代码已放到码云
https://gitee.com/photographer_adam/Based-on-image-processing-and-tensorflow-to-realize-GTA5-vehicle-automatic-driving
效果
第六节实现的效果
![]()
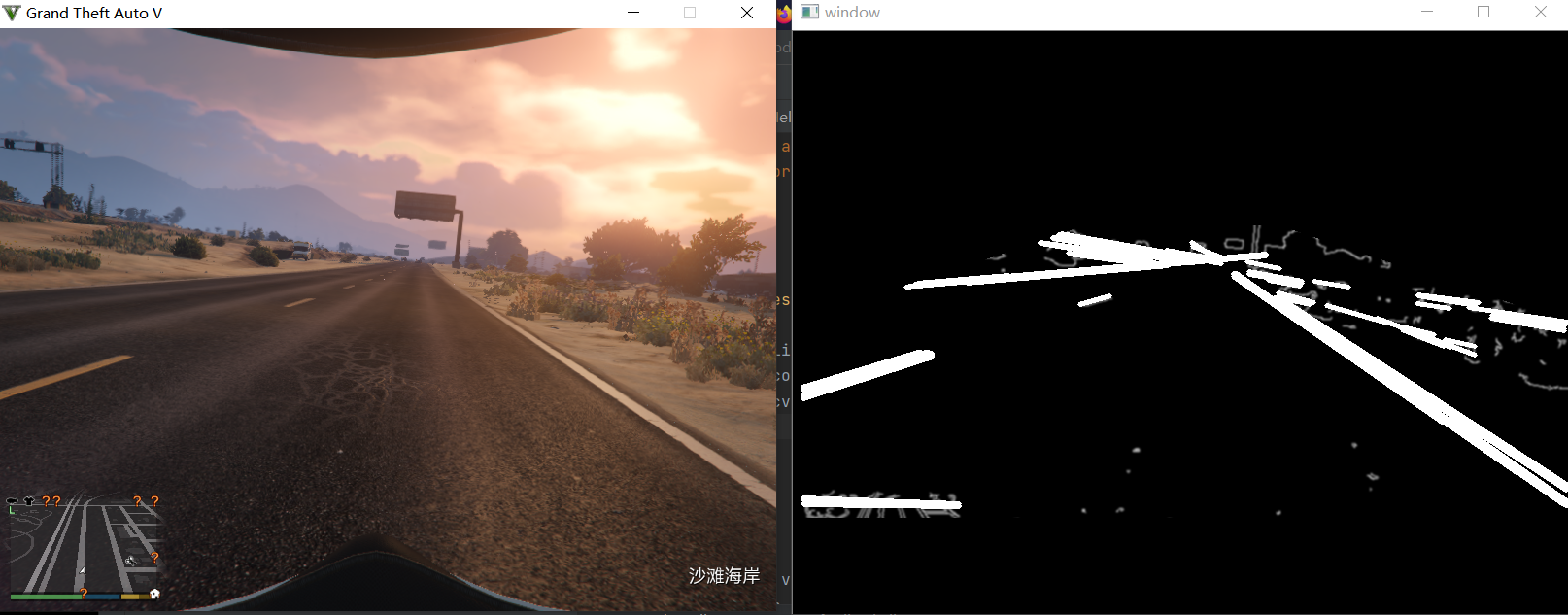
本节效果
![]()
注:
本节作者一开篇就说了这句话:![]()
实现的效果确实可以,但是代码很复杂,我看了下也不想加注释了 :(,等整个项目实现的时候再回来填这个坑吧
本节代码修改的较多,我直接附上整个源代码好了
import numpy as np
from PIL import ImageGrab
import cv2
import time
def compare_lines(lines, color=[0, 255, 255], thickness=3):
'''
try:
for line in lines:
coords = line[0]
cv2.line(img=img, pt1=(coords[0], coords[1]),
pt2=(coords[2], coords[3]), color=[255, 255, 255], thickness=3
)
except:
pass
'''
# if this fails, go with some default line
try:
# finds the maximum y value for a lane marker
# (since we cannot assume the horizon will always be at the same point.)
ys = []
for i in lines:
for ii in i:
ys += [ii[1], ii[3]]
min_y = min(ys)
max_y = 600
new_lines = []
line_dict = {}
for idx, i in enumerate(lines):
for xyxy in i:
# These four lines:
# modified from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21565994/method-to-return-the-equation-of-a-straight-line-given-two-points
# Used to calculate the definition of a line, given two sets of coords.
x_coords = (xyxy[0], xyxy[2])
y_coords = (xyxy[1], xyxy[3])
A = np.vstack([x_coords, np.ones(len(x_coords))]).T
m, b = np.linalg.lstsq(A, y_coords)[0]
# Calculating our new, and improved, xs
x1 = (min_y - b) / m
x2 = (max_y - b) / m
line_dict[idx] = [m, b, [int(x1), min_y, int(x2), max_y]]
new_lines.append([int(x1), min_y, int(x2), max_y])
final_lanes = {}
for idx in line_dict:
final_lanes_copy = final_lanes.copy()
m = line_dict[idx][0]
b = line_dict[idx][1]
line = line_dict[idx][2]
if len(final_lanes) == 0:
final_lanes[m] = [[m, b, line]]
else:
found_copy = False
for other_ms in final_lanes_copy:
if not found_copy:
if abs(other_ms * 1.2) > abs(m) > abs(other_ms * 0.8):
if abs(final_lanes_copy[other_ms][0][1] * 1.2) > abs(b) > abs(
final_lanes_copy[other_ms][0][1] * 0.8):
final_lanes[other_ms].append([m, b, line])
found_copy = True
break
else:
final_lanes[m] = [[m, b, line]]
line_counter = {}
for lanes in final_lanes:
line_counter[lanes] = len(final_lanes[lanes])
top_lanes = sorted(line_counter.items(), key=lambda item: item[1])[::-1][:2]
lane1_id = top_lanes[0][0]
lane2_id = top_lanes[1][0]
def average_lane(lane_data):
x1s = []
y1s = []
x2s = []
y2s = []
for data in lane_data:
x1s.append(data[2][0])
y1s.append(data[2][1])
x2s.append(data[2][2])
y2s.append(data[2][3])
return int(np.mean(x1s)), int(np.mean(y1s)), int(np.mean(x2s)), int(np.mean(y2s))
l1_x1, l1_y1, l1_x2, l1_y2 = average_lane(final_lanes[lane1_id])
l2_x1, l2_y1, l2_x2, l2_y2 = average_lane(final_lanes[lane2_id])
return [l1_x1, l1_y1, l1_x2, l1_y2], [l2_x1, l2_y1, l2_x2, l2_y2]
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
def draw_lines(image, gray_img, lines):
try:
l1, l2 = compare_lines( lines)
cv2.line(image, (l1[0], l1[1]), (l1[2], l1[3]), [0, 255, 0], 30)
cv2.line(image, (l2[0], l2[1]), (l2[2], l2[3]), [0, 255, 0], 30)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
pass
try:
for coords in lines:
coords = coords[0]
try:
cv2.line(gray_img, (coords[0], coords[1]), (coords[2], coords[3]), [255, 0, 0], 3)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
except Exception as e:
pass
def roi(img, vertices):
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, 255)
masked = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked
def convert_To_gray(image):
# to gray
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# canny
gray_img = cv2.Canny(gray_img, threshold1=100, threshold2=200)
# 高斯模糊
gray_img = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_img, ksize=(5,5), sigmaX=0)
# mask img 只取红色区域的数据
vertices = np.array([[10, 500], [10, 300], [300, 200], [500, 200], [800, 300], [800, 500],
], np.int32)
gray_img = roi(gray_img, [vertices])
# 划线
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(gray_img, rho=1, theta=np.pi / 180, threshold=180, lines=np.array([]),minLineLength=150, maxLineGap=5)
draw_lines(image=image, gray_img=gray_img, lines=lines)
def screen_record():
last_time = time.time()
while True:
# 800x600 windowed mode for GTA 5, at the top left position of your main screen.
# 40 px accounts for title bar.
printscreen = np.array(ImageGrab.grab(bbox=(0, 40, 800, 640)))
print('loop took {} seconds'.format(time.time() - last_time))
last_time = time.time()
gray_img = convert_To_gray(printscreen)
# cv2.imshow('window', gray_img)
cv2.imshow('window', cv2.cvtColor(printscreen, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
break
screen_record()

![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号