创建型设计模式
模板方法
定义
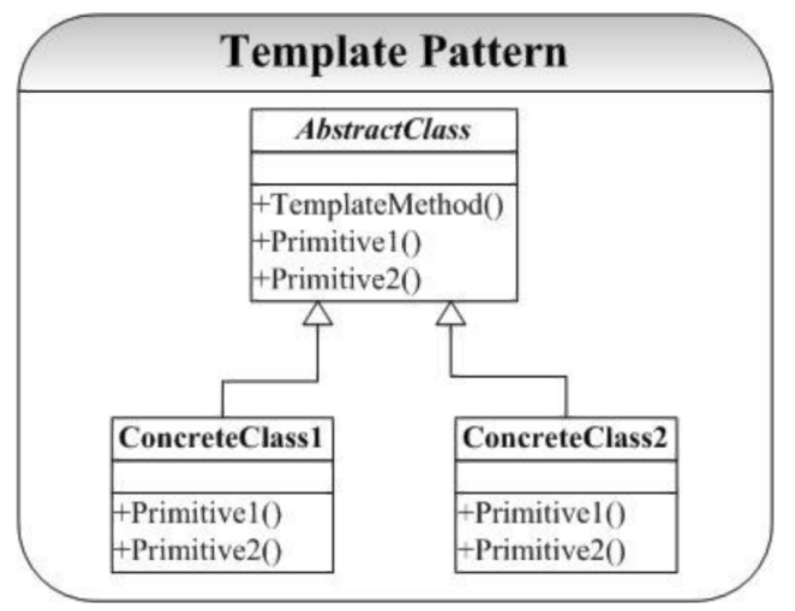
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架 ,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。 Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。 ——《 设计模式》 GoF
背景
某个品牌动物园,有一套固定的表演流程,但是其中有若干个表演子流程可创新替换,以尝试迭代更新表演流程;
要点
- 最常用的设计模式,子类可以复写父类子流程,使父类的骨架流程丰富;
- 反向控制流程的典型应用;
- 父类 protected 保护子类需要复写的子流程;这样子类的子流程只能父类来调用;
本质
- 通过固定算法骨架来约束子类的行为;
结构图
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 不满足开闭原则 对扩展开放 继承(虚函数覆盖)
// 扩展功能:继承 (虚函数覆盖) 组合
class ZooShow {
public:
void Show() {
if (Show0())
PlayGame();
Show1();
Show2();
Show3();
}
private:
void PlayGame() {
cout << "after Show0, then play game" << endl;
}
protected:
virtual bool Show0(){
cout << "show0" << endl;
return true;
}
virtual void Show2(){
cout << "show2" << endl;
}
virtual void Show1() {
}
virtual void Show3() {
}
};
class ZooShowEx1 : public ZooShow {
protected:
virtual bool Show0(){
cout << "show1" << endl;
return true;
}
virtual void Show2(){
cout << "show3" << endl;
}
};
class ZooShowEx2 : public ZooShow {
protected:
virtual void Show1(){
cout << "show1" << endl;
}
virtual void Show2(){
cout << "show3" << endl;
}
};
class ZooShowEx3 : public ZooShow {
protected:
virtual void Show1(){
cout << "show1" << endl;
}
virtual void Show3(){
cout << "show3" << endl;
}
virtual void Show4() {
//
}
};
/*
*/
int main () {
ZooShow *zs = new ZooShowEx3;
// ZooShow *zs1 = new ZooShowEx1;
// ZooShow *zs2 = new ZooShowEx2;
zs->Show();
return 0;
}
观察者模式
定义
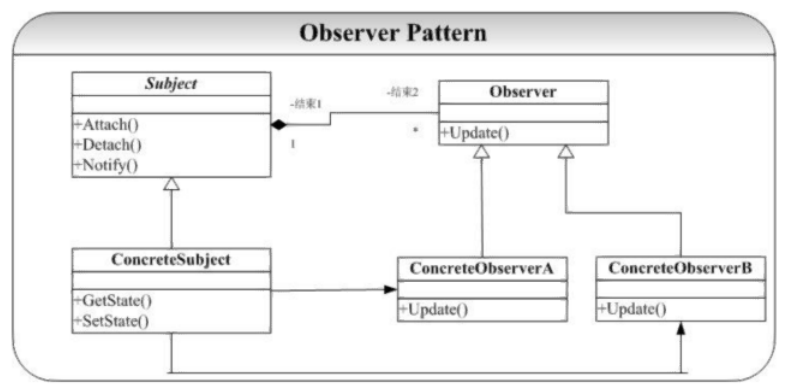
定义对象间的一种一对多(变化)的依赖关系,以便当一个对象(Subject)的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动更新。 ——《 设计模式》 GoF
背景
气象站发布气象资料给数据中心,数据中心经过处理,将气象信息更新到两个不同的显示终端(A和B);
要点
- 观察者模式使得我们可以独立地改变目标与观察者,从而使二者之间的关系松耦合;
- 观察者自己决定是否订阅通知,目标对象并不关注谁订阅了;
- 观察者不要依赖通知顺序,目标对象也不知道通知顺序;
- 常用在基于事件的ui框架中,也是 MVC 的组成部分;
- 常用在分布式系统中、actor框架中;
本质
- 触发联动
结构图
#include <vector>
//
class IDisplay {
public:
virtual void Show(float temperature) = 0;
virtual ~IDisplay() {}
};
class DisplayA : public IDisplay {
public:
virtual void Show(float temperature);
private:
void jianyi();
};
class DisplayB : public IDisplay{
public:
virtual void Show(float temperature);
};
class DisplayC : public IDisplay{
public:
virtual void Show(float temperature);
};
class WeatherData {
};
class DataCenter {
public:
void Attach(IDisplay * ob);
void Detach(IDisplay * ob);
void Notify() {
float temper = CalcTemperature();
for (auto iter = obs.begin(); iter != obs.end(); iter++) {
(*iter)->Show(temper);
}
}
// 接口隔离
private:
virtual WeatherData * GetWeatherData();
virtual float CalcTemperature() {
WeatherData * data = GetWeatherData();
// ...
float temper/* = */;
return temper;
}
std::vector<IDisplay*> obs;
};
int main() {
DataCenter *center = new DataCenter;
IDisplay *da = new DisplayA();
IDisplay *db = new DisplayB();
IDisplay *dc = new DisplayC();
center->Attach(da);
center->Attach(db);
center->Attach(dc);
center->Notify();
//-----
center->Detach(db);
center->Notify();
return 0;
}
策略模式
定义
定义一系列算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可互相替换。该模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户程序而变化。 ——《设计模式》 GoF
背景
某商场节假日有固定促销活动,为了加大促销力度,现提升国庆节促销活动规格;
要点
- 策略模式提供了一系列可重用的算法,从而可以使得类型在运⾏时方便地根据需要在各个算法之间进行切换;
- 策略模式消除了条件判断语句;也就是在解耦合;
本质
- 分离算法,选择实现;
结构图

class Context {
};
class ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx) = 0;
virtual ~ProStategy();
};
// cpp
class VAC_Spring : public ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
// cpp
class VAC_QiXi : public ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
class VAC_QiXi1 : public VAC_QiXi {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
// cpp
class VAC_Wuyi : public ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
// cpp
class VAC_GuoQing : public ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
class VAC_Shengdan : public ProStategy {
public:
virtual double CalcPro(const Context &ctx){}
};
class Promotion {
public:
Promotion(ProStategy *sss) : s(sss){}
~Promotion(){}
double CalcPromotion(const Context &ctx){
return s->CalcPro(ctx);
}
private:
ProStategy *s;
};
int main () {
Context ctx;
ProStategy *s = new VAC_QiXi1();
Promotion *p = new Promotion(s);
p->CalcPromotion(ctx);
return 0;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· AI Agent开发,如何调用三方的API Function,是通过提示词来发起调用的吗