POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(倍增)
题目
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
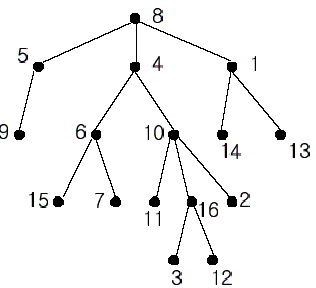
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2 16 1 14 8 5 10 16 5 9 4 6 8 4 4 10 1 13 6 15 10 11 6 7 10 2 16 3 8 1 16 12 16 7 5 2 3 3 4 3 1 1 5 3 5
Sample Output
4 3
题解
倍增模版题
AC代码
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAX = 10000 + 10; const int LOG = 16; int cnt = 0; int head[MAX]; bool vis[MAX]; //找root //-------存边---------- struct Edge{ int to,next; }edge[MAX]; void addedge(int u, int v){ edge[cnt].next = head[u]; //存的是在next边在edge中的下标 edge[cnt].to = v; //to指向点 head[u] = cnt++; } //-----初始化anc[x][0]和深度------- int dep[MAX]; int anc[MAX][LOG]; void dfs(int u, int p, int d){ //p代表父节点 anc[u][0] = p; dep[u] = d; for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next){ int v= edge[i].to; //if(v == p) continue; 这里不可能,因为题目里已经给明父子关系,但是其他地方有用 dfs(v, u, d + 1); } } //----初始化anc[x][j]---------- void anc_init(int n){ //n为点的个数 for(int j = 1; j < LOG; ++j) for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) //将所有的点跳跃2^j步的结果算完后,再接着算2^(j+1)的情况 anc[i][j] = anc[ anc[i][j - 1] ][j - 1]; } //----使两点高度相等--- void up(int &u, int h){ for(int j = 0; h; ++j){ if(h&1) u = anc[u][j]; h >>= 1; } } //----LCA-------- int LCA(int u, int v){ if(dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v); //置u为较深点 up(u, dep[u] - dep[v]); if(u == v) return u; for(int i = LOG - 1; i >= 0; --i){ if(anc[u][i] != anc[v][i]){ u = anc[u][i]; v = anc[v][i]; } } return anc[u][0]; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); int T; cin >> T; int N; while(T--){ cin >> N; int f, s; cnt = 0; fill(head, head + MAX, -1); //通过head数组访问对应边在edge中的下标 fill(vis, vis + MAX, true); for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; ++i){ cin >> f >> s; addedge(f, s); vis[s] = false; } int root; for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) if(vis[i]){ root = i; break; } dfs(root, root, 1); //?? anc_init(N); int a, b; cin >> a >> b; cout << LCA(a, b) << endl; } return 0; }

