HIAST Collegiate Programming Contest 2024(非完全题解)
C题(简单数据结构+二分)
转化成对每个i,求最长区间使得区间与为ai。左右边界可以二分出来(类似24新生赛B),区间与用st表
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
// //如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
// inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
#define N 100005
int f[25][N];
int Log2[N];
int n,a[N];
int query(int l,int r)
{
int k = Log2[r-l+1];
return f[k][l] & f[k][r-(1<<k)+1];
}
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin>>a[i], f[0][i]=a[i];
for(int j=1;j<=Log2[n];++j)
{
for(int i=1;i+(1<<j-1)<=n;++i)
{
f[j][i] = (f[j-1][i] & f[j-1][i+(1<<j-1)]);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
int l,r,mid;
int L,R;
l=1; r=i;
while(l<r)
{
mid = (l+r)>>1;
if(query(mid, i) == a[i]) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
L=l;
l=i, r=n;
while(l<r)
{
mid = (l+r+1)>>1;
if(query(i, mid) == a[i]) l=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
R=l;
cout<<(ll)(R-i+1)*(i-L+1)<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
Log2[0]=-1;
for(int i=1;i<N;++i) Log2[i] = Log2[i/2]+1;
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
H(博弈)
\(关注到不管是移动一个还是三个都会改变sum的奇偶性\)
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
// //如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int a;
ll sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
cin>>a;
sum += a;
}
cout<<((sum&1)?("YES\n"):("NO\n"));
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
I(纯签到)
\(注意find函数若没找到是!=npos没有括号\)
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
//如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
// inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
void solve()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
string std = "bitset";
if(s.find(std) != s.npos)
{
cout<<"7as\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"no 7as for you today\n";
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
K题(LCA,dfs序,思维)
倒水问题,可以发现对一个子树,从根开始倒水,结点进水顺序为dfs序。
对每个询问,从v开始倒水要想去u,必定经过lca(u,v),过程可以分为两部分,从v到r和从r到u,分类讨论求代价即可。
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
//如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
#define N 100005
int n,q;
vector<int> e[N];
vector<int> edfn[N];
int fa[N], siz[N], dep[N], son[N], top[N];
int dfn[N];
int tot;
void dfs_init(int u)
{
siz[u] = 1;
son[u] = 0;
dfn[u] = ++tot;
for(auto &&v:e[u])
{
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
dfs_init(v);
siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = v;
}
edfn[u].resize(e[u].size());
for(int i=0;i<e[u].size();++i)
{
edfn[u][i] = dfn[e[u][i]];
}
}
void dfs_shupou(int u,int topx)
{
top[u] = topx;
if(son[u]) dfs_shupou(son[u], topx);
for(auto &&v:e[u])
{
if(v==son[u]) continue;
dfs_shupou(v, v);
}
}
int lca(int x,int y)
{
while(top[x] != top[y])
{
if(dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
x = fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) return x;
else return y;
}
void solve()
{
cin>>n>>q;
tot = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) e[i].clear(), edfn[i].clear();
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)
{
cin>>fa[i];
e[fa[i]].push_back(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) sort(e[i].begin(),e[i].end());
dep[1]=0;
dfs_init(1);
dfs_shupou(1,1);
while(q--)
{
int v,x,u; cin>>v>>x>>u;
auto f = [&](int y){cout<<(x>=y?"YES\n":"NO\n");};
if(u==v) {f(1); continue;}
int r = lca(v,u);
// int fu = e[r][upper_bound(edfn[r].begin(), edfn[r].end(), dfn[u])-1-edfn[r].begin()];
if(dfn[u] < dfn[v])
{
int fv = e[r][upper_bound(edfn[r].begin(), edfn[r].end(), dfn[v])-1-edfn[r].begin()];
f(dfn[u]-dfn[r]+1 + siz[fv]);
}
else
{
f(dfn[u]-dfn[r]+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
H题(简单构造)
\(当x为10次幂时显然无解,否则为离他最近的10次幂\)
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
//如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
set<ll> P;
void solve()
{
ll x;
cin>>x;
ll inf = 1e18;
if(P.find(x)!=P.end()) cout<<"-1\n";
else
{
auto it = P.lower_bound(x);
cout<<*it<<'\n';
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
ll tmp = 1;
P.insert(1);
for(int i=1;i<=18;++i) {tmp = 10*tmp;P.insert(tmp);}
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
D(数学)
\(原先两个式子经过简单推导后(真的很简单)可变成 x^3 =a_i^2a_j , y^3 =a_j^2a_i ,我们考虑x,y,a_i,a_j质因数分解,假设对于某个质数p,四个数分解出的质数分别x_p,y_p,\)
\((a_i)_p,(a_j)_p,那么有3*x_p = 2*(a_i)_p+(a_j)_p和3*y_p = 1*(a_i)_p+2*(a_j)_p。注意到等式左边mod3 = 0 所以解这个式子最后得到(a_i)_p = (a_j)_p(mod3),也\)
\(就是说有价值的i,j对他们质因数分解后得到的次幂在mod3意义下每个数字相等,那么我们对于每个输入的x = p ^ 3*s,用x除去最大的这个数可以看作x的质因数分解后在mod3下的的唯一合法表示\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
// inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
#define N 50005
int n, x;
unordered_map<int,int> mp;
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
mp.clear();
ll ans = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
cin>>x;
int p = pow(x,1.0/3);
p ++;
for( ;p ; --p)
{
int p3 = p*p*p;
if(x % p3) continue;
ans += mp[x / p3];
++mp[x / p3];
break;
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
J(找规律)
\(显然考虑重合边当且仅当为中线,否则对于与X轴垂直坐标为x来说寻找Y轴坐标为x或A-x(排除四等分),或者是X轴为2\times x,A-x,Y轴同理\)
// #pragma GCC optimize("O3,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC target("avx2,bmi,bmi2,lzcnt,popcnt")
//如果在不支持 avx2 的平台上将 avx2 换成 avx 或 SSE 之一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef vector<string> VS;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef vector<vector<int>> VVI;
vector<int> vx;
inline void divide() {sort(vx.begin(),vx.end());vx.erase(unique(vx.begin(),vx.end()),vx.end());}
inline int mp(int x) {return upper_bound(vx.begin(),vx.end(),x)-vx.begin();}
inline int log_2(int x) {return 31-__builtin_clz(x);}
inline int popcount(int x) {return __builtin_popcount(x);}
inline int lowbit(int x) {return x&-x;}
inline ll Lsqrt(ll x) { ll L = 1,R = 2e9;while(L + 1 < R){ll M = (L+R)/2;if(M*M <= x) L = M;else R = M;}return L;}
int n;
map<int,int> mpx,mpy;
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
int xs,ys,xe,ye;
cin>>xs>>ys>>xe>>ye;
int A = xe-xs;
bool ok=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
int x1,y1,x2,y2;
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
x1-=xs; y1-=ys;
x2-=xs; y2-=ys;
if(x1==x2)
{
if(x1*2==A && mpx.find(x1) != mpx.end())
{
cout<<mpx[x1]<<' '<<i<<'\n';
ok = true;
break;
}
mpx[x1]=i;
}
else if(y1==y2)
{
if(y1*2==A && mpy.find(y1) != mpy.end())
{
cout<<mpy[y1]<<' '<<i<<'\n';
ok = true;
break;
}
mpy[y1]=i;
}
}
if(ok) return;
for(auto &&[x,i]:mpx)
{
if(2*x == A) continue;
if(mpy.find(x) != mpy.end()) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpy[x]<<'\n'; return;}
if(mpy.find(A-x) != mpy.end()) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpy[A-x]<<'\n'; return;}
if(mpx.find(2*x) != mpx.end() && 3*x != A) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpx[2*x]<<'\n'; return;}
if(mpx.find(A-x) != mpx.end() && 3*x != A) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpx[A-x]<<'\n'; return;}
}
for(auto &&[y,i]:mpy)
{
if(2*y == A) continue;
if(mpy.find(2*y) != mpy.end() && 3*y != A) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpy[2*y]<<'\n'; return;}
if(mpy.find(A-y) != mpy.end() && 3*y != A) {cout<<i<<' '<<mpy[A-y]<<'\n'; return;}
}
cout<<"-1 -1\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int T=1;
// cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
L(不好想的构造)
\(奇数没有,偶数可以,直接贴图,借鉴自O_start\)
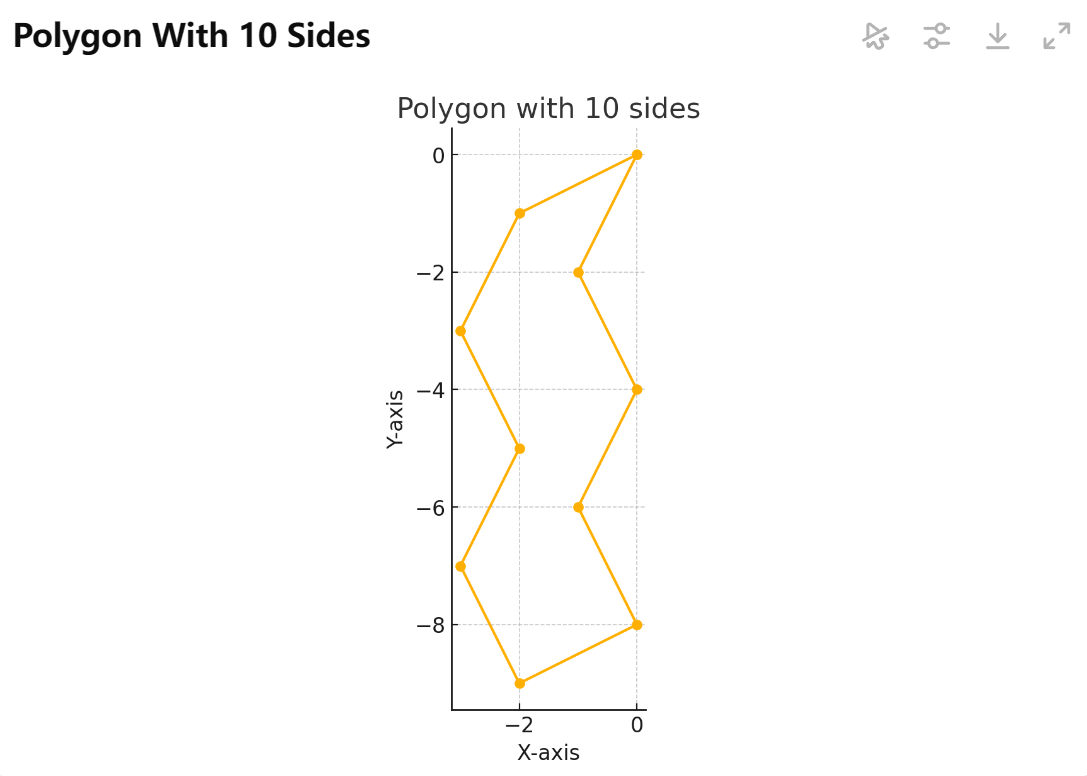
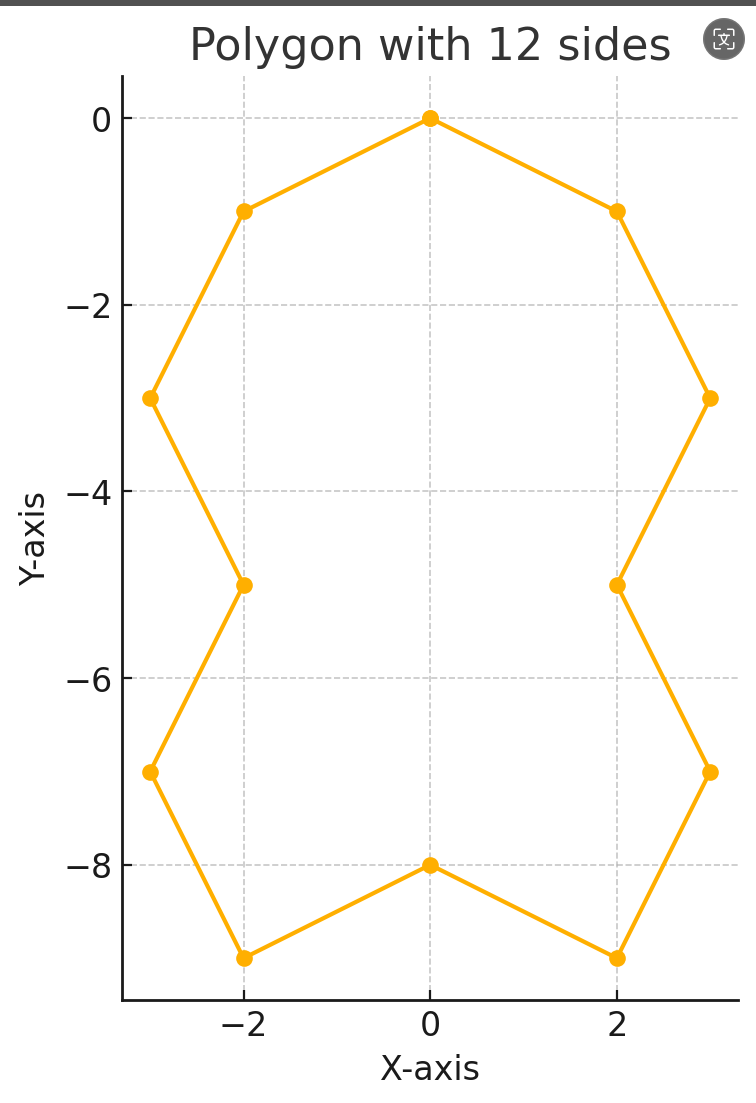
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def solve():
t = int(input()) # 读取测试用例的数量
for _ in range(t):
n = int(input()) # 读取每个测试用例的多边形顶点数
# 如果 n 是奇数,直接输出 -1
if n % 2 != 0:
print("-1")
else:
# 如果 n == 4,直接输出正方形的坐标
if n == 4:
print(f"0 0")
print(f"0 1")
print(f"1 1")
print(f"1 0")
else:
# 如果 n 是 4 的倍数
if n % 4 == 0:
tmp = Node(0, 0)
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
tmp.x += 2
tmp.y -= 1
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
for i in range(2, n // 2):
if i % 2 != 0:
tmp.x += 1
tmp.y -= 2
else:
tmp.x -= 1
tmp.y -= 2
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
tmp.x -= 2
tmp.y += 1
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
tmp.x -= 2
tmp.y -= 1
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
for i in range(2, n // 2):
if i % 2 != 0:
tmp.x += 1
tmp.y += 2
else:
tmp.x -= 1
tmp.y += 2
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
# 如果 n 不是 4 的倍数但仍为偶数
else:
tmp = Node(0, 0)
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
for i in range(1, n // 2):
if i % 2 != 0:
tmp.x -= 1
tmp.y -= 2
else:
tmp.x += 1
tmp.y -= 2
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
tmp.x -= 2
tmp.y -= 1
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
for i in range(1, n // 2):
if i % 2 != 0:
tmp.x -= 1
tmp.y += 2
else:
tmp.x += 1
tmp.y += 2
print(f"{tmp.x} {tmp.y}")
# 调用解决函数
solve()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号