201771010106东文财《面向对象程序设计(java)》实验9
实验九 异常、断言与日志
实验时间 2018-10-25
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握java异常处理技术;
(2) 了解断言的用法;
(3) 了解日志的用途;
(4) 掌握程序基础调试技巧;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:用命令行与IDE两种环境下编辑调试运行源程序ExceptionDemo1、ExceptionDemo2,结合程序运行结果理解程序,掌握未检查异常和已检查异常的区别。
|
//异常示例1 public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 0; System.out.println(5 / a); } } |
|
//异常示例2 import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 int b; while((b=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(b); } fis.close(); } } |
package tt; public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 0; System.out.println(5 / a); } }
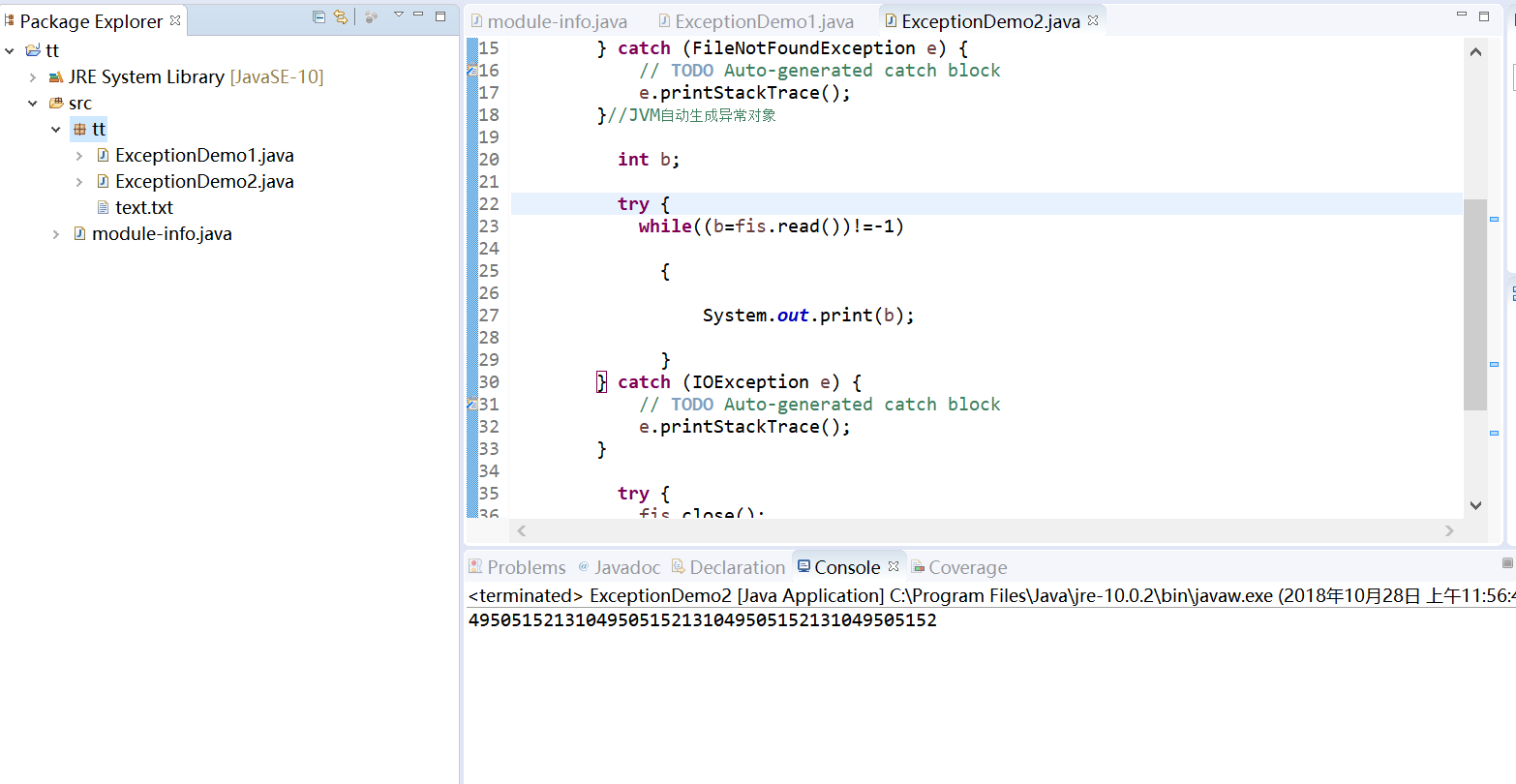
package tt; import java.io.*; public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { FileInputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\LENOVO\\Desktop\\text.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }//JVM自动生成异常对象 int b; try { while((b=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(b); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
实验结果:
实验2: 导入以下示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中编辑、编译、调试运行教材281页7-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 掌握Throwable类的堆栈跟踪方法;
package stackTrace; import java.util.*; /** * A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call. * @version 1.01 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class StackTraceTest { /** * Computes the factorial of a number * @param n a non-negative integer * @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n */ public static int factorial(int n) { System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):"); Throwable t = new Throwable();//构造一个Throwable 对象 StackTraceElement[] frames = t.getStackTrace();//获得构造这个对象时调用的对战的跟踪 for (StackTraceElement f : frames) System.out.println(f); int r; if (n <= 1) r = 1; else r = n * factorial(n - 1); System.out.println("return " + r); return r; } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter n: "); int n = in.nextInt(); factorial(n); } }
实验结果:

测试程序2:
l Java语言的异常处理有积极处理方法和消极处理两种方式;
l 下列两个简答程序范例给出了两种异常处理的代码格式。在elipse IDE中编辑、调试运行源程序ExceptionalTest.java,将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt,要求将文件内容读入内容,并在控制台显示;
l 掌握两种异常处理技术的特点。
|
//积极处理方式 import java.io.*;
class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) { try{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } catch(FileNotFoundExcption e) { …… } …… } } |
|
//消极处理方式
import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) throws FileNotFoundExcption { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } } |
package tt; //积极处理方式 import java.io.*; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (String args[]) { File fis=new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\LENOVO\\\\Desktop\\\\身份证号.txt"); try{ FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); try { String s, s2 = new String(); while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { s2 += s + "\n "; } br.close(); System.out.println(s2); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package tt; //消极处理方式 import java.io.*; class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException { File fis=new File("C:\\Users\\LENOVO\\Desktop\\身份证号.txt"); FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); String s, s2 = new String(); while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { s2 += s + "\n "; } br.close(); System.out.println(s2); } }
实验结果:

实验3: 编程练习
练习1:
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
注:以下实验课后完成
package gh; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Collections; public class tt { public static People findPeopleByname(String name) { People flag = null; for (People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getName().equals(name)) { flag = people; } } return flag; } public static People findPeopleByid(String id) { People flag = null; for (People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getnumber().equals(id)) { flag = people; } } return flag; } private static ArrayList<People> agenear(int yourage) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int j=0,min=53,d_value=0,k = 0; ArrayList<People> plist = new ArrayList<People>(); for (int i = 0; i < peoplelist.size(); i++) { d_value = peoplelist.get(i).getage() > yourage ? peoplelist.get(i).getage() - yourage : yourage - peoplelist.get(i).getage() ; k = d_value < min ? i : k; min = d_value < min ? d_value : min; } for(People people : peoplelist) { if(people.getage() == peoplelist.get(k).getage()) { plist.add(people); } } return plist; } private static ArrayList<People> peoplelist; public static void main(String[] args) //throws IOException { peoplelist = new ArrayList<People>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("D:\\身份证号.txt"); try { FileInputStream files = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(files)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { String[] information = temp.split("[ ]+"); People people = new People(); people.setName(information[0]); people.setnumber(information[1]); int A = Integer.parseInt(information[3]); people.setage(A); people.setsex(information[2]); for(int j = 4; j<information.length;j++) { people.setplace(information[j]); } peoplelist.add(people); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件未找到"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("文件读取错误"); e.printStackTrace(); } boolean isTrue = true; while (isTrue) { System.out.println("******************************************"); System.out.println(" 1.按姓名典序输出人员信息"); System.out.println(" 2.查询最大年龄人员信息"); System.out.println(" 3.查询最小年龄人员信息"); System.out.println(" 4.输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近的人"); System.out.println(" 5.查询人员中是否有你的同乡"); System.out.println(" 6.退出"); System.out.println("******************************************"); int nextInt = scanner.nextInt(); switch (nextInt) { case 1: Collections.sort(peoplelist); System.out.println(peoplelist.toString()); break; case 2: int max=0; int j,k1 = 0; for(int i=1;i<peoplelist.size();i++) { j = peoplelist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max = j; k1 = i; } } System.out.println("年龄最大:"+peoplelist.get(k1)); break; case 3: int min = 100; int j1,k2 = 0; for(int i=1;i<peoplelist.size();i++) { j1 = peoplelist.get(i).getage(); if(j1<min) { min = j1; k2 = i; } } System.out.println("年龄最小:"+peoplelist.get(k2)); break; case 4: System.out.println("年龄:"); int input_age = scanner.nextInt(); ArrayList<People> plist = new ArrayList<People>(); plist = agenear(input_age); for(People people : plist) { System.out.println(people.toString()); } break; case 5: System.out.println("请输入省份"); String find = scanner.next(); for (int i = 0; i <peoplelist.size(); i++) { String [] place = peoplelist.get(i).getplace().split("\t"); for(String temp : place) { if(find.equals(temp)) { System.out.println("你的同乡是 "+peoplelist.get(i)); break; } } } break; case 6: isTrue = false; System.out.println("byebye!"); break; default: System.out.println("输入有误"); } } } } }
实验结果:


练习2:
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作;
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
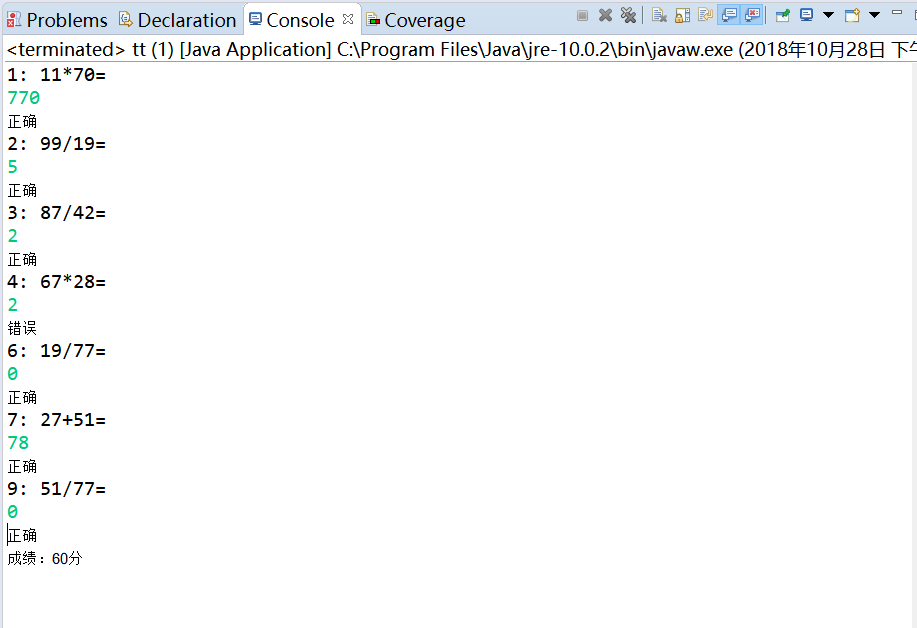
package rt; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Scanner; public class tt { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); tt1 computing=new tt1(); PrintWriter output = null; try { output = new PrintWriter("tt.txt"); } catch (Exception e) { } int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) { int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(s) { case 1: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"="); while(b==0){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } double c = in.nextDouble(); output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c); if (c == (double)computing.division(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确"); } else { System.out.println("错误"); } break; case 2: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1); if (c1 == computing.multiplication(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确"); } else { System.out.println("错误"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2); if (c2 == computing.addition(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确"); } else { System.out.println("错误"); } break ; case 4: System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"="); int c3 = in.nextInt(); output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3); if (c3 == computing.subtraction(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("正确"); } else { System.out.println("错误"); } break ; } } System.out.println("成绩:"+sum+"分"); output.println("成绩:"+sum+"分"); output.close(); } } class tt1 { private int a; private int b; public int addition(int a,int b) { return a+b; } public int subtraction(int a,int b) { if((a-b)<0) return 0; else return a-b; } public int multiplication(int a,int b) { return a*b; } public int division(int a,int b) { if(b!=0) return a/b; else return 0; } }
实验结果:

实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验。
实验程序1:
|
//断言程序示例 public class AssertDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { test1(-5); test2(-3); }
private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } } |
l 在elipse下调试程序AssertDemo,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 注释语句test1(-5);后重新运行程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握断言的使用特点及用法。
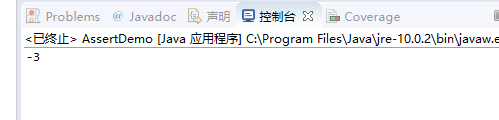
package rt; public class tt { public static void main(String[] args) { // test1(-5); test2(-3); } private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } }
实验结果:

实验程序2:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 并掌握Java日志系统的用途及用法。
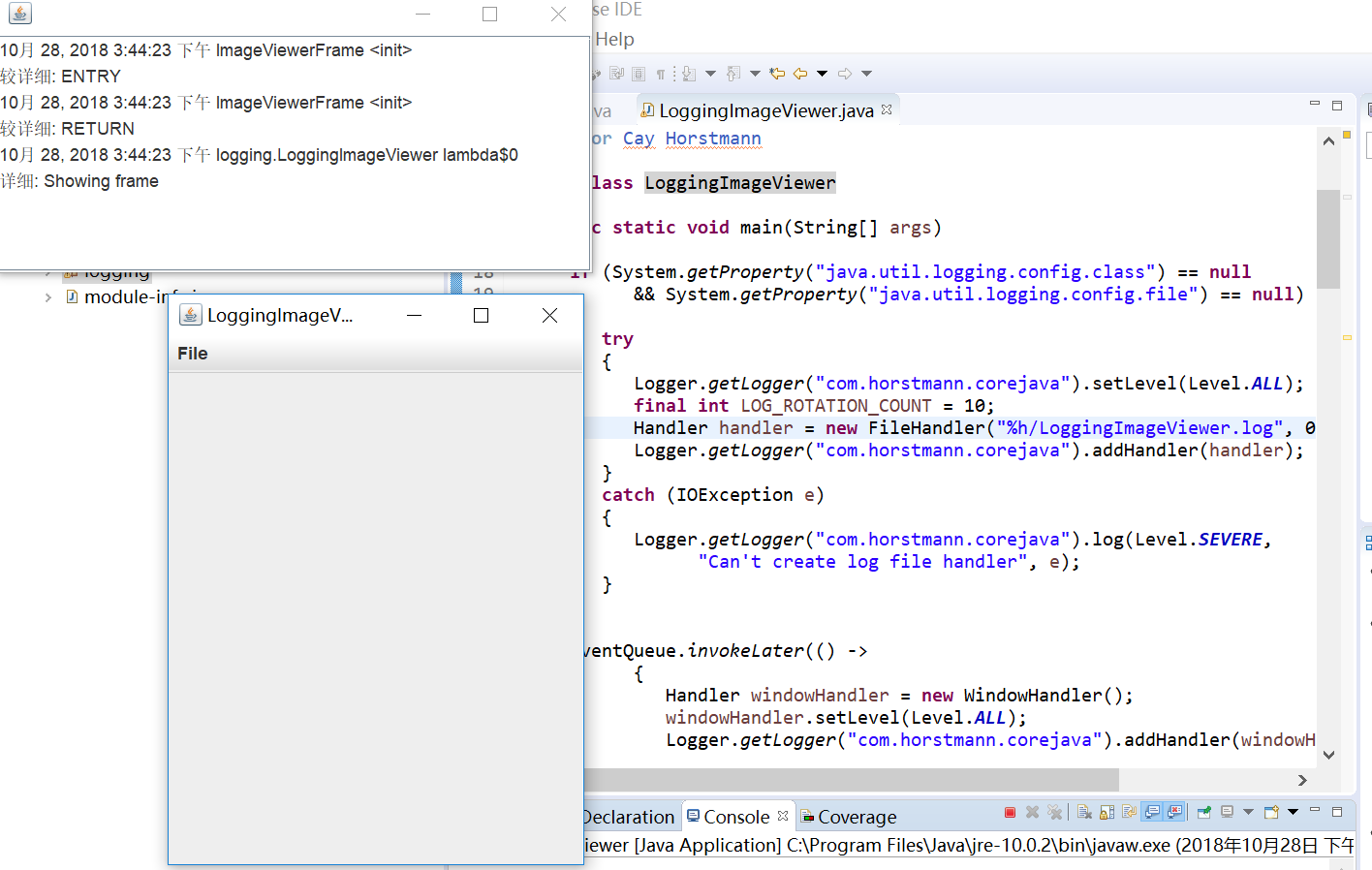
package logging; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.logging.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A modification of the image viewer program that logs various events. * @version 1.03 2015-08-20 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class LoggingImageViewer { public static void main(String[] args) { if (System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.class") == null && System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.file") == null) { try { Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").setLevel(Level.ALL); final int LOG_ROTATION_COUNT = 10; Handler handler = new FileHandler("%h/LoggingImageViewer.log", 0, LOG_ROTATION_COUNT); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(handler); } catch (IOException e) { Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").log(Level.SEVERE, "Can't create log file handler", e); } } EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { Handler windowHandler = new WindowHandler(); windowHandler.setLevel(Level.ALL); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(windowHandler); JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); frame.setTitle("LoggingImageViewer"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").fine("Showing frame"); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * The frame that shows the image. */ class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; private JLabel label; private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava"); public ImageViewerFrame() { logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // set up menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); menu.add(openItem); openItem.addActionListener(new FileOpenListener()); JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); menu.add(exitItem); exitItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { logger.fine("Exiting."); System.exit(0); } }); // use a label to display the images label = new JLabel(); add(label); logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); } private class FileOpenListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed", event); // set up file chooser JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); // accept all files ending with .gif chooser.setFileFilter(new javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter() { public boolean accept(File f) { return f.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif") || f.isDirectory(); } public String getDescription() { return "GIF Images"; } }); // show file chooser dialog int r = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); // if image file accepted, set it as icon of the label if (r == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); logger.log(Level.FINE, "Reading file {0}", name); label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); } else logger.fine("File open dialog canceled."); logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed"); } } } /** * A handler for displaying log records in a window. */ class WindowHandler extends StreamHandler { private JFrame frame; public WindowHandler() { frame = new JFrame(); final JTextArea output = new JTextArea(); output.setEditable(false); frame.setSize(200, 200); frame.add(new JScrollPane(output)); frame.setFocusableWindowState(false); frame.setVisible(true); setOutputStream(new OutputStream() { public void write(int b) { } // not called public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) { output.append(new String(b, off, len)); } }); } public void publish(LogRecord record) { if (!frame.isVisible()) return; super.publish(record); flush(); } }
实验结果:
实验程序3:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 按课件66-77内容练习并掌握Elipse的常用调试技术。

实验总结:
本次实验我的收获还是挺大的,通过一些示例程序的的编译、运行,我对本章的知识有了一定的了解,知道了对于程序中的一些错误的改正方法,也知道了断言的用法和日志的用途。不过本章中依然有一些知识点不是很了解,在今后的学习中我会继续加油,争取搞懂这些不懂的知识点。多多敲代码,希望以后我的编程技术会有很大的进步。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号