JavaSE-集合
JavaSE-集合
集合类提供一种存储空间可变的存储模型,存储数据的容量可以随时发生改变,比如ArrayList。
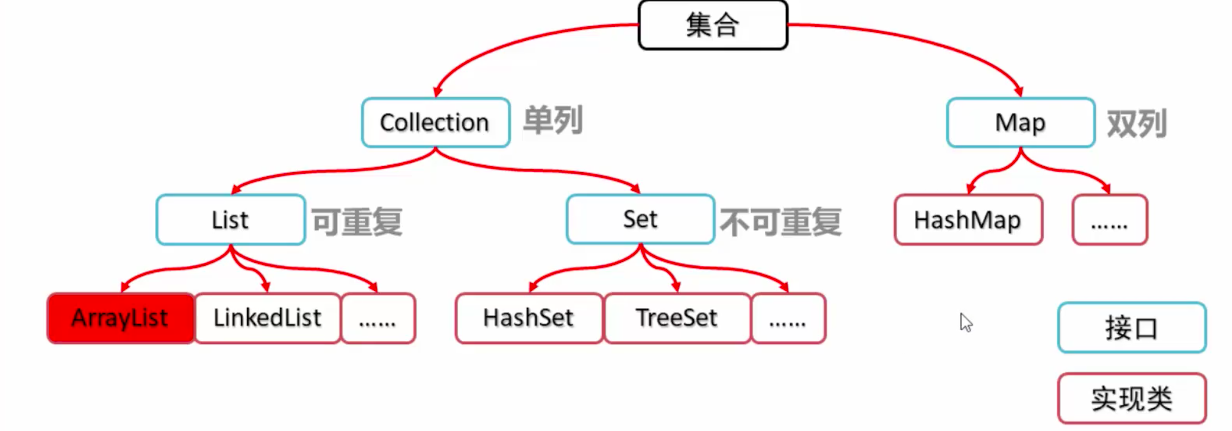
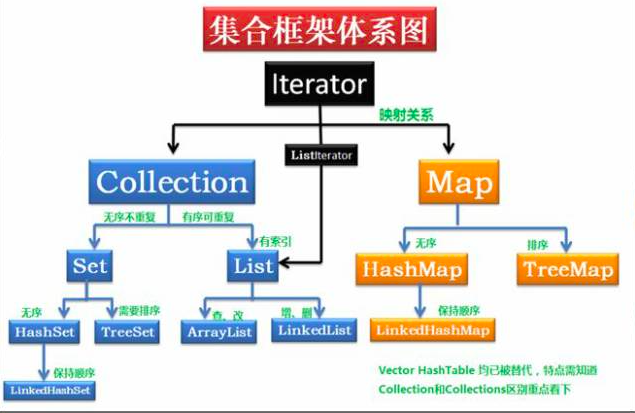
集合按照存储的结构可以分为两类,分别是单列集合java.util.Collection和双列集合java.util.Map,这里就先来讲讲collection集合。
List的特点是存储的元素有序,元素可以重复。而set的特点是元素无序、存储的元素不可重复。List的接口主要实现类有ArrayList 和LinkedList,Set接口的主要实现类有HashSet和TreeSet;Map集合主要有HashMap
Collection
* `public boolean add(E e)`: 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 。
* `public void clear()` :清空集合中所有的元素。
* `public boolean remove(E e)`: 把给定的对象在当前集合中删除。
* `public boolean contains(E e)`: 判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象。
* `public boolean isEmpty()`: 判断当前集合是否为空。
* `public int size()`: 返回集合中元素的个数。
* `public Object[] toArray()`: 把集合中的元素,存储到数组中。
简单使用下这个几个方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
c.add("zh1z3ven");
c.add("agou");
c.add("cafei");
c.add("xiaoming");
System.out.println(c);
Boolean a = c.isEmpty();
System.out.println(a);
int a2 = c.size();
System.out.println(a2);
c.remove(2);
System.out.println(c);
Boolean a3 = c.contains("cafei");
System.out.println(a3);
}
Iterator迭代器
java给我们提供了Iterator接口,也就是迭代器,该接口也是集合的一种。也是集合专用的一种遍历方式。
Iterator<String> it = col.iterator();
集合的iterator()方法返回该集合元素的一个迭代器对象,之后就可以通过此对象的hashNext()和next()遍历这个集合。
next():返回迭代的下一个元素。
hasNext():如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true,否则返回false。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> col = new ArrayList<String>();
col.add("Hello");
col.add("World");
col.add("Java");
System.out.println(col);
Iterator<String> it = col.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
List
List接口是Collection的子接口,
List接口里面允许出现重复元素得,在程序中可以通过索引来访问。
List接口存储的数据是有序的。
List的特有方法
void add(int index, Element) 在指定位置插入指定的元素
E remove(int index) 删除指定位置处的元素,返回被删除的元素
E set(int index, Element) 修改指定位置处的元素,返回被修改的元素
E get(int index) 返回指定位置处的元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
list.add("Java");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1,"agou");
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(1);
System.out.println(list);
}
//
[Hello, World, Java]
[Hello, agou, World, Java]
[Hello, World, Java]
LinkedList
LinkedList集合特有方法
public void addFirst(E e) 在该列表开头插入指定的元素
public void addLast(E e) 将指定元素追加到此列表末尾
public E getFirst() 返回此列表第一个元素
public E getLast() 返回次列表末尾元素
public E removeFirst() 删除并返回此列表第一个元素
public E removeLast() 删除并返回此列表最后一个元素
set
set接口也是继承了Collection接口,也是单列集合。
set接口中元素无序,并且都会以某种规则保证存入的元素不出现重复。
HashSet
无序,不保证元素的迭代顺序
不包含重复元素的集合
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
简单例子
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add("hello");
hashSet.add("world");
hashSet.add("java");
//迭代器循环
Iterator<String> iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
//foreach循环
for (String s : hashSet
) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
LinkedHashSet
上面提到HashSet是无序的,如果想要有序,就需要用到LinkedHashSet
Collections类
conections是集合的工具类。
- public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<T> c, T... elements) `:往集合中添加一些元素。
- `public static void shuffle(List<?> list) 打乱顺序`:打乱集合顺序。
- `public static <T> void sort(List<T> list)`:将集合中元素按照默认规则排序。
- `public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> )`:将集合中元素按照指定规则排序。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//addAll()
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(arrayList, "hello","world","java","agou");
Iterator<String> iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("================================");
//sort()
ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(integers, 11,22,12,45,67453,213,123456);
System.out.println(integers);
Collections.sort(integers);
System.out.println(integers);
}
Map
在 Collection中,元素都是单个存在的。
而map中的集合,元素是成对存在的(类似于python中的字典)
每个元素都由键和值组成,通过键可以找到对应的值。
Map接口中的方法
public V put(K key, V value) : 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。
public V remove(Object key) : 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的
值。
public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。
public Set<K> keySet() : 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中。
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() : 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)
Map接口中的集合都有两个泛型变量,在使用时,要为两个泛型变量赋予数据类型。两个泛型变量的数
据类型可以相同,也可以不同。
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> stringIntegerHashMap = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//put() 添加元素
stringIntegerHashMap.put(1, "xiaoming");
stringIntegerHashMap.put(2, "xiaohong");
stringIntegerHashMap.put(3, "xiaobai");
stringIntegerHashMap.put(4, "agou");
stringIntegerHashMap.put(5, "zhendegou");
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap);
//size() 获取长度
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.size());
//remove() 删除指定key所对应的value
stringIntegerHashMap.remove(3);
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap);
//get() 获取指定key对应的value
System.out.println(stringIntegerHashMap.get(4));
}
HashMap循环遍历value
map里面提供了一个获取所以键值的方法keyset。
public class HashMapKeySetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> integerStringHashMap = new HashMap<>();
integerStringHashMap.put(1,"xiao");
integerStringHashMap.put(2,"a");
integerStringHashMap.put(3,"gou");
Set<Integer> integers = integerStringHashMap.keySet();
for (int key : integers
) {
String value = integerStringHashMap.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
HashMap循环遍历Key Value
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
Entry将键值对的对应关系封装成了对象。即键值对对象,这样我们在遍历Map集合时,就可以从每一个键值对(Entry)对象中获取对应的键与对应的值。
public K getKey():获取Entry对象中的键。
public V getValue()`:获取Entry对象中的值。
public class HashMapEntrySetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> integerStringHashMap = new HashMap<>();
integerStringHashMap.put(1,"xiao");
integerStringHashMap.put(2,"a");
integerStringHashMap.put(3,"gou");
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = integerStringHashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
int key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + " " + "Value:" + value);
}
}
}
Key:1 Value:xiao
Key:2 Value:a
Key:3 Value:gou
LinkedHashMap
Hashmap的存放是无序的,如果需要有序存储数据的话,就需要用到LinkedHashMap。
public class LinkedHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> integerStringLinkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
integerStringLinkedHashMap.put(1, "xiao");
integerStringLinkedHashMap.put(2, "bei");
integerStringLinkedHashMap.put(3, "bei");
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = integerStringLinkedHashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries
) {
String value = entry.getValue();
int key = entry.getKey();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + " " + "Value:" + value);
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号