springboot-3-web开发
一、视图层技术thymeleaf
我们一般都是基于3.x版本
1、流程:
导入依赖
<!--整合thymeleaf技术-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
<!--不需要版本号-->
</dependency>
在yaml配置文件中修改配置
# Thymeleaf
thymeleaf:
# 是否开启缓存
cache: true
# 检查模板是否存在
check-template: true
# 模板文件编码
encoding: UTF-8
# 检查模板位置是否存在
check-template-location: true
# 模板文件位置
prefix: classpath:/templates/
# content-type配置
servlet:
content-type: text/html
# 文件后缀名
suffix: .html
在control中创建一个控制器,放入model数据
@GetMapping("/thymeleaf")
public String thymeleafTest(Model model){
model.addAttribute("message","hello~~~!!!!");
return "success";
}
在template下创建.html文件
再加入命名空间,xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${message}"></h1>
</body>
</html>
2、常用命名空间
xmlns:th=http://www.thymeleaf.org
xmlns:sec=http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security
xmlns:shiro=http://www.pollix.at/thymeleaf/shiro
3、其他常用属性
https://www.cnblogs.com/hjwublog/p/5051732.html
二、返回JSON:
springmvc中使用消息转换器HttpMessageConverter对Json数据的转换提供了很好的支持,在springboot中更近一步,对相关配置做了进一步简化
1、流程:
导入web依赖即可,这个依赖中加入了jackson-databind作为JSON处理器
创建pojo类
这些额外的注解可以理解为就是在配置这个pojo类的转换器
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
@JsonIgnore
private Float price;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date publishedDate;
}
控制器
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/book")
public Book getBook(){
return new Book("西游记","吴承恩",30f,new Date());
}
测试:postman得到数据,价格被忽略了,日期也被格式化了
{
"name": "西游记",
"author": "吴承恩",
"publishedDate": "2021-07-12"
}
2、自定义转换器:
springboot默认使用的就是jackson-databind,但还有其他json转换器,Gson,fastjson,这里讲一讲fastjson转换器
fastjson转换器是JSON转换速度最快的开源框架
流程:
导入依赖,注意需要先将web-starter中的jackson-databind去掉,然后再加上fastjson
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>
配置fastjson的HttpMessageConverter,主要两个部分
- MediaType
- MediaType媒体类型:决定浏览器将以什么形式、什么编码对资源进行解析
- 也就是Content-Type:也属于MediaType媒体类型,主要用于在请求头中指定资源的MediaType
- FastJsonConfig
- 主要配置在传输给浏览器的json数据中的一些配置规则
@Configuration
public class MyFastJsonConfig {
@Bean
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastJsonHttpMessageConverter(){
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig config = new com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig();
config.setDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
config.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
config.setSerializerFeatures(
//输出类名
SerializerFeature.WriteClassName,
//输出value为null的map数据
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
//输出好看的json格式
SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat,
//当list为空时,输出空list,而不是null
SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,
//当字符串为空时,输出空字符串,而不是null
SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty
);
converter.setFastJsonConfig(config);
return converter;
}
}
还需要再配置一下响应编码,否则返回的json会乱码
server.servlet.encoding.force-response=true
写一个pojo类
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private Float price;
private Date publishedDate;
}
控制器
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/book")
public Book getBook(){
return new Book("西游记","吴承恩",30f,new Date());
}
测试:

在fastjson中怎么忽略字段:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
@JSONField(serialize=false)
private Float price;
private Date publishedDate;
}
三、静态资源访问
1、访问本地资源:
流程:
配置webmvc
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class MyWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/");
}
}
也可以用参数配置代替
# 拦截规则
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
# 静态资源放置位置
spring.web.resources.static-locations= classpath:/static/
把1.png放在classpath:/static/下,即:resource下的static目录下
测试:
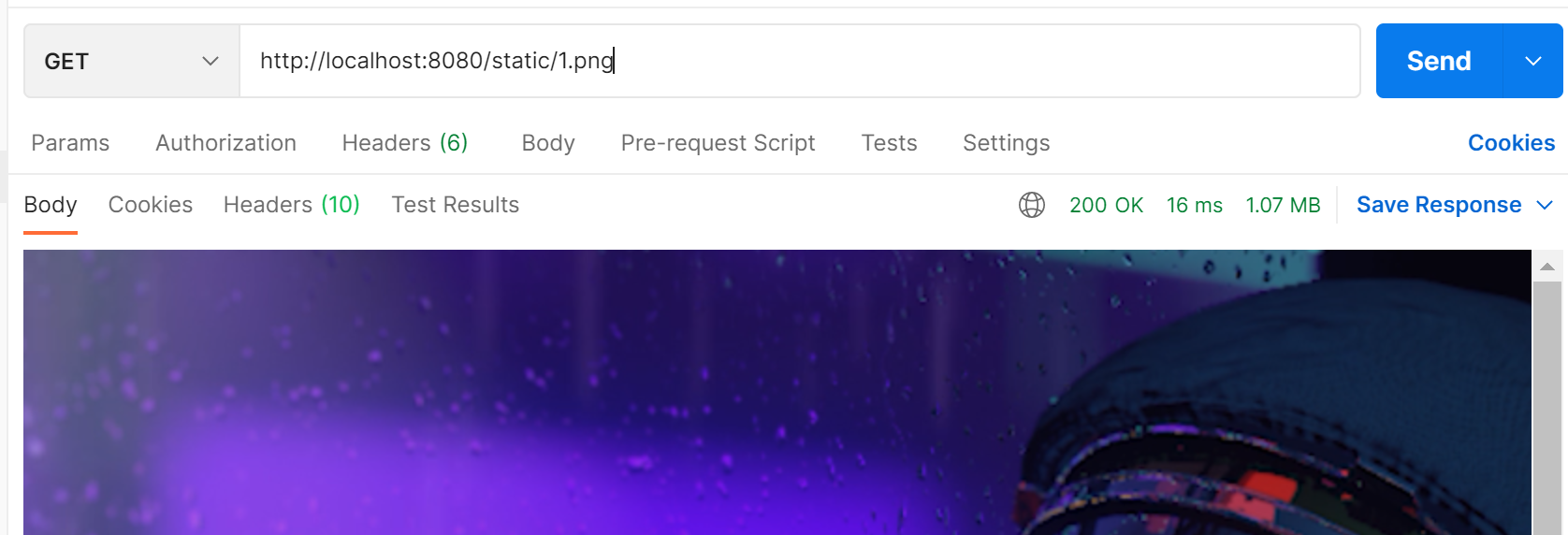
如果没成功,clean一下,亲证
2、用依赖加载jquery
流程:
在https://www.webjars.org/上查询到相应的依赖,再导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.6.0</version>
</dependency>
重启项目,再访问:http://localhost:9090/webjars/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js就发现能访问到jquery.js文件了
为什么是webjars/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js访问地址
在文件中的位置:
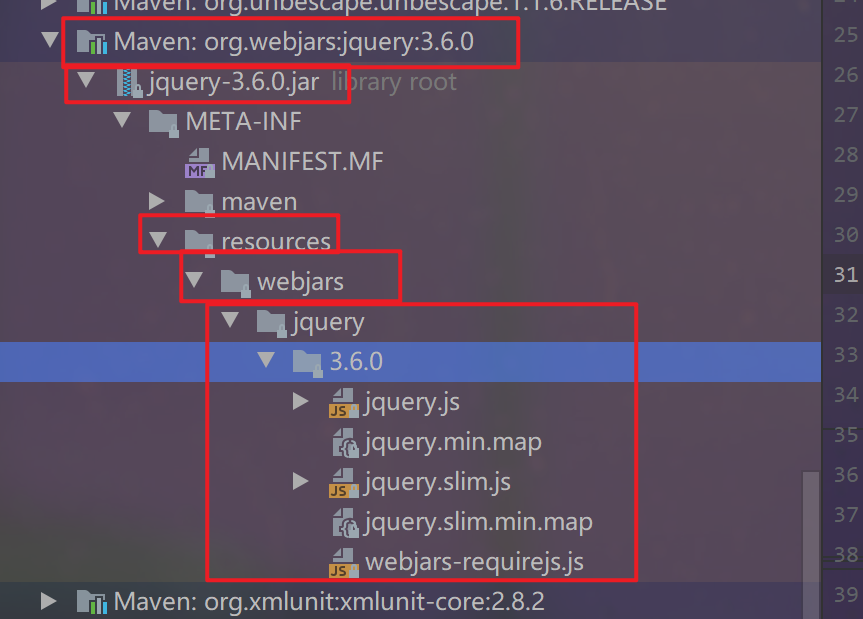
因为再automvc类中的配置中有了映射,所以只要导入了依赖就可以直接访问到这个静态文件
3、上传文件
涉及到两个组件:
CommonsMultipartResolver和StandardServletMultipartResolver,前者使用commons-fileupload来处理multipart请求,后者基于servlet3.0来处理multipart请求(在tomcat7.0就开始支持,不需要添加额外的jar包)springboot中的文件上传自动化配置类
MultipartAutoConfiguration,默认使用了StandardServletMultipartResolver
流程:
导入web-starter依赖
配置参数
# 文件上传
#支持文件上传
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true
# 文件些入磁盘的阈值,默认为0
spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold=0
# 文件上传的临时保存位置
spring.servlet.multipart.location=D://temp
# 单文件上传的最大大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=1MB
# 多文件上传的最大总大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=10MB
# 表示是否进行延迟解析
spring.servlet.multipart.resolve-lazily=false
在classpath:/static/目录下创建一个upload.html文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>文件上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="uploadFile" value="请选择文件"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
创建文件上传接口(控制器)
这里建议把字符串的操作看一看:https://www.cnblogs.com/huxiuqian/p/10167415.html
最好还要会议正则表达式:https://www.runoob.com/java/java-regular-expressions.html
@RestController
public class UploadControl {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("/yyyy/MM/dd");
@PostMapping(value = "upload")
public String upload(MultipartFile uploadFile, HttpServletRequest request) {
//获取"/uploadFile"文件的全路径
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/uploadFile");
//获取当前的时间,并格式化
String time = sdf.format(new Date());
//合并得到的文件路径和时间格式得到新文件名
File folder = new File(realPath + time);
System.out.println("文件放置--->>>>" + folder);
//放入文件
if (!folder.isDirectory()) {
folder.mkdirs();
}
String oldName = uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf('.'));
System.out.println("新名字--->>>"+newName);
try {
uploadFile.transferTo(new File(folder, newName));
String filepath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/uploadFile" + time +"/"+ newName;
return filepath;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "上传失败";
}
}
form中的enctype属性
enctype 属性规定在发送到服务器之前应该如何对表单数据进行编码。
默认地,表单数据会编码为 "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"。就是说,在发送到服务器之前,所有字符都会进行编码(空格转换为 "+" 加号,特殊符号转换为 ASCII HEX 值)。
| application/x-www-form-urlencoded | 在发送前编码所有字符(默认) |
|---|---|
| multipart/form-data | 不对字符编码。在使用包含文件上传控件的表单时,必须使用该值。 |
| text/plain | 空格转换为 "+" 加号,但不对特殊字符编码。 |
多文件上传
upload.html
<form action="/uploads" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="uploadFiles" value="请选择多文件上传" multiple>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
control(就是多了一个遍历器)
@PostMapping(value = "uploads")
public List upload(MultipartFile[] uploadFiles,HttpServletRequest request){
//获取"/uploadFile"文件的全路径
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/uploadFile");
//获取当前的时间,并格式化
String time = sdf.format(new Date());
//合并得到的文件路径和时间格式得到新文件名
File folder = new File(realPath + time);
System.out.println("文件放置--->>>>" + folder);
//放入文件
if (!folder.isDirectory()) {
folder.mkdirs();
}
List<String> newFiles = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile uploadFile : uploadFiles){
String oldName = uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf('.'));
System.out.println("新名字--->>>"+newName);
try {
uploadFile.transferTo(new File(folder, newName));
String filepath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/uploadFile" + time +"/"+ newName;
newFiles.add(filepath);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
newFiles.add("上传已失败");
}
}
return newFiles;
}
4、整合阿里云oss上传文件
流程:
导入依赖:
<!--oss-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</dependency>
在注册好的oss中找到下面的消息
public static String ENDPOINT = "http://oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com";
public static String ACCESSKEYID = "LTAI9rV1x0TmtGjq";
public static String ACCESSKEYSECRET = "3QCJw4MhlyZC8zQUATKaLxWZpk4bFY";
public static String BUCKETNAME = "songsiraliyun";
public static String KEY = "springbootTest/";
html界面
<form action="/uploadOss" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="uploadFile" value="请选择文件"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
图片接收接口
@PostMapping("/uploadOss")
public String uploadOss(MultipartFile uploadFile, HttpServletRequest request) {
try{
String fileName = uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
InputStream input = uploadFile.getInputStream();
//创建OSSClient实例
OSSClient ossClient = new OSSClient(ENDPOINT, ACCESSKEYID, ACCESSKEYSECRET);
ossClient.putObject(BUCKETNAME,KEY+fileName,input);
ossClient.shutdown();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello";
}
5、配置CORS
Cross-Orgin Resource Sharing是w3c制定得一种跨域共享技术标准,主要用来解决前端得跨域问题,在javaEE中,最常见得前端跨域请求解决方案是Jsonp,但是Jsonp只支持GET请求,这是一个巨大得缺陷,而CORS可以支持多种HTTP请求方法
流程:
导入了web-starter依赖即可
配置跨域CORS
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class MyMvcWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:63343")
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.maxAge(1800);
}
}
四、注册拦截器
springmvc 提供了AOP风格的拦截器,拥有更加精细化的拦截处理能力,springboot的拦截器更加方便
复习拦截器工作流程:
perhandle-->control-->postcontrol-->aftercontrol
流程:
通过MvcWebConfig去注册拦截器,需要我们自己重写一个拦截器类
注意这个类上不需要加注解@Configuration
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor-->preHandle");
return false;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor-->postHandle");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor-->afterCompletion");
}
}
再把这个拦截器配置到MvcWebConfig中
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/dologin");
}
五、启动系统任务
有一些特殊的任务再系统启动的时候执行,例如文件配置、数据库初始化等操作,没有用ssm阶段这些问题在Listener中可以解决,springboot对此提供了两种解决方案:CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner,这连个方法基本一致,主要差别主要体现在参数上
1、CommandLineRunner
springboot项目在启动时会遍历所有CommandLineRunner的实现类并调用其中的run方法,如果整个系统中含有多个CommandLineRunner的实现类,那么可以使用@Order注解对这些实现类的调用顺序进行排序
流程:
@Component
@Order(1)
public class MyCommandLineRunner1 implements CommandLineRunner {
/*run方法调用的核心逻辑
参数是系统启动时传入的参数,即入口类中main方法的参数,即springApplication.run方法的参数*/
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("runner1>>>"+ Arrays.toString(args));
}
}
@Component
@Order(2)
public class MyCommandLineRunner2 implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("runner2>>>"+ Arrays.toString(args));
}
}
然后需要我们配置传入的参数
先打开配置项目
再操作
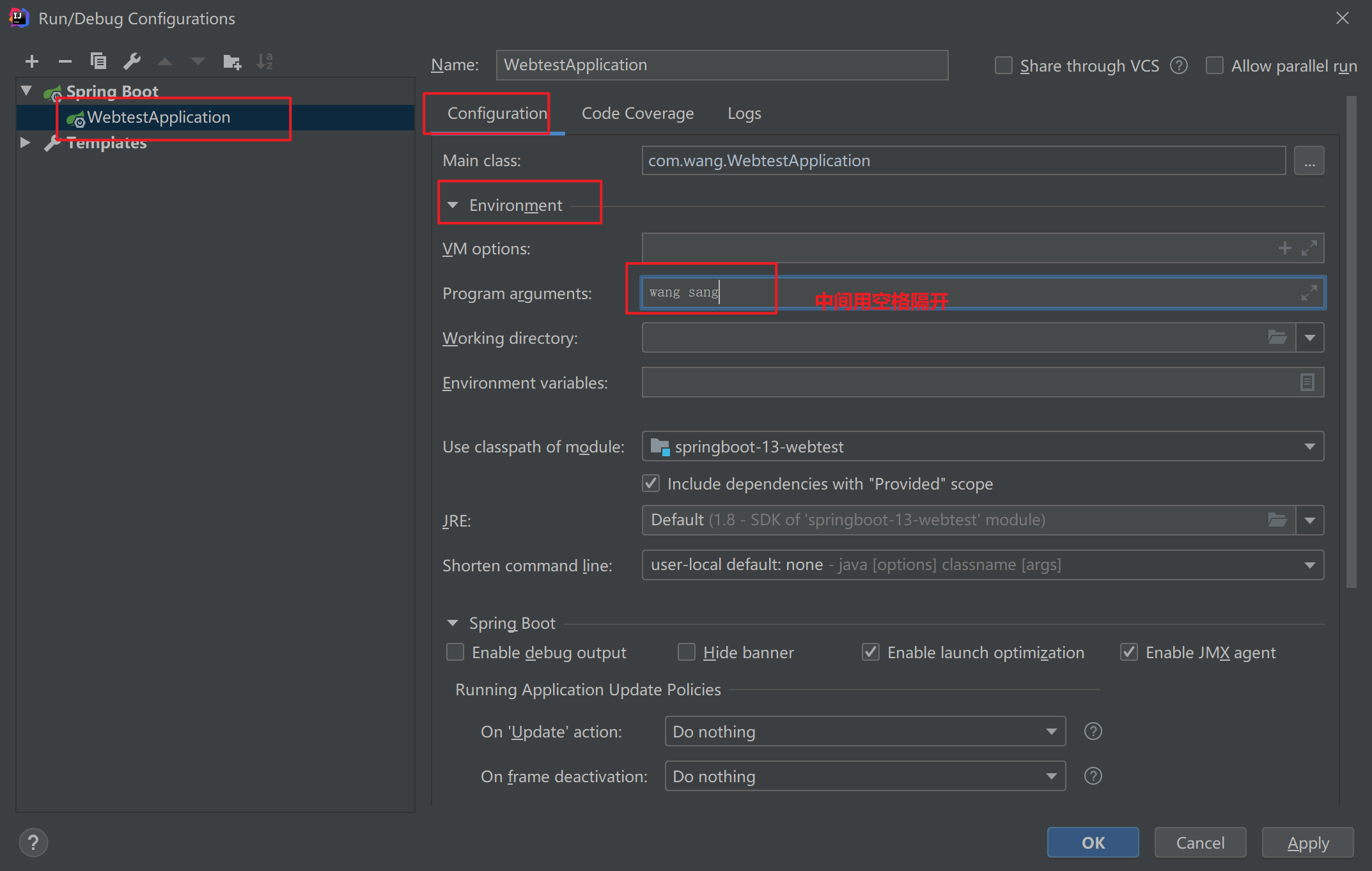
然后启动项目即可
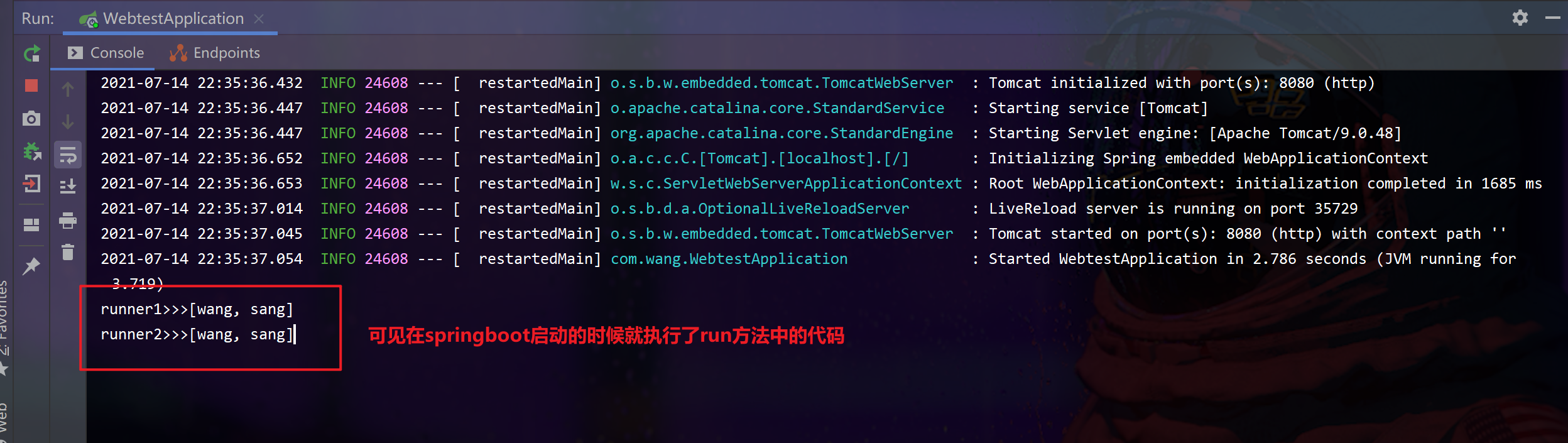
2、ApplicationRunner
与CommandLineRunner的差别主要体现在run方法的参数上
流程:
@Component
@Order(2)
public class MyApplicationRunner1 implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
/*
* args是一个ApplicationArgument对象
*getNonOptionArgs获取到项目启动参数
*getOptionNames获取到命令行启动项目的参数map中的name
* getOptionValues(optionName)获取到命令行启动项目的参数map中的optionName对应的value
* */
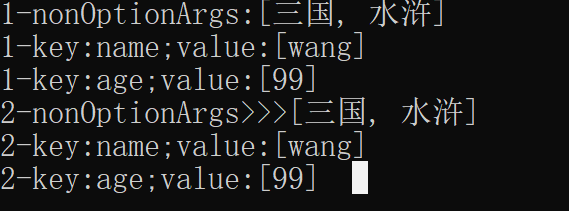
List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs();
System.out.println("2-nonOptionArgs>>>"+ nonOptionArgs);
Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames();
for (String optionName:optionNames){
System.out.println("2-key:"+optionName+";value:"+args.getOptionValues(optionName));
}
}
}
@Component
@Order(1)
public class MyApplicationRunner2 implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs();
System.out.println("1-nonOptionArgs:"+nonOptionArgs);
Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames();
for (String optionName:optionNames){
System.out.println("1-key:"+optionName+";value:"+args.getOptionValues(optionName));
}
}
}
命令行操作
mvn package
java -jar webtest-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --name=wang --age=99 三国 水浒
结果:
六、整合Servlet、Filter、Listener
一般情况下,spring,springmvc这些框架之后,基本就告别了Servlet,filter,Listener了,但是有时在整合一些第三方框架时,可能还是不得不使用Servlet,比如在整合某报表插件时时就需要使用Servlet。springboot对于这些web组件也提供了很好的支持
流程:
建一个servlet的包,包下再放这些类,因为需要springboot去扫描
Servlet,Filter,Listener刚好对应三个注解@WebServlet("/my")、@WebFilter("/")、@WebListener
Servlet
@WebServlet("/my")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
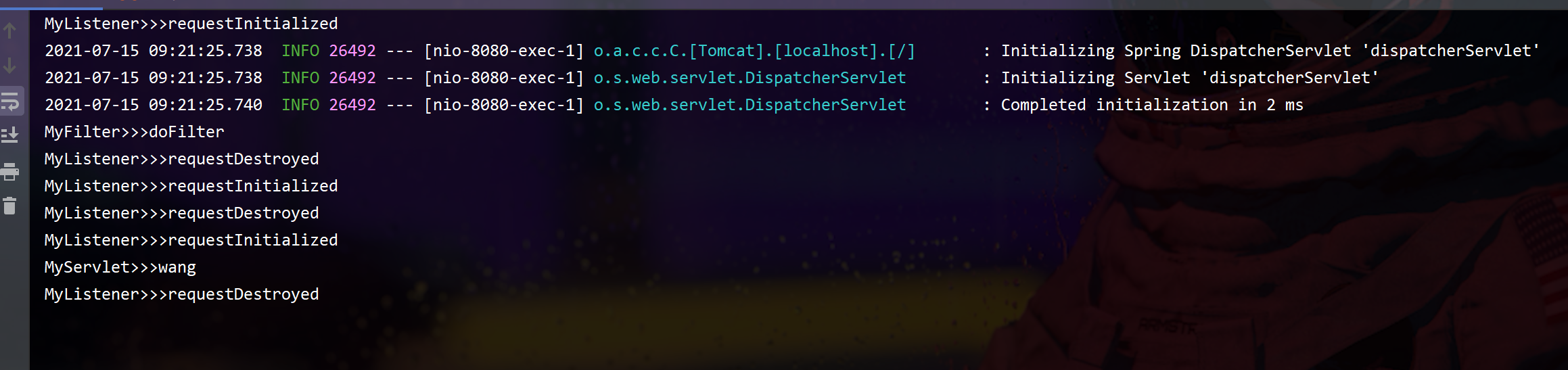
System.out.println("MyServlet>>>"+req.getParameter("name"));
}
}
Filter
@WebFilter("/")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("MyFilter>>>init");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("MyFilter>>>doFilter");
chain.doFilter(request,response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyFilter>>>destroy");
}
}
Listener
//这里只举了ServletRequestListener的例子,还可以是HttpSessionListener、ServletContextListener
@WebListener
public class MyListener implements ServletRequestListener {
@Override
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("MyListener>>>requestDestroyed");
}
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("MyListener>>>requestInitialized");
}
}
在项目入口上添加@ServletComponentScan注解表示对Servlet的组件进行扫描
@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
public class WebtestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WebtestApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试:
运行,然后浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/my?name=wang
七、路径映射
流程:
直接重写WebMvcConfigurer中的addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry)方法即可
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class MyWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
}
}
效果类似于
@Controller
public class LoginControl {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String getLogin(){
return "login";
}
@GetMapping("/index")
public String getIndex(){
return "index";
}
}
八、配置AOP
复习AOP概念:
AOP,即面向切片编程(Aspect-Oriented Programming),有时我们的系统在运行的时候我们发现了bug,或者需要进行其他在系统运行的时候动态添加代码的方式,被称为AOP操作,spring对AOP提供了很好的支持,还有一些常见的概念,
- JoinPoint(连接点):类里面可以加强的方法被称为连接点,例如:想修改哪个方法,该方法就是一个JoinPoint。
- PointCut(切入点):对连接点进行拦截的定义即为切入点,例如:拦截所有以insert开始的方法,这个定义即为切入点。
- Advice(通知):拦截到JoinPoint之后的事情就是通知,例如:上文说到了打印日志就是通知操作,通知分为:
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
- 环绕通知
- Aspect(切面):PointCut和Advice的结合
- Target(目标对象):要增强的类称为Target
流程:
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
在service包下建立UserService
@Service
public class UserService {
public String getUserById(Integer id){
System.out.println("get>>>"+id);
return "user";
}
public int deleteUserById(Integer id){
System.out.println("delete>>>"+id);
return 1;
}
}
创建切面:
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
//切入点定义
@Pointcut("execution(* com.wang.service.*.*(..))")
public void pc1(){};
@Before(value = "pc1()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//joinPoint对象可以获得目标方法的方法名、修饰符等信息
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行.....");
}
@After(value = "pc1()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行.....");
}
/*表明这是一个最终通知,可以获取到目标方法的放回值
* 注解中,returning参数对应的是目标方法的放回值的变量名,对应方法的参数
* 而在方法中,result可以是任意类型,不同类型代表处理不同类定的放回值
* Object表明处理任何类型放回值
* Long表明只处理Long类型放回值
* */
@AfterReturning(value = "pc1()",returning = "result")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法放回值为:"+result);
}
//方法的参数为Exception e表明所有的异常都会进入这个通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "pc1()",throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法抛出异常,异常是:"+e.getMessage());
}
/*
* 环绕通知是功能最强大的一个通知
* 可以实现前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,返回通知的功能
* 目标方法进入环绕通知之后,通过过返回proceedingJoinPoint.proceed()来让方法继续执行
* 可以在这里修改方法的执行参数,返回值,异常等。
* */
@Around(value = "pc1()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint)throws Throwable{
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
}
}
九、其他
1、自定义欢迎页
想要静态的欢迎页只需要在resource/static下放上index.html
想要动态的欢迎页只需要在resource/template下创建对应的thymeleaf页面
2、自定义favicon
使用在线网站:https://jinaconvert.com/cn/convert-to-ico.php或
http://www.favicon-icon-generator.com/favicon对图片进行转换
然后把这个文件改名为favicon.icon,放到resource/static下即可
一时加载不出来可能是因为浏览器缓存的问题
3、除去某个自动配置类
例如:除去ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置
//@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class})
@ComponentScan()
public class WebtestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WebtestApplication.class, args);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号