[CF737E] Tanya is 5!
Tanya is 5!
题意
有 \(n\) 个孩子,\(m\) 种机器,\(b\) 块钱。一开始,每种机器只有一个,但每种机器你有且仅有一次机会花 \(p_i\) 块再购买一台。第 \(i\) 个孩子想在第 \(j\) 种机器上工作 \(C_{i,j}\) 时间,工作可以中断,工作时间累加。孩子可以不花费时间中断工作和跑去另一个机器工作。每个时刻一个孩子只能在一台机器上工作,每台机器于同一时刻只能被一个孩子工作。
求完成所有工作的最少时间,并输出工作的方案。注意,你可以任意花费钱,只要在 \(b\) 块以内。
\(n\leq 40,1\leq m\leq 10,0\leq b\leq 10^6,1\leq p_i \leq10^6,0\leq C_{i,j} \leq 2500\)
分析
首先我们考虑没有购买机器的机会我们可以怎么做。
设 \(T_j = \sum_i C_{i,j},S_i = \sum_j = C_{i,j}\),其中 \(S_i\) 表示第 \(i\) 个孩子希望工作的总时间,\(T_j\) 表示第 \(j\) 台机器需要被工作的总时间。显然,我们答案一个显然的下界为 \(max(max\{ T_j\},max\{ S_i\})\),设为 \(X\)。
那么我们证明 \(X\) 是可以被取得的。
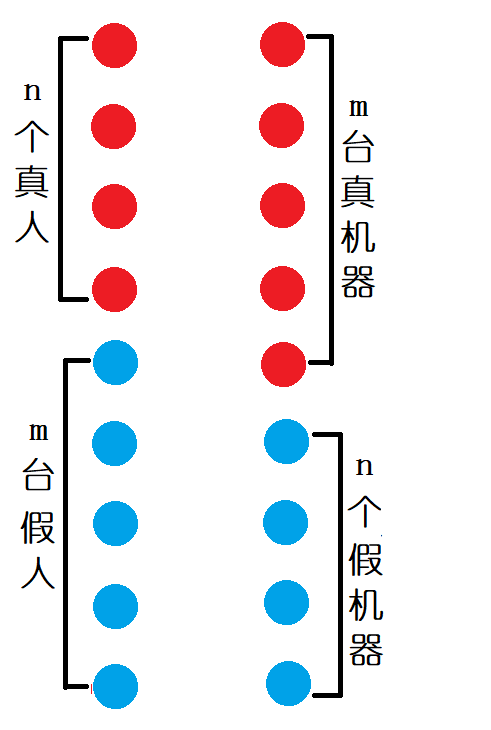
考虑建二分图,人为左部节点,机器为右部节点。
对于每个人,我们建一个对应的假机器,对于每个机器,我们建一个对应的假人。
-
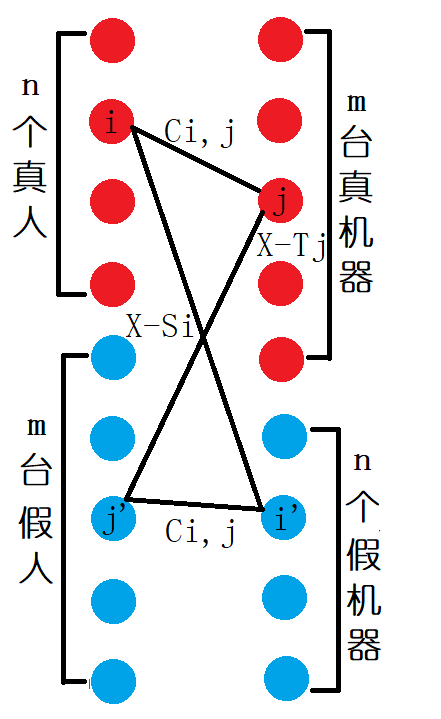
对于第 \(i\) 个真人和第 \(j\) 个真机器,连边权值为 \(C_{i,j}\)。
-
对于第 \(i\) 个真人和第 \(j\) 个假机器,连边权值为 \(X - S_i\)。
-
对于第 \(j\) 个假人和第 \(j\) 个真机器,连边权值为 \(X - T_j\)。
-
对于第 \(j\) 个假人和第 \(i\) 个假机器,连边权值为 \(C_{i,j}\)。
这个时候,能够发现二分图两边的节点数量相同,且每个点度数都是 \(X\)。根据 \(Hall\) 定理,显然该图可以分解为 \(X\) 个完美匹配,每一次找出一个匹配,我们就能够取到 \(X\)。
事实上,假人和假机器的作用只在于补充度数,每一次匹配中,如果真人匹配真机器,说明这个时刻该人在这台机器上工作,否则说明人或者机器轮空。
考虑怎么购买机器可以让决策更优。
注意到我们的下界只和 \(S_i\) 和 \(T_j\) 有关,显然,购买机器只能够影响到 \(T_j\),我们每次复制机器,相当于把某个 \(T_j\) 分成两份 \(\lceil \frac{T_j}{2}\rceil\),\(\lfloor \frac{T_j}{2}\rfloor\),那我们只需要尽量把最大的买了即可。
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50, M = 1e6 + 10, K = 1e5 + 10;
inline int read()
{
int s = 0, w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if(ch == '-') w *= -1; ch = getchar(); }
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') s = s * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return s * w;
}
struct node{ int p, id; }ch[N];
struct edge{
int u, v;
}e[M];
int n, m, b, tot, ans, cnt;
int id[2 * N], pos[N], sum[N], col[M];
int R[N], Z[N], c[N][N], match[2 * N][K];
bool buy[N];
set<int> s[2 * N];
inline bool cmp1(node x, node y) { return Z[x.id] > Z[y.id]; }
inline bool cmp2(node x, node y) { return x.id < y.id; }
inline void dfs(int u, int x, int y)
{
int id = match[u][x], v = (e[id].u == u ? e[id].v : e[id].u);
match[u][x] = match[v][x] = 0;
if(match[v][y]) dfs(v, y, x);
else s[v].insert(x), s[v].erase(y);
match[v][y] = match[u][y] = id, col[id] = y;
}
int main()
{
n = read(), m = read(), b = read();
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++) ch[i].p = read(), ch[i].id = i;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x = read();
for(register int j = 1, y; j <= x; j++) y = read(), c[i][y] = read();
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(register int j = 1; j <= m; j++) R[i] += c[i][j], Z[j] += c[i][j];
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = max(ans, R[i]);
sort(ch + 1, ch + m + 1, cmp1);
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if(ch[i].p <= b) b -= ch[i].p, buy[ch[i].id] = true;
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
ans = max(ans, buy[i] ? (Z[i] + 1) / 2 : Z[i]);
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
pos[i] = ++tot, id[tot] = i;
if(buy[i]) id[++tot] = i;
}
sort(ch + 1, ch + m + 1, cmp2);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(register int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
while(c[i][j]--){
sum[j]++;
if(!buy[j]) e[++cnt] = (edge){i, pos[j] + n};
else if(sum[j] <= Z[j] / 2) e[++cnt] = (edge){i, pos[j] + n};
else e[++cnt] = (edge){i, pos[j] + 1 + n}; //第二个点连边
}
}
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n + tot; i++)
for(register int j = 1; j <= ans; j++) s[i].insert(j);
for(register int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
int u = e[i].u, v = e[i].v, c1 = *s[u].begin(), c2 = *s[v].begin();
if(match[v][c1]) dfs(v, c1, c2), s[v].erase(c2);
match[u][c1] = match[v][c1] = i, col[i] = c1;
s[u].erase(c1), s[v].erase(c1);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++) printf("%d", buy[i]);
puts("");
cout << cnt << "\n";
for(register int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) printf("%d %d %d 1\n", e[i].u, id[e[i].v - n], col[i] - 1);
return 0;
}



