信息安全系统设计与实现:第五章学习笔记
信息安全系统设计与实现:第五章学习笔记
20191331 lyx
教材学习内容总结
第五章 定时器及时钟服务
学习目标
通过学习本章理解定时器和定时服务。了解硬件定时器的原理和基于Intelx86的PC中的硬件定时器;理解CPU操作和中断处理。学习Linux中与定时器相关的系统调用、库函数和定时器服务命令。通过示例理解进程间隔定时器。Linux进程的实时模式间隔定时器被设计为定期生成SIGALRM信号,充当虚拟CPU的定时器中断,虚拟CPU使用SIGALRM信号捕捉器作为定时器的中断处理程序。定时器还可以防止任务和中断处理程序之间出现竞态条件。
硬件定时器
定时器是由时钟源和可编程计数器组成的硬件设备。时钟源通常是一个晶体振荡器,会产生周期性电信号,以精确的频率驱动计数器。
硬件定时器能够按照一定的频率周期性的有规律的给CPU发送中断信号,发送中断的频率(周期)可以通过软件编程来设置,硬件定时器产生的中断信号可以称之为时钟中断。
个人计算机定时器
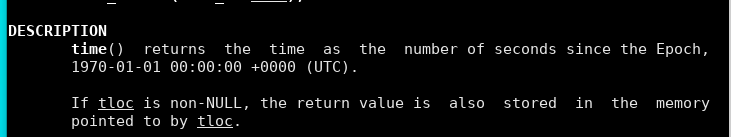
- 实时时钟(RTC):RTC由一个小型备用电池供电。在所有类Unix系统中,时间变量是一个长整数,包含从1970年1月1日起经过的秒数。
time() returns the time as the number of seconds since the Epoch,1970-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 (UTC).
-
可编程间隔定时器(PIT)(Wang2015):PIT是与CPU分离的一个硬件定时器。可对它进行编程,以提供以毫秒为单位的定时器刻度。
-
多核CPU中的本地定时器(Intel1997;Wang2015):在多核CPU中,每个核都是一个独立的处理器,它有自已的本地定时器,由CPU时钟驱动。
-
高分辨率定时器:大多数电脑都有一个时间戳定时器(TSC),由系统时钟驱动。它的内容可通过64位TSC寄存器读取。
CPU操作
每个CPU都有一个程序计数器(PC),也称为指令指针(IP),以及一个标志或状态寄存器(SR)、一个堆栈指针(SP)和几个通用寄存器,当 PC指向内存中要执行的下一条指令时,SR包含 CPU 的当前状态,如操作模式、中断掩码和条件码,SP指向当前堆栈栈顶。CPU操作可通过无限循环进行建模。
while (power-on){
1. fetch instruction:load*PC as instruction,increment PC to point to the next instruction in memory;
2. decode instruction: interpret the instruction's operation code and generate operandis;
3. execute instruction: perform operation on operands,write results to memory if needed;
execution may use the stack,implicitly change PC, etC.
4. check for pending interrupts; may handle interrupts;
}
中断和异常处理都在操作系统内核中进行。大多数情况下,用户级程序无法访问他们。
中断操作
书上讲的比较晦涩
中断是指在CPU正常运行期间,由于内外部事件或由程序预先安排的事件引起的CPU暂时停止正在运行的程序,转而为该内部或外部事件或预先安排的事件服务的程序中去,服务完毕后再返回去继续运行被暂时中断的程序。
从广义上讲,中断又可分为四类:中断、故障、陷阱、终止。
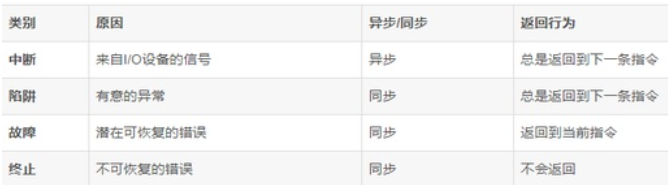

时钟服务函数
- 在几乎所有的操作系统中,操作系统内核都会提供与时钟相关的各种服务。
linux系统中与时钟有关的系统调用:

gettimeofday&settimeofday
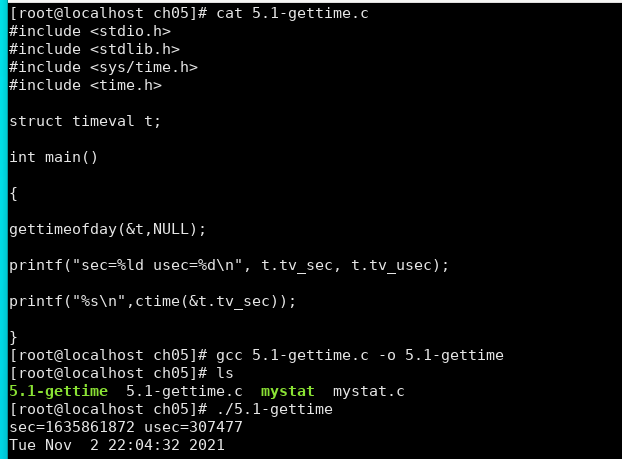
gettimeofday:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
struct timeval t;
int main(){
gettimeofday(&t,NULL);
printf("sec=%ld usec=%d\n", t.tv_sec, t.tv_usec);
printf((char *)ctime(&t.tv_sec));
}
编译运行:
出现错误
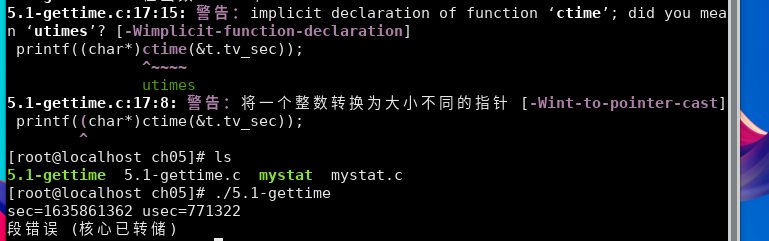
代码中对于ctime函数调用缺少必要的头文件time.h
并且不需要强制类型转换为char* ,直接以字符串输出就好了。
settimeofday:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
struct timeval t;
int main(){
int r;
t.tv_sec = 123456789;
t.tv_usec = 0;
r = settimeofday(&t,NULL);
if(!r){
printf("settimeofday() faild\n");
exit(1);
}
gettimeofday(&t,NULL);
printf("sec=%ld usec=%ld\n",t.tv_sec,t.tv_usec);
printf("%s",ctime(&t.tv_sec));
}
编译运行:

猜测失败原因:系统保护当前时间不被篡改
time系统调用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>
time_t start,end;
int main(){
int i;
start=time(NULL);
printf("start=%ld\n",start);
for(i=0;i<123456789;i++);
end=time(NULL);
printf("end =%ld time=%ld\n",end,end-start);
}
编译运行:
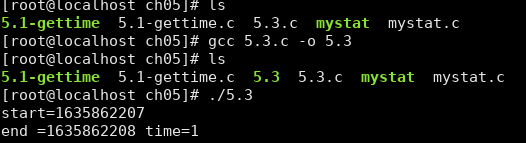
间隔定时器
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
int count = 0;
struct itimerval t;
time_t start,end ;
void timer_handler(int sig){
end =time(NULL);
printf("timer_handler : signal %d count=%d , diff: %ld \n",sig, ++count,end -start);
start = end;
if( count >= 8){
printf("cancel timer \n");
t.it_value.tv_sec = 0 ;
t.it_value.tv_usec = 0;
setitimer(ITIMER_VIRTUAL, &t , NULL);
}
}
int main(){
struct itimerval timer ;
signal (SIGVTALRM ,timer_handler);
timer.it_value.tv_sec = 0;
timer.it_value.tv_usec = 100000;
//every 1s afterward
timer.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
timer.it_interval.tv_usec = 0;
// start a virtual itimer
start = time(NULL);
setitimer( ITIMER_VIRTUAL , &timer ,NULL );
printf("press Ctrl + C to terminate \n");
while(1);
}
编译运行:
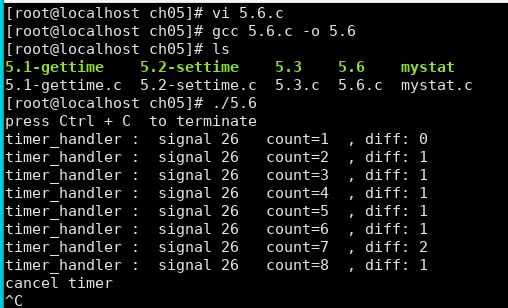
参考资料
Linux驱动开发——定时器 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37596943/article/details/103760395
Linux内核中断系统处理机制-详细分析 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/342614491



