课时32:异常处理:你不可能总是对的
目录:
一、什么是异常?
二、异常的总结
三、课时32课后习题及答案
*******************
一、什么是异常?
*******************
程序出现逻辑错误或者用户输入不合法都会引起异常,但这些异常并不是致命的,不会导致程序崩溃死掉。可以利用Python提供的异常处理机制,在异常出现的时候及时捕获,并从内部消化掉。
那么什么是异常呢?举个例子:
file_name = input("请输入要打开的文件名:") f = open(file_name,'r') print("文件的内容是:") for each_line in f: print(each_line)
这里当然假设用户输入的是正确的,但只要用户输入一个不存在的文件名,那么上面的代码就不堪一击:
请输入要打开的文件名:我为什么是一个文档.txt Traceback (most recent call last): File "C:\Users\14158\Desktop\lalallalalal.py", line 2, in <module> f = open(file_name,'r') FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '我为什么是一个文档.txt'
上面的例子就抛出了一个FileNotFoundError的异常,那么Python通常还可以抛出哪些异常呢?这里给大家做总结,今后遇到这些异常就不会陌生了。
******************
二、异常的总结
******************
1、AssertionError:断言语句(assert)失败
大家还记得断言语句吧?在关于分支和循环的章节里讲过。当assert这个关键字后边的条件为假的时候,程序将停止并抛出AssertionError异常。assert语句一般是在测试程序的时候用于在代码中置入检查点:
>>> my_list = ["小甲鱼"] >>> assert len(my_list) > 0 >>> my_list.pop() '小甲鱼' >>> assert len(my_list) > 0 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#3>", line 1, in <module> assert len(my_list) > 0 AssertionError
2、AttributeError:尝试访问未知的对象属性
>>> my_list = [] >>> my_list.fishc Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module> my_list.fishc AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'fishc'
3、IndexError:索引超出序列的范围
>>> my_list = [1,2,3] >>> my_list[3] Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#7>", line 1, in <module> my_list[3] IndexError: list index out of range
4、KeyError:字典中查找一个不存在的关键字
>>> my_dict = {"one":1,"two":2,"three":3}
>>> my_dict["one"]
1
>>> my_dict["four"]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#12>", line 1, in <module>
my_dict["four"]
KeyError: 'four'
5、NameError:尝试访问一个不存在的变量
当尝试访问一个不存在的变量时,Python会抛出NameError异常:
>>> fishc Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#13>", line 1, in <module> fishc NameError: name 'fishc' is not defined
6、OSError:操作系统产生的异常
OSError顾名思义就是操作系统产生的异常,像打开一个不存在的文件会引发FileNotFoundError,而这个FileNotFoundError就是OSError的子类。例子上面已经演示过,这里就不重复了。
7、SyntaxError:Python语法错误
如果遇到SyntaxError是Python语法的错误,这时Python的代码并不能继续执行,你应该先找到并改正错误:
>>> print "I love fishc.com" SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print("I love fishc.com")?
8、TypeError:不同类型间的无效操作
有些类型不同是不能相互进行计算的,否则会抛出TypeError异常:
>>> 1 + "1" Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#14>", line 1, in <module> 1 + "1" TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'
9、ZeroDivisionError:除数为零
地球人都知道除数不能为零,所以除以零就会引发ZeroDivisionError异常:
>>> 5/0 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#15>", line 1, in <module> 5/0 ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
我们知道了这些异常,那如何捕获这些异常呢?
捕获异常可以用try语句实现,任何出现在try语句范围内的异常都会被及时捕获到。try语句有两种实现形式:一种是 try-except,另一种是try-finally。
*******************************
三、课时32课后习题及答案
*******************************
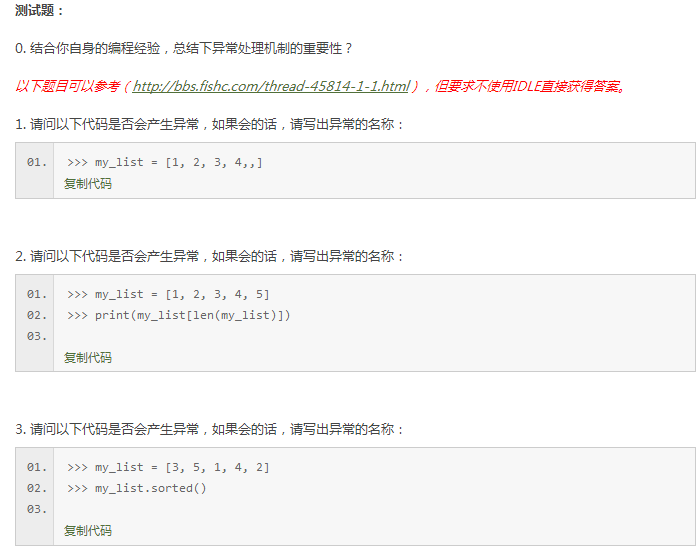
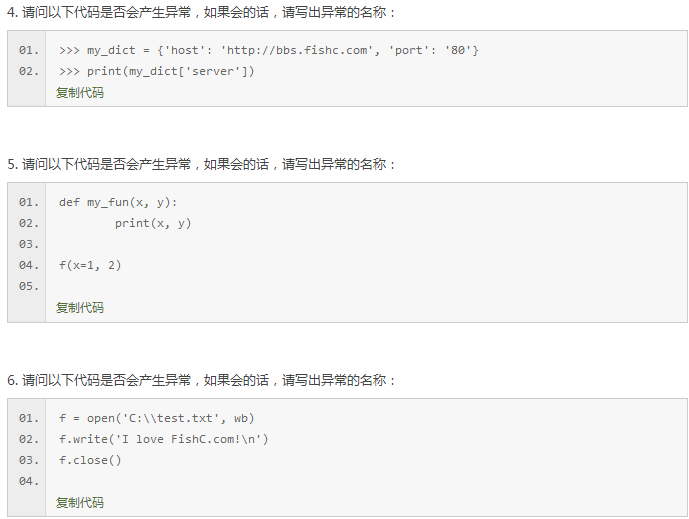

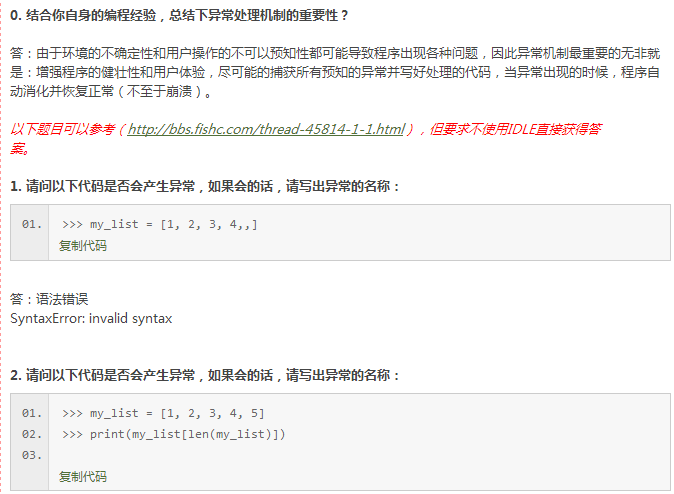

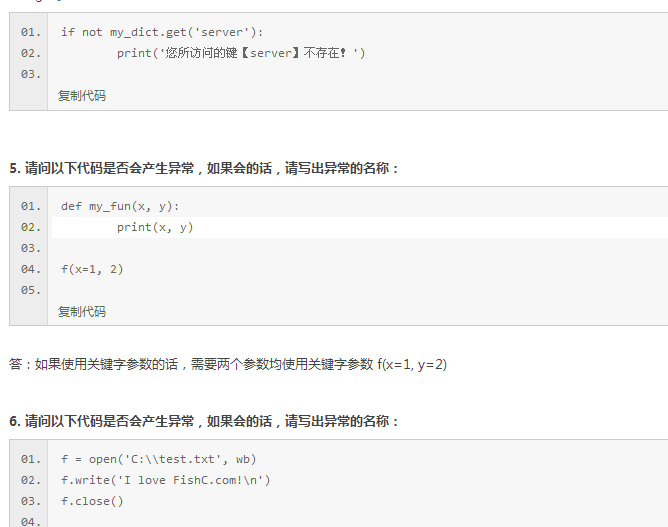



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号