[2019HDU多校第五场][HDU 6626][C. geometric problem]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6626
题目大意:给出平面上六个点\(A,B,M,N,X,Y\)以及两条直线\(L1,L2\),要求在四边形\(ABNM\)内,直线\(L1\)上选一点\(S\),在四边形\(XYNM\)内,直线\(L2\)上选一点\(T\),使得\(S_{ASB}=S_{SMTN}=S_{XYT}\)
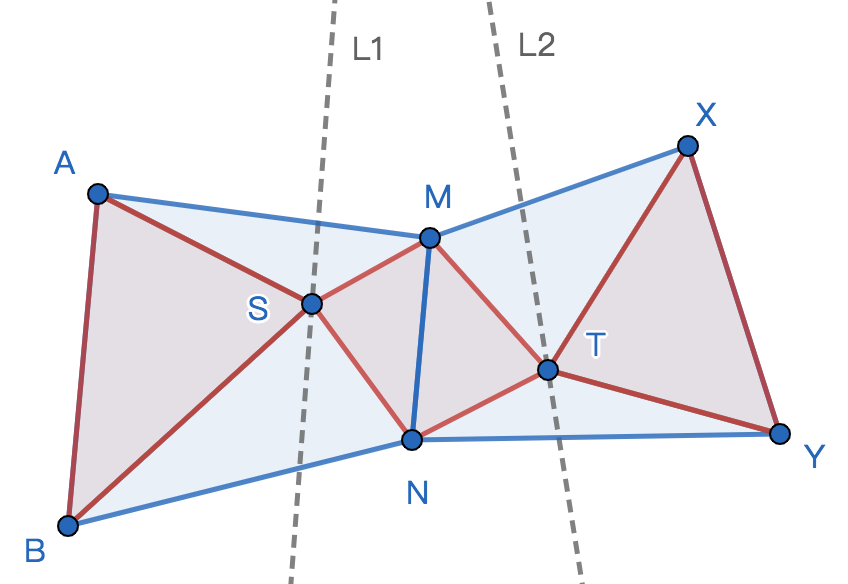
题解:设\(L1\)交\(ABNM\)于点\(P,Q\),不妨设\(S=P+t\cdot (Q-P), 0\leq t \leq 1\),则有$$2S_{ASB}=\vec{AB}\times \vec{AS}=\vec{AB}\times (\vec{AP}+t\cdot \vec{PQ})=\vec{AB}\times \vec{AP}+t\cdot \vec{AB}\times \vec{PQ}$$
这个式子可以转换成为\(A+t\cdot B\)的形式。同理,三角形\(SMN,MNT,XYT\)均可以表示成这种形式,且\(ASB,SMN\)对应的\(t\)是\(S\)的坐标,不妨设为\(x\),另外两个三角形对应的\(t\)则设为\(y\)。这样我们就能得到$$\left\{\begin{matrix}
2S_{ASB}=\vec{AB}\times \vec{AP}+x\cdot \vec{AB}\times \vec{PQ}\\
2S_{SMN}=\vec{MN}\times \vec{MP}+x\cdot \vec{MN}\times \vec{PQ}\\
2S_{MNT}=\vec{MN}\times \vec{MP'}+y\cdot \vec{MN}\times \vec{P'Q'}\\
2S_{XYT}=\vec{XY}\times \vec{XP'}+y\cdot \vec{XY}\times \vec{P'Q'}
\end{matrix}\right.$$
根据题目要求,我们就能得出$$\left\{\begin{matrix}
2S_{ASB}-2S_{XYT}=\vec{AB}\times \vec{AP}-\vec{XY}\times \vec{XP'}+x\cdot \vec{AB}\times \vec{PQ}-y\cdot \vec{XY}\times \vec{P'Q'}=0\\
2S_{ASB}-2S_{SMN}-2S_{MNT}=\vec{AB}\times \vec{AP}-\vec{MN}\times \vec{MP}-\vec{MN}\times \vec{MP'}+x\cdot(\vec{AB}\times \vec{PQ}-\vec{MN}\times \vec{PQ})-y\cdot \vec{MN}\times \vec{P'Q'}=0
\end{matrix}\right.$$
这是一个二元一次方程组,当然我们也可以将其当成两条直线的标准式来看,求出他们的交点就能得出对应的答案了。
这里要注意,这里求出来的表达式可能不会有对应的直线(比如\(0\cdot x+0\cdot y=c \neq 0\)),或者会出现两直线没有交点,重合等情况,需要进行特判。另外还需要注意\(x,y\)解出来的值必须在\([0,1]\)这个范围内,否则也是无解。
另外,由于这题要求在多解时输出字典序最小的解,所以在我们求交点的时候就可以让点\(P\)的字典序比\(Q\)小,这样只要尽量让\(x,y\)取到最小值就好了
由于为了防止爆精度,看到坐标范围较小,想练习手写分数运算等种种原因,这题我除了输出外都是纯整数运算,不用担心爆精度了以后感觉改代码都方便了许多(指不需要调\(eps\)←_←)

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Frac { long long p,q; void read(){q=1,scanf("%lld",&p);} void simp() {int d=abs(__gcd(p,q)); p/=d,q/=d; if(q<0)p*=-1,q*=-1; if(p==0)q=abs(q); } Frac operator +(const Frac &t)const { Frac res={p*t.q+t.p*q,q*t.q}; res.simp();return res; } Frac operator -(const Frac &t)const { Frac res={p*t.q-t.p*q,q*t.q}; res.simp();return res; } Frac operator *(const Frac &t)const { Frac res={p*t.p,q*t.q}; res.simp();return res; } Frac operator /(const Frac &t)const { Frac res={p*t.q,q*t.p}; res.simp();return res; } bool operator <(const Frac &t)const { return p*t.q<q*t.p; } bool operator ==(const Frac &t)const { return p==t.p && q==t.q; } void print(){printf("%.12f",1.0*p/q);} }; int sgn(Frac k) { if(k.p>0)return 1; if(k.p<0)return -1; return 0; } struct Point { Frac x,y; void read(){x.read(),y.read();} Point operator +(const Point &t)const{return {x+t.x,y+t.y};} Point operator -(const Point &t)const{return {x-t.x,y-t.y};} Frac operator *(const Point &t)const{return x*t.y-y*t.x;} Point operator *(const Frac &t)const{return {x*t,y*t};} Point operator /(const Frac &t)const{return {x/t,y/t};} bool operator <(const Point &t)const{return x==t.x?y<t.y:x<t.x;} bool operator ==(const Point &t)const{return x==t.x && y==t.y;} void print(){x.print(),putchar(' '),y.print();} bool check() { if(sgn(x)<0 || sgn(y)<0)return false; if((Frac){1,1}<x || (Frac){1,1}<y)return false; return true; } }A,B,M,N,X,Y,f[5],g[5],ans[5]; struct Line { Point p1,p2; void read(){p1.read(),p2.read();} bool check_isct(const Point &A,const Point &B)const {return sgn((p2-p1)*(A-p1))*sgn((p2-p1)*(B-p1))<=0;} Point isct_Point(const Line &t)const { Frac a=(p2-p1)*(t.p1-p1); Frac b=(p2-p1)*(p1-t.p2); return (t.p1*b+t.p2*a)/(a+b); } }L1,L2; struct Line_Standard { Frac A,B,C; bool check(){return sgn(A) || sgn(B) || !sgn(C);} bool check_isct(const Line_Standard &t)const { Frac tmp=A*t.B-B*t.A; if(sgn(tmp))return true; return sgn(C*t.B-B*t.C)==0; } Point isct_Point(const Line_Standard &t)const { Frac tmp=A*t.B-B*t.A; if(!sgn(tmp)) { if(sgn(C)==0)return {{0,1},{0,1}}; if(sgn(B)==0)return {{0,1},{1,1}}; if(sgn(A)==0)return {{1,1},{0,1}}; } return {(B*t.C-C*t.B)/tmp,(C*t.A-A*t.C)/tmp}; } void print() { A.print(),putchar(' '); B.print(),putchar(' '); C.print(),putchar('\n'); } }h1,h2; int T,cnt; void rua(const Line &L,const Point &A,const Point &B,const int &lim) { if(L.check_isct(A,B) && sgn((L.p2-L.p1)*(A-B)) && cnt<lim) if(!(L.isct_Point({A,B})==f[cnt]) || cnt==lim-2) f[++cnt]=L.isct_Point({A,B}); } void cal(const Point &A,const Point &B,const Point &C,const Point &D) { Frac st=(B-A)*(C-A); Frac delta=(B-A)*(D-C); Frac ed=(B-A)*(D-A); if(sgn(st)<0 || sgn(ed)<0) st.p=-st.p,delta.p=-delta.p; g[++cnt]={st,delta}; } void print(const Point &P) { Point S=f[1]+(f[2]-f[1])*P.x; Point T=f[3]+(f[4]-f[3])*P.y; S.print(),putchar(' '); T.print(),putchar('\n'); } void init() { cnt=0; A.read(),B.read(); M.read(),N.read(); X.read(),Y.read(); L1.read(),L2.read(); rua(L1,A,B,2),rua(L1,B,N,2); rua(L1,N,M,2),rua(L1,M,A,2); rua(L2,X,Y,4),rua(L2,Y,N,4); rua(L2,N,M,4),rua(L2,M,X,4); if(f[2]<f[1])swap(f[1],f[2]); if(f[4]<f[3])swap(f[3],f[4]); cnt=0; cal(A,B,f[1],f[2]); cal(M,N,f[1],f[2]); cal(M,N,f[3],f[4]); cal(X,Y,f[3],f[4]); h1={g[1].y,(Frac){0,1}-g[4].y,g[1].x-g[4].x}; h2={g[1].y-g[2].y,(Frac){0,1}-g[3].y,g[1].x-g[2].x-g[3].x}; if(!h1.check() || !h2.check()) {printf("-1\n");return;} cnt=0; Frac tmp=h1.A*h2.B-h1.B*h2.A; if(sgn(tmp)==0) { if(sgn(h1.C*h2.B-h1.B*h2.C)) {printf("-1\n");return;} if(!sgn(h1.A) && !sgn(h1.B)) swap(h1,h2); if(h1.check_isct({{1,1},{0,1},{0,1}})) ans[++cnt]=h1.isct_Point({{1,1},{0,1},{0,1}}); if(h1.check_isct({{0,1},{1,1},{0,1}})) ans[++cnt]=h1.isct_Point({{0,1},{1,1},{0,1}}); if(h1.check_isct({{0,1},{1,1},{-1,1}})) ans[++cnt]=h1.isct_Point({{0,1},{1,1},{-1,1}}); if(h1.check_isct({{1,1},{0,1},{-1,1}})) ans[++cnt]=h1.isct_Point({{1,1},{0,1},{-1,1}}); for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) if(ans[i].check()) {print(ans[i]);return;} printf("-1\n"); return; } ans[++cnt]=h1.isct_Point(h2); if(ans[1].check()) {print(ans[1]);return;} printf("-1\n"); } int main() { scanf("%d",&T); while(T--)init(); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号