的URL找不到对应的action,就会使用默认Action
【找不到默认action的原因和解决方法】
<default-action-ref name="index"></default-action-ref> <action name="index"> <result>/error.jsp</result> </action> <br> <action name="log_*" method="{1}" class="com.wayne.action.LoginAction"> <result name="login">/login.jsp</result> <result name="logout">/logout.jsp</result> </action>
将上面代码放到package标签中 这里定义了一个index的默认标签
通配符会覆盖掉默认action,所以不能有【*_*】这样子的action,要改成【log_*_*】这类型的命名,
否则,【*_*】里面的第一个*就包括了所有的字符,直接进入了这个action进行处理,无法进入默认的action了。
6.Struts 后缀
三种方式:
1.struts.properties中:struts.action.extension=action,do,struts2
2.struts.xml中增加常量constant:
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do,struts2"></constant>
3.在web.xml过滤器中配置intt-param参数:
<init-param>
<param-name>struts.action.extension</param-name>
<param-value>do,action,strtus2</param-value>
</init-param>
7.接收参数
之前我们说到struts项目中 我们写了前台jsp页面 写了后台action页面 那么要想两者进行关联就需要在配置文件中配置关联关系(真是麻烦。)
下面我们用项目示例来说明下接收参数问题:
首先我们建立一个login.jsp页面

1 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" 2 pageEncoding="utf-8"%> 3 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> 4 <html> 5 <head> 6 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> 7 <title>Insert title here</title> 8 </head> 9 <body> 10 <form action="LoginAction.action" method="post"> 11 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /> 12 密码:<input type="password" name="password" /> 13 <input type="submit" value="提交"/> 14 </form> 15 </body> 16 </html>
然后我们创建一个后台Class LoginAction.java

package com; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { public String login(){ return SUCCESS; } }
然后我们在struts.xml配置文件中配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd" > <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="HelloWorld2" class="com.HelloWorldAction"> <result>/result.jsp</result> </action> <action name="LoginAction" method="login" class="com.LoginAction"> <result >/success.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
这里添加了一个过滤器 指定了访问LoginAction的login方法
然后我们如何通过action的属性获取form提交的值
第一种方式:直接在action类中实现--使用Action的属性接收参数(不利于面向对象)

1 package com; 2 3 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 4 5 public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { 6 //创建两个属性的get set方法 7 private String username; 8 private String password; 9 10 public String login(){ 11 System.out.println(username); 12 return SUCCESS; 13 } 14 15 public String getUsername() { 16 return username; 17 } 18 19 public void setUsername(String username) { 20 this.username = username; 21 } 22 23 public String getPassword() { 24 return password; 25 } 26 27 public void setPassword(String password) { 28 this.password = password; 29 } 30 31 32 }
然后访问:http://localhost:8080/StrutsDemo/login.jsp 输入用户名密码 提交 会发现控制台中打印输出了 用户名
第二种方式:使用DomainModel接收参数
这里要把第一种属性声明的方式 单独放到一个类中去
建立一个User类

1 package com.po; 2 3 public class User { 4 //创建两个属性的get set方法 5 private String username; 6 private String password; 7 8 public String getUsername() { 9 return username; 10 } 11 12 public void setUsername(String username) { 13 this.username = username; 14 } 15 16 public String getPassword() { 17 return password; 18 } 19 20 public void setPassword(String password) { 21 this.password = password; 22 } 23 }
然后action中去掉属性相关 声明一个user类

package com; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.po.User; public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } private User user; public String login(){ System.out.println(user.getUsername()); return SUCCESS; } }
login.jsp页面中需要更改name的值

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="LoginAction.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user.username" /> 密码:<input type="password" name="user.password" /> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
然后再次启动下 访问:http://localhost:8080/StrutsDemo/login.jsp 输入用户名密码 提交 会发现控制台中同样打印输出了 用户名
第三种方式:使用ModelDriven接收参数(推荐方式)
这里我们需要实现ModelDriven接口

package com; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; import com.po.User; public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User>{ private User user=new User(); //这里需要实例化 去掉了 get set方法 实现了ModelDriven的方法 public String login(){ System.out.println(user.getUsername()); return SUCCESS; } @Override public User getModel() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return user; } }
这里我们也不再需要指定jsp中的name 对象 去掉user.

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="LoginAction.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username" /> 密码:<input type="password" name="password" /> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
如果我们传递一个List方式一样的道理 在jsp中 我们声明
书籍1:<input type="text" name="BookList[0]"/>
书籍2:<input type="text" name="BookList[1]"/>
后台User类中我们创建List BookList对象

private List<String> BookList; public List<String> getBookList() { return BookList; } public void setBookList(List<String> bookList) { BookList = bookList; }
这里我们就简单介绍这几种方式 最后做一个总结:
1 接收参数 2 1,使用Action的属性接受参数,在Action中定义需要接受的属性,并写它的set/get方法。 3 2,使用DomainModel接受参数,创建实体类定义需要接受的属性,并set/get方法,在Action中创建实体类名属性。并在界面进行指定。 4 3,使用ModelDriver接受参数,在Action中实现ModelDriver<实体类名>接口,并实现方法返回当前需要转换的对象,删除set/get方法,并对 对象 进行实例化,并取消指定。 5 4,request 6 5,获取List集合中的参数。获取多个参数。 7 8 第一种接收参数的方法:直接在action类中创建相应的属性和getter和setter,和前端的name名字相同。eg:前端的username,在action类中就要建立一个private String username; Struts会自动映射为这个属性赋值 9 10 第二种接受参数的方法:使用DomainModel,将username 和password两个属性封装为一个类User(必须是标准的JavaBean),在action中声明这个属性:private User user; 同时为user设置getter和setter;在前端中的name需要设置为user.name和user.password,才能映射成功 11 12 第三种接收参数的方法:使用ModelDriven<T>接口,这个action必须实现这个接口的public T getModel()方法。此时声明的属性必须实例化,eg: private User user = new User(); 同时不需要getter和setter。前端的name也只需要写username和password就可以,不需要再加域了。这种方法时最推荐的方法,因为可以减少前后端的耦合
8.处理结果类型

我们来看一下struts.xml中过滤器的一句话
<result name="success">/result.jsp</result> 这句话等同于<result >/result.jsp</result> 说明name的默认值就是success
【Structs2处理流程】
用户请求Structs框架控制器(Action)Structs框架视图资源
返回String,提供代码复用性,有利于框架分离。
【Action中五种内置属性(com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action)】




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号