C++异常之七 标准库里的异常类
标准库里的异常类
C++标准提供了一组标准异常类,这些类以基类 Exception 开始,标准程序库抛出的所有异常,都派生于该基类,这些类构成如图所示的异常类的派生继承关系,该基类提供一个成员函数 what(),用于返回错误信息(返回类型为 const char*)。在 Exception 类中,what() 函数的声明如下:
1 virtual const char* what() const whrow();
该函数可以再派生类中重定义。
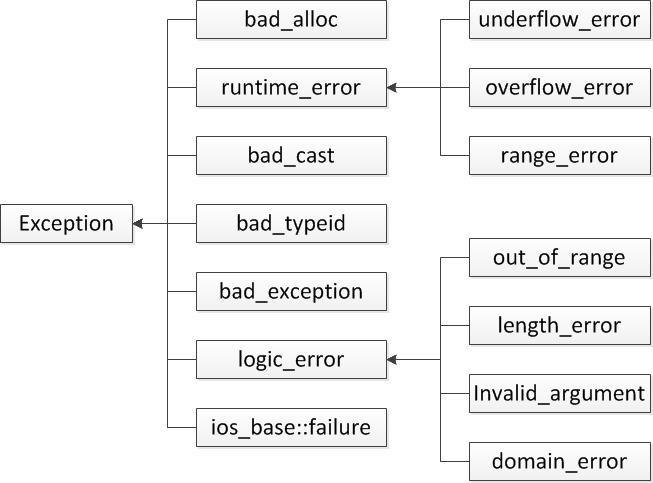
下表中列出了各个具体异常类的含义以及定义他们的头文件。runtime_error 和 logic_error 是一些具体的异常类的基类,他们分别表示两大异常,logic_error 表示那些可以再程序中被预先检测到的异常。也就是说如果小心的编写程序,这类异常能够避免;而 runtime_error 则表示那些难以被预先检测的异常。

一些编程语言规定,只能抛掷某个类的派生类(如Jave中允许抛掷的类必须派生自Exception类),C++虽然没有这项强制的要求,但任然可以这样实践。例如,在程序中可以使得所有抛出的异常皆派生自 Exception (或直接抛出标准程序库提供的异常类型,或者从标准程序库提供的异常类派生出新的类),这样会带来很多方便。
logic_error 和 runtime_error 两个类及其派生类,都有一个接受 const string & 型参数的构造函数。在构造异常对象时需要将具体的错误信息传递给该参数,如果调用该对象的 what() 函数,就可以得到构造时提供的错误信息。
out_of_range 用法举例, what()方法可以将异常 out_of_range 后边的内容返回:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdexcept> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Student 7 { 8 public: 9 Student(int age); 10 11 private: 12 int age = 0; 13 }; 14 15 Student::Student(int age) 16 { 17 if (age > 150) 18 { 19 throw out_of_range("年龄输入出错"); 20 } 21 this->age = age; 22 } 23 24 int main() 25 { 26 try 27 { 28 Student* role = new Student(151); 29 } 30 catch (const out_of_range& err) 31 { 32 cout << "捕捉到异常:" << err.what() << endl; 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 }
程序运行结果:
捕捉到异常:年龄输入出错
bad_alloc 用法举例,用上边的代码,做一个内存分配溢出的异常,bad_alloc 与其他的用法有些不同,你不需要在 try 包含的方法中去手动抛出,只需要直接在 try 块后的 catch 后接收匹配便可,他会自动接收 try 内分配内存导致的报错:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <exception> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Student 7 { 8 public: 9 Student(int age); 10 ~Student(); 11 12 private: 13 int age = 0; 14 int* m_space = NULL; 15 }; 16 17 Student::Student(int age) 18 { 19 if (age > 150) 20 { 21 printf("年龄输入出错"); 22 } 23 this->age = age; 24 m_space = new int[1024 * 1024 * 100]; 25 } 26 27 Student::~Student() 28 { 29 if (m_space) 30 { 31 delete[] m_space; 32 } 33 } 34 35 int main() 36 { 37 try 38 { 39 for (int i = 0; i < 1024; i++) 40 { 41 Student* role = new Student(18); 42 } 43 } 44 catch (bad_alloc & err) 45 { 46 cout << "捕捉到异常" << err.what() << endl; 47 } 48 49 return 0; 50 }
程序运行结果:
捕捉到异常bad allocation



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号