第一次博客作业
一、前言:
大一下学期才开始接触Java,感觉到Java的难度远大于上学期学的C语言,C语言的核心在于:数据结构+算法(类似于美团外卖的设计流程),而Java的核心是对象,而且是实例化类的对象,泛指就是类 + 消息,Java就是两个对象或类之间的交互手段。从前几周的题目集中我学到了很多。
这三次的题目集总的来说涵盖知识面不同,难度参差不齐。
1).首先就题目集一来,题目集一的难度相对来说比较低但知识点涵盖却并不匮乏,共七道题,主要是字符串的截取,以及输出数据精度的控制。
2).其次题目集二,题目集二的难度就略微提升了一些,运用到了字母与字符的转换还有不同数据控制输出不同的结果。
3).最后是题目集三,虽然只有四道题,但是难度提高了不少,第一道题目先让我们使用类解决问题,第二题,第三题不仅使用不同的类解决不同的问题,层层递进,使类似题目的代码不断优化。
二、设计与分析:
题目1).
串口字符解析
RS232是串口常用的通信协议,在异步通信模式下,串口可以一次发送5~8位数据,收发双方之间没有数据发送时线路维持高电平,相当于接收方持续收到数据“1”(称为空闲位),发送方有数据发送时,会在有效数据(5~8位,具体位数由通信双方提前设置)前加上1位起始位“0”,在有效数据之后加上1位可选的奇偶校验位和1位结束位“1”。请编写程序,模拟串口接收处理程序,注:假定有效数据是8位,奇偶校验位采用奇校验。
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Scanner input = new Scanner (System.in); String a = input.nextLine(); int count1 = 0; int num = 1;int flag = 0; for(int m = 0; m < a.length();m++) { if(a.charAt(m) == '1') count1++; } if(a.length()< 11) System.out.println("null data"); if(count1 == a.length()) System.out.println("null data"); for(int i = 0;i < a.length();i++) { int count = 0; if(i+10>a.length()-1) break; else if(a.charAt(i) == '0') { for(int j = i + 1;j <= i + 8;j++) { if(a.charAt(j) == '1') count++; } if(a.charAt(i + 10) != '1' ) { System.out.print(num + ":"); System.out.println("validate error"); num++; i = i + 10; } else if((a.charAt(i + 10) == '1' && count % 2 == 0 && a.charAt(i + 9) != '1') || (a.charAt(i + 10) == '1' && count % 2 != 0 && a.charAt(i + 9) == '1')) { System.out.print(num + ":"); System.out.println("parity check error"); num++; i = i + 10; } else { System.out.print(num + ":"); num++; for(int j = i+1;j <=i + 8;j++) { System.out.print(a.charAt(j)); } System.out.print("\n"); i = i + 10; } } } } }
我认为这次代码if语句连续使用太多,没有做到先画好流程图并且把情况分类在进行分析,然后再进行编写代码。
题目2).
用类解一元二次方程式
定义一个代表一元二次方程ax2+bx+c=0的类QuadraticEquation,其属性为三个系数a、b、c(均为私有属性),类中定义的方法参考main方法中的代码。PowerDesigner类图与main方法源码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double a = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); double b = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); double c = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); if(a == 0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } //create a QuadraticEquation object QuadraticEquation equation = new QuadraticEquation(a, b, c); //get value of b * b - 4 * a * c double discriminant = equation.getDiscriminant(); System.out.println("a=" + equation.getA() + ",b=" + equation.getB() + ",c=" + equation.getC()+":"); if (discriminant < 0) { System.out.println("The equation has no roots."); } else if (discriminant == 0) { System.out.println("The root is " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1())); } else // (discriminant > 0) { System.out.println("The roots are " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1()) + " and " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot2())); } } } class QuadraticEquation{ private double a; private double b; private double c; public QuadraticEquation(double a , double b , double c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } public double getA() {//返回a的值 return a; } public double getB() {//返回b的值 return b; } public double getC() {//返回c的值 return c; } public double getDiscriminant() {//计算并返回discriminant的值 double discriminant; discriminant = b * b - 4 * a * c; return discriminant; } public double getRoot1() {//计算并返回root1的值 if(getDiscriminant() >= 0) { double root1; root1 = (- b + Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 / a; return root1; } else//getDiscriminant() < 0 return 0; } public double getRoot2() {//计算并返回root2的值 if(getDiscriminant() >= 0) { double root2; root2 = (- b - Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 / a; return root2; } else//getDiscriminant() < 0 return 0; } }
在此次编码之前分析了不同情况,所以没有漏掉a = 0时不是一元二次方程的情况,并且控制输出Wrong Format。
题目3).
日期类设计
参考题目集二中和日期相关的程序,设计一个类DateUtil,该类有三个私有属性year、month、day(均为整型数),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 除了创建该类的构造方法、属性的getter及setter方法外,需要编写如下方法:
public boolean checkInputValidity();//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
public boolean isLeapYear(int year);//判断year是否为闰年
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n);//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date);//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date);//判断两个日期是否相等
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date);//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
public String showDate();//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
PowerDesigner类图与源码如下:
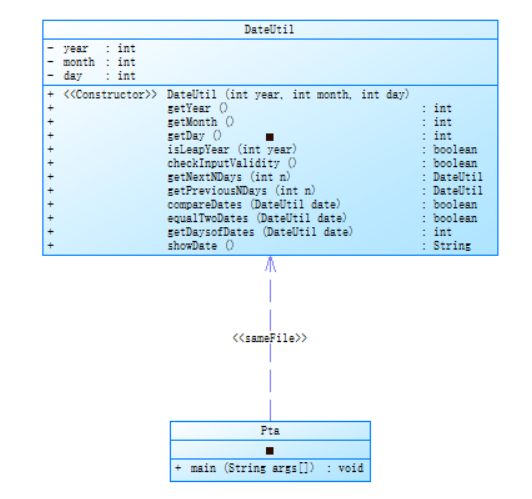
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print( date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class DateUtil { private int year; private int month; private int day; public DateUtil(int year , int month , int day) { this.year = year; this.month = month; this.day = day; } public int getYear() { return year; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public int getDay() { return day; } public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { //判断是否为闰年 if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) return true; else return false; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { //判断输入数据是否合法 if(getYear() < 1820 || getYear() > 2020) return false; else if(getMonth() < 1 || getMonth() > 12) return false; else if(getDay() < 1 || getDay() > 31) return false; else if((getMonth() == 4 && getDay() >= 31) || (getMonth() == 6 && getDay() >= 31) || (getMonth() == 9 && getDay() >= 31) || (getMonth() == 11 && getDay() >= 31)) return false; else if(getMonth() == 2 && isLeapYear(getYear()) == true && getDay() > 29) return false; else if(getMonth() == 2 && isLeapYear(getYear()) == false && getDay() > 28) return false; else return true; } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { //得到之后m天的日期 int[] months = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; while(n > 366) { if(month == 2 && day == 29) { n = n - 366; year ++; month = 3; day = 1; } else if((isLeapYear(year) && month<= 2) || (isLeapYear(year+1) && month > 2)) { year ++; n = n - 366; } else { n = n - 365; year ++; } } for (int i = 0;i < n;i ++) { if(isLeapYear(year)) months[2] = 29; else months[2] = 28; if(day == months[month]) { if(month == 12) { year ++; month = 1; day = 1; } else { month ++; day = 1; } } else day ++; } return new DateUtil(year,month,day); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { for(int i = -1;i >= -n;i --) { if(month == 12 || month == 10 || month == 7 || month == 5) { if(day == 1) { month = month - 1; day = 30; } else day = day - 1; } else if(month == 2 || month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 8 || month == 9 || month == 11) { if(day == 1) { month = month - 1; day = 31; } else day = day - 1; } else if(month == 3) { if(day == 1 && isLeapYear(year) == true) { month = 2; day = 29; } else if(day == 1 && isLeapYear(year) == false) { month = 2; day = 28; } else day = day - 1; } else if(month == 1) { if(day == 1) { year = year - 1; month = 12; day = 31; } else day = day - 1; } } return new DateUtil(year,month,day); } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.year > date.getYear()) return true; else if(this.year == date.getYear() && this.month > date.getMonth()) return true; else if(this.year == date.getYear() && this.month == date.getMonth() && this.day > date.getDay()) return true; else return false; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.year != date.getYear() || this.day != date.getDay() || this.month != date.getMonth()) return false; else return true; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { int sum1 = 0; int sum2 = 0; int[] months = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; for(int i = 1;i < date.getYear();i++) { if(isLeapYear(i) == true) sum1 = sum1 + 366; else sum1 = sum1 + 365; } for(int j = 1;j < date.getMonth();j ++){ sum1 = sum1 + months[j]; if(isLeapYear(date.getYear()) == true && j== 2) sum1 = sum1 + 1; } sum1 = sum1 + date.getDay(); for(int x = 1;x < this.year;x++) { if(isLeapYear(x) == true) sum2 = sum2 + 366; else sum2 = sum2 + 365; } for(int y = 1;y < this.month;y ++){ sum2 = sum2 + months[y]; if(isLeapYear(this.year) == true && y == 2) sum2 = sum2 + 1; } sum2 = sum2 + this.day; int result = sum1 - sum2; return result; } public String showDate(){ return year + "-" + month + "-" + day; } }
题目4).
日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
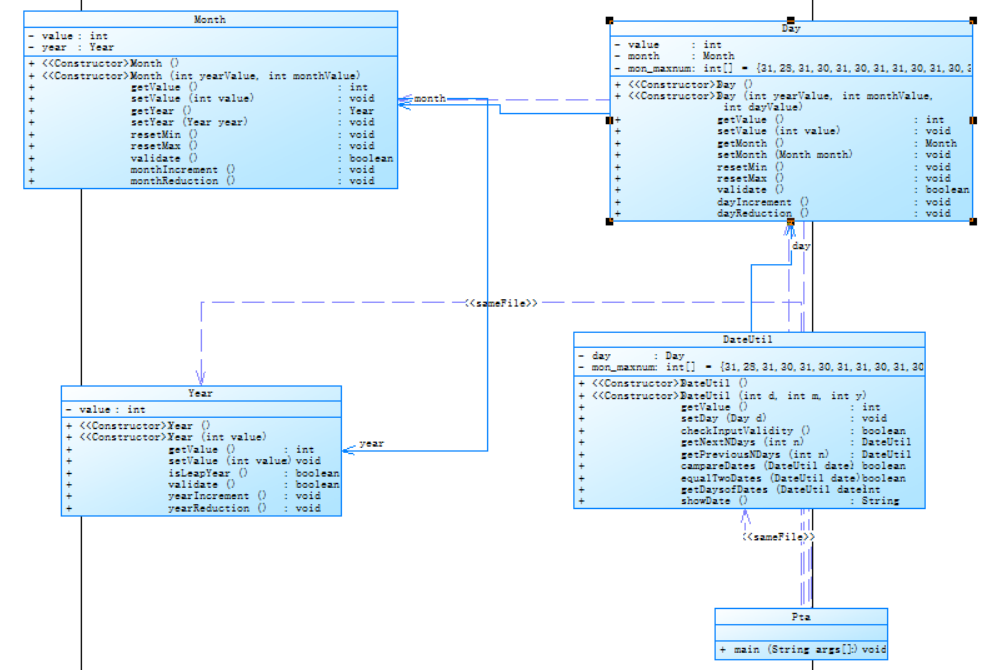
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class Year { private int value; public Year() { super(); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public Year(int value) { super(); this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear() { if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || (value % 400 == 0)) return true; else return false; } public boolean validate() { if(value < 1900 || value > 2050) return false; else return true; } public void yearIncrement() { value ++; } public void yearReduction() { value --; } } class Month { private int value; private Year year; public Month() { super(); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public Month(int yearValue, int monthValue) { super(); this.year=new Year(yearValue); this.value=monthValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public void resetMin() { value = 1; } public void resetMax() { value = 12; } public boolean validate() { if(value > 12 || value < 1) return false; else return true; } public void monthIncrement() { value ++; } public void monthReduction() { value --; } } class Day { private int value; private Month month; private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public Day() { super(); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) { super(); this.month=new Month(yearValue, monthValue); this.value=dayValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public void resetMin() { value = 1; } public void resetMax() { if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()) { mon_maxnum[1] = 29; } value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]; } public boolean validate() { if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 29; else mon_maxnum[1] = 28; if(value < 1 || value > mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]) return false; else return true; } public void dayIncrement() { value++; } public void dayReduction() { value--; } } class DateUtil { private Day day; private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public DateUtil() { super(); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public DateUtil (int d,int m,int y) { this.day = new Day( d, m, y); } public int getValue() { return day.getValue(); } // public Day getDay() { // return day.getValue(); // } public void setDay(Day d) { this.day = d; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { if(!day.getMonth().getYear().validate()) return false; else if(!day.getMonth().validate()) return false; else { if(!day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 28; else mon_maxnum[1] = 29; if((day.getValue() > mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue() - 1])) return false; else return true; } } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; while(n > 366) { if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() == 29) { n = n - 366; this.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); this.day.getMonth().setValue(3); this.day.setValue(1); } else if((this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() <= 2) || ((((this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1) % 4 == 0 && (this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1) % 100 != 0) || (this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1) % 400 == 0) && this.day.getMonth().getValue() > 2)) { this.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); n = n - 366; } else { n = n - 365; this.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); } // System.out.println(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue()+" "+n); } for (int i = 1;i <=n;i ++) { if(!this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 28; else mon_maxnum[1] = 29; if(this.day.getValue() == mon_maxnum[this.day.getMonth().getValue() - 1]) { if(this.day.getMonth().getValue() == 12) { this.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); this.day.getMonth().resetMin(); this.day.resetMin(); } else { this.day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.day.resetMin(); } } else this.day.dayIncrement(); // System.out.println(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue()+" "+i); } return new DateUtil(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),this.day.getMonth().getValue(),this.day.getValue()); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { for(int i = -1;i >= -n;i --) { if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 12 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 10 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 7 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 5) { if(day.getValue() == 1) { day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.setValue(30); } else day.dayReduction(); } else if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 2 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 4 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 6 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 8 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 9 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 11) { if(day.getValue() == 1) { day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.setValue(31); } else day.dayReduction(); } else if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 3) { if(day.getValue() == 1 && day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { day.getMonth().setValue(2); day.setValue(29); } else if(day.getValue() == 1 && !day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { day.getMonth().setValue(2); day.setValue(28); } else day.dayReduction(); } else if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1) { if(day.getValue() == 1) { day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); day.getMonth().setValue(12); day.setValue(31); } else day.dayReduction(); } } return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); } public boolean campareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() > day.getMonth().getValue()) return true; else if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.day.getMonth().getValue() == day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()) return true; else return false; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() != date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() || this.day.getValue() != date.day.getValue() || this.day.getMonth().getValue() != day.getMonth().getValue()) return false; else return true; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { int sum1 = 0; int sum2 = 0; int[] months = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; for(int i = 1;i < this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();i++) { if((i % 4 == 0 && i % 100 != 0) || (i % 400 == 0)) sum1 = sum1 + 366; else sum1 = sum1 + 365; } for(int j = 1;j < this.day.getMonth().getValue();j ++){ sum1 = sum1 + months[j]; if(this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && j == 2) sum1 = sum1 + 1; } sum1 = sum1 + this.day.getValue(); for(int x = 1;x < date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();x++) { if((x % 4 == 0 && x % 100 != 0) || (x % 400 == 0)) sum2 = sum2 + 366; else sum2 = sum2 + 365; } for(int y = 1;y < date.day.getMonth().getValue();y ++){ sum2 = sum2 + months[y]; if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && y == 2) sum2 = sum2 + 1; } sum2 = sum2 + date.day.getValue(); int result = sum1 - sum2; return Math.abs(result); } public String showDate() { return this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); } }
这道题目与上一道题目基本一致,但是耦合度更低,遇上道题目相比创建了Year Month Day三个类,并且通过Year调用Month,Month调用Day,这样使代码的耦合度更低,也就是说降低了类与类之间关系的紧密程度,将实现不同功能的代码放置在不同的类中,且类与类的紧密程度更低,是代码更加优化。
三、踩坑心得
1).题目1
2.出现问题
在没了解奇偶校验具体判断时就凭借主观臆断只理解字面意思,以所理解的字面意思编写代码判断是否校验错误。奇偶校验的意思为:在输入有效数据中1的个数为偶数时,奇偶校验位数字正确应为1,在输入有效数据中1的个数为奇数时,奇偶校验位数字正确应为0。根据奇偶校验位是否错误以及其他种类错误综合判断输出什么结果。并且再判断完一组数据之后,用来计算有效数据中1出现次数的计数器要归零,若不归零且上次1出现次数为奇数则会影响下一次奇偶校验的判断。
出现问题2)
在判断完一组数据的结果后,利用for循环循环判断下一组数据,在找到下一组数据起始位时未考虑在for循环内已经将所定义的字符串下标加1,如下图:
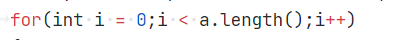
所以每次在判断完一组结果后只需要将字符串下标加上一组数据的位数减一就达到了下一组有效数据的起始位。如下图:

总结:
1)在编写程序前要搞清楚题目每一个要求的意思,不能望文生义,导致缩写出来的代码与题目要求完全不一致,这不仅导致浪费许多时间,还养成了这种习惯,造成类似这种的错误,下次依旧会犯。
2)在编写出程序时,要看清自己的代码,根据自己的需求,根据自己的想法,写出能够符合题目要求的代码,就像这次出现的问题2一样,不能只想着自己此时要满足的题目需求还要根据自己的之前写出的代码对现在进行的操作进行更改。
1)题目2
2.出现问题)
在定义类时,将类放在主方法里,导致编译器报错(这个错误也是很不应该了),导致检查了很久都没发现。
总结:
1)这道题写的很快,我认为是在写这道题之前画出了流程图,将每一种情况都分清出来,这样使我在编写程序时思路清晰并且每一种情况都没有遗漏,再加上这道题目之前也用C语言写过,用Java写第二遍感觉自己的思路更加清晰,逻辑更加有条理。
2)在编写代码时一边写出了注释,不用反复看自己已经写过什么代码,在定义变量名时也更加规范,增加了代码可读性,并且提高了编写速度。
3)题目3
2.出现问题)
1)在刚开始编写这道题程序时,第一个出现的错误就是越界错误:
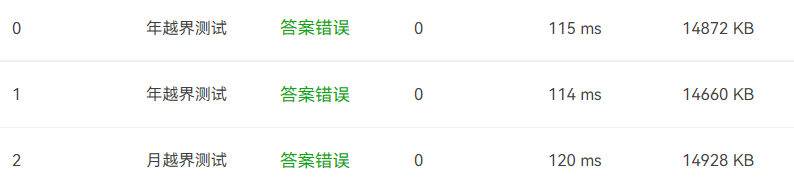
未考虑数据是否合法,这样导致输出结果不正确。
2)第二个问题就是算法不够优化
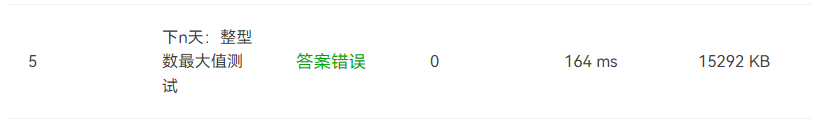
这导致在输入很大数据时,运行错误,于是我重新写了算法,如下图:
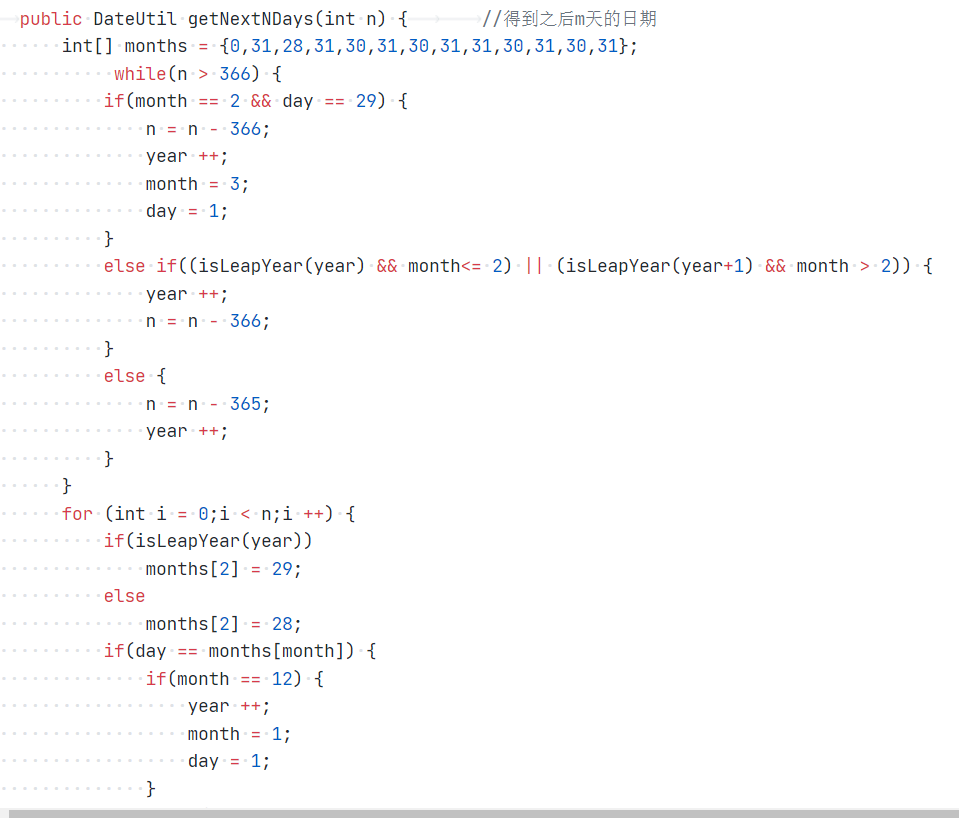
通过先一整年一整年的加在起始日期,在剩余天数不足一年后,再逐天逐天的加,这样大大缩短了编译时间。
总结:
1)在根据题目需求设计算法的同时要考虑算法是否足够优化,不断优化自己的算法才能不断提高代码的质量。
4)题目4
2.出现问题)
1)在确定其属性时没有注意是私有或公有,导致错误。
2)在根据上一题代码的基础上修改时,没有考虑类间关系,例如:在需要调用Year时要通过Day调用Month,再通过Month调用Year,达到间接调用的满足代码需求。
总结:
题目集3的第二题与第三题层层递进,一步一步实现降低耦合度,使代码的可复用性更高。
四、改进建议:
我认为这三次题目集的难度是逐级递增的,在遇到简单问时不能轻视,也需要严格按照写代码步骤:
1)其次就是看清题目,清晰题目所有的要求,在此基础上开始想如何解决,如何编写代码。
2)先画流程图以便于整理自己的思路,这样就不会导致简单的问题代码反复来回修改,养成一个良好习惯。
3)我认为在编写代码时应该更加专心,如果打断很难沿着的思路继续编写代码,这会导致逻辑混乱,写出很多无用且错误的代码。
五 、总结:
1)这几次的作业让我感受到了编写代码需要严谨,要考虑每种不同的情况,这样才能保证程序没有漏洞,在不严谨的思绪下写出来的代码,可能你用数据测试最后得到的结果却是正确的,最后找不到漏洞在哪,需要花更大量的时间去找到漏洞并且修复。
2)从题目集3的第二第三两道题中深深的体会的到了流程图的重要性,在类的数量很多,且类间关系复杂时就更体现了流程图的重要性,如果不画流程图就会陷入无从下手的处境。
posted on 2022-04-10 22:56 21206104-戴奕为 阅读(82) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号