平衡树小结
引用一句百经: 在计算机科学中,平衡树能够保持数据有序。这种数据结构能够让查找数据、顺序访问、插入数据及删除的动作,都在对数时间内完成。平衡树,概括来说是一个一般化的二叉查找树(binary search tree),可以拥有多于2个子节点。与自平衡二叉查找树不同,B树为系统大块数据的读写操作做了优化。B树减少定位记录时所经历的中间过程,从而加快存取速度。B树这种数据结构可以用来描述外部存储。这种数据结构常被应用在数据库和文件系统的实现上。
所以看一下二叉查找树的性质。
将序列
换言之,在二叉查找树
这告诉我们:平衡树就是维护一个递增序列,在其上进行各种操作查询。
平衡树的复杂度为
Splay
关于 Splay:
别名伸展树。
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,cnt,siz;
}tree[MAXN];
现在说两个核心操作:
旋转的本质是将某个节点上移一个单位,且必须保证:
- 旋转后的 Splay 中序遍历不变。
- 旋转影响到的节点信息正确有效。
- 节点
设等待旋转至根节点的节点为
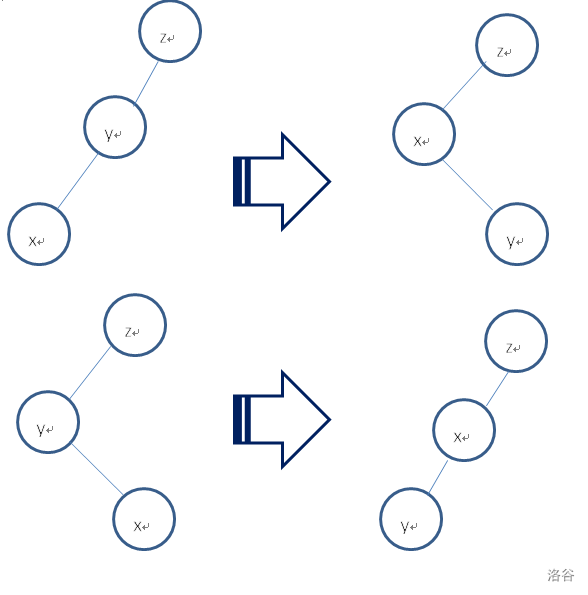
多次试验后发现规律:旋转节点
旋转后子树大小
旋转时重新分配节点父子关系,之后更新有变动的节点
节点
注:此处的父子关系是指左/右儿子。
根据这个规律得到
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[tree[p].son[0]].siz+tree[tree[p].son[1]].siz+tree[p].cnt;
}//重新统计当前节点子树信息。
inline void rotate(int p){
int f1=tree[p].fa;
int f2=tree[f1].fa;
int k=tree[f1].son[1]==p;//令son[0]代表左节点,son[1]为右节点。
//这样可以获取当前节点在父节点中的位置。
tree[f2].son[tree[f2].son[1]==f1]=p;
tree[p].fa=f2;//重新分配 x 为 z 的儿子,位置不变。
tree[f1].son[k]=tree[p].son[k^1];
tree[tree[p].son[k^1]].fa=f1;
tree[p].son[k^1]=f1;
tree[f1].fa=p;//重新分配 y 为 x 的儿子,位置取反。
update(f1),update(p);
}
你要问我如果不存在
Splay 函数时基于
特别的,
我们考虑实现。
如果
- 重复进行以下操作直到
- 终止条件,如果
又令
我们使用图片方便理解这个过程。
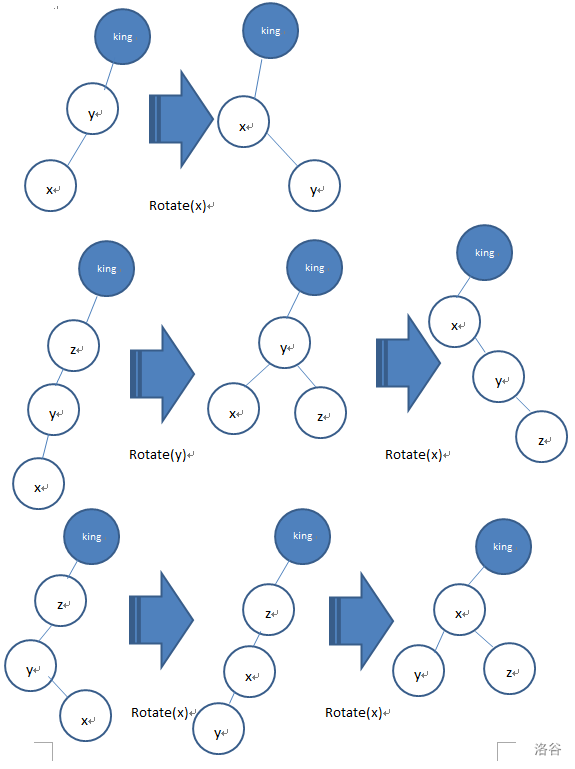
然后就可以看着写出代码。
inline void splay(int p,int king){
while(tree[p].fa!=king){
int f1=tree[p].fa,f2=tree[f1].fa;
if(f2!=king)(tree[f2].son[0]==f1)^(tree[f1].son[0]==p)?rotate(p):rotate(f1);//上文提到的处理方法。
rotate(p);//无论如何当前节点(x)是一定会旋转一次的。
}
if(!king)root=p;//特判上文提到的换根操作。
}
根据这两个操作写出
Q:为什么要将
A:我们回归二叉搜索树的性质,当前节点
- 令递归用节点
- 在当前
- 找到之后将
inline void find(int p){
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
while(tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val]&&p!=tree[u].val)u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
现在来看例题:需要实现以下操作:
- 插入一个元素
- 删除一个元素
- 查询元素
- 查询第
- 查询
插入元素:
由于这是一颗二叉搜索树,所以直接从根节点向下查询
如果发现这是个新点,那么考虑使用动态开点的思想。就地赋予点编号
inline void insert(int p){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=p){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
}
if(u)++tree[u].cnt;
else{
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[p>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].son[0]=tree[u].son[1]=0;
tree[tot].fa=fa;
tree[tot].val=p;
tree[tot].cnt=tree[tot].siz=1;
}
splay(u,0);
}
寻找前驱/后继:
出于二叉搜索树的优秀性质,我们把
注意到本题中节点
inline int nxt(int p,int f){//f是操作类型 0前驱,1后继
find(p);
int u=root;
if((tree[u].val>p&&f)||(tree[u].val<p&&!f))return u;
u=tree[u].son[f];//找到对应儿子
while(tree[u].son[f^1])u=tree[u].son[f^1];
//左儿子的最右儿子与右儿子的最左儿子
return u;
}
删除节点:
我们需要用到当前节点
把
对找到的
此操作可以扩展到一段数,之后说。
inline void Delete(int p){
int last=nxt(p,0),next=nxt(p,1);
splay(last,0);splay(next,last);
int del=tree[next].son[0];
if(tree[del].cnt>1){
--tree[del].cnt;
splay(del,0);
}
else tree[next].son[0]=0;
}
区间第k大
之前维护的
将
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
int lson=tree[u].son[0];
if(x>tree[lson].siz+tree[u].cnt){
x-=tree[lson].siz+tree[u].cnt;
u=tree[u].son[1];
}
else{
if(tree[lson].siz>=x)u=lson;
else{
splay(u,0);
return tree[u].val;
}
}
}
}
如何查询
BT.find(x);
printf("%d\n",BT.tree[BT.tree[BT.root].son[0]].siz);
放一下完整码子。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 200005
using namespace std;
const int inf=1e9;
struct Splay_Tree{
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,cnt,siz;
}tree[MAXN];
int root,tot;
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[tree[p].son[0]].siz+tree[tree[p].son[1]].siz+tree[p].cnt;
}
inline void rotate(int p){
int f1=tree[p].fa;
int f2=tree[f1].fa;
tree[f2].son[tree[f2].son[1]==f1]=p;
tree[p].fa=f2;
int k=tree[f1].son[1]==p;
tree[f1].son[k]=tree[p].son[k^1];
tree[tree[p].son[k^1]].fa=f1;
tree[p].son[k^1]=f1;
tree[f1].fa=p;
update(f1),update(p);
}
inline void splay(int p,int king){
while(tree[p].fa!=king){
int f1=tree[p].fa,f2=tree[f1].fa;
if(f2!=king)(tree[f2].son[0]==f1)^(tree[f1].son[0]==p)?rotate(p):rotate(f1);
rotate(p);
}
if(!king)root=p;
}
inline void find(int p){
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
while(tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val]&&p!=tree[u].val)u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
inline void insert(int p){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=p){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
}
if(u)++tree[u].cnt;
else{
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[p>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].son[0]=tree[u].son[1]=0;
tree[tot].fa=fa;
tree[tot].val=p;
tree[tot].cnt=tree[tot].siz=1;
}
splay(u,0);
}
inline int nxt(int p,int f){
find(p);
int u=root;
if((tree[u].val>p&&f)||(tree[u].val<p&&!f))return u;
u=tree[u].son[f];
while(tree[u].son[f^1])u=tree[u].son[f^1];
return u;
}
inline void Delete(int p){
int last=nxt(p,0),next=nxt(p,1);
splay(last,0);splay(next,last);
int del=tree[next].son[0];
if(tree[del].cnt>1){
--tree[del].cnt;
splay(del,0);
}
else tree[next].son[0]=0;
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
int lson=tree[u].son[0];
if(x>tree[lson].siz+tree[u].cnt){
x-=tree[lson].siz+tree[u].cnt;
u=tree[u].son[1];
}
else{
if(tree[lson].siz>=x)u=lson;
else return tree[u].val;
}
}
}
}BT;
int n;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
BT.insert(inf);
BT.insert(-inf);
while(n--){
int opt,x;
scanf("%d%d",&opt,&x);
if(opt==1)BT.insert(x);
if(opt==2)BT.Delete(x);
if(opt==3){
BT.find(x);
printf("%d\n",BT.tree[BT.tree[BT.root].son[0]].siz);
}
if(opt==4)printf("%d\n",BT.kth(x+1));
if(opt==5)printf("%d\n",BT.tree[BT.nxt(x,0)].val);
if(opt==6)printf("%d\n",BT.tree[BT.nxt(x,1)].val);
}
return 0;
}
记得往里头先加两个极值避免查找前驱后继时溢出。
因为出现了简便做法导致蓝降黄。
提供原先的平衡树做法。
按时间加入元素,在这之前找它的前驱后继比对求和。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 200005
using namespace std;
const int inf=1e9;
struct Splay_Tree{
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val;
}tree[MAXN];
int root,tot;
inline void rotate(int p){
int f1=tree[p].fa;
int f2=tree[f1].fa;
tree[f2].son[tree[f2].son[1]==f1]=p;
tree[p].fa=f2;
int k=tree[f1].son[1]==p;
tree[f1].son[k]=tree[p].son[k^1];
tree[tree[p].son[k^1]].fa=f1;
tree[p].son[k^1]=f1;
tree[f1].fa=p;
}
inline void splay(int p,int king){
while(tree[p].fa!=king){
int f1=tree[p].fa,f2=tree[f1].fa;
if(f2!=king)(tree[f2].son[0]==f1)^(tree[f1].son[0]==p)?rotate(p):rotate(f1);
rotate(p);
}
if(!king)root=p;
}
inline void find(int p){
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
while(tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val]&&p!=tree[u].val)u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
inline void insert(int p){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=p){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
}
if(u)return;
else{
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[p>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].son[0]=tree[u].son[1]=0;
tree[tot].fa=fa;
tree[tot].val=p;
}
splay(u,0);
}
inline int nxt(int p,int f){
find(p);
int u=root;
if((tree[u].val>=p&&f)||(tree[u].val<=p&&!f))return tree[u].val;
u=tree[u].son[f];
while(tree[u].son[f^1])u=tree[u].son[f^1];
return tree[u].val;
}
}BT;
int n,ans;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
BT.insert(inf);
BT.insert(-inf);
for(int i=1,val;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&val);
if(i==1)ans+=val;
else{
int k1=BT.nxt(val,1);
int k2=BT.nxt(val,0);
ans+=min(abs(val-k1),abs(val-k2));
}
BT.insert(val);
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
把上面的板子挪下来就行。
发现还是找前驱后继,但是有两种物品即顾客和宠物,都有可能成为待寻找前驱后继的对象。
然注意到:一种物品存在于平衡树时,另一种物品一定不存在于其中。
所以可以只开一颗平衡树,通过外部维护当前树内物品类型进行操作。
规定
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define MAXN 80005
using namespace std;
int T,cnt,ans;
const int inf=1e18;
const int mod=1000000;
struct Splay_Tree{
#define ls(p) tree[p].son[0]
#define rs(p) tree[p].son[1]
int root,tot;
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,cnt,siz;
}tree[MAXN];
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+tree[p].cnt;
return ;
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
int k=(rs(y)==x);
tree[z].son[rs(z)==y]=x;
tree[x].fa=z;
tree[y].son[k]=tree[x].son[k^1];
tree[tree[x].son[k^1]].fa=y;
tree[x].son[k^1]=y;
tree[y].fa=x;
update(y),update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int king){
while(tree[x].fa!=king){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
if(z!=king)((rs(y)==x)^(rs(z)==y))?rotate(x):rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
if(!king)root=x;
}
inline void insert(int x){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=x){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val];
}
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[x>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].fa=fa;
tree[u].val=x;
tree[u].cnt=tree[u].siz=1;
ls(u)=rs(u)=0;
splay(u,0);
}
inline void find(int x){
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
while(tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val]&&x!=tree[u].val)u=tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
inline int nxt(int x,int f){
find(x);
int u=root;
if((tree[u].val<x&&!f)||(tree[u].val>x&&f))return u;
u=tree[u].son[f];
while(tree[u].son[f^1])u=tree[u].son[f^1];
return u;
}
inline int txn(int x,int f){
find(x);
int u=root;
if((tree[u].val<=x&&!f)||(tree[u].val>x&&f))return u;
u=tree[u].son[f];
while(tree[u].son[f^1])u=tree[u].son[f^1];
return u;
}
inline void Del(int x){
int last=nxt(x,0),next=nxt(x,1);
splay(last,0),splay(next,last);
ls(next)=0;
}
}BT;
signed main(){
scanf("%lld",&T);
BT.insert(-inf),BT.insert(inf);
while(T--){
int opt,val;
scanf("%lld%lld",&opt,&val);
if(!cnt)BT.insert(val);
if(cnt<0){
if(!opt)BT.insert(val);
else{
int k0=BT.txn(val,0),k1=BT.txn(val,1);
int v0=BT.tree[k0].val,v1=BT.tree[k1].val;
if(val-v0<=v1-val)BT.Del(v0),ans=(ans+(val-v0)%mod)%mod;
else BT.Del(v1),ans=(ans+(v1-val)%mod)%mod;
}
}
if(cnt>0){
if(opt)BT.insert(val);
else{
int k0=BT.txn(val,0),k1=BT.txn(val,1);
int v0=BT.tree[k0].val,v1=BT.tree[k1].val;
if(val-v0<=v1-val)BT.Del(v0),ans=(ans+(val-v0)%mod)%mod;
else BT.Del(v1),ans=(ans+(v1-val)%mod)%mod;
}
}
cnt+=(opt?1:-1);
}
printf("%lld",ans);
return 0;
}
细节:规定了宠物间与顾客间的权值各不相同,但没有规定宠物与顾客间的权值不同,因此在
上文提到的 Splay 为 权值 Splay。事实上 Splay 也可以进行区间操作。
从序列中提取区间
当我们需要区间
inline int split(int l,int r){
l=kth(l),r=kth(r+2);
splay(l,0);
splay(r,l);
return tree[r].son[0];
}
由于树中已经有节点
区间修改
参考线段树,首先需要一个
也就是上文板子中的
修改可以使用线段树同款懒标记
inline void spread(int p){
if(tree[p].tag){
tree[ls(p)].val+=tree[p].tag*tree[ls(p)].siz;
tree[rs(p)].val+=tree[p].tag*tree[rs(p)].siz;
tree[ls(p)].tag=1;
tree[rs(p)].tag=1;
tree[p].tag=0;
}
}
给定一个序列与
我们发现将序列中的节点安排给一些父节点后,反转一段区间就是把管辖他们的所有父亲节点的左右儿子反转。
规定
inline void spread(int p){
if(tree[p].tag){
swap(ls(p),rs(p));
tree[ls(p)].tag^=1;
tree[rs(p)].tag^=1;
tree[p].tag=0;
}
}
由于没有查询操作,
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 200005
using namespace std;
int n,m;
struct Splay_Tree{
#define ls(p) tree[p].son[0]
#define rs(p) tree[p].son[1]
int root,tot;
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,siz;
int tag;
}tree[MAXN];
inline void push_up(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+1;
}
inline void spread(int p){
if(tree[p].tag){
swap(ls(p),rs(p));
tree[ls(p)].tag^=1;
tree[rs(p)].tag^=1;
tree[p].tag=0;
}
}
inline void rotate(int p){
int f1=tree[p].fa;
int f2=tree[f1].fa;
int k=tree[f1].son[1]==p;
tree[f2].son[rs(f2)==f1]=p;
tree[p].fa=f2;
tree[f1].son[k]=tree[p].son[k^1];
tree[tree[p].son[k^1]].fa=f1;
tree[p].son[k^1]=f1;
tree[f1].fa=p;
push_up(f1),push_up(p);
}
inline void splay(int p,int king){
while(tree[p].fa!=king){
int f1=tree[p].fa,f2=tree[f1].fa;
if(f2!=king)(tree[f2].son[1]==f1)^(tree[f1].son[1]==p)?rotate(p):rotate(f1);
rotate(p);
}
if(!king)root=p;
}
inline void insert(int p){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=p){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[p>tree[u].val];
}
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[p>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].son[0]=tree[u].son[1]=0;
tree[u].fa=fa;
tree[u].siz=1;
tree[u].val=p;
splay(u,0);
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
spread(u);
if(x>tree[ls(u)].siz+1){
x-=tree[ls(u)].siz+1;
u=rs(u);
}
else{
if(tree[ls(u)].siz>=x)u=ls(u);
else return tree[u].val;
}
}
}
inline void Reserve(int l,int r){//split 函数可以就地包进别的函数里
l=kth(l),r=kth(r+2);
splay(l,0);
splay(r,l);
tree[ls(rs(root))].tag^=1;
}
inline void print(int p){
spread(p);
if(ls(p))print(ls(p));
if(tree[p].val>1&&tree[p].val<n+2)printf("%d ",tree[p].val-1);
if(rs(p))print(rs(p));
}
}BT;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n+2;i++)BT.insert(i);
for(int i=1,l,r;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
BT.Reserve(l,r);
}
BT.print(BT.root);
return 0;
}
题意:维护一种数据结构,能够添加权值为
注意到只有扣工资时才可能有员工离职,且员工的工资是同升同降的。
不妨转而考虑
如果某个员工的初始工资低于最低工资标准,那么将不计入最后的答案内。
如何实现踢人?每次减工资使用
规定变量
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 300005
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,nval,delta,tmp;
const int inf=1e18;
struct Splay_Tree{
#define ls(p) tree[p].son[0]
#define rs(p) tree[p].son[1]
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,siz,cnt;
}tree[MAXN];
int tot,root;
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+tree[p].cnt;
return;
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
int k=(rs(y)==x);
tree[z].son[rs(z)==y]=x;
tree[x].fa=z;
tree[y].son[k]=tree[x].son[k^1];
tree[tree[x].son[k^1]].fa=y;
tree[x].son[k^1]=y;
tree[y].fa=x;
update(y),update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int king){
while(tree[x].fa!=king){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
if(z!=king)((rs(z)==y)^(rs(y)==x))?rotate(x):rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
if(!king)root=x;
}
inline void insert(int x){
int u=root,fa=0;
while(u&&tree[u].val!=x){
fa=u;
u=tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val];
}
if(u)++tree[u].cnt;
else{
u=++tot;
if(fa)tree[fa].son[x>tree[fa].val]=u;
tree[u].fa=fa;
tree[u].val=x;
tree[u].siz=tree[u].cnt=1;
ls(u)=rs(u)=0;
}
splay(u,0);
}
inline void find(int x){
int u=root;
if(!u)return;
u=tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val];
while(tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val])u=tree[u].son[x>tree[u].val];
splay(u,0);
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
if(x>tree[ls(u)].siz+tree[u].cnt){
x-=tree[ls(u)].siz+tree[u].cnt;
u=rs(u);
}
else{
if(tree[ls(u)].siz>=x)u=ls(u);
else{
splay(u,0);
return tree[u].val;
}
}
}
}
inline void Del(){
int x=root,u=root,val=nval-delta;
while(x){
if(tree[x].val<val)x=rs(x);
else u=x,x=ls(x);
}
if(tree[u].val<val){
root=0;
return ;
}
splay(u,0);
ls(u)=0;//不用一个一个点删,直接断掉儿子就行了
update(u);
}
}BT;
signed main(){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&nval);
for(int i=1,val;i<=n;i++){
char opt[5];
scanf("%s%lld",opt+1,&val);
if(opt[1]=='I'){
if(val>=nval){
++tmp;
BT.insert(val-delta);
}
}
if(opt[1]=='A')delta+=val;
if(opt[1]=='S')delta-=val,BT.Del();
if(opt[1]=='F'){
if(val>BT.tree[BT.root].siz)printf("-1\n");
else printf("%lld\n",BT.kth(BT.tree[BT.root].siz-val+1)+delta);
}
}
printf("%lld",tmp-BT.tree[BT.root].siz);
return 0;
}
题意:给定一个字符串,要求实现以下操作:替换或添加一个字符,求两个字符的最长公共前缀
序列比对考虑 hash,然求最长,注意到单调性,考虑二分。
序列上的操作显然是平衡树,如何用平衡树维护 hash?
考虑区间 Splay。中序遍历不变则左子树维护当前位前的字符,右子树维护当前位后。
关于替换操作:将待转换位
如何插入新点:由于要插到
注意插入两个极值。
还有一个大坑:出现插入操作后
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAXN 150005
#define ull unsigned long long
#define int long long
using namespace std;
char str[MAXN];
ull pw[MAXN];
const int p=131;
int n,m;
struct Splay_Tree{
#define ls(p) tree[p].son[0]
#define rs(p) tree[p].son[1]
int tot,root;
struct TREE{
int fa,son[2];
int val,siz;
ull has;
}tree[MAXN];
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+1;
tree[p].has=tree[rs(p)].has+(ull)tree[p].val*pw[tree[rs(p)].siz]+tree[ls(p)].has*pw[tree[rs(p)].siz+1];
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
int k=(rs(y)==x);
tree[x].fa=z;
tree[z].son[rs(z)==y]=x;
tree[tree[x].son[k^1]].fa=y;
tree[y].son[k]=tree[x].son[k^1];
tree[y].fa=x;
tree[x].son[k^1]=y;
update(y);
update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int king){
while(tree[x].fa!=king){
int y=tree[x].fa,z=tree[y].fa;
if(z!=king)((rs(y)==x)^(rs(z)==y))?rotate(x):rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
if(!king)root=x;
}
inline void build(int l,int r,int x){
if(l>r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
tree[x].son[mid>=x]=mid;
tree[mid].fa=x,tree[mid].siz=1;
if(l==r)return;
build(l,mid-1,mid);
build(mid+1,r,mid);
update(mid);
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
if(x==tree[ls(u)].siz+1)return u;
else if(x>tree[ls(u)].siz+1)x-=tree[ls(u)].siz+1,u=rs(u);
else u=ls(u);
}
}
inline ull gethas(int l,int r){
int k0=kth(l),k1=kth(r+2);
splay(k0,0),splay(k1,k0);
return tree[ls(rs(root))].has;
}
inline void insert(char ch){
ls(rs(root))=++tot;
tree[tot].fa=rs(root);
tree[tot].val=tree[tot].has=ch;
splay(tot,0);
}
}BT;
signed main(){
pw[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<MAXN;i++)pw[i]=pw[i-1]*p;
scanf("%s%lld",str+1,&m);
n=strlen(str+1);
for(int i=2;i<=n+1;i++)BT.tree[i].val=BT.tree[i].has=str[i-1];
BT.build(1,n+2,BT.root);
BT.root=(n+3)>>1;
BT.tot=n+2;
for(int i=1,x,y;i<=m;i++){
char opt[3],ch[3];
scanf("%s",opt+1);
if(opt[1]=='Q'){
scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y);
if(x>y)swap(x,y);
int l=0,r=(BT.tot-2-y+1),res=0;//就是这块有坑!
while(r>=l){
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(BT.gethas(x,x+mid-1)==BT.gethas(y,y+mid-1))res=mid,l=mid+1;
else r=mid-1;
}
printf("%lld\n",res);
}
if(opt[1]=='R'){
scanf("%lld%s",&x,ch+1);
int k=BT.kth(x+1);
BT.splay(k,0);
BT.tree[k].val=ch[1];
BT.update(k);
}
if(opt[1]=='I'){
scanf("%lld%s",&x,ch+1);
int k0=BT.kth(x+1),k1=BT.kth(x+2);
BT.splay(k0,0);
BT.splay(k1,k0);
BT.insert(ch[1]);
}
}
return 0;
}
改多测获取双倍经验。
update:2024.2.28。
关于平衡树的建树
当初始时已经给出序列,可以使用
注意到线段树中的递归建树技巧是可以沿袭的,对于区间
inline void build(int l,int r,int x){
if(l>r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
tree[mid].fa=x;
tree[x].son[mid>=x]=mid;
tree[mid].val=mid;
tree[mid].siz=1;
tree[mid].rev=0;
if(l==r)return;
build(l,mid-1,mid);
build(mid+1,r,mid);
update(mid);
}
另一核心操作
上文的
提取区间
可以改写
inline void insert(int x,int p){
int k0=kth(x),k1=kth(x+1);
splay(k0,0),splay(k1,k0);
ls(rs(root))=++tot;
tree[tot].fa=k1;
tree[tot].val=p,tree[tot].siz=1;
...
}
Treap
与Splay不同,Treap 的特点是能实现可持久化,但是时间复杂度看脸,大多数情况保持在
Treap 分为 有旋 Treap 和 无旋 Treap。
上文对 Splay 的介绍中可以发现:同一中序遍历对应的树有很多棵。
平衡树为了保证查询节点的时间复杂度,会通过一些操作使得任意节点的子树高度差不超过 1。Splay 的
Treap 在保证 BST 结构的基础之上,通过给节点随机权值实现随机安排父子关系,由于数据的随机性导致了权值大小分布一定程度上平衡。
因此 Treap 实际的复杂度显然会大于
我在网上没有找到 Treap 时间复杂度的严格证明。不过想当然地,只要随机出的序列不是基本严格递增的,那么 Treap 的复杂度不可能退化到
带旋 Treap 需要大量指针,我晕针,介绍无旋 Treap:FHQ_Treap
权值 FHQ_Treap:例题。
核心操作:
我们按照
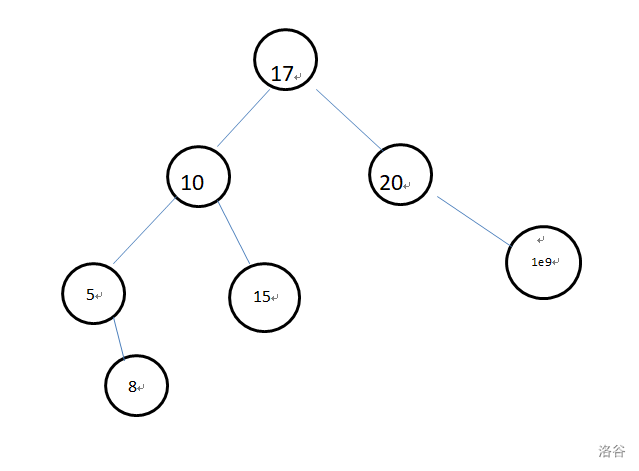
则分裂后的平衡树如下:
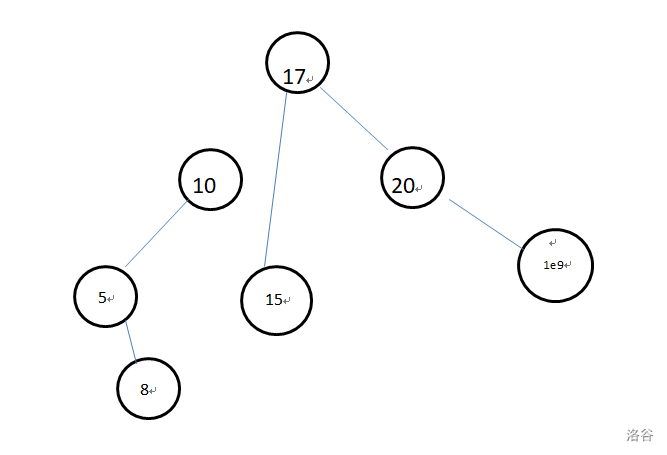
分裂后可以获得两棵子树的根节点编号,研究如何分裂:
考虑从根节点递归分裂,将点权小于
于是使用取址符递归传参。具体地,规定
此时
特别地,如果当前阶段的分裂已经完成,也就是
提供代码。
inline void split(int val,int p,int &x,int &y){
if(!p){
x=y=0;
return;
}
if(val>=tree[p].val){
x=p;
split(val,rs(p),rs(p),y);
}
else if(val<tree[p].val){
y=p;
split(val,ls(p),x,ls(p));
}
update(p);
}
核心操作:
显然也是要递归合并的,由于分裂时已经按照权值分裂了,所以依次合并时 BST 的性质是不变的,
写法和线段树合并很像。
inline int merge(int x,int y){//x 为左节点,y右节点
if(!x||!y)return x^y;
if(tree[x].key>tree[y].key){
rs(x)=merge(rs(x),y);
update(x);
return x;
}
else{
ls(y)=merge(x,ls(y));
update(y);
return y;
}
}
这里注意,平衡树
现在来看例题:需要实现以下操作:
- 插入一个元素
- 删除一个元素
- 查询元素
- 查询第
- 查询
莫名熟悉(?
插入元素:
FHQ_Treap 的码量优势在此体现。插入权值
inline int newnode(int val){
tree[++tot].val=val;
tree[tot].lson=tree[tot].rson=0;
tree[tot].siz=1;
tree[tot].key=rng();
return tot;
}
造好之后把点编号
inline void insert(int val){
int x=0,y=0;
split(val,root,x,y);
root=merge(x,merge(newnode(val),y));
}
删除节点:
不难想,把树按照删除值
并且此时
inline void Delete(int val){
int x=0,y=0,z=0;
split(val,root,x,y);
split(val-1,root,x,y);
split(val,y,y,z);
y=merge(ls(y),rs(y));
root=merge(x,merge(y,z));
}
区间第k大
只要是一颗 BST 那么查找方式固定,跟着维护
查询
inline int getrk(int val){
int x=0,y=0,res;
split(val-1,root,x,y);
res=tree[x].siz+1;
root=merge(x,y);
return res;
}
寻找前驱/后继:
很容易发现,
在 FHQ_Treap 中,寻找前驱可以按
inline int nxt(int val,int f){//0 q 1 h
int v[2]={0,0};
split(val-(f^1),root,v[0],v[1]);
int u=v[f];
while(f?ls(u):rs(u))u=f?ls(u):rs(u);
int res=tree[u].val;
root=merge(v[0],v[1]);
return res;
}
提供完整代码。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define MAXN 100005
using namespace std;
int n,m;
std::mt19937 rng(114514);
struct FHQ{
#define ls(p) tree[p].lson
#define rs(p) tree[p].rson
struct TREE{
int lson,rson;
int val,siz,key;
}tree[MAXN];
int tot,root;
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+1;
}
inline int newnode(int val){
tree[++tot].val=val;
tree[tot].lson=tree[tot].rson=0;
tree[tot].siz=1;
tree[tot].key=rng();
return tot;
}
inline void split(int val,int p,int &x,int &y){
if(!p){
x=y=0;
return;
}
if(val>=tree[p].val){
x=p;
split(val,rs(p),rs(p),y);
}
else if(val<tree[p].val){
y=p;
split(val,ls(p),x,ls(p));
}
update(p);
}
inline int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x^y;
if(tree[x].key>tree[y].key){
rs(x)=merge(rs(x),y);
update(x);
return x;
}
else{
ls(y)=merge(x,ls(y));
update(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int val){
int x=0,y=0;
split(val,root,x,y);
root=merge(x,merge(newnode(val),y));
}
inline void Delete(int val){
int x=0,y=0,z=0;
split(val-1,root,x,y);
split(val,y,y,z);
y=merge(ls(y),rs(y));
root=merge(x,merge(y,z));
}
inline int getrk(int val){
int x=0,y=0,res;
split(val-1,root,x,y);
res=tree[x].siz+1;
root=merge(x,y);
return res;
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
if(tree[ls(u)].siz+1==x)return tree[u].val;
else if(tree[ls(u)].siz>=x)u=ls(u);
else x-=tree[ls(u)].siz+1,u=rs(u);
}
}
inline int nxt(int val,int f){//0 q 1 h
int v[2]={0,0};
split(val-(f^1),root,v[0],v[1]);
int u=v[f];
while(f?ls(u):rs(u))u=f?ls(u):rs(u);
int res=tree[u].val;
root=merge(v[0],v[1]);
return res;
}
}BT;
int T;
signed main(){
scanf("%lld",&T);
while(T--){
int opt,x;
scanf("%lld%lld",&opt,&x);
if(opt==1)BT.insert(x);
else if(opt==2)BT.Delete(x);
else if(opt==3)printf("%lld\n",BT.getrk(x));
else if(opt==4)printf("%lld\n",BT.kth(x));
else if(opt==5)printf("%lld\n",BT.nxt(x,0));
else printf("%lld\n",BT.nxt(x,1));
}
return 0;
}
码量明显少于 Splay。
同理地,Treap 也可以实现区间操作。
不难想,在 FHQ_Treap 中提取一段区间
注意到一旦左右儿子进行翻转,BST 的性质会被破坏,之后再跑的时候就会出问题。
引入技巧:考虑按子树大小分裂。
我们需要把当前中序遍历下的前
inline void split(int val,int p,int &x,int &y){
if(!p){
x=y=0;
return;
}
spread(p);
if(tree[ls(p)].siz+1<=val){
x=p;
split(val-tree[ls(p)].siz-1,rs(p),rs(p),y);
}
else{
y=p;
split(val,ls(p),x,ls(p));
}
update(p);
}
别的不变。
例题
显然对于每次于
其中
不过序列是动态的,这意味着不能使用
注意到
于是考虑先用平衡树构造完整序列,获得每个点的添加次序,开线段树维护
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define MAXN 100005
using namespace std;
int n;
std::mt19937 rng(1919810);
struct FHQ_Treap{
#define ls(p) tree[p].lson
#define rs(p) tree[p].rson
struct TREE{
int lson,rson;
int val,siz;
int key;
}tree[MAXN];
int root,tot;
inline void update(int p){
tree[p].siz=tree[ls(p)].siz+tree[rs(p)].siz+1;
}
inline int newnode(int val){
tree[++tot].val=val;
tree[tot].siz=1;
tree[tot].key=rng();
ls(tot)=rs(tot)=0;
return tot;
}
inline void split(int val,int p,int &x,int &y){
if(!p){
x=y=0;
return;
}
if(tree[ls(p)].siz+1<=val){
x=p;
split(val-tree[ls(p)].siz-1,rs(p),rs(p),y);
}
else{
y=p;
split(val,ls(p),x,ls(p));
}
update(p);
}
inline int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x^y;
if(tree[x].key>=tree[y].key){
ls(y)=merge(x,ls(y));
update(y);
return y;
}
else{
rs(x)=merge(rs(x),y);
update(x);
return x;
}
}
inline void insert(int loc,int val){
int x=0,y=0;
split(loc,root,x,y);
root=merge(x,merge(newnode(val),y));
}
inline int kth(int x){
int u=root;
if(tree[u].siz<x)return 0;
while(1){
if(x==tree[ls(u)].siz+1)return u;
else if(x<tree[ls(u)].siz+1)u=ls(u);
else x-=tree[ls(u)].siz+1,u=rs(u);
}
}
}BT;
int Loc[MAXN];
int ans;
struct Segment_Tree{
#define lsn(p) p<<1
#define rsn(p) p<<1|1
#define push_up(p) tree[p].val=max(tree[lsn(p)].val,tree[rsn(p)].val)
struct TREE{
int l,r;
int val;
}tree[MAXN<<2];
inline void build(int l,int r,int p){
tree[p].l=l,tree[p].r=r,tree[p].val=0;
if(l==r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build(l,mid,lsn(p));
build(mid+1,r,rsn(p));
}
inline void update(int x,int k,int p){
if(tree[p].l==tree[p].r){
tree[p].val=k;
return;
}
int mid=tree[p].l+tree[p].r>>1;
if(x<=mid)update(x,k,lsn(p));
else update(x,k,rsn(p));
push_up(p);
}
inline int query(int l,int r,int p){
if(tree[p].l>=l&&tree[p].r<=r)return tree[p].val;
int mid=tree[p].l+tree[p].r>>1;
int res=0;
if(l<=mid)res=max(res,query(l,r,lsn(p)));
if(r>mid)res=max(res,query(l,r,rsn(p)));
return res;
}
}ST;
signed main(){
// #define wzw sb
#ifdef wzw
freopen("1.in","r",stdin);
#endif
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=1,x;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&x);
BT.insert(x,i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)Loc[BT.tree[BT.kth(i)].val]=i;
ST.build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(Loc[i]==1)ans=max(ans,(int)1),ST.update(1,1,1);
else{
int tmp=ST.query(1,Loc[i]-1,1);
ans=max(ans,tmp+1);
ST.update(Loc[i],tmp+1,1);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了