mysql 8.0.28 查询语句执行顺序实测结果
TL;NRs
根据实测结果,MySQL8.0.28 中 SQL 语句的执行顺序为:
(7) SELECT
(5) DISTINCT <select_list>
(1) FROM <left_table>
(3) <join_type> JOIN <right_table>
(2/4) ON <join_condition>
(2) WHERE <where_condition>
(6) GROUP BY <group_by_list>
(8) HAVING <having_condition>
(9) ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
(10) LIMIT <limit_number>
引言
关于 SQL 语句的执行顺序,常见的是以下版本。然而该版本却与实测结果不符。
(7) SELECT
(8) DISTINCT <select_list>
(1) FROM <left_table>
(3) <join_type> JOIN <right_table>
(2) ON <join_condition>
(4) WHERE <where_condition>
(5) GROUP BY <group_by_list>
(6) HAVING <having_condition>
(9) ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
(10) LIMIT <limit_number>
MySQL 可以通过 EXPLAIN ANALYZE sql_statement 显示真实的执行过程。那么可以通过一个复杂的语句完成测试。
准备数据
准备三个表 t1, t2, t3, 其中数据分别为:
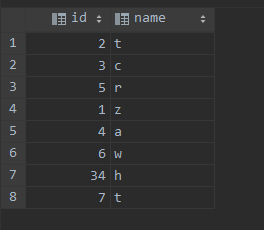
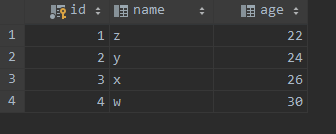

测试
执行以下语句
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT
DISTINCT COUNT(p.id) AS cnt, COUNT(e.id) AS nn
FROM t1 p
LEFT JOIN t2 q ON p.id > q.id
INNER JOIN t2 w ON q.id < w.id
RIGHT JOIN t3 e ON w.id = e.id
WHERE p.id < 10
GROUP BY p.id
HAVING cnt > 3
ORDER BY cnt DESC, nn DESC
LIMIT 1;
结果为:
-> Limit: 1 row(s) (actual time=0.394..0.395 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Sort with duplicate removal: cnt DESC, nn DESC (actual time=0.393..0.394 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Filter: (cnt > 3) (actual time=0.372..0.374 rows=5 loops=1)
-> Table scan on <temporary> (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=6 loops=1)
-> Aggregate using temporary table (actual time=0.370..0.372 rows=6 loops=1)
-> Inner hash join (e.id = w.id) (cost=4.73 rows=3) (actual time=0.314..0.324 rows=32 loops=1)
-> Table scan on e (cost=0.13 rows=5) (actual time=0.008..0.016 rows=5 loops=1)
-> Hash
-> Filter: (q.id < w.id) (cost=3.15 rows=3) (actual time=0.265..0.282 rows=32 loops=1)
-> Inner hash join (no condition) (cost=3.15 rows=3) (actual time=0.259..0.271 rows=72 loops=1)
-> Covering index scan on w using PRIMARY (cost=0.13 rows=3) (actual time=0.007..0.010 rows=4 loops=1)
-> Hash
-> Nested loop inner join (cost=2.10 rows=3) (actual time=0.084..0.232 rows=18 loops=1)
-> Filter: (p.id < 10) (cost=1.05 rows=3) (actual time=0.036..0.051 rows=7 loops=1)
-> Table scan on p (cost=1.05 rows=8) (actual time=0.034..0.046 rows=8 loops=1)
-> Filter: (p.id > q.id) (cost=0.13 rows=1) (actual time=0.021..0.025 rows=3 loops=7)
-> Covering index range scan on q (re-planned for each iteration) (cost=0.13 rows=3) (actual time=0.021..0.024 rows=3 loops=7)
结果分析
这是一个调用栈,还原其执行过程为:
筛选 LIMIT 10 {
排序 ORDER BY cnt DESC, nn DESC {
调用 HAVING cnt > 3 过滤器 {
读取临时聚合表 {
聚合 {
第三次联结 RIGHT JOIN t3 e ON w.id = e.id {
扫描表 e ;
第二次联结 INNER JOIN t2 w ON q.id < w.id {
扫描表 w {
使用主键扫描
得到 4 行
}
第一次联结 t1 p LEFT JOIN t2 q ON p.id > q.id {
扫描表 p {
使用 WHERE p.id < 10 过滤器
共 8 行,返回 7 行
}
循环扫描表 q {
7 次循环 {
使用过滤器 ON p.id > q.id
}
}
执行哈希,共 21 行,返回 18 行
}
执行全连接,获得 4 * 18 = 72 行
执行 ON q.id < w.id 过滤器,剩余 32 行
}
执行相等联结 e.id = w.id, 返回 32 行
}
完成所有的联结,获得 32 行
进行聚合 GROUP BY p.id 获得 6 行
}
读取临时聚合表,获得 6 行
}
执行过滤,剩余 5 行
}
去重,剩余 2 行
排序
返回 1 行
}
输出前 1 项
}
可以看到:
- 首先进行表的扫描,也就是所谓的 FROM 第一
- 有主键的表会使用主键索引
- 有索引的表会使用索引
- 有多个表需要扫描时,根据 SQL 语句进行倒序执行
- WHERE 会在表的扫描过程中执行,也就是 WHERE 第二
- 只与一个表相关的 ON 条件,也会在表的扫描过程中执行,因此 ON 可以是第二
- 读取到表后,会执行连接
- 有多个联结时,同样是倒序执行
- 首先执行全连接,也就是 JOIN 第三
- 全连接完成后会马上执行连接后的 ON 的过滤,也就是 ON 也可以第四
- 完成连接后,会执行去重,也就是 DISTINCT 第五
- 完成去重后,会进行上一层的连接
- 所有连接都完成后,会执行聚合,也就是 GROUP BY 第六
- 聚合完成后,会执行一次扫描,也就是 SELECT 第七
- 扫描结束后,会执行 HAVING 过滤,也就是 HAVING 第八
- 完成过滤后,会进行排序,也就是 ORDER BY 第九
- 最后进行 LIMIT 的限制,也就是 LIMIT 第十
- 需要注意的是,LIMIT 的参数在 sort 函数的返回结果中就已经起作用,合理推测是使用的堆排序
结论
根据实测结果,MySQL8.0.28 中 SQL 语句的执行顺序为:
(7) SELECT
(5) DISTINCT <select_list>
(1) FROM <left_table>
(3) <join_type> JOIN <right_table>
(2/4) ON <join_condition>
(2) WHERE <where_condition>
(6) GROUP BY <group_by_list>
(8) HAVING <having_condition>
(9) ORDER BY <order_by_condition>
(10) LIMIT <limit_number>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号