spring的依赖注入的四种方式,数组与集合注入;引用注入;内部bean注入
三种注入方式
第一种: 基于构造函数
hi.java (bean)
package test_one; public class hi { private String name; public hi(String name) { this.name=name; } public void sayhi() { System.out.println("你好呀 "+this.name); } }
<bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="斌斌"/> </bean>
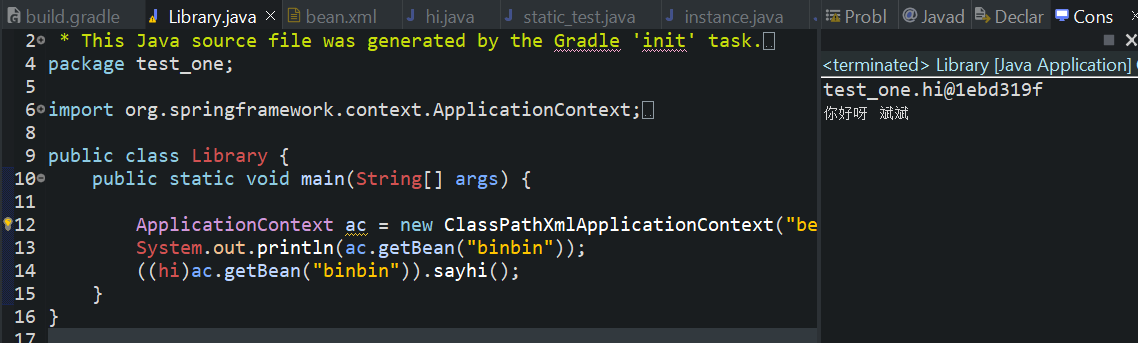
上面是通过配置文件注入字符串
我们来看看如何注入bean
<bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton"> <constructor-arg ref="No"/> </bean> <bean id="No" class="test_one.no"></bean>
<!--通过构造函数,将id="No"的bean 注入到 hi 中
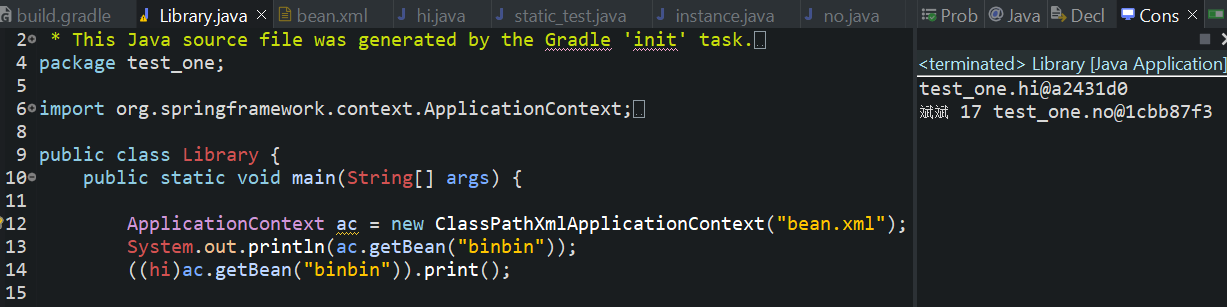
总结:
constructor-arg 元素表示通过构造函数注入
属性: index: 对应构造函数参数列表的位置
type:对应构造函数列表里的的数据类型
name:对应在构造函数列表里的变量名
value: 赋值
ref:对应bean类型的id名
一般都是通过name="" value="" 去注入
而注入bean只要 ref="id名"
其他用法:
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="45"/>
<constructor-arg index="0" value="20"/>
值得注意的是通过参数名称来匹配的方法,代码必须启用了调试标记编译,这样spring才可以从构造函数中查找参数名称
开发者也可以使用@ConstructorProperties注解来显式声明构造函数的名称
public class ExampleBean{
/***省略字段**/
@ConstructorProperties({"years","ultimateAnswer"})
public ExampleBean(int years,String ultimateAnswer){
this.years=years;
this.ultimateAnswer=ultimateAnswer;
}
}
注意: spring的便利之处就是,将value属性的字符串类型自动转换为指定类型
第二种: 基于set方法
hi.java (bean)
package test_one; public class hi { private String name; private int age; private no a; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void setA(no a) { this.a = a; } public void print() { System.out.print(name+" "+age+" "+a); } }
<bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton"> <property name="name" value="斌斌"/> <property name="age" value="17"/> <property name="a" ref="No"/> </bean> <bean id="No" class="test_one.no"></bean>
总结:
property 表示基于set方法注入
属性: name: 对应变量名匹配
ref: 如果注入的是bean,对应bean的id名
value: 赋值,spring会自动将字符串类型转换为对应类型
注意:如果注入的是bean,那么对于property来说就要加上name
<property name="a" ref="No"/>
第三种: 使用p命名空间注入
本质还是基于set注入,不过xml的配置更加简单,主要一个命名空间就可以对所有的bean赋值,不用多余的嵌套property
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用无参构造函数实例化,使用p命令空间注入--> <bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton" p:name="斌斌" p:age="17" p:a-ref="No"></bean> <bean id="No" class="test_one.no" p:name="明明"></bean>
第四种:使用c命名空间注入
与p命名空间注入一样,不过是基于构造函数注入
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
<bean id="C" class="test_one.c_name" c:name="i'm c"/>
如果注入的是数组,List , Set , map, Properties
hi.java (bean)
package test_one; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public class hi { private String[] myStrs; private List<String> myList; private Set<Integer> mySet; private Map<String,String> myMap; private Properties myProps; public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) { this.myStrs = myStrs; } public void setMyList(List<String> myList) { this.myList = myList; } public void setMySet(Set<Integer> mySet) { this.mySet = mySet; } public void setMyMap(Map<String, String> myMap) { this.myMap = myMap; } public void setMyProps(Properties myProps) { this.myProps = myProps; } public String[] getMyStrs() { return myStrs; } public List<String> getMyList() { return myList; } public Set<Integer> getMySet() { return mySet; } public Map<String, String> getMyMap() { return myMap; } public Properties getMyProps() { return myProps; } public void print() { System.out.println("array:"+myStrs[0]+" "+myStrs[1]+"\nList:"+myList+"\nSet:"+mySet+"\nMap:"+myMap+"\nProperties:"+myProps); } }
<!--使用无参构造函数实例化--> <bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton"> <!--给数组注入数据--> <property name="myStrs"> <array> <value>array_one</value> <value>array_two</value> </array> </property> <!--给List注入数据--> <property name="myList"> <array> <value>List_one</value> <value>List_two</value> </array> </property> <!--给set集合注入数据--> <property name="mySet"> <list> <value>1314</value> <value>520</value> </list> </property> <!--注入map数据--> <property name="myMap"> <props> <prop key="testA">map_one</prop> <prop key="testB">map_two</prop> </props> </property> <!--注入Properties数据--> <property name="myProps"> <map> <entry key="testA" value="properties_one"/> <entry key="testB"> <value>properties_two</value> </entry> </map> </property> </bean>
可以发现我将array, list,set 的元素混用了,将map和props混用了
也就是说 array,list ,set之间可以混用,map与props之间可以混用。 不过在实际开发时还是元素和数据类型对应使用
如果集合的数据类型是其他类型,在配置文件中,会自动将value的值转化为对应类型
注入Properties数据的另一种方式,更加简便
key=value 的写法
<!--注入Properties数据--> <property name="myProps"> <value> testA=Properties_one testB=Properties_two </value> </property>
引用bean注入
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/CloudComputing-binbin/p/15939822.html
内部bean注入
内部bean也称为内部匿名bean, 如果需要注入bean并且只用于一个特定的属性,建议使用内部bean
内部bean无法被外部bean引用,哪怕你加上id,她会无视scope标签

<bean id="binbin" class="test_one.hi" scope="singleton"> <!--给数组注入数据--> <property name="myStrs"> <array> <bean class="test_one.no" parent="parent"/> </array> </property> </bean>
那个内部bean是通过抽象bean注入的,想了解抽象bean请参考:三种实例化bean以及非实例化抽象bean
Null以及空字符的值
<bean class="ExampleBean"> <property name="email" value=""/> </bean>
什么示例与下列java代码效果一样
ExampleBean.setEmail("");
<null/>元素表示null(空指针)
<bean class="ExampleBean"> <property name="email"> <null/> </property> </bean>
与下面的java代码效果一样
ExampleBean.setEmail(null);




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号