结构型设计模式
单例模式
定义
保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个该实例的全局访问点。 ——《设计模式》GoF
// c++11 magic static 特性:如果当变量在初始化的时候,并发同时进⼊声明语句,并发线程将会阻塞等待初始化结束。
// c++ effective
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton &GetInstance() {
static Singleton instance;
return instance;
}
private:
Singleton() {}
~Singleton() {}
Singleton(const Singleton &) {}
Singleton &operator=(const Singleton &) {}
};
// 继承 Singleton
// g++ Singleton.cpp -o singleton -std=c++11
/*该版本具备的优点:
1. 利⽤静态局部变量特性,延迟加载;
2. 利⽤静态局部变量特性,系统⾃动回收内存,⾃动调⽤析构函数;
3. 静态局部变量初始化时,没有 new 操作带来的cpu指令reorder操作;
4. c++11 静态局部变量初始化时,具备线程安全;
*/
模板类版本
template<typename T>
class Singleton {
public:
static T &GetInstance() {
static T instance; // 这⾥要初始化DesignPattern,需要调⽤DesignPattern构造函数,同时会调⽤⽗类的构造函数。
return instance;
}
protected:
virtual ~Singleton() {}
Singleton() {} // protected修饰构造函数,才能让别⼈继承
Singleton(const Singleton &) {}
Singleton &operator=(const Singleton &) {}
};
class DesignPattern : public Singleton<DesignPattern> {
friend class Singleton<DesignPattern>; // friend 能让Singleton<T> 访问到DesignPattern构造函数
public:
~DesignPattern() {}
private:
DesignPattern() {}
DesignPattern(const DesignPattern &) {}
DesignPattern &operator=(const DesignPattern &) {}
};
结构图
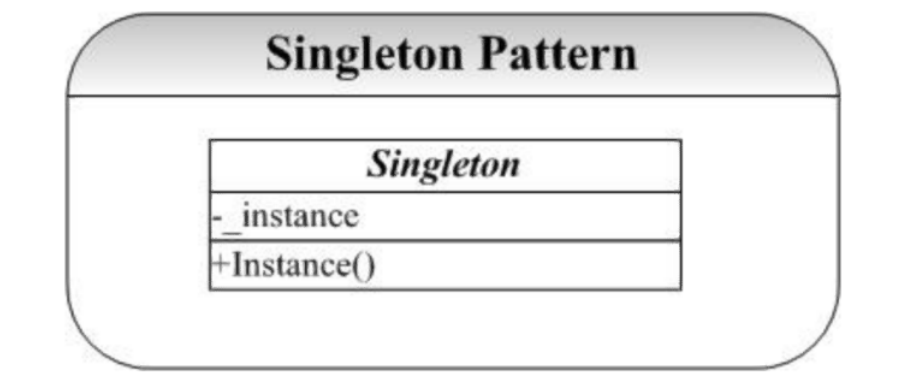
工厂方法
定义
定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。Factory Method使得一个类的实例化延迟到子类。 ——《设计模式》GoF
背景
实现一个导出数据的接口,让客户选择数据的导出方式;
要点
解决创建过程比较复杂,希望对外隐藏这些细节的场景;
- 比如连接池、线程池
- 隐藏对象真实类型;
- 对象创建会有很多参数来决定如何创建;
- 创建对象有复杂的依赖关系;
本质
- 延迟到子类来选择实现;
结构图
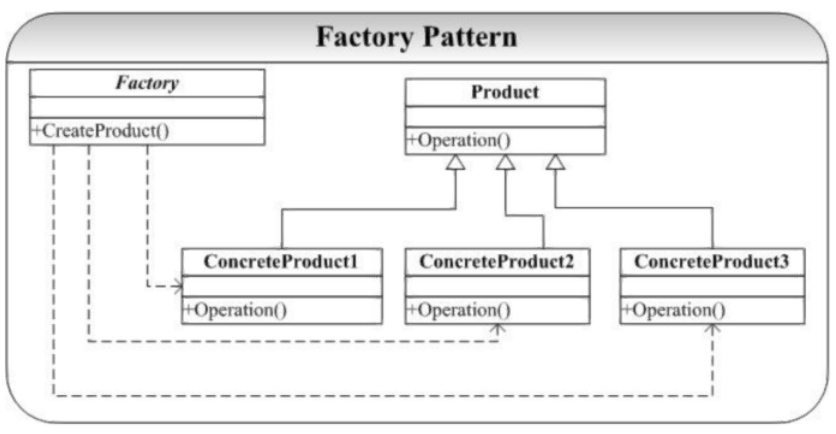
#include <string>
// 实现导出数据的接口, 导出数据的格式包含 xml,json,文本格式txt 后面可能扩展excel格式csv
class IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) = 0;
virtual ~IExport(){}
};
class ExportXml : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportJson : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportTxt : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportCSV : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class IExportFactory {
public:
IExportFactory() {
_export = nullptr;
}
virtual ~IExportFactory() {
if (_export) {
delete _export;
_export = nullptr;
}
}
bool Export(const std::string &data) {
if (_export == nullptr) {
_export = NewExport();
}
return _export->Export(data);
}
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) = 0;
private:
IExport* _export;
};
class ExportXmlFactory : public IExportFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportXml();
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class ExportJsonFactory : public IExportFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportJson;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class ExportTxtFactory : public IExportFactory {
protected:
IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportTxt;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class ExportCSVFactory : public IExportFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportCSV;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
int main () {
IExportFactory *factory = new ExportTxtFactory();
factory->Export("hello world");
return 0;
}
抽象工厂
定义
提供一个接口,让该接口负责创建一系列“相关或者相互依赖的对象”,无需指定它们具体的类。——《设计模式》GoF
背景
实现一个拥有导出导入数据的接口,让客户选择数据的导出导入方式;
结构图
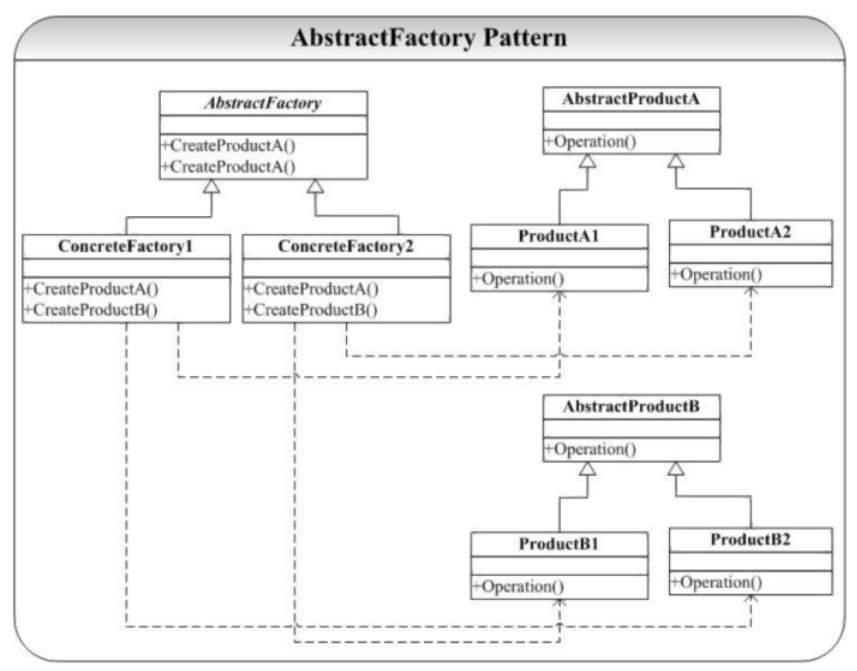
#include <string>
// 实现导出数据的接口, 导出数据的格式包含 xml,json,文本格式txt 后面可能扩展excel格式csv
class IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) = 0;
virtual ~IExport(){}
};
class ExportXml : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportJson : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportTxt : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ExportCSV : public IExport {
public:
virtual bool Export(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class IImport {
public:
virtual bool Import(const std::string &data) = 0;
virtual ~IImport(){}
};
class ImportXml : public IImport {
public:
virtual bool Import(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ImportJson : public IImport {
public:
virtual bool Import(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
class ImportTxt : public IImport {
public:
virtual bool Import(const std::string &data) {
return true;
}
};
// 对于初学者: 知道扩展代码
// 5年
class ImportCSV : public IImport {
public:
virtual bool Import(const std::string &data) {
// ....
return true;
}
};
class IDataApiFactory {
public:
IDataApiFactory() {
_export = nullptr;
_import = nullptr;
}
virtual ~IDataApiFactory() {
if (_export) {
delete _export;
_export = nullptr;
}
if (_import) {
delete _import;
_import = nullptr;
}
}
bool Export(const std::string &data) {
if (_export == nullptr) {
_export = NewExport();
}
return _export->Export(data);
}
bool Import(const std::string &data) {
if (_import == nullptr) {
_import = NewImport();
}
return _import->Import(data);
}
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) = 0;
virtual IImport * NewImport(/* ... */) = 0;
private:
IExport *_export;
IImport *_import;
};
class XmlApiFactory : public IDataApiFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportXml;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
virtual IImport * NewImport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IImport * temp = new ImportXml;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class JsonApiFactory : public IDataApiFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportJson;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
virtual IImport * NewImport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IImport * temp = new ImportJson;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class TxtApiFactory : public IDataApiFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportTxt;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
virtual IImport * NewImport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IImport * temp = new ImportTxt;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
class CSVApiFactory : public IDataApiFactory {
protected:
virtual IExport * NewExport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IExport * temp = new ExportCSV;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
virtual IImport * NewImport(/* ... */) {
// 可能有其它操作,或者许多参数
IImport * temp = new ImportCSV;
// 可能之后有什么操作
return temp;
}
};
// 相关性 依赖性
int main () {
IDataApiFactory *factory = new CSVApiFactory();
factory->Import("hello world");
factory->Export("hello world");
return 0;
}
责任链
定义
使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。 ——《设计模式》GoF
背景
请求流程,1 天内需要主程序批准,3 天内需要项目经理批准,3 天以上需要老板批准;
要点
- 解耦请求方和处理方,请求方不知道请求是如何被处理,处理方的组成是由相互独立的子处理构成,子处理流程通过链表的方式连接,子处理请求可以按任意顺序组合;
- 责任链请求强调请求最终由一个子处理流程处理;通过了各个子处理条件判断;
- 责任链扩展就是功能链,功能链强调的是,一个请求依次经由功能链中的子处理流程处理;
- 将职责以及职责顺序运行进行抽象,那么职责变化可以任意扩展,同时职责顺序也可以任意扩展;
本质
- 分离职责,动态组合;
结构图
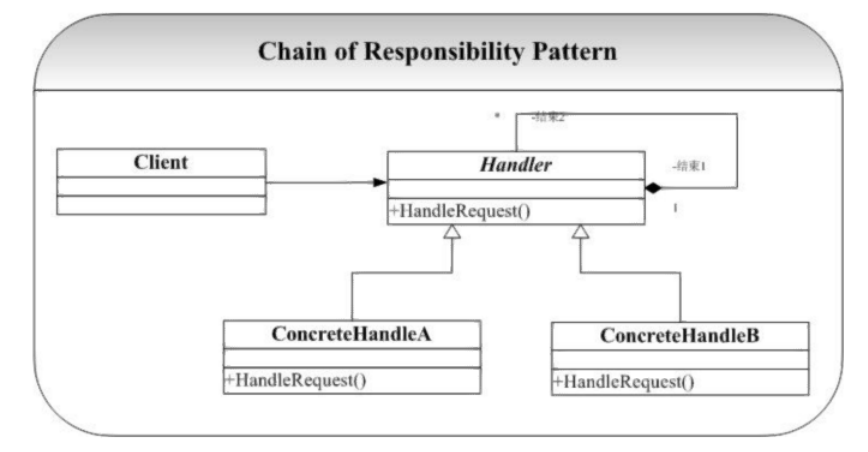
#include <string>
class Context {
public:
std::string name;
int day;
};
// 稳定点 抽象 变化点 扩展
class IHandler {
public:
virtual ~IHandler() {}
void SetNextHandler(IHandler *next) { // 链表关系
next = next;
}
// 抽象稳定点,对扩展开放
// 模板模式:固定算法骨架,通过子类去扩展子流程
bool Handle(const Context &ctx) {
if (CanHandle(ctx)) {
return HandleRequest(ctx);
} else if (GetNextHandler()) {
return GetNextHandler()->Handle(ctx);
} else {
// err
}
return false;
}
protected:
virtual bool HandleRequest(const Context &ctx) = 0;
virtual bool CanHandle(const Context &ctx) =0;
IHandler * GetNextHandler() {
return next;
}
private:
IHandler *next;
};
// 能不能处理,以及怎么处理
class HandleByMainProgram : public IHandler {
protected:
virtual bool HandleRequest(const Context &ctx){
//
return true;
}
virtual bool CanHandle(const Context &ctx) {
//
if (ctx.day <= 10)
return true;
return false;
}
};
class HandleByProjMgr : public IHandler {
protected:
virtual bool HandleRequest(const Context &ctx){
//
return true;
}
virtual bool CanHandle(const Context &ctx) {
//
if (ctx.day <= 20)
return true;
return false;
}
};
class HandleByBoss : public IHandler {
protected:
virtual bool HandleRequest(const Context &ctx){
//
return true;
}
virtual bool CanHandle(const Context &ctx) {
//
if (ctx.day < 30)
return true;
return false;
}
};
class HandleByBeauty : public IHandler {
protected:
virtual bool HandleRequest(const Context &ctx){
//
return true;
}
virtual bool CanHandle(const Context &ctx) {
//
if (ctx.day <= 3)
return true;
return false;
}
};
int main() {
// IHandler * h1 = new HandleByMainProgram();
// IHandler * h2 = new HandleByProjMgr();
// IHandler * h3 = new HandleByBoss();
// h1->SetNextHandler(h2);
// h2->SetNextHandler(h3);
// 抽象工厂
// nginx http 处理
IHandler * h0 = new HandleByBeauty();
IHandler * h1 = new HandleByMainProgram();
IHandler * h2 = new HandleByProjMgr();
IHandler * h3 = new HandleByBoss();
h0->SetNextHandler(h1);
h1->SetNextHandler(h2);
h2->SetNextHandler(h3);
// 设置下一指针
Context ctx;
h0->Handle(ctx);
return 0;
}
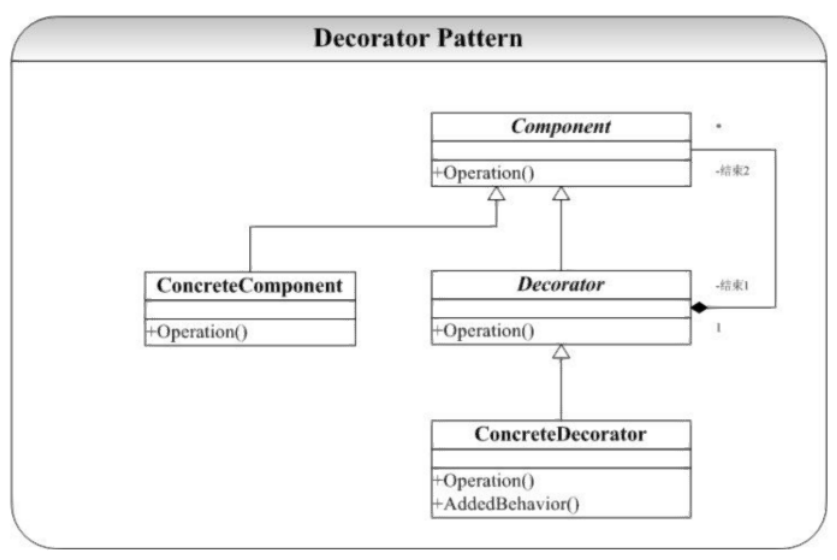
装饰器
定义
动态地给一个对象增加一些额外的职责。就增加功能而言,装饰器模式比生产子类更为灵活。—— 《设计模式》GoF
背景
普通员工有销售奖金,累计奖金,部门经理除此之外还有团队奖金;后面可能会添加环比增长奖金,同时可能针对不同的职位产生不同的奖金组合;
要点
- 通过采用组合而非继承的手法, 装饰器模式实现了在运行时动态扩展对象功能的能力,而且可以根据需要扩展多个功能。 避免了使用继承带来的“灵活性差”和“多子类衍生问题”。
- 不是解决“多子类衍生问题”问题,而是解决“父类在多个方向上的扩展功能”问题;
- 装饰器模式把一系列复杂的功能分散到每个装饰器当中,一般一个装饰器只实现一个功能,实现复用装饰器的功能;
本质
- 动态组合
结构图
#include <iostream>
// 普通员工有销售奖金,累计奖金,部门经理除此之外还有团队奖金;后面可能会添加环比增长奖金,同时可能产生不同的奖金组合;
// 销售奖金 = 当月销售额 * 4%
// 累计奖金 = 总的回款额 * 0.2%
// 部门奖金 = 团队销售额 * 1%
// 环比奖金 = (当月销售额-上月销售额) * 1%
// 销售后面的参数可能会调整
using namespace std;
class Context {
public:
bool isMgr;
// User user;
// double groupsale;
};
class CalcBonus {
public:
CalcBonus(CalcBonus * c = nullptr) : cc(c) {}
virtual double Calc(Context &ctx) {
return 0.0; // 基本工资
}
virtual ~CalcBonus() {}
protected:
CalcBonus* cc;
};
class CalcMonthBonus : public CalcBonus {
public:
CalcMonthBonus(CalcBonus * c) : CalcBonus(c) {}
virtual double Calc(Context &ctx) {
double mbonus /*= 计算流程忽略*/;
return mbonus + cc->Calc(ctx);
}
};
class CalcSumBonus : public CalcBonus {
public:
CalcSumBonus(CalcBonus * c) : CalcBonus(c) {}
virtual double Calc(Context &ctx) {
double sbonus /*= 计算流程忽略*/;
return sbonus + cc->Calc(ctx);
}
};
class CalcGroupBonus : public CalcBonus {
public:
CalcGroupBonus(CalcBonus * c) : CalcBonus(c) {}
virtual double Calc(Context &ctx) {
double gbnonus /*= 计算流程忽略*/;
return gbnonus + cc->Calc(ctx);
}
};
class CalcCycleBonus : public CalcBonus {
public:
CalcCycleBonus(CalcBonus * c) : CalcBonus(c) {}
virtual double Calc(Context &ctx) {
double gbnonus /*= 计算流程忽略*/;
return gbnonus + cc->Calc(ctx);
}
};
int main() {
// 1. 普通员工
Context ctx1;
CalcBonus *base = new CalcBonus();
CalcBonus *cb2 = new CalcSumBonus(base);
CalcBonus *cb1 = new CalcMonthBonus(cb2);
cb2->Calc(ctx1);
// 2. 部门经理
Context ctx2;
CalcBonus *cb3 = new CalcGroupBonus(cb2);
cb3->Calc(ctx2);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号