Java审计之文件上传
Java审计之文件上传
写在前面
本篇文章打算把遇到的和可能会遇到的关于任意文件上传的审计点总结一下,但是总结肯定不会全面,后续遇到了待补充的内容会继续更新。前面部分会梳理一下文件上传的实现,后部分会提一部分遇到的关于文件上传限制的绕过。
Tips
0x01 multipart/form-data
multipart/form-data这种编码方式的表单会以二进制流的方式来处理表单数据,这种编码方式会把文件域指定文件的内容也封装到请求参数里。通常会见到配合method=post去搭配使用,而后端采取inputstream等方式读取客户端传入的二进制流来处理文件。
0x02 Java中的00截断问题
PHP中:PHP<5.3.29,且GPC关闭
Java中:
同时考虑到00截断绕过的问题,在JDK1.7.0_40(7u40)开始对\00进行了检查,相关代码如下:
final boolean isInvalid(){ if(status == null){ status=(this.path.indexOf('\u0000')<0)?PathStatus.CHECKED:PathStatus.INVALID; } return status == PathStatus.INVALID; }也就是说在后面的版本Java就不存在这个问题了。
0x03 上传表单中的enctype
关于集中enctype属性值的解读
application/x-www-form-urlencoded:默认编码方式,只处理表单中的value属性值,这种编码方式会将表单中的值处理成URL编码方式
multipart/form-data:以二进制流的方式处理表单数据,会把文件内容也封装到请求参数中,不会对字符编码
text/plain:把空格转换为+ ,当表单action属性为mailto:URL形式时比较方便,适用于直接通过表单发送邮件方式
0x04 处理文件时常用方法
separatorChar
public static final char separatorChar
与系统有关的默认名称分隔符。此字段被初始化为包含系统属性 file.separator 值的第一个字符。在 UNIX 系统上,此字段的值为 '/';在 Microsoft Windows 系统上,它为 ''。
separator(主要用来做分隔符,防止因为跨平台时各个操作系统之间分隔符不一样出现问题)
public static final String separator
与系统有关的默认名称分隔符,为了方便,它被表示为一个字符串。此字符串只包含一个字符,即 separatorChar。
equalsIgnoreCase(判断文件文件后缀名)
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写。如果两个字符串的长度相同,并且其中的相应字符都相等(忽略大小写),则认为这两个字符串是相等的。
在忽略大小写的情况下,如果下列至少一项为 true,则认为 c1 和 c2 这两个字符相同。这两个字符相同(使用 == 运算符进行比较)。
对每个字符应用方法 Character.toUpperCase(char) 生成相同的结果。
对每个字符应用方法 Character.toLowerCase(char) 生成相同的结果。参数:
anotherString - 与此 String 进行比较的 String。
返回:
如果参数不为 null,且这两个 String 相等(忽略大小写),则返回 true;否则返回 false。
Servlet Part
Servlet3.0提供了对文件上传的支持,通过@MultipartConfig标注和HttpServletRequest的两个新方法getPart()和getParts()
@MultipartConfig注解主要是为了辅助Servlet3.0中HttpServletRequest提供的对上传文件的支持。该注解写在Servlet类的声明之前,一表示该Servlet希望处理的请求是multipart/form-data类型的。另外,该注解还提供了若干属性用于简化对上传文件的处理。

http.part接口
在一个有多部分请求组成的请求中,每一个表单域,包括非文件域,都会被转换成一个个Part。
HttpServletRequest接口定义了以下方法来获取Part:
Part getPart(String name) 返回与指定名称相关的Part,名称为相关表单域的名称(name)
Colleciton
getParts() 返回这个请求中的所有Part
Part中的方法
String getName() 获取这部分的名称,例如相关表单域的名称
String getContentType() 如果Part是一个文件,那么将返回Part的内容类型,否则返回null(可以利用这一方法来识别是否为文件域)
Collection
getHeaderNames() 返回这个Part中所有标头的名称 String getHeader(String headerName) 返回指定标头名称的值
void write(String path) 将上传的文件写入服务器中项目的指定地址下,如果path是一个绝对路径,那么将写入指定的路径,如果path是一个相对路径,那么将被写入相对于location属性值的指定路径。
InputStream getInputStream() 以inputstream的形式返回上传文件的内容
实现上传核心代码
String savePath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/uploadFile");
//Servlet3.0将multipart/form-data的POST请求封装成Part,通过Part对上传的文件进行操作。
Part part = request.getPart("file");//通过表单file控件(<input type="file" name="file">)的名字直接获取Part对象
//Servlet3没有提供直接获取文件名的方法,需要从请求头中解析出来
//获取请求头,请求头的格式:form-data; name="file"; filename="snmp4j--api.zip"
String header = part.getHeader("content-disposition");
//获取文件名
String fileName = getFileName(header);
//把文件写到指定路径
part.write(savePath+File.separator+fileName);
SpringMVC MultipartResolver
SpringMVC可以支持文件上传,使用Apache Commons FileUpload技术实现了一个MultipartResolver实现类。但是默认在上下文中没有装配MultipartResolver,所以不能处理文件上传的操作,需要手动装配,MultipartResolver。使用时需要在SpringMVC配置文件中加上:
<!-- 文件上传配置-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- 需要与jsp中的pageEncoding配置一致,默认为iso-8859-1-->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="utf-8"/>
<!-- 设置上传大小上限,单位为字节,这里1048570=10M-->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="1048570"/>
<property name="maxInMemorySize" value="40960"/>
</bean>
CommonsMultipartFile常用方法
- String getOriginalFilename():获取上传文件的原名
- InputStream getInputStream():获取文件流
- void transferTo(File dest):将上传文件保存到一个目录文件中
CommonsMultipartFile+IO流
示例代码
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
//@RequestParam("file") 将name=file控件得到的文件封装成CommonsMultipartFile 对象
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String fileUpload(@RequestParam("file") CommonsMultipartFile file , HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//获取文件名 : file.getOriginalFilename();
String uploadFileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
if ("".equals(uploadFileName)){
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
System.out.println("上传文件名 : "+uploadFileName);
//上传路径
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
//如果路径不存在,创建一个
File realPath = new File(path);
if (!realPath.exists()){
realPath.mkdir();
}
System.out.println("上传文件地址:"+realPath);
InputStream is = file.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File(realPath,uploadFileName));
//读取写出
int len=0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
os.flush();
}
os.close();
is.close();
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
基本实现文件上传功能的代码逻辑与Commons-FileUpload类似,只不过是通过@RequestParam("file")拿到前端传来的文件数据流并封装成CommonsMultipartFile对象来实现文件上传的操作。
CommonsMultipartFile+transferTo
利用transferTo,通过指定一个文件名(new File(realPath +"/"+ file.getOriginalFilename())),将文件内容写入此文件。
@RequestMapping("/upload2")
public String fileUpload2(@RequestParam("file") CommonsMultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//上传路径保存设置
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File realPath = new File(path);
if (!realPath.exists()){
realPath.mkdir();
}
//上传文件地址
System.out.println("上传文件保存地址:"+realPath);
//通过CommonsMultipartFile的方法直接写文件(注意这个时候)
file.transferTo(new File(realPath +"/"+ file.getOriginalFilename()));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
Commons-FileUpload组件
这个应该是平常用的也是遇到的最多的
About Commons-FileUpload
Commons-FileUpload是Apache的一个组件,依赖于Commons-io,也是目前用的比较广泛的一个文件上传组件之一。
像Spring MVC、Struts2、Tomcat等底层处理文件上传请求都是使用的这个库。
FileUpload基本步骤
- 创建磁盘工厂:DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
- 创建处理工具:ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
- 设置上传文件大小:upload.setFileSizeMax(3145728);
- 接收全部内容:List
items = upload.parseRequest(request);
Commons-FileUpload审计
servlet
public class FileUpload extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//设置文件上传路径
String uploadDir = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload/");
File uploadFile = new File(uploadDir);
//若不存在该路径则创建之
if (!uploadFile.exists()&&!uploadFile.isDirectory()){
uploadFile.mkdir();
}
String message = "";
try {
//创建一个磁盘工厂
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//创建文件上传解析器
ServletFileUpload fileupload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//三个照顾要上传的文件大小
fileupload.setFileSizeMax(3145728);
//判断是否为multipart/form-data类型,为false则直接跳出该方法
if (!fileupload.isMultipartContent(req)){
return;
}
//使用ServletFileUpload解析器解析上传数据,解析结果返回的是一个List<FileItem>集合,每一个FileItem对应一个Form表单的输入项
List<FileItem> items = fileupload.parseRequest(req);
for (FileItem item : items) {
//isFormField方法用于判断FileItem类对象封装的数据是否属于一个普通表单字段,还是属于一个文件表单字段,如果是普通表单字段则返回true,否则返回false。
if (item.isFormField()){
String name = item.getFieldName();
//解决普通输入项的数据的中文乱码问题
String value = item.getString("UTF-8");
String value1 = new String(name.getBytes("iso8859-1"),"UTF-8");
System.out.println(name + " : " + value );
System.out.println(name + " : " + value1);
}else {
//获得上传文件名称
String fileName = item.getName();
System.out.println(fileName);
if(fileName==null||fileName.trim().equals("")){
continue;
}
//注意:不同的浏览器提交的文件名是不一样的,有些浏览器提交上来的文件名是带有路径的,如: c:\a\b\1.txt,而有些只是单纯的文件名,如:1.txt
//处理获取到的上传文件的文件名的路径部分,只保留文件名部分
fileName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(File.separator)+1);
//获取item中的上传文件的输入流
InputStream is = item.getInputStream();
//创建一个文件输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(uploadDir+File.separator+fileName);
//创建一个缓冲区
byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
//判断输入流中的数据是否已经读完的标识
int length = 0;
//循环将输入流读入到缓冲区当中,(len=in.read(buffer))>0就表示in里面还有数据
while((length = is.read(buffer))>0){
//使用FileOutputStream输出流将缓冲区的数据写入到指定的目录(savePath + "\\" + filename)当中
fos.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
//关闭输入流
is.close();
//关闭输出流
fos.close();
//删除处理文件上传时生成的临时文件
item.delete();
message = "文件上传成功";
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
message = "文件上传失败";
e.printStackTrace();
}
req.setAttribute("message", message);
req.getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
fileupload.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
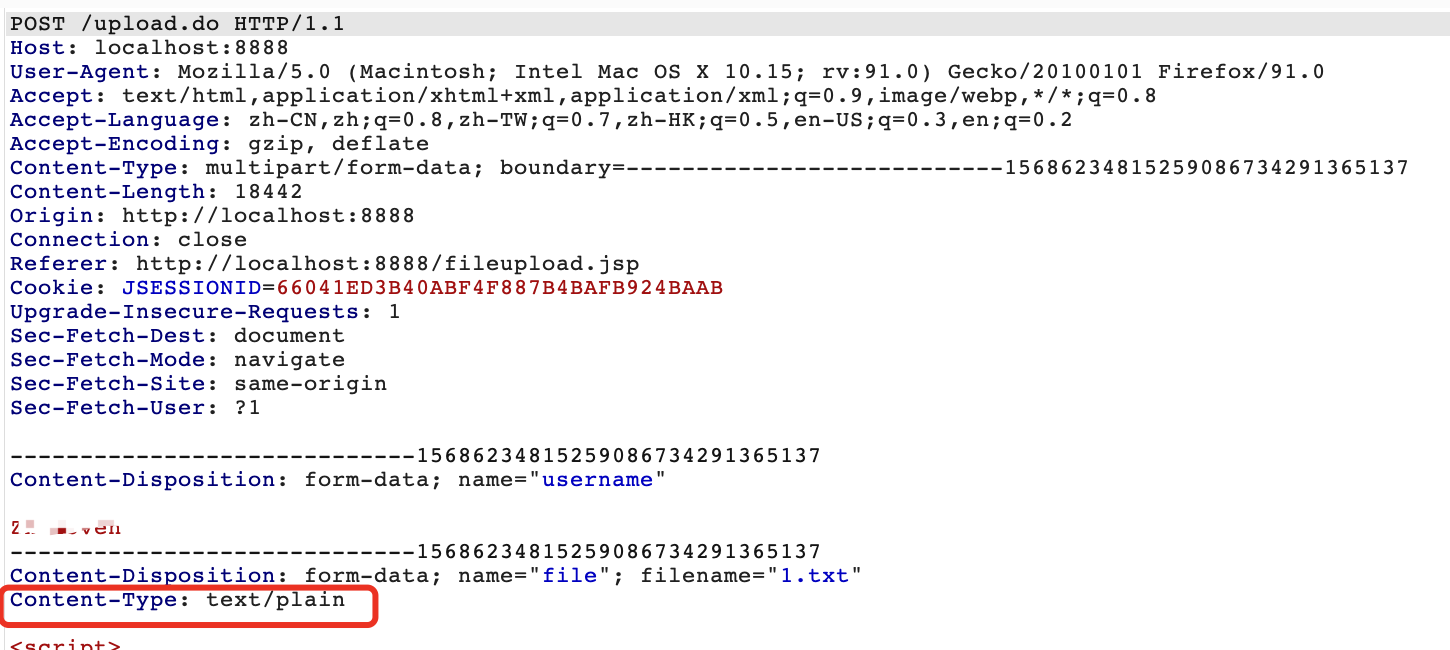
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/upload.do" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<p>
用户名: <input name="username" type="text"/>
文件: <input id="file" name="file" type="file"/>
</p>
<input name="submit" type="submit" value="Submit"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
主要对于文件上传的逻辑限制在于if (item.isFormField())的else部分,只是判断了文件是否非空,没有对文件类型等等进行判断限制,从而导致任意文件上传。
if(fileName==null||fileName.trim().equals("")){
continue;
}
那么看一下可能会遇到的情况,比如如下的代码,通过new File(item.getContentType()).getName()拿到 ContentType/后的值,而最后在item.write( new File(filePath + File.separator + name));时直接拼接文件名,只判断了ContentType没有对后缀进行处理,导致任意文件上传。
String name = new File(item.getFieldName()).getName();
String type = new File(item.getContentType()).getName();
if(type.equalsIgnoreCase("jpeg")||type.equalsIgnoreCase("pdf")||
type.equalsIgnoreCase("jpg")||type.equalsIgnoreCase("png")
) {
item.write( new File(filePath + File.separator + name));
res.setStatus(201);
}else {
res.sendError(501);
}
示例代码2:这里处理filePath部分的if else就显得很蠢,只是对文件不同文件后缀存放的目录做了处理,并没限制上传,直接上传jsp找路径就行。
public ModelAndView upload(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
{
FileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
List items = upload.parseRequest(request);
String recievedFileName = request.getParameter("fileName");
Iterator itr = items.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
FileItem item = (FileItem) itr.next();
if (!item.isFormField()) {
String fileName = item.getName().toLowerCase();
String filePath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
String fileType = fileName.substring(fileName
.lastIndexOf("."));
if (fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".xls")
|| fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".xlsx")) {
filePath = filePath + request.getParameter("folder");
} else if (fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".jpg")
|| fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".jpeg")
|| fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".png")
|| fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".gif")) {
filePath = filePath + "StudentPhotos/";
} else if (fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(".zip")) {
filePath = filePath + request.getParameter("folder");
}
File file = new File(filePath);
file.mkdirs();
filePath = filePath + recievedFileName;
byte[] data = item.get();
FileOutputStream fileOutSt = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
fileOutSt.write(data);
fileOutSt.close();
}
}
return null;
}
小结
主要分为前端和后端,一般在看java代码时,可以直接搜索关键函数或特殊的关键词,比如;
DiskFileItemFactory
@MultipartConfig
MultipartFile
File
upload
InputStream
OutputStream
write
fileName
filePath
......
而在前端的话可以直接搜索multipart/form-data ,之后定位后端的接口;
也可以通过依赖中存在commons-fileupload,或者SpringMVC中有关MultipartResolver的配置。
而定位到上传功能点后进行审计需要注意
判断是否有检查后缀名,同时要查看配置文件是否有设置白名单或者黑名单或者对上传后的文件进行重命名等操作
1、对上传后的文件重命名,uuid或者时间戳等+写死的后缀。
String filename = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-","")+".jpg";
File file = new File(uploadPath+filename);
2、或者这种写法也是直接把后缀限制死了
String type = new File(item.getContentType()).getName();
if(type.equalsIgnoreCase("jpeg")||type.equalsIgnoreCase("pdf")||
type.equalsIgnoreCase("jpg")||type.equalsIgnoreCase("png")
) {
item.write( new File(filePath + File.separator + name + '.' + type));
res.setStatus(201);
}
3、又或者以如下方式检查后缀
item.write( new File(filePath + File.separator + name + '.' + type));
当然遇到这种后缀限制的比较死的时候可以找一下文件重命名的漏洞,可以组合起来getshell。
4、上传位置可控
比如filepath写死,但是filename可控,可以通过../进行目录穿越那么即使当前目录不能解析jsp,也可以换个目录去尝试是否可以解析。
参考文章
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg2NTAzMTExNg==&mid=2247484026&idx=1&sn=eba24b51963e8c3293d023cbcf3318dc&scene=19#wechat_redirect
https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/13698256.html#%E9%AA%8C%E8%AF%81mime%E7%B1%BB%E5%9E%8B%E6%96%87%E4%BB%B6%E4%B8%8A%E4%BC%A0%E6%A1%88%E4%BE%8B
https://github.com/proudwind/javasec_study/blob/master/java%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%AE%A1%E8%AE%A1-%E6%96%87%E4%BB%B6%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.md


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号