DSP_ADC_Example_2833xAdcSoc
中斷副程式的宣告
__interrupt void adc_isr(void);
宣告全域變量
float ADCV1[10]; //自己增加 float ADCV2[10]; //自己增加 float Voltage1[10]; //uint改為float float Voltage2[10]; //uint改為float
進入Main後,先系統初始化
InitSysCtrl();
進入該程式後
void InitSysCtrl(void) { DisableDog(); //Disable看門狗計數器 InitPll(DSP28_PLLCR,DSP28_DIVSEL); //初始SYSCLKOUT?? InitPeripheralClocks(); }
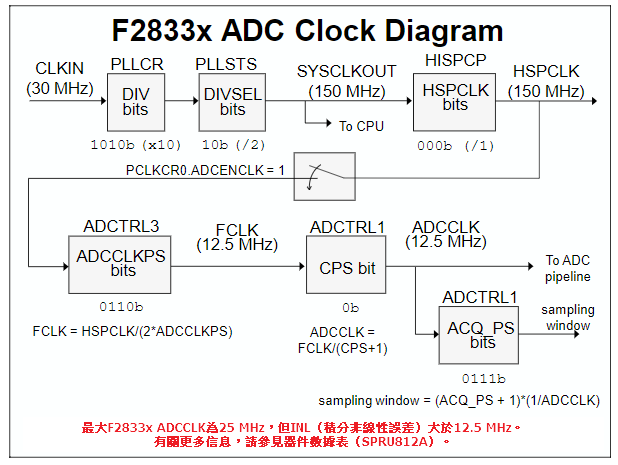
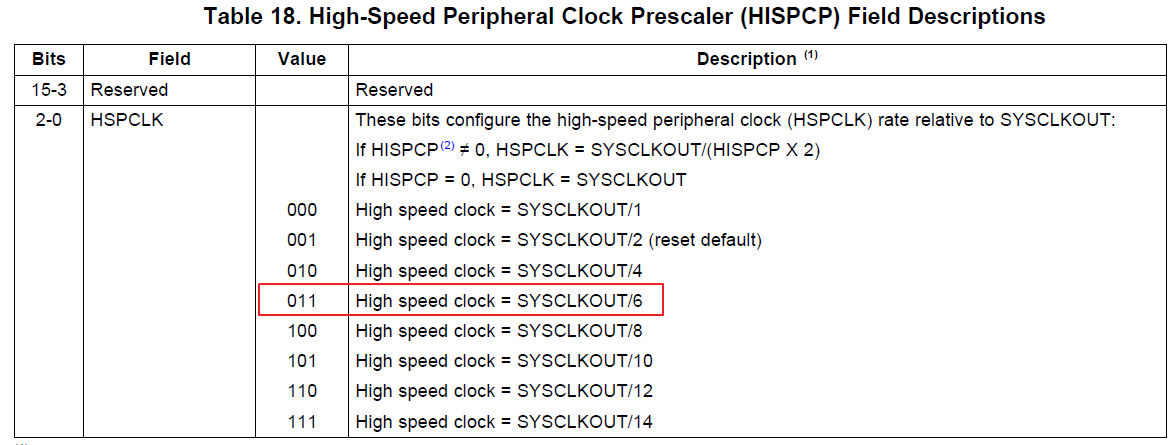
Set HSPCLK Freq=25MHz
EALLOW; #if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default - 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT #define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz #endif #if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ) #define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz #endif EDIS; // Define ADCCLK clock frequency ( less than or equal to 25 MHz ) // Assuming InitSysCtrl() has set SYSCLKOUT to 150 MHz EALLOW; SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; //ADC_MODCLK=3 EDIS;
Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
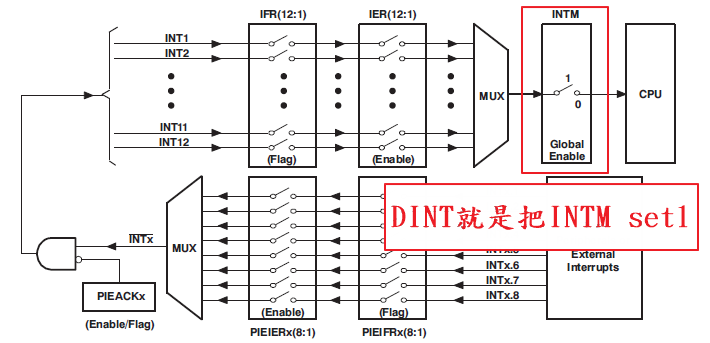
初始PIE控制、Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags
- 初始化PIE向量表
DINT;
InitPieCtrl();
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
InitPieVectTable();
可參閱DSP_CPU_Example_2833x_CpuTimer
將中斷向量表指向ADC中斷副程式
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to // ISR functions found within this file. EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr; EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
中斷向量表屬於ADCINT1的部分,連結到adc_isr
也就是等一下會設定我們用ADCINT1,去做一個類比轉數位中斷
中斷一旦發生即進入中段副程式
(即當有ADC轉換時就會觸發這個中斷,我們即可在中斷副程式中去做一些我們要做的事情)
ADC中斷副程式 void adc_isr(void)
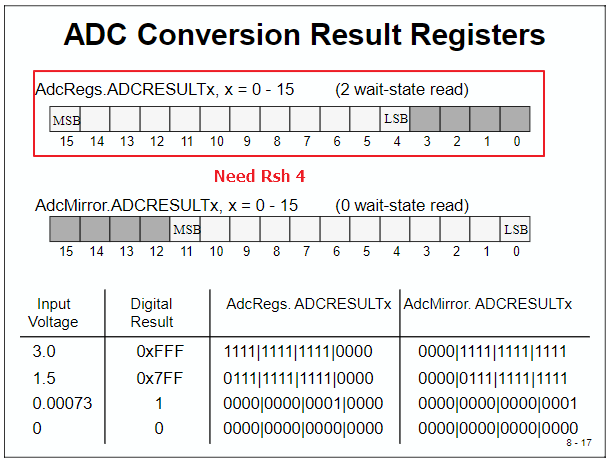
__interrupt void adc_isr(void) { ADCV1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4; ADCV2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4; Voltage1[ConversionCount] = ((float)ADCV1[ConversionCount]/4095)*3.0; //自己修改 Voltage2[ConversionCount] = ((float)ADCV2[ConversionCount]/4095)*3.0; //自己修改 // If 40 conversions have been logged, start over 如果記錄了40次轉換,請重新開始 if(ConversionCount == 9) { ConversionCount = 0; } else { ConversionCount++; } // Reinitialize for next ADC sequence AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1 將SEQ1的狀態機重置為其初始狀態。這意味著下一個觸發器將開始對CONV00中定義的通道進行新的轉換 AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit 向該位寫入1將清除SEQ1中斷標誌位INT_SEQ1。該位不影響EOS_BUF1位。 PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE 把PIEACK清除,才能接受其他周邊中斷 return; }
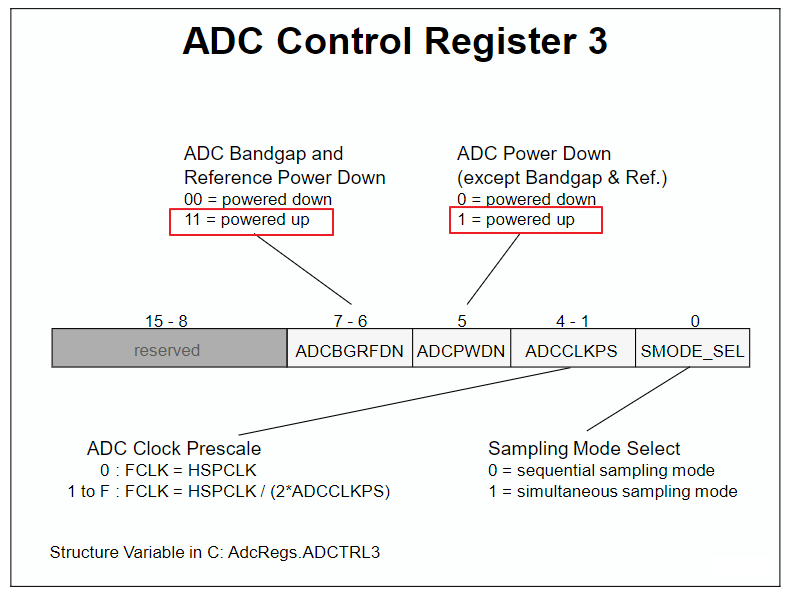
初始ADC
InitAdc();
進入該程式
InitAdc(void) { extern void DSP28x_usDelay(Uint32 Count); EALLOW; SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.ADCENCLK = 1; //ADC時脈啟動 ADC_cal(); EDIS; // AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.all = 0x00E0; // Power up bandgap/reference/ADC circuits DELAY_US(ADC_usDELAY); // Delay before converting ADC channels }

User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1; IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1 EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM LoopCount = 0; ConversionCount = 0;
Configure ADC
// Configure ADC AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1 兩次轉換 AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x3; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv. AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x2; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv. AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1 位8(“ePWM_SOCA_SEQ1”)是允許ePWM信號作為“SOCA”用作轉換觸發器的Mask bit。 AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
Set 2 conv's
ADCINA3 -> ADCRESULT0 ADCINA2 -> ADCRESULT1
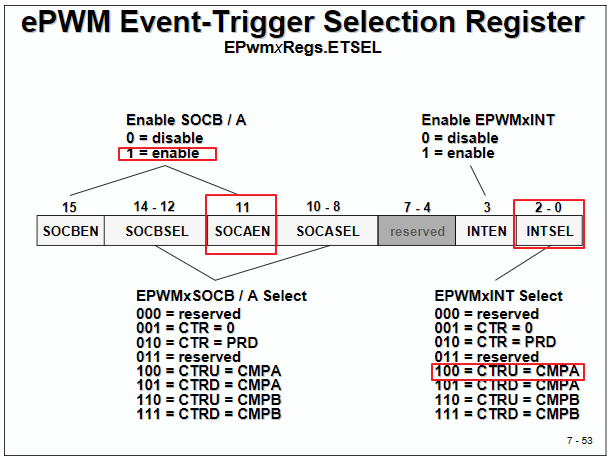
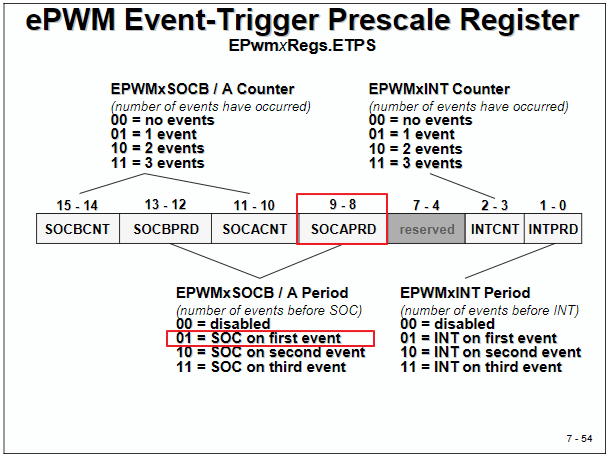
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl(); EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1 EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start 上數計時器
ALL Code
//########################################################################### // Description //! \addtogroup f2833x_example_list //! <h1> ADC Start of Conversion (adc_soc)</h1> //! //! This ADC example uses ePWM1 to generate a periodic ADC SOC on SEQ1. //! Two channels are converted, ADCINA3 and ADCINA2. //! //! \b Watch \b Variables \n //! - Voltage1[10] - Last 10 ADCRESULT0 values //! - Voltage2[10] - Last 10 ADCRESULT1 values //! - ConversionCount - Current result number 0-9 //! - LoopCount - Idle loop counter // // //########################################################################### // $TI Release: F2833x/F2823x Header Files and Peripheral Examples V142 $ // $Release Date: November 1, 2016 $ // $Copyright: Copyright (C) 2007-2016 Texas Instruments Incorporated - // http://www.ti.com/ ALL RIGHTS RESERVED $ //########################################################################### #include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File // Prototype statements for functions found within this file. __interrupt void adc_isr(void); // Global variables used in this example: Uint16 LoopCount; Uint16 ConversionCount; float ADCV1[10]; float ADCV2[10]; float Voltage1[10]; float Voltage2[10]; main() { // Step 1. Initialize System Control: // PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks // This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file. InitSysCtrl(); EALLOW; #if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default - 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT #define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz #endif #if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ) #define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz #endif EDIS; // Define ADCCLK clock frequency ( less than or equal to 25 MHz ) // Assuming InitSysCtrl() has set SYSCLKOUT to 150 MHz EALLOW; SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; EDIS; // Step 2. Initialize GPIO: // This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and // illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state. // InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example // Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table: // Disable CPU interrupts DINT; // Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state. // The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags // are cleared. // This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file. InitPieCtrl(); // Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags: IER = 0x0000; IFR = 0x0000; // Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt // Service Routines (ISR). // This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt // is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes. // The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c. // This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c. InitPieVectTable(); // Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to // ISR functions found within this file. EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr; EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers // Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals: // This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c // InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC // Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts: // Enable ADCINT in PIE PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1; IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1 EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM LoopCount = 0; ConversionCount = 0; // Configure ADC AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1 AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x3; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv. AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x2; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv. AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1 AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS) // Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl(); EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1 EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start // Wait for ADC interrupt for(;;) { LoopCount++; } } __interrupt void adc_isr(void) { ADCV1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4; ADCV2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4; Voltage1[ConversionCount] = ((float)ADCV1[ConversionCount]/4096)*3.0; Voltage2[ConversionCount] = ((float)ADCV2[ConversionCount]/4096)*3.0; // If 40 conversions have been logged, start over if(ConversionCount == 9) { ConversionCount = 0; } else { ConversionCount++; } // Reinitialize for next ADC sequence AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1 AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE return; }





