KVM虚拟化
KVM虚拟化
虚拟化介绍
虚拟化:在一台计算机上虚拟出多个逻辑的计算机,而且每个逻辑计算机
它可以是不同操作系统
虚拟化技术:可以扩大硬件容量,单个cpu模拟出多个cpu并行,
允许一个平台上同时运行多个操作系统,应用程序都可以在相互独立
的空间内运行,而且互不影响。
为什么企业使用虚拟化技术
1、节约成本
2、提高效率,物理机我们一般称为宿主机(Host),宿主机上面的虚拟机称为客户机(Guest)。
那么 Host 是如何将自己的硬件资源虚拟化,并提供给 Guest 使用的呢?
这个主要是通过一个叫做 Hypervisor 的程序实现的。
Hypervisor:一种运行在物理服务器硬件与操作系统之间的中间软件层
可允许多个操作系统和应用来共享硬件资源
根据 Hypervisor 的实现方式和所处的位置,虚拟化又分为两种:
完全虚拟化:直接在物理机上部署虚拟化,且不需要修改操作系统内核
半虚拟化:需要修改操作系统内核,使其支持虚拟化驱动来实现虚拟化技术
全虚拟化

半虚拟化

KVM简介
KVM 全称是 Kernel-Based Virtual Machine。也就是说 KVM 是基于 Linux 内核实现的。
KVM有一个内核模块叫 kvm.ko,只用于管理虚拟 CPU 和内存。
那 IO 的虚拟化,比如存储和网络设备则是由 Linux 内核与Qemu来实现。
Qemu-KVM虚拟化
KVM本身不执行任何设备模拟,需要用户空间程序QEMU通过/dev/kvm接口设置一个虚拟客户机的地址空间。
KVM和Qemu的关系
Qemu是一个独立的虚拟化解决方案,通过intel-VT 或AMD SVM实现全虚拟化,安装qemu的系统,可以直接模拟出另一个完全不同的系统环境。QEMU本身可以不依赖于KVM,但是如果有KVM的存在并且硬件(处理器)支持比如Intel VT功能,那么QEMU在对处理器虚拟化这一块可以利用KVM提供的功能来提升性能。
KVM是集成到Linux内核的Hypervisor,是X86架构且硬件支持虚拟化技术(Intel-VT或AMD-V)的Linux的全虚拟化解决方案。它是Linux的一个很小的模块,利用Linux做大量的事,如任务调度、内存管理与硬件设备交互等。准确来说,KVM是Linux kernel的一个模块。
Qemu的三种运行模式:
1.第一种模式是通过kqemu模块实现内核态的加速。
2.第二种模式是在用户态直接运行QEMU,由QEMU对目标机的 所有 指令进行翻译后执行,相当于全虚拟化。
3.第三种模式则是KVM官方提供的kvm-qemu加速模式。
qmeu的两种特点:
1.QEMU可以在没有主机内核驱动程序的情况下运行。
2.它适用于多种操作系统(GNU / Linux,* BSD,Mac OS X,Windows)和体系结构。
3.它执行FPU的精确软件仿真。
QEMU的两种操作模式:完整的系统仿真和用户模式仿真。
QEMU用户模式仿真具有以下功能:
1.通用Linux系统调用转换器,包括大部分ioctls。
2.使用本机CPU clone的仿真为线程使用Linux调度程序。
3.通过将主机信号重新映射到目标信号来实现精确信号处理。
QEMU全系统仿真具有以下特点:
1.QEMU使用完整的软件MMU来实现最大的便携性。
2.QEMU可以选择使用内核加速器,如kvm。加速器本地执行大部分客户代码,同时继续模拟机器的其余部分。
3.可以仿真各种硬件设备,并且在某些情况下,客户机操作系统可以透明地使用主机设备(例如串行和并行端口,USB,驱动器)。主机设备传递可用于与外部物理外围设备(例如网络摄像头,调制解调器或磁带驱动器)交谈。
4.对称多处理(SMP)支持。目前,内核加速器需要使用多个主机CPU进行仿真。
部署KVM
环境
| 主机名 | ip | 系统 |
|---|---|---|
| localhost | 192.168.118.128 | centos 8 |
内存尽量8G以上,CPU虚拟化功能都勾选,再加上一块新的虚拟硬盘,虚拟计数器看情况勾选
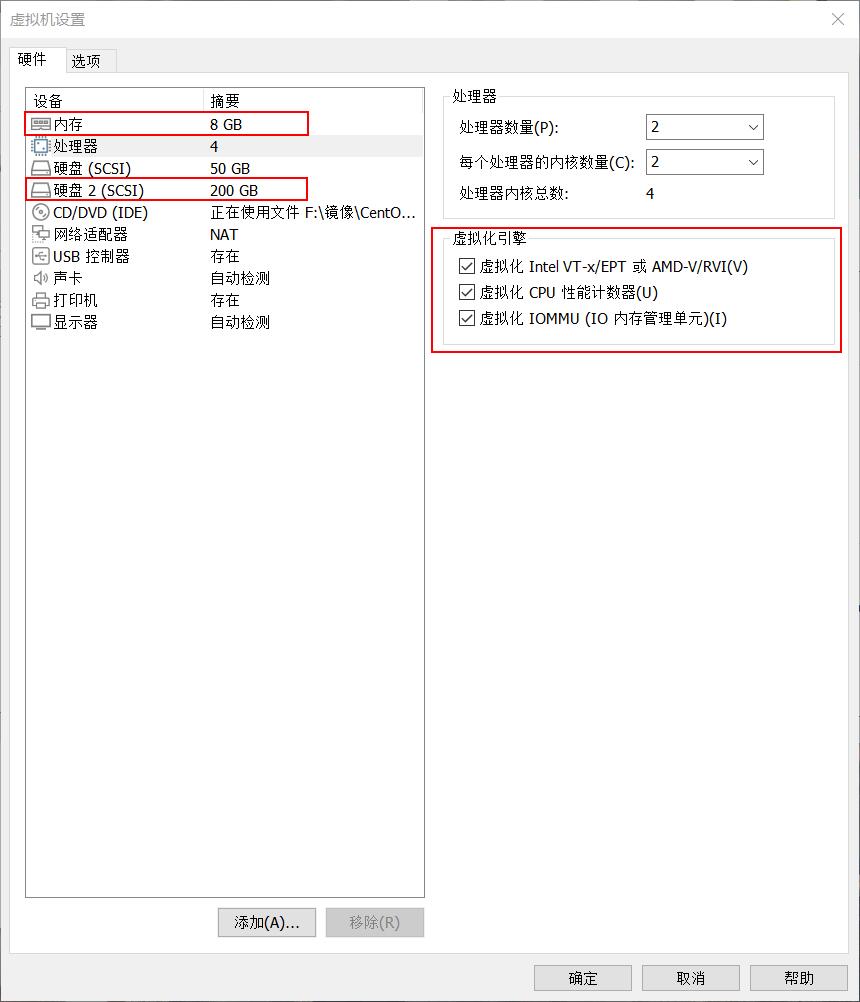
新建分区,将硬盘所有大小都给这个分区
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk
|-sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
`-sda2 8:2 0 49G 0 part
|-cs-root 253:0 0 44G 0 lvm /
`-cs-swap 253:1 0 5G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 200G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 10.5G 0 rom
[root@localhost ~]# parted /dev/sdb
GNU Parted 3.2
Using /dev/sdb
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
(parted) mklabel
New disk label type? msdos
(parted) unit
Unit? [compact]? MiB
(parted) p
Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi)
Disk /dev/sdb: 204800MiB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
(parted) mkpart
Partition type? primary/extended? primary
File system type? [ext2]? xfs
Start? 10MiB
End? 204790MiB
(parted) p
Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi)
Disk /dev/sdb: 204800MiB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
1 10.0MiB 204790MiB 204780MiB primary xfs lba
(parted) q
Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab.
//刷新分区表
[root@localhost ~]# udevadm settle
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk
|-sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
`-sda2 8:2 0 49G 0 part
|-cs-root 253:0 0 44G 0 lvm /
`-cs-swap 253:1 0 5G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 200G 0 disk
`-sdb1 8:17 0 200G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 10.5G 0 rom
//格式化,挂载
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=13105920 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=1, sparse=1, rmapbt=0
= reflink=1 bigtime=0 inobtcount=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=52423680, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0, ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=25597, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
[root@localhost ~]# blkid /dev/sdb1
/dev/sdb1: UUID="0ac8518e-9fad-4b64-9e99-c16a8271749c" BLOCK_SIZE="512" TYPE="xfs" PARTUUID="92298139-01"
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /kvmdata
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab
UUID=0ac8518e-9fad-4b64-9e99-c16a8271749c /kvmdata xfs defaults 0 0
[root@localhost ~]# mount -a
[root@localhost ~]# df -Th
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs devtmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 3.8G 9.0M 3.8G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/cs-root xfs 44G 2.1G 42G 5% /
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 212M 803M 21% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 774M 0 774M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/sdb1 xfs 200G 1.5G 199G 1% /kvmdata
KVM安装
//关闭防火墙和selinux
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# sed -ri 's/^(SELINUX=).*/\1disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
//部署yum源
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# rm -rf *
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-vault-8.5.2111.repo
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 2495 100 2495 0 0 3723 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 3718
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# sed -i -e '/mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/d' -e '/mirrors.aliyuncs.com/d' /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
//安装所需软件包
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install epel-release
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install vim wget net-tools unzip zip gcc gcc-c++ qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer libguestfs-tools --allowerasing
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/qemu-kvm-tools-1.5.3-175.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/libvirt-python-4.5.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/bridge-utils-1.5-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps libvirt-python-4.5.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps qemu-kvm-tools-1.5.3-175.el7.x86_64.rpm
//验证cpu是否支持kvm,vmx是intel的 svm是AMD的
[root@localhost ~]# egrep -o 'vmx|svm' /proc/cpuinfo
vmx
//安装kvm
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install qemu-kvm \
qemu-kvm \
qemu-img \
virt-manager \
libvirt \
libvirt-python3 \
libvirt-client \
virt-install \
virt-viewer \
bridge-utils \
libguestfs-tools
//配置网络,因为虚拟机中的网络,我们一般是都和公司服务器处在同一网段的,所以我们需要把kvm的网卡配置成桥接模式
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@localhost network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-br0
[root@localhost network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-br0
TYPE=Bridge
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=br0
NAME=br0
IPADDR=192.168.118.128
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.118.2
DNS1=8.8.8.8
ONBOOT=yes
[root@localhost network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens33
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=ens33
NAME=ens33
ONBOOT=yes
BRIDGE=br0
//重启网卡服务
[root@localhost network-scripts]# nmcli connection reload
[root@localhost network-scripts]# nmcli connection up ens33
[root@localhost network-scripts]# nmcli connection up br0
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel master br0 state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:9a:13 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: br0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:b5:9a:13 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.118.128/24 brd 192.168.118.255 scope global noprefixroute br0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb5:9a13/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
//重启libvirtd服务,并设置下次启动生效
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable --now libvirtd
//查看kvm模块是否加载
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod |grep kvm
kvm_intel 344064 0
kvm 905216 1 kvm_intel
irqbypass 16384 1 kvm
//将qemu-kvm这个命令做一个软链接到/usr/bin/qemu-kvm
[root@localhost ~]# ln -s /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
[root@localhost ~]# ll /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 21 Oct 7 01:09 /usr/bin/qemu-kvm -> /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install console-bridge console-bridge-devel
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh bridge-utils-1.5-9.el7.x86_64.rpm
//查看网桥信息
[root@localhost ~]# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.000c29b59a13 no ens33
virbr0 8000.5254004517fa yes virbr0-nic
KVM管理界面安装
Kvm的web界面是由webvirtmgr程序提供的
//安装依赖包
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install git python2-pip supervisor nginx python2-devel
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/Packages/libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://download-ib01.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/p/python-websockify-0.6.0-2.el7.noarch.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps libxml2-python-2.9.1-6.el7.5.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps python-websockify-0.6.0-2.el7.noarch.rpm
//升级pip
[root@localhost ~]# pip2 install --upgrade pip
[root@localhost ~]# pip -V
pip 20.3.4 from /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pip (python 2.7)
//从github上下载webvirtmgr代码
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@localhost src]# git clone http://github.com/retspen/webvirtmgr.git
[root@localhost src]# cd webvirtmgr/
[root@localhost webvirtmgr]# ls
MANIFEST.in conf deploy images locale requirements.txt servers templates
README.rst console dev-requirements.txt instance manage.py secrets setup.py vrtManager
Vagrantfile create hostdetail interfaces networks serverlog storages webvirtmgr
//安装webvirtmgr
[root@localhost webvirtmgr]# pip install -r requirements.txt
//检查sqlite3是否安装
[root@localhost webvirtmgr]# python3
Python 3.6.8 (default, Jan 19 2022, 23:28:49)
[GCC 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-7)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import sqlite3
>>> exit()
//初始化账号信息
[root@localhost webvirtmgr]# python2 manage.py syncdb
WARNING:root:No local_settings file found.
Creating tables ...
Creating table auth_permission
Creating table auth_group_permissions
Creating table auth_group
Creating table auth_user_groups
Creating table auth_user_user_permissions
Creating table auth_user
Creating table django_content_type
Creating table django_session
Creating table django_site
Creating table servers_compute
Creating table instance_instance
Creating table create_flavor
You just installed Django's auth system, which means you don't have any superusers defined.
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): root
Email address: dxy@qq.com
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully.
Installing custom SQL ...
Installing indexes ...
Installed 6 object(s) from 1 fixture(s)
//拷贝web网页到指定目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /var/www/
[root@localhost ~]# cp -r /usr/local/src/webvirtmgr/ /var/www/
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/www/webvirtmgr/
//生成一对公钥与私钥,由于这里webvirtmgr和kvm服务部署在同一台主机中,所以这里本地信任。如果kvm部署在其他机器上的时候,那么就需要把公钥发送到kvm主机中
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:BWwd9RaSlkDDyuYihe+yLgggsTv4OTt6wF76HXM+3Ro root@localhost.localdomain
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| ..+=+oo. |
|. o.o.+o . |
| o . o ... o |
|+ . . +. . |
|=. o oS |
|*. .. o . |
|o=o. = o.E. |
|.oB o *. ... |
|.ooBo+ .... |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.118.128
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.118.128 (192.168.118.128)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:+RwKWt1ErJuzJKcNeLslD46lbAtIO3wmNQk9BhIrtxs.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.118.128's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.118.128'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
//配置端口转发
[root@localhost ~]# ssh 192.168.118.128 -L localhost:8000:localhost:8000 -L localhost:6080:localhost:60
[root@localhost ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
//配置nginx
[root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.bak
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
//在server参数中进行修改
删除listen [::]:80;行
参数server_name行改成server_name localhost;
删除root /usr/share/nginx/html;行
server {
listen 80 ;
server_name localhost;
//在include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;行下添加
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
//配置nginx虚拟主机
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name $hostname;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/webvirtmgr_access_log;
location /static/ {
root /var/www/webvirtmgr/webvirtmgr;
expires max;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $remote_addr;
proxy_connect_timeout 600;
proxy_read_timeout 600;
proxy_send_timeout 600;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
}
}
//确保bind绑定本机的8000端口
[root@localhost ~]# grep "bind" /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
# bind - The socket to bind.
bind = '127.0.0.1:8000'
//重启nginx服务,查看端口是否开启
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@localhost ~]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
//设置supervisor
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/supervisord.conf
在最后一行添加
[program:webvirtmgr]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/manage.py run_gunicorn -c /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr.log
log_stderr=true
user=nginx
[program:webvirtmgr-console]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/console/webvirtmgr-console
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr-console.log
redirect_stderr=true
user=nginx
//启动supervisor并设置开机自启
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable --now supervisord
//配置nginx用户
[root@localhost ~]# su - nginx -s /bin/bash
[nginx@localhost ~]$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/var/lib/nginx/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:nl0AxJl4H+2Ypu4hm6e2vbKHquIKPCr6sy62zqZTqWY nginx@localhost.localdomain
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| +oo . |
| . =.. . |
| . ..= |
| =.. |
| . So . |
|. o ..o . |
|.= .o+ . |
|XEo +=+. |
|^@*+.o*O+. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[nginx@localhost ~]$ echo -e "StrictHostKeyChecking=no\nUserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null" >> ~/.ssh/config
[nginx@localhost ~]$ cat .ssh/config
StrictHostKeyChecking=no
UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null
[nginx@localhost ~]$ chmod 600 .ssh/config
[nginx@localhost ~]$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.118.128
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.118.128' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@192.168.111.141's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.118.128'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[nginx@localhost ~]$ exit
logout
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[Remote libvirt SSH access]
Identity=unix-user:root
Action=org.libvirt.unix.manage
ResultAny=yes
ResultInactive=yes
ResultActive=yes
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R root.root /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
//重启服务
[root@localhost ~]# reboot
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart libvirtd
[root@localhost ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 100 0.0.0.0:6080 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*
使用浏览器访问
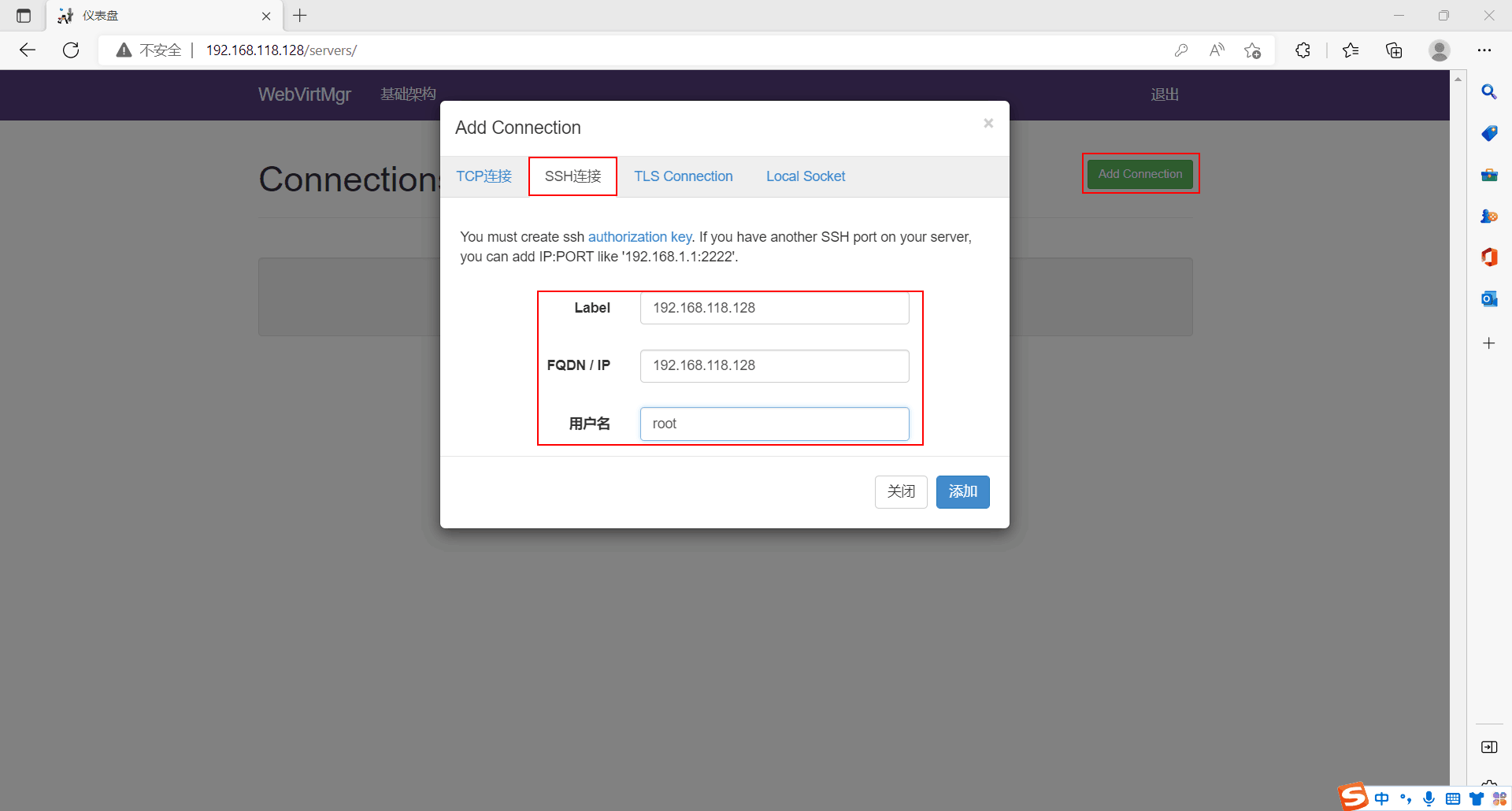
新建链接
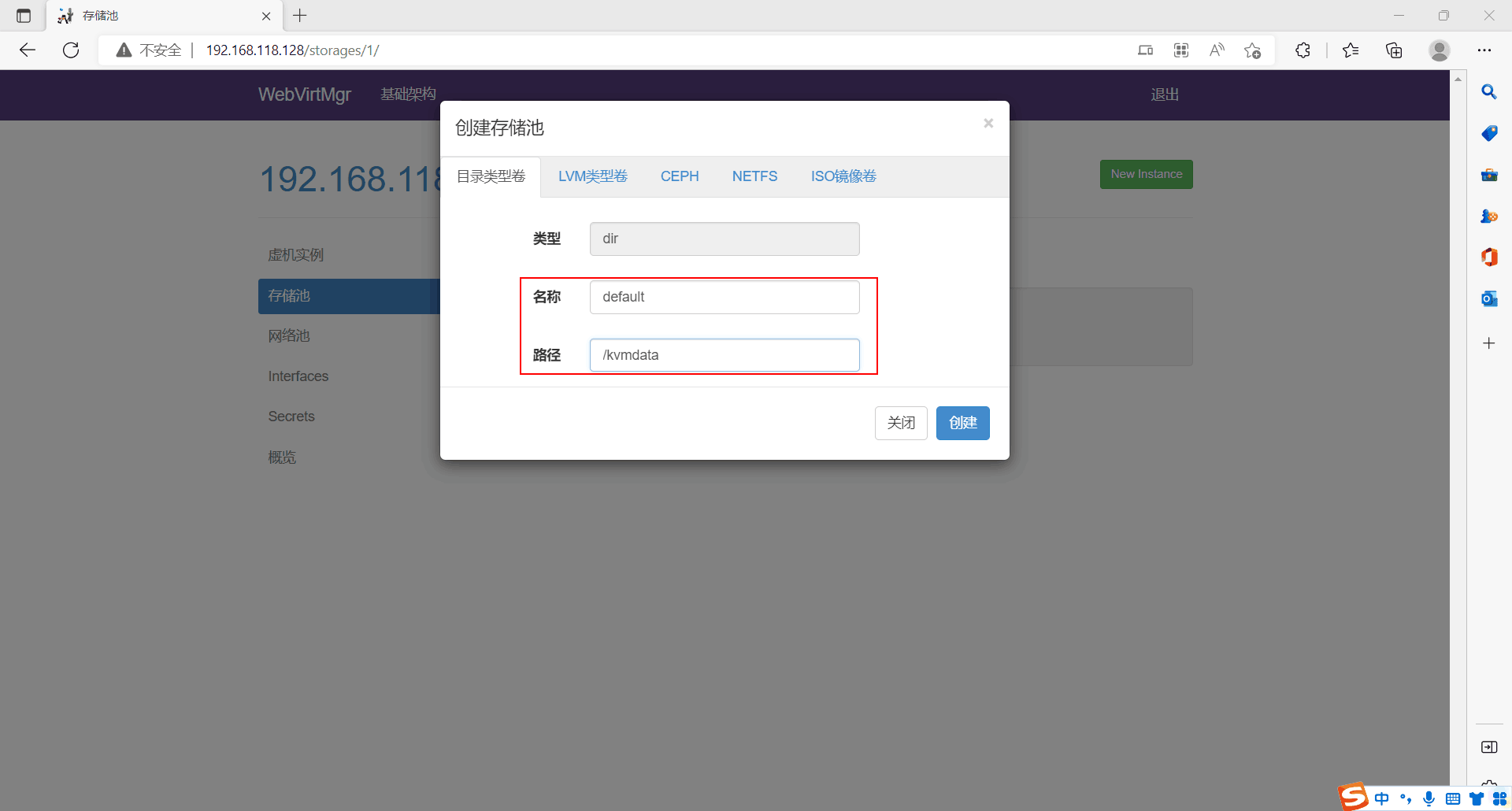
新建主机池
通过工具上传镜像
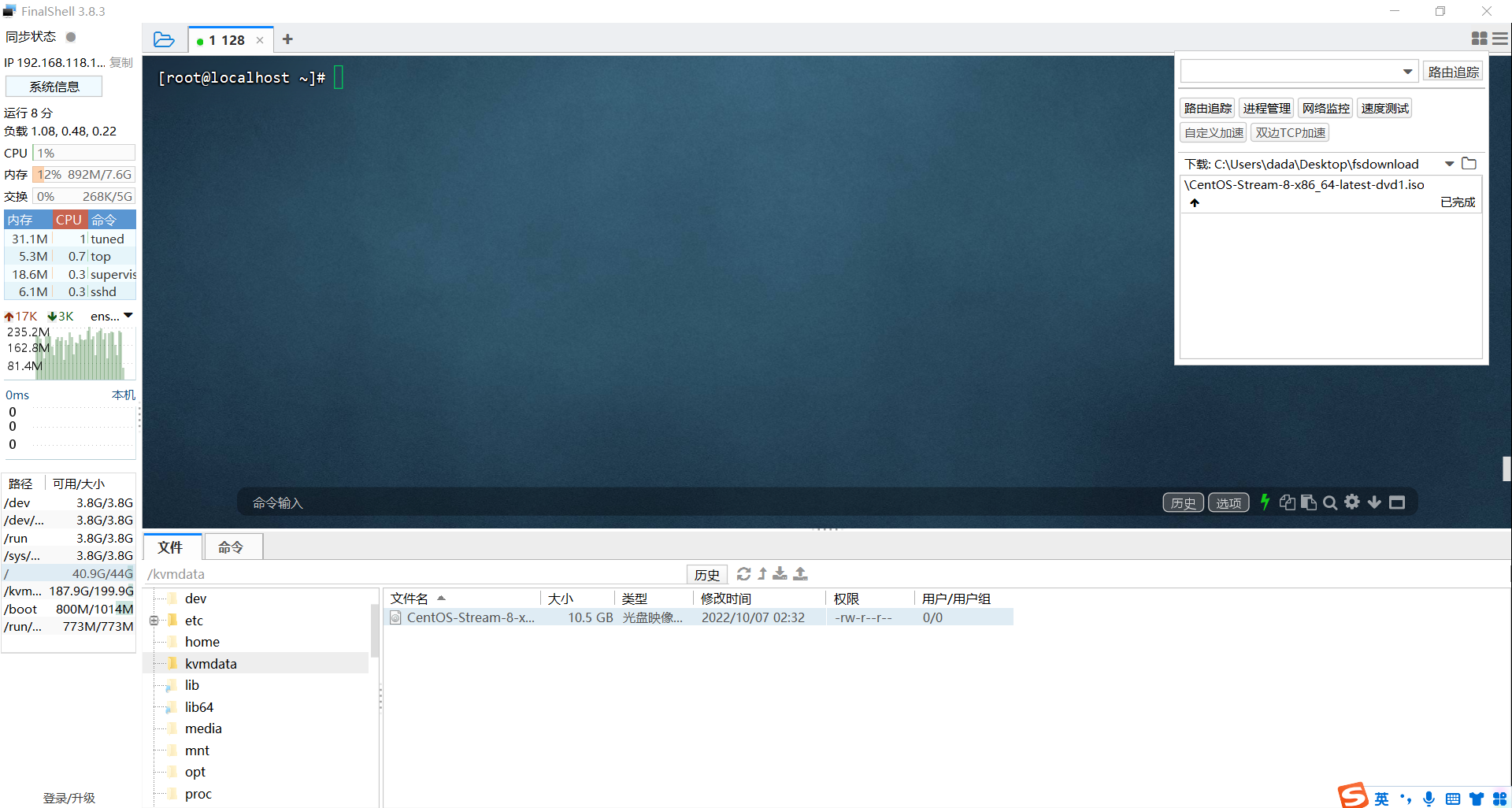
新建镜像
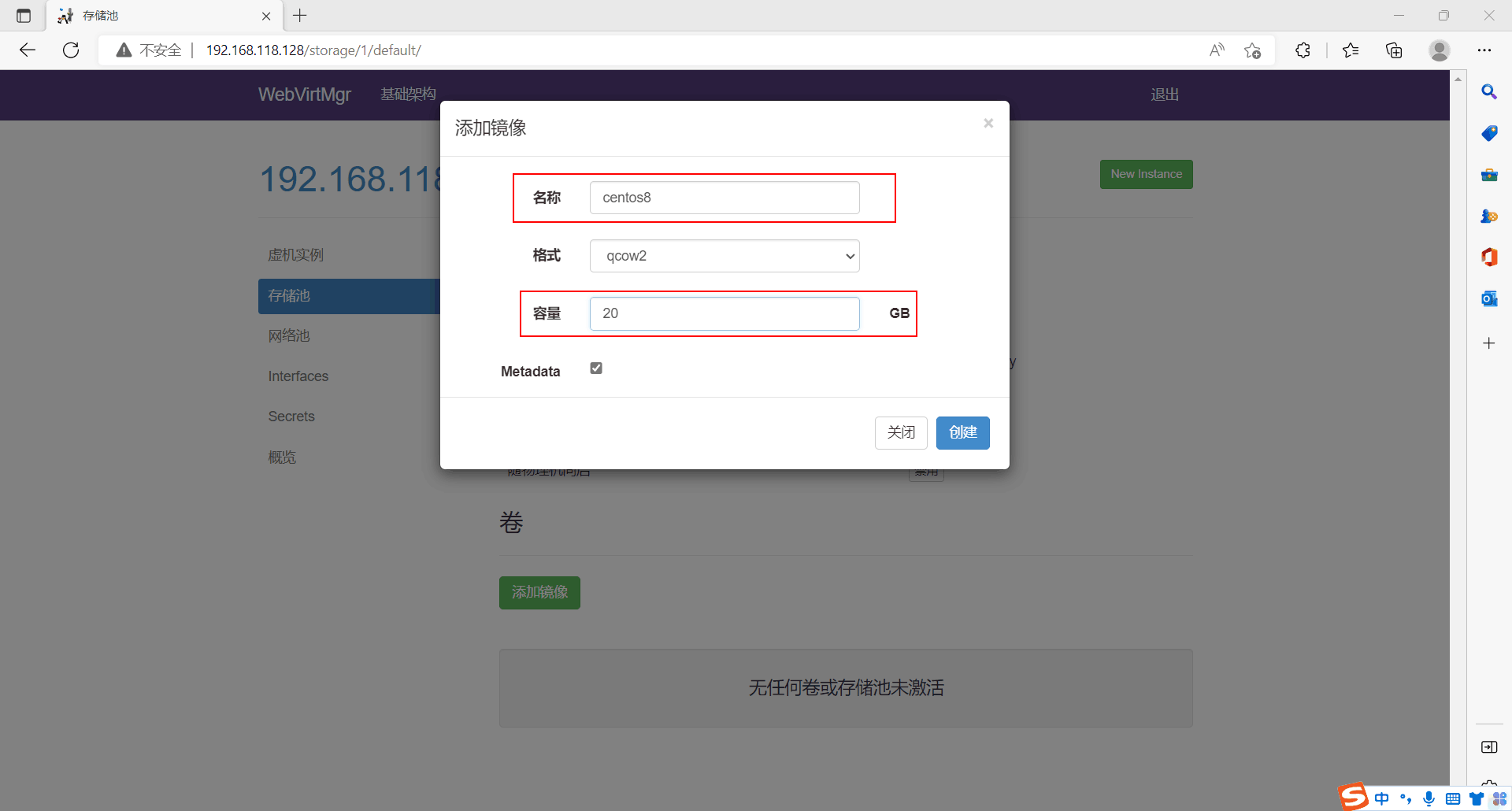
网络池新建网络
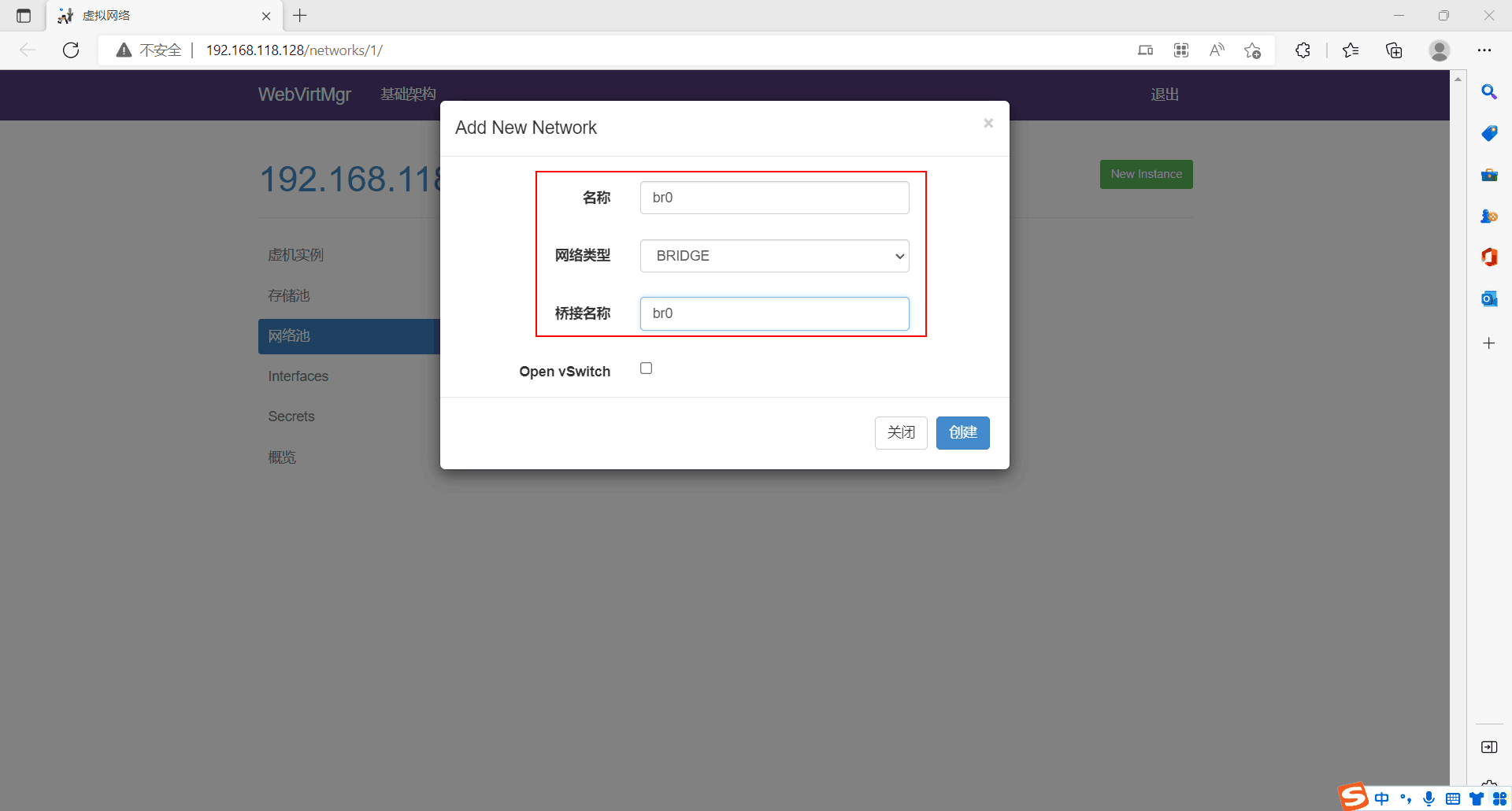
自定义创建虚拟机
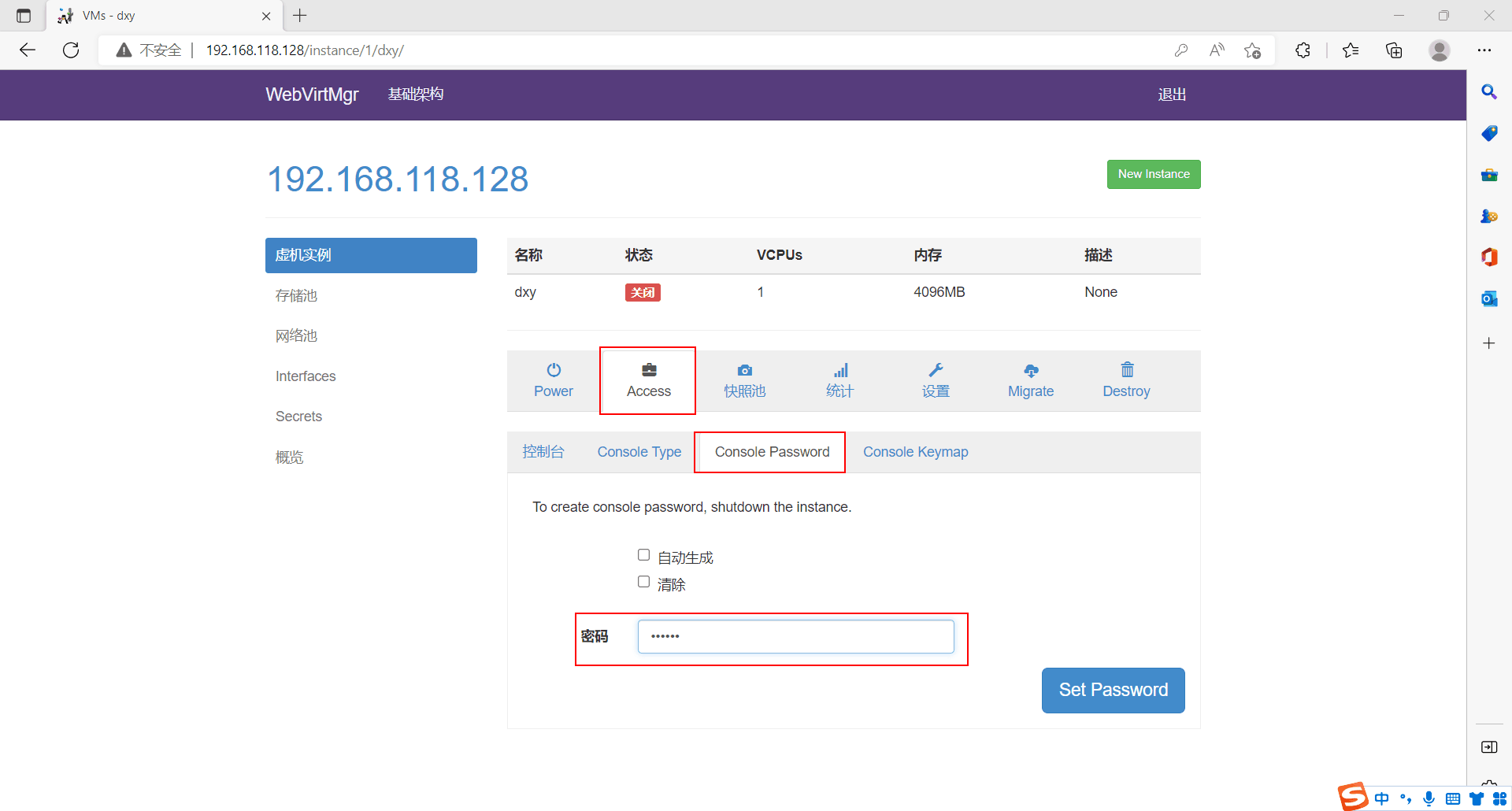
设置网页会话密码
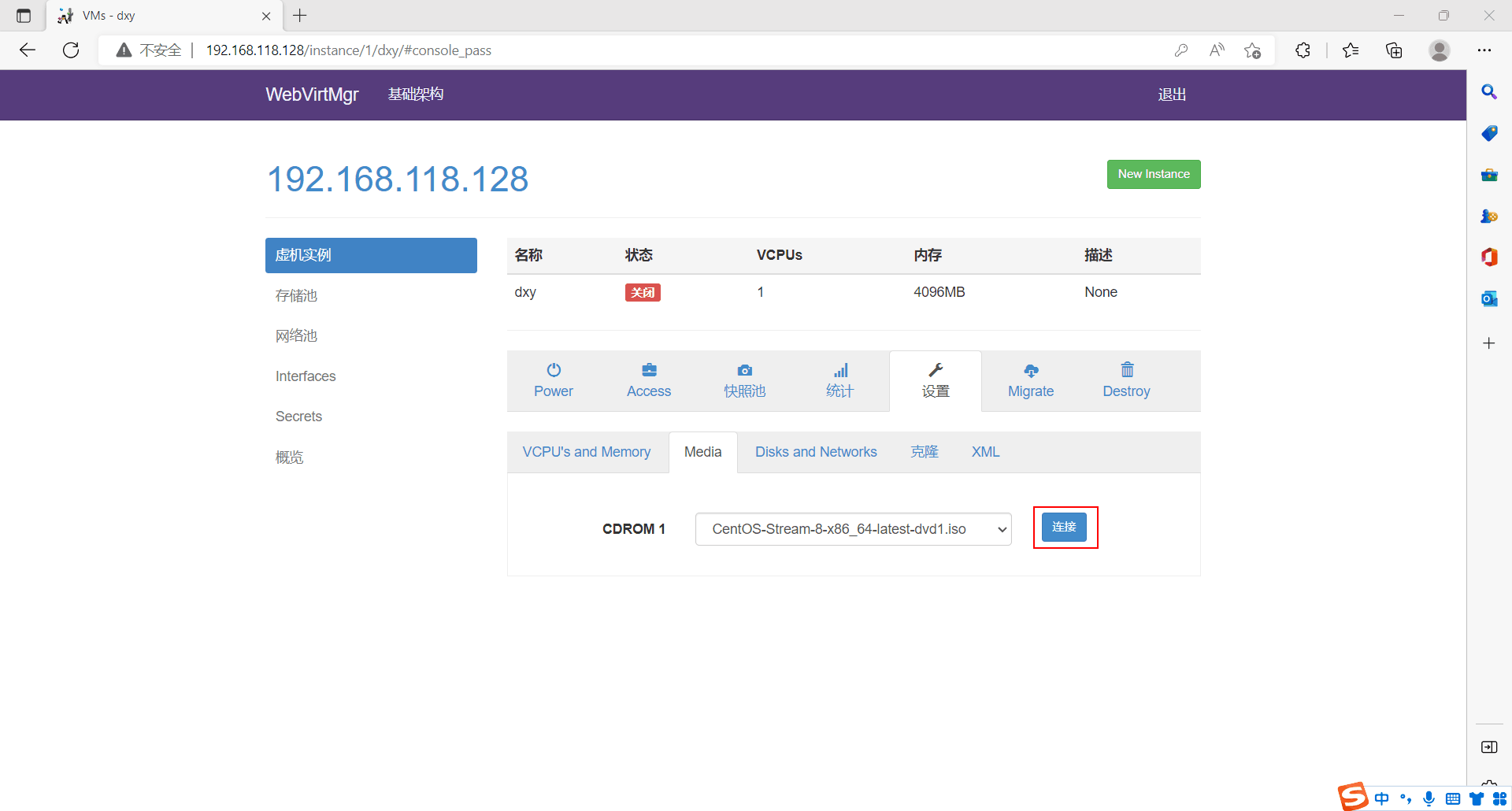
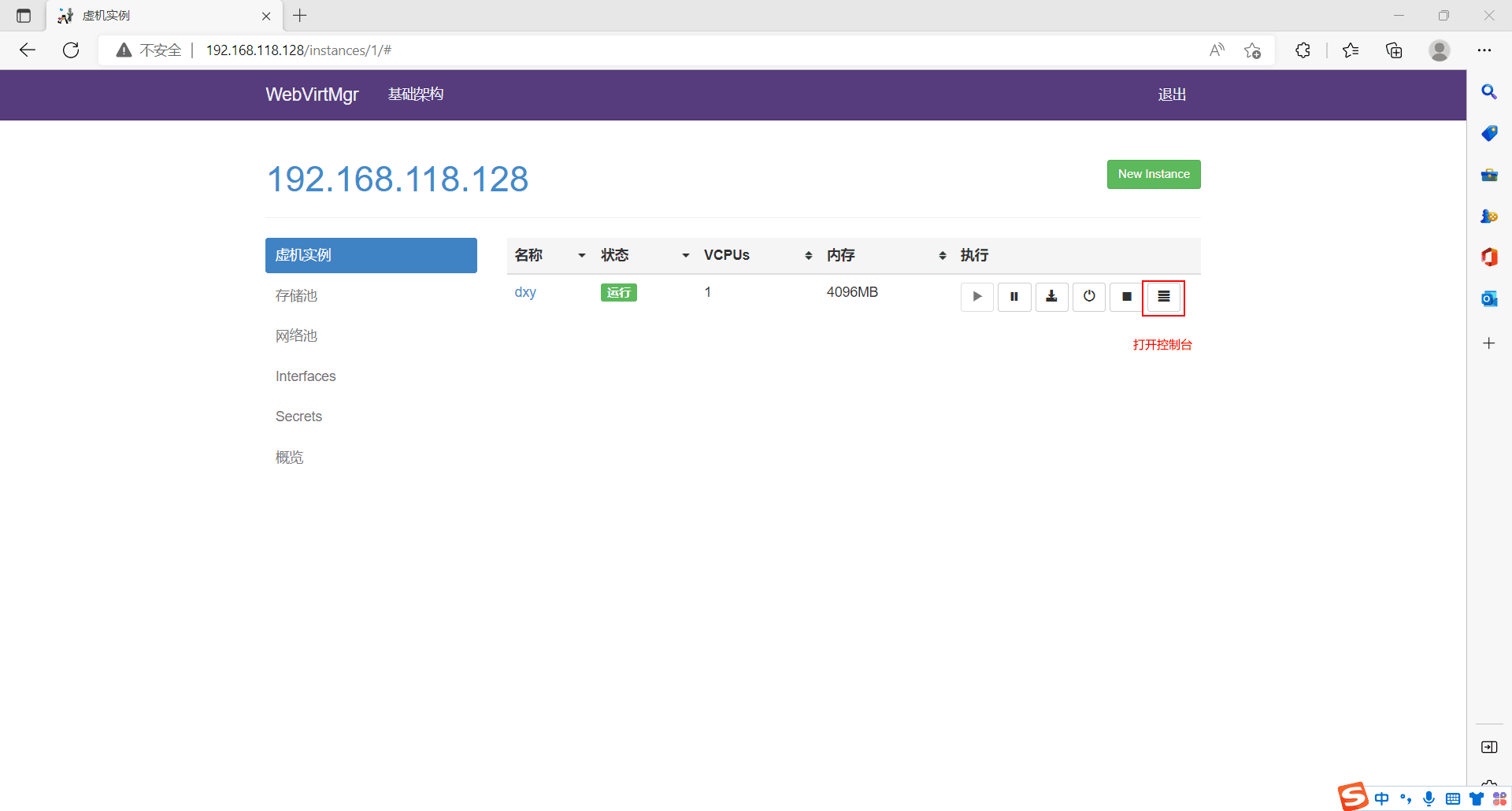
启动主机打开控制台
控制台报错
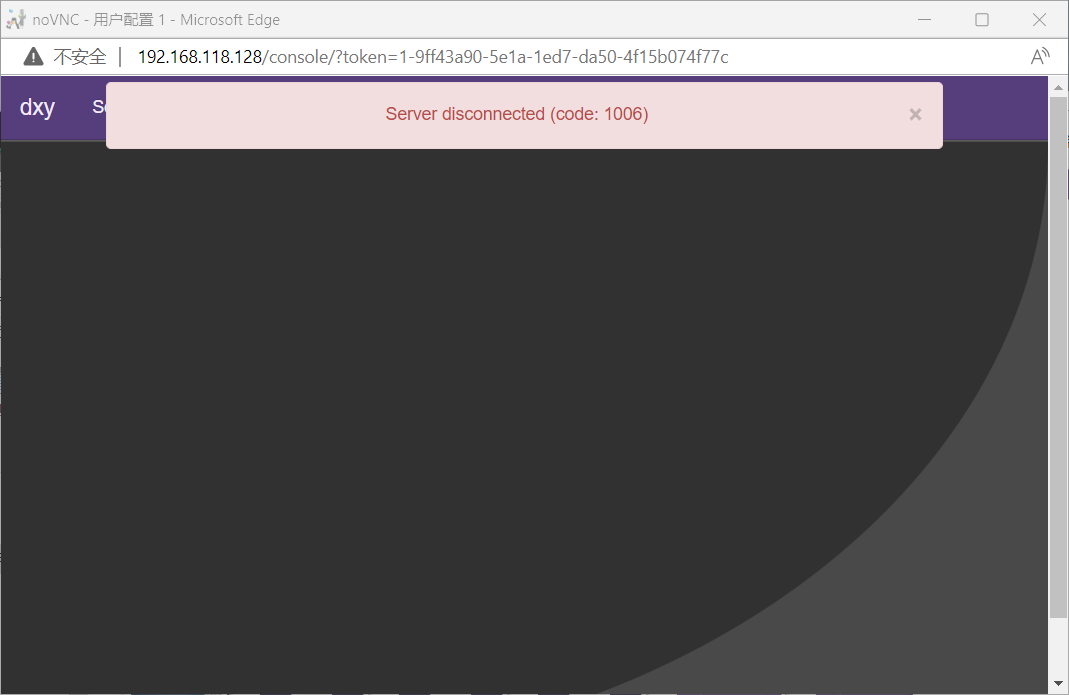
报错解决方法
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install novnc
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@localhost ~]# echo "nohup novnc_server 192.168.118.128:5920 &" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@localhost ~]# . /etc/rc.d/rc.local
开始安装
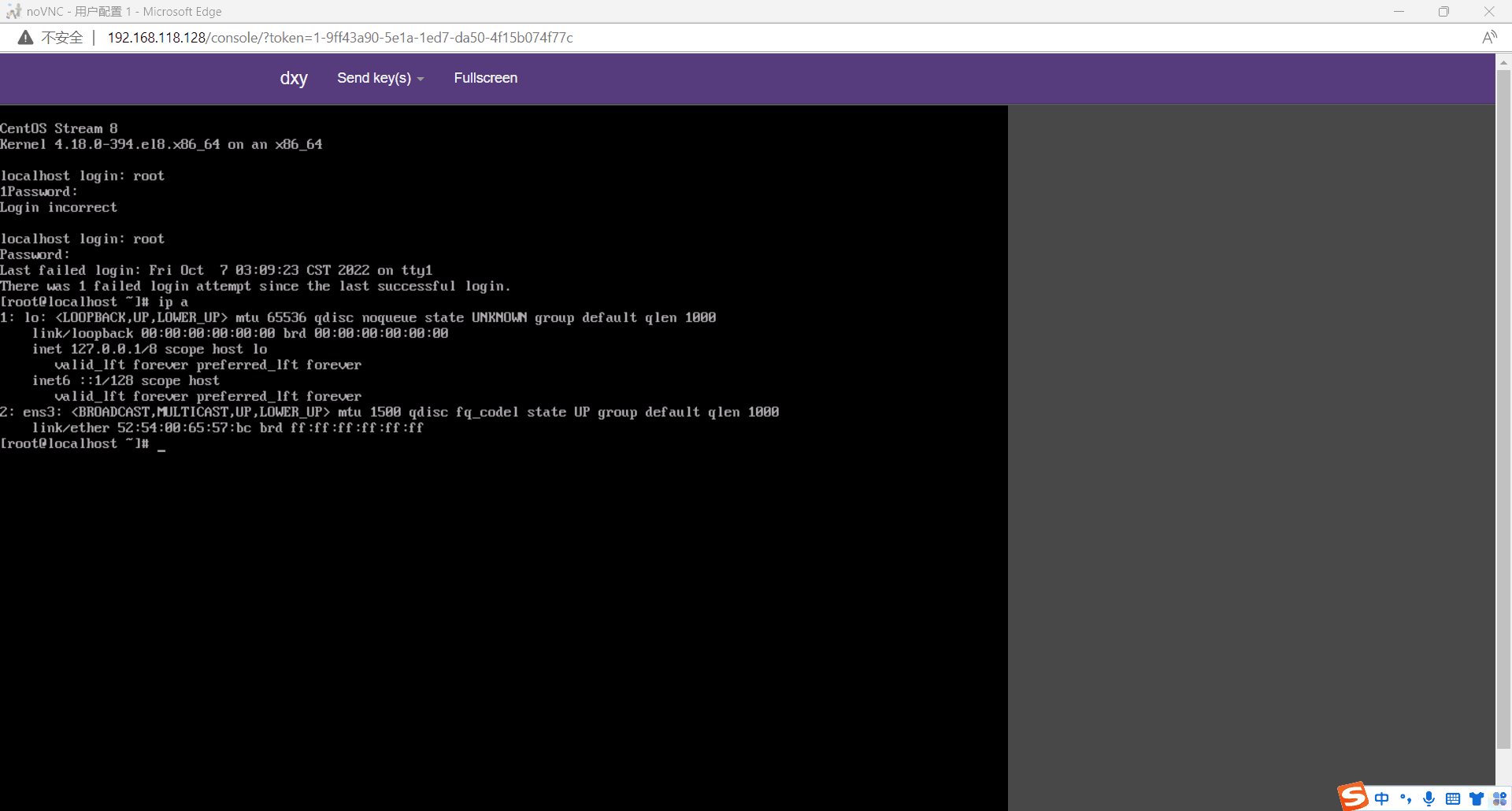
安装完成





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通