bzoj1272 Gate Of Babylon(计数方法+Lucas定理+乘法逆元)
Description

Input

Output

Sample Input
2 1 10 13
3
Sample Output
12

Source
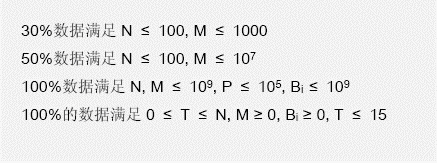
看到t很小,想到用容斥原理,推一下发现n种数中选m个方法为C(n+m,m)。然后有的超过的就是先减掉b[i]+1,再算。由于n,m较大,p较小,故可用Lucas定理+乘法逆元搞。
把老师给的题解也放在这吧:
首先,看到有限制的只有15个,因此可以考虑使用容斥原理:Ans=全部没有限制的方案-有1个超过限制的方案数+有2个超过限制的方案数-有3个超过限制的方案数…。以此类推。我们先考虑没有限制的,在m组无限制的数中选n个的方案数,显然就是C(n+m-1,n),因为这道题是要求不超过m的方案数,也就是那么运用加法原理发现答案也就是C(n+0-1,0)+C(n+1-1,1)+C(n+2-1,2)+...+C(n+m-1,m)=C(n+m,m),然后考虑有限制的情况,有一个超过限制直接用总数减去(这个的限制+1)就是当前的总数,相当于强制要选限制+1个为空。然后只要DFS,记录到当前为止选了几个,答案要记是b[i]+1,判断加减,最后累加答案。最后,n、m过大,发现p是一个质数,所以可以用Lucas定理,Lucas(n,m,p)=Lucas(n/p,m/p,p)*C(n%p,m%p),其中C(n%p,m%p)求的时候要用到乘法逆元。
1 program babylon(input,output); 2 var 3 t,i:longint; 4 ans,n,m,j,p:int64; 5 b:array[0..20]of int64; 6 a:array[0..100010]of int64; 7 function pow(x,y:int64):int64; 8 begin 9 pow:=1; 10 while y>0 do 11 begin 12 if y mod 2=1 then pow:=pow*x mod p; 13 x:=x*x mod p; 14 y:=y>>1; 15 end; 16 end; 17 function z(n,m:int64):int64; 18 begin 19 if n<m then exit(0); 20 exit(a[n]*pow(a[n-m]*a[m] mod p,p-2) mod p); 21 end; 22 function c(n,m:int64):int64; 23 begin 24 if n<m then exit(0); 25 c:=1; 26 while (n>0) and (m>0) do 27 begin 28 c:=c*z(n mod p,m mod p) mod p; 29 n:=n div p;m:=m div p; 30 end; 31 end; 32 procedure dfs(k:longint;r,s:int64); 33 begin 34 if k=t+1 then 35 begin 36 ans:=(ans+r*c(n+m-s,n)) mod p; 37 exit; 38 end; 39 dfs(k+1,r,s); 40 dfs(k+1,-r,s+b[k]+1); 41 end; 42 begin 43 assign(input,'babylon.in');assign(output,'babylon.out');reset(input);rewrite(output); 44 readln(n,t,m,p); 45 for i:=1 to t do read(b[i]); 46 a[0]:=1;j:=0; 47 while j<p do begin inc(j);a[j]:=a[j-1]*j mod p; end; 48 ans:=0; 49 dfs(1,1,0); 50 if ans<0 then ans:=ans+p;write(ans); 51 close(input);close(output); 52 end.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号