【LeetCode二叉树#02】二叉树层序遍历(广度优先搜索),十合一专题
二叉树层序遍历(广度优先搜索)
102 二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。

思路
层序遍历时需要使用队列进行辅助操作
每次我们将一层节点加入队列后,记录当前队列的长度,作为当前队列弹出元素的次数
每弹出一个节点,就去寻找其是否存在左右子节点,如果有,就直接加入队列(这样并不会影响当前层节点的弹出,因为我们已经将当前层中节点数量记录,即队列长度)
当循环完成(即弹出与队列长度相同的次数),将当前记录值加入结果数组
以下是图示:

代码
按照上面的思路来写
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
//创建队列
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//判断根节点是否为空,不为空加入根节点
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
//创建二维数组保存各层遍历结果
vector<vector<int>> res;
//开始遍历,循环条件为队列是否为空
while(!(que.empty())){
//记录当前队列长度,即当前遍历层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
//创建用于保存当前层元素的数组
vector<int> vec;
//遍历,将当前层节点弹出
while(size--){
//获取当前弹出节点
TreeNode* node = que.front();
//弹出节点
que.pop();
//保存节点的值
vec.push_back(node->val);
//判断当前节点有无左右子节点
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
return res;
}
};
易错点
1、队列、栈的操作都是push、pop,vector才是push_back
队列
数据存取:
push(elem);//往队尾添加元素pop();//从队头移除第一个元素back();//返回最后一个元素front();//返回第一个元素
大小操作:
empty();//判断堆栈是否为空size();//返回栈的大小
栈
数据存取:
push(elem);//向栈顶添加元素pop();//从栈顶移除第一个元素top();//返回栈顶元素
大小操作:
empty();//判断堆栈是否为空size();//返回栈的大小
107 二叉树的层序遍历 II
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)

思路
从结果来看,原理上和前一题一样,只是结果相反
所以把结果数组翻转即可
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
//创建 队列
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//创建二维数组保存各层遍历结果
vector<vector<int>> res;
//判断根节点是否为空,不为空加入根节点
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
//开始遍历,循环条件为队列是否为空
while(!(que.empty())){
//创建用于保存当前层元素的数组
vector<int> vec;
//记录当前队列长度,即当前遍历层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
//遍历,将当前层节点弹出
while(size--){
//记录当前节点
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);//记录当前节点值
//判断当前节点有无左右子节点
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
//做翻转处理即可
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
199 二叉树的右视图
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。

初见思路
返回右侧是吧?那我只遍历右边子节点不就好了
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//创建数组保存各层遍历结果
vector<int> res;
//判断根节点是否为空,不为空加入根节点
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
//开始遍历,循环条件为队列是否为空
while(!(que.empty())){
//记录当前队列长度,即当前遍历层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
while(size--){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
实际上这样是错的
因为“右侧”的定义还包括以下情况
1
/
2
此时代码应该返回[1,2]
但如果像上面的思路,结果只会返回[1]
正确思路
仍然使用之前层序遍历的模板
但是在弹出当前层节点时,我们不使用while,而是使用for(这样可以获取到当前遍历的位置)
如果遍历到当前层的最后一个元素,我们就保存它的值,其余的不管
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
//创建 队列
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//判断根节点是否为空,不为空加入根节点
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
//创建数组保存各层遍历结果
vector<int> res;
while(!que.empty()){
//记录当前队列长度,即当前遍历层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
//使用for遍历可以获取当前遍历位置
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
//记录当前节点
TreeNode* node = que.front();
//弹出
que.pop();
//遍历到当前层的最后一个数,保存
if(i == (size - 1)) res.push_back(node->val);//只保存每一层的最后一个遍历值
//判断当前节点有无左右子节点
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
注意点
当遍历每层元素时,使用for循环而不是while,这样可以获得当前遍历位置
637 二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。

思路
还是层序遍历的标准模板,只不过至此返回值是每一层的平均值
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
//创建队列
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//判断根结点是否为空
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
//创建结果数组,注意保存的数据类型
vector<double> res;
while(!que.empty()){
//获取层大小
int size = que.size();
//定义变量,保存层元素之和
double sum = 0;
//使用for循环进行遍历
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
sum += node->val;
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
////会改变size的值导致计算平均值出错,因此需要使用for循环
// while(size--){
// TreeNode* node = que.front();
// que.pop();
// sum += node->val;
// if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
// if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
// }
res.push_back(sum/size); //将平均值保存
}
return res;
}
};
这里和199右视图一样,在遍历层元素时,需要使用for循环,而不是while
否则计算的平均值会有误
举个例子:
int a = 3;
for(int i = 0; i < a; ++i){//不会改变a的值
....
}
while(a--){//这里使用条件表达式作为while循环条件,因此a会被改变(a为全局变量)
....
}
429 N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
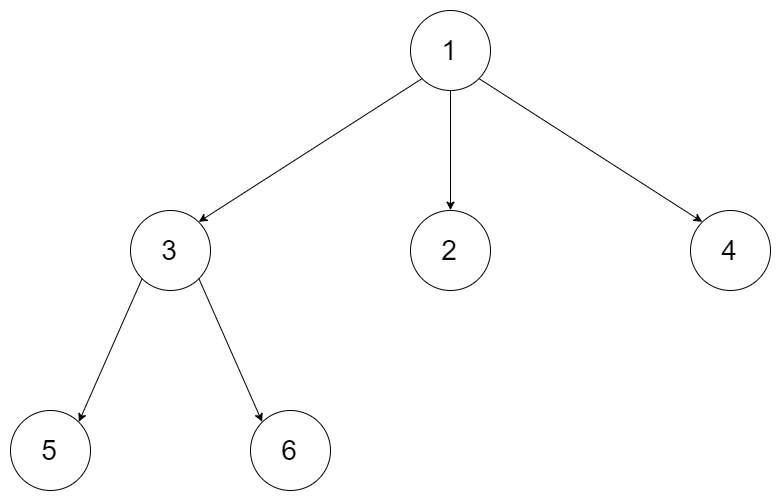
返回其层序遍历:
[ [1], [3,2,4], [5,6] ]
思路
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>> res;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
//遍历当前层,仍然使用for
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
//如果当前树为N叉树,那么其节点可能有多个子节点,数量不确定
//先从node获取子节点数组children
//遍历所有子节点加入队列
for(int i = 0; i < node->children.size(); ++i){//两个以上(N叉树)才这样获取
//如果当前节点确实有多个子节点
//逐个将节点加入队列
if(node->children[i]) que.push(node->children[i]);
}
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
return res;
}
};
注意点
这里我把答题模板的注释一块复制了
因为,N叉树再实现时与二叉树不太一样
其提供了一个vector用于存放子节点
因此我们获取子节点的时候就需要去遍历该数组
590 N叉树的层序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-postorder-traversal/
给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 后序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[5,6,3,2,4,1]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[2,6,14,11,7,3,12,8,4,13,9,10,5,1]
提示:
节点总数在范围 [0, 104] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 104
n 叉树的高度小于或等于 1000
思路
有两种方法,一个是递归,一个是迭代
用递归的方式会相对简单一些,整体代码就是在二叉树的后序遍历(递归版)的基础上,加入对N个节点的遍历就可以了
值得注意的是,二叉树的后序遍历顺序是左右中,在N叉树中,区分左右就没有意义了,因此只需要把所有存在的节点遍历完毕,然后再最后处理中序的逻辑,就是对N叉树进行后序遍历了
class Solution {
private:
//确定递归函数的参数和返回值,参数是根节点和结果数组
void traversal(Node* cur, vector<int>& res){
if(cur == NULL) return;//遇到叶子节点就返回
//因为是N叉树,所以左右的顺序就不用分了,只需要把所有分支都边 遍历了然后最后处理中序逻辑就行
for(int i = 0; i < cur->children.size(); ++i){//获取并遍历children数组,遍历所有子节点
traversal(cur->children[i], res);
}
return res.push_back(cur->val);//将遍历的节点值加入结果数组中,此时顺序就是子数组 中
}
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
};
515 在每个树行中找最大值
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
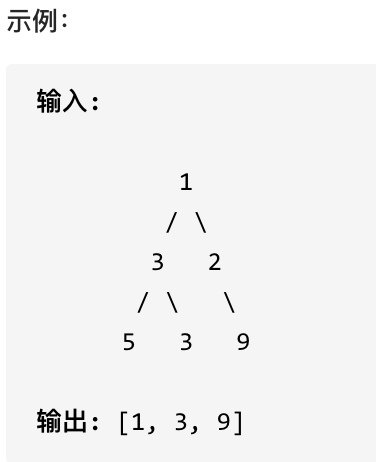
思路
还是常规的层序遍历,只是在每层遍历开始前设定一个初始值为最小整数的变量用于记录当前最大值
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> res;
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
//初始化一个最大值
int maxValue = INT_MIN; //初始值为整数最小值
//遍历当前层节点的值,更新最大值
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
maxValue = node->val > maxValue ? node->val : maxValue;// 更新最大值
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
//每层结束后,将当前层的最大值添加到结果数组
res.push_back(maxValue);
}
return res;
}
};
116 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
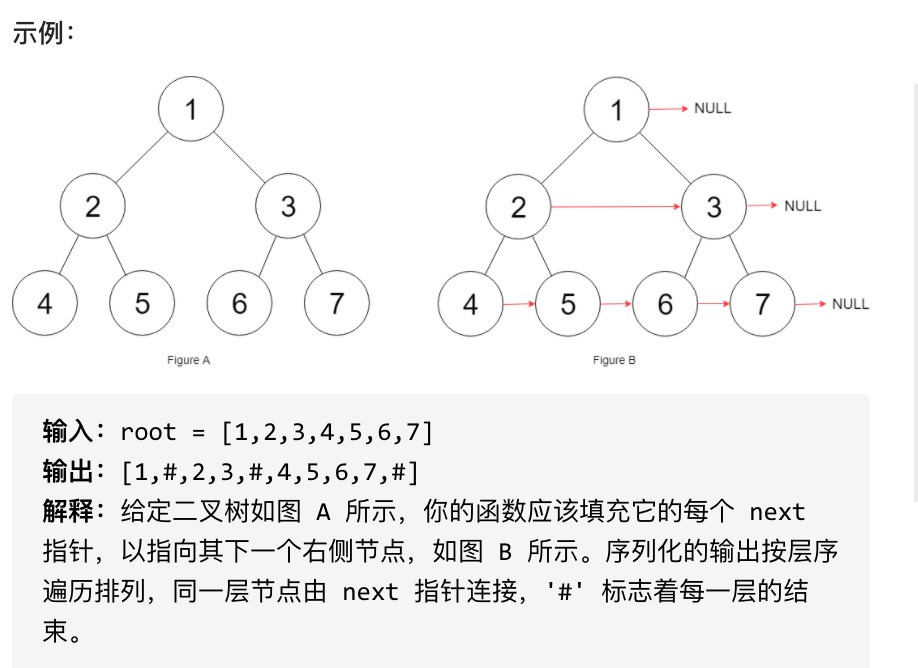
思路
遍历的方式还是按层,只是要将第一个遍历到的节点记录下来
实际操作时要定义两个节点变量,一个用于存放当前节点,一个用于存放前一个节点
遍历过程中,只需要让前一个节点指向当前节点,然后不断更新前一个节点指向的位置即可
代码
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
// vector<Node*> res;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
//定义两个节点变量分别存放当前节点和前一节点
Node* curNode;//当前节点
Node* perNode;//前一节点
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
//判断当前节点是否为当前层的第一个节点
if(i == 0){//刚开始遍历时,perNode与curNode指向同一节点
perNode = que.front();
que.pop();
curNode = perNode;
}else{//当不是头节点时,curNode先更新(往后取一个节点)
curNode = que.front();
que.pop();
perNode->next = curNode;//前一节点指向当前节点
perNode = curNode;//更新前一节点的位置
}
if(curNode->left) que.push(curNode->left);
if(curNode->right) que.push(curNode->right);
}
}
return root;//返回根节点
}
};
117 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
思路
和116一模一样
代码直接复制就能过
104 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
知识补充:深度和高度
高度 深度
3 1 3
/ \
2 2 6 9
/ / \
1 3 8 2 1
使用后序遍历(左右中)我们可以得到二叉树的高度(具体做法,TBD)
使用前序遍历(中左右)我们可以得到二叉树的深度
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数后者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
思路
层序遍历,统计层数即可
代码
dfs(前序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int res;
void getDepth(TreeNode* root, int depth){
res = depth > res ? depth : res;
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) return ;
if(root->left != nullptr){
depth++;
getDepth(root->left, depth);
depth--;
}
if(root->right != nullptr){
depth++;
getDepth(root->right, depth);
depth--;
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
res = 0;
if(root == nullptr) return res;
getDepth(root, 1);
return res;
}
};
dfs(后序遍历)
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root->right);
int depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int depth = getDepth(root);
return depth;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
int floorCount = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
floorCount++;
}
return floorCount;
}
};
111 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
思路
从根节点到叶子节点的最短路径,那只要判断出当前的节点是否为叶子节点即可
即当前节点是否同时没有左右子节点
代码
dfs前序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int res;
void getDepth(TreeNode* root, int depth){
if(root == nullptr) return ;
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) res = min(res, depth);
if(root->left) getDepth(root->left, depth + 1);
if(root->right) getDepth(root->right, depth + 1);
return ;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
res = INT_MAX;
getDepth(root, 1);
return res;
}
};
dfs后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root->right);
if(root->left != nullptr && root->right == nullptr){
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr){
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
int res = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return res;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
int minD = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
minD++;
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(node->left) q.push(node->left);
if(node->right) q.push(node->right);
if(!node->left && !node->right) return minD;
}
}
return minD;
}
};
关于求最大/小深度的说明
处理中间节点的位置之所以不同,是因为它们的求解目标不同。
在求最大深度时,我们需要遍历整个二叉树,计算从根节点到叶子节点的最长路径。因此,在前序遍历中,我们首先更新当前的最大深度 res,然后再递归地处理左子树和右子树。这样可以确保在递归返回到上层节点时,res 中保存的是整个树的最大深度。
而在求最小深度时,我们需要找到从根节点到最近的叶子节点的最短路径。因此,在前序遍历中,我们首先判断当前节点是否为叶子节点,如果是,则更新 res 为当前深度 depth 和 res 中的较小值。然后再递归地处理左子树和右子树。这样可以确保在递归返回到上层节点时,res 中保存的是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最小深度。
因此,根据不同的求解目标,处理中间节点的位置会有所不同。在最大深度的情况下,我们在更新 res 之后再递归处理子树;而在最小深度的情况下,我们在判断当前节点为叶子节点之后再更新 res。这样可以确保得到正确的最大深度和最小深度的计算结果。
559 N 叉树的最大深度
给定一个 n 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :

我们应返回其最大深度,3。
思路
与429一致,依然采用层序遍历,只不过这次不需要获取节点的值,每层遍历结束之后记录层数即可
代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
//创建队列
queue<Node*> que;
//判断root
if(root != NULL) que.push(root);
int floorcount = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
//记录当前队列长度
int size = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
//获取n叉树的所有子节点
for(int i = 0; i < node->children.size(); ++i){
if(node->children[i])que.push(node->children[i]);
}
}
//遍历一层后计数
floorcount++;
}
return floorcount;
}
};
注意
1、N叉树在定义时,在类属性中维护了一个vector children用于存放子节点信息
因此在查询N叉树的子节点时,我们需要先拿到children数组,再对其进行遍历


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号