MYSQL必会的知识
新学的MySQL小技能:
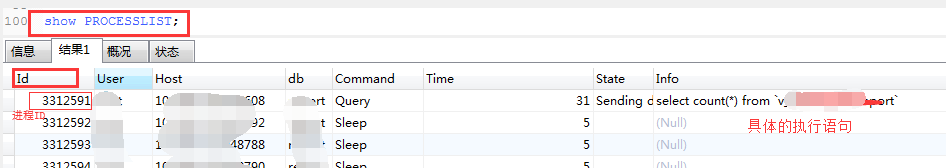
show PROCESSLIST; #查看当前数据库的进程 (也就是正在进行的sql操作)
kill Id; #终止Id对应的sql的执行
例如我想中止上面Id为 3312591 的进程,中止执行 select count(*) from `v_xxxx`; 语句的执行
kill 3312591; -- 即可
- 命令行 启动mysql: mysql -u用户名 -p密码
- 显示表中的各列详细信息: show columns form tablename 等价于 desc tablename
- 查看所有show命令: help show
- 查询数据时未使用排序,显示的结果是没有顺序意义的
- 去掉重复的行使用distinct: select distinct id from user
- limit关键字的使用: select * from user limit 5; 查询出不多于5行数据 select * from user limit 5,5; 从第五行数据开始查询,返回5条记录 (即5到10 的记录)
- 使用order by 进行排序,默认的是升序排列: select *from user order by age desc,name ; 按照年龄降序排列,年龄相同时按照姓名升序排列
- 查询name字段为null的记录: select * from user where name is null;
- 关键字 and 和 or,优先处理and,然后再处理or旁边的语句,并且每个只执行一次。
- 通配符: % 匹配一个或多个字符 select * from user where name='a%'; 查询所有name以a开头的记录 这里的查询条件区分大小写
- 查询条件为‘%’时 select * from user where name='%';不会匹配name为null的记录
- 通配符 “-” 只匹配一个字符
- mysql的正则表达式关键字 regexp: select *from user where age regexp '10' ; 查询所有年龄为10的记录
- 正则表达式符号“.” 一个点表示匹配任意一个字符 select * from user where age regexp '.0';查询出所有年龄为整10的记录,可以是10,20,30,等等。
- 就加入需要使用正则表达式去匹配.点这个符号,则需要转义,使用 \\. 去匹配
- 符号 ^ 的作用有两个:一个是表示指定串的开始,另一个是在集合中表示否定集合
- 符号 $ 的作用: 表达式的结束
- 拼接字符串使用关键字contact, contact(a,'(',b,')')
- RTrim(name) 去掉name这一列的右边的所有空格
- LTrim(name) 去掉name这一列的左边的所有空格
- Trim(name) 去掉name这一列的两边的全部空格
- 函数left() ,使用示例: select left('zhangsan',1); 返回字符串zhangsan的一个字符z
- 函数Locate(),使用示例: select locate('a','bbabc'); 返回第一个字符串在第二个字符串中出现的位置 3
- 函数Soundex() 使用示例: select * from user where Soundex(name) = Soundex('li');返回所有name的读音和 li 相似的记录
- 查看系统时间的函数: select CurDate() ;查看当前日期 ,select CurTime() ; 查看当前时间
- 函数max()和函数min()都会忽略掉职位null的行
- 聚集函数中可以使用distinct ,例如: select avg(distinct age) as ageavg from user;
- 关键字group by必须在where后和order by 之前
- where用来过滤行,having用来过滤分组 例如: select id ,count(*) as nums from user group by id having count(*)>=2;
- 关键字union链接查询语句,至少由两条select语句组成,多个之间都是用union连接(使用union时会自动去掉重复的行记录,如果不想去掉就使用 union all)
- 全文本搜索 Match() 指定搜索的列,Aganist()指定要使用的表达式
- 全文搜索示例:select text from mail where Match(text) Aganist('right'); 其中text是定义表的时候指定的索引字段,FULLTEXT(text)定义
- 创建表,id自增时设置 id int(10) primary key auto_increment
- 修改列名和数据类型: alter table 表名 change column 旧列名 新列名 列类型; alter table user change column name username varchar(30); 将user表中的name列变为username.
- 添加列: alter table user ADD hobby varchar(30);为user表中添加新列hobby,类型为varchar
- 删除列: alter table user DROP column age ; 删除user表中age那一列
- 重命名表: rename table 旧表名 to 新表名; alter table user to person; 将名为user的表改名为 person.
- 添加索引: create index isd_rs_demo on rs_demo(statisdate) ;
- 使得索引生效: ANALYZE TABLE rs_demo;


 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号