1. 软件下载:下载 .deb
dpkg -i .deb //download pkg -install
2. 软件安装: apt / apt-get (advanced pkg tool)
apt install/upgrade/remove 软件
3. shell的配置:
远程连接方式: ssh 用户名@主机
新建用户: adduser 有用户名
添加用户到‘sudo' 组: usermod -G sudo 用户名
修改密码: passwd
切换用户: su - 用户名
更改主机名: sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <newhostname>
查看主机名: hostname/hostnamectl
更新远程连接配置: /etc/ssh/sshd_config 文件中更改下面的设定,然后重启sshd(ssh datacenter) 服务(service sshd restart)
ClientAliveInterval 30 #客户端每隔多少秒向服务发送一个心跳数据; ClientAliveCountMax 86400 #客户端多少秒没有相应,服务器自动断掉连接。
使用zsh,兼容bash,插件强大:oh-my-zsh , 智能跳转autojmp
安装zsh: sudo apt install zsh
修改默认shell: chsh -s /bin/zsh

#!/bin/sh # # This script should be run via curl: # sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)" # or wget: # sh -c "$(wget -qO - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)" # # As an alternative, you can first download the install script and run it afterwards: # wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh # sh install.sh # # You can tweak the install behavior by setting variables when running the script. For # example, to change the path to the Oh My Zsh repository: # ZSH=~/.zsh sh install.sh # # Respects the following environment variables: # ZSH - path to the Oh My Zsh repository folder (default: $HOME/.oh-my-zsh) # REPO - name of the GitHub repo to install from (default: ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh) # REMOTE - full remote URL of the git repo to install (default: GitHub via HTTPS) # BRANCH - branch to check out immediately after install (default: master) # # Other options: # CHSH - 'no' means the installer will not change the default shell (default: yes) # RUNZSH - 'no' means the installer will not run zsh after the install (default: yes) # KEEP_ZSHRC - 'yes' means the installer will not replace an existing .zshrc (default: no) # # You can also pass some arguments to the install script to set some these options: # --skip-chsh: has the same behavior as setting CHSH to 'no' # --unattended: sets both CHSH and RUNZSH to 'no' # --keep-zshrc: sets KEEP_ZSHRC to 'yes' # For example: # sh install.sh --unattended # set -e args=$1 USER_PASSWD=$1 REPO=suyelu/ohmyzsh # Default settings ZSH=${ZSH:-~/.oh-my-zsh} REPO=${REPO:-ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh} REMOTE=${REMOTE:-https://gitee.com/${REPO}.git} BRANCH=${BRANCH:-master} # Other options CHSH=${CHSH:-yes} RUNZSH=${RUNZSH:-yes} KEEP_ZSHRC=${KEEP_ZSHRC:-no} command_exists() { command -v "$@" >/dev/null 2>&1 } error() { echo ${RED}"Error: $@"${RESET} >&2 } setup_color() { # Only use colors if connected to a terminal if [ -t 1 ]; then RED=$(printf '\033[31m') GREEN=$(printf '\033[32m') YELLOW=$(printf '\033[33m') BLUE=$(printf '\033[34m') BOLD=$(printf '\033[1m') RESET=$(printf '\033[m') else RED="" GREEN="" YELLOW="" BLUE="" BOLD="" RESET="" fi } setup_ohmyzsh() { # Prevent the cloned repository from having insecure permissions. Failing to do # so causes compinit() calls to fail with "command not found: compdef" errors # for users with insecure umasks (e.g., "002", allowing group writability). Note # that this will be ignored under Cygwin by default, as Windows ACLs take # precedence over umasks except for filesystems mounted with option "noacl". umask g-w,o-w echo "${BLUE}Cloning Oh My Zsh...${RESET}" command_exists git || { error "git is not installed" exit 1 } if [ "$OSTYPE" = cygwin ] && git --version | grep -q msysgit; then error "Windows/MSYS Git is not supported on Cygwin" error "Make sure the Cygwin git package is installed and is first on the \$PATH" exit 1 fi git clone -c core.eol=lf -c core.autocrlf=false \ -c fsck.zeroPaddedFilemode=ignore \ -c fetch.fsck.zeroPaddedFilemode=ignore \ -c receive.fsck.zeroPaddedFilemode=ignore \ --depth=1 --branch "$BRANCH" "$REMOTE" "$ZSH" || { error "git clone of oh-my-zsh repo failed" exit 1 } echo } setup_zshrc() { # Keep most recent old .zshrc at .zshrc.pre-oh-my-zsh, and older ones # with datestamp of installation that moved them aside, so we never actually # destroy a user's original zshrc echo "${BLUE}Looking for an existing zsh config...${RESET}" # Must use this exact name so uninstall.sh can find it OLD_ZSHRC=~/.zshrc.pre-oh-my-zsh if [ -f ~/.zshrc ] || [ -h ~/.zshrc ]; then # Skip this if the user doesn't want to replace an existing .zshrc if [ $KEEP_ZSHRC = yes ]; then echo "${YELLOW}Found ~/.zshrc.${RESET} ${GREEN}Keeping...${RESET}" return fi if [ -e "$OLD_ZSHRC" ]; then OLD_OLD_ZSHRC="${OLD_ZSHRC}-$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S)" if [ -e "$OLD_OLD_ZSHRC" ]; then error "$OLD_OLD_ZSHRC exists. Can't back up ${OLD_ZSHRC}" error "re-run the installer again in a couple of seconds" exit 1 fi mv "$OLD_ZSHRC" "${OLD_OLD_ZSHRC}" echo "${YELLOW}Found old ~/.zshrc.pre-oh-my-zsh." \ "${GREEN}Backing up to ${OLD_OLD_ZSHRC}${RESET}" fi echo "${YELLOW}Found ~/.zshrc.${RESET} ${GREEN}Backing up to ${OLD_ZSHRC}${RESET}" mv ~/.zshrc "$OLD_ZSHRC" fi echo "${GREEN}Using the Oh My Zsh template file and adding it to ~/.zshrc.${RESET}" sed "/^export ZSH= / c\\ export ZSH=\"$ZSH\" " "$ZSH/templates/zshrc.zsh-template" > ~/.zshrc-omztemp mv -f ~/.zshrc-omztemp ~/.zshrc echo } setup_shell() { # Skip setup if the user wants or stdin is closed (not running interactively). if [ $CHSH = no ]; then return fi # If this user's login shell is already "zsh", do not attempt to switch. if [ "$(basename "$SHELL")" = "zsh" ]; then return fi # If this platform doesn't provide a "chsh" command, bail out. if ! command_exists chsh; then cat <<-EOF I can't change your shell automatically because this system does not have chsh. ${BLUE}Please manually change your default shell to zsh${RESET} EOF return fi echo "${BLUE}Time to change your default shell to zsh:${RESET}" # Prompt for user choice on changing the default login shell # Check if we're running on Termux case "$PREFIX" in *com.termux*) termux=true; zsh=zsh ;; *) termux=false ;; esac if [ "$termux" != true ]; then # Test for the right location of the "shells" file if [ -f /etc/shells ]; then shells_file=/etc/shells elif [ -f /usr/share/defaults/etc/shells ]; then # Solus OS shells_file=/usr/share/defaults/etc/shells else error "could not find /etc/shells file. Change your default shell manually." return fi # Get the path to the right zsh binary # 1. Use the most preceding one based on $PATH, then check that it's in the shells file # 2. If that fails, get a zsh path from the shells file, then check it actually exists if ! zsh=$(which zsh) || ! grep -qx "$zsh" "$shells_file"; then if ! zsh=$(grep '^/.*/zsh$' "$shells_file" | tail -1) || [ ! -f "$zsh" ]; then error "no zsh binary found or not present in '$shells_file'" error "change your default shell manually." return fi fi fi # We're going to change the default shell, so back up the current one if [ -n "$SHELL" ]; then echo $SHELL > ~/.shell.pre-oh-my-zsh else grep "^$USER:" /etc/passwd | awk -F: '{print $7}' > ~/.shell.pre-oh-my-zsh fi # Actually change the default shell to zsh if [[ ${USER_PASSWD}x == x ]];then chsh -s "$zsh" else (sleep 1 echo ${USER_PASSWD} ) | chsh -s "$zsh" fi if [[ ! $? -eq 0 ]]; then error "chsh command unsuccessful. Change your default shell manually." else export SHELL="$zsh" echo "${GREEN}Shell successfully changed to '$zsh'.${RESET}" fi echo } main() { # Run as unattended if stdin is closed if [ ! -t 0 ]; then RUNZSH=no CHSH=no fi # Parse arguments while [ $# -gt 0 ]; do case $1 in --unattended) RUNZSH=no; CHSH=no ;; --skip-chsh) CHSH=no ;; --keep-zshrc) KEEP_ZSHRC=yes ;; esac shift done setup_color if ! command_exists zsh; then echo "${YELLOW}Zsh is not installed.${RESET} Please install zsh first." exit 1 fi if [ -d "$ZSH" ]; then cat <<-EOF ${YELLOW}You already have Oh My Zsh installed.${RESET} You'll need to remove '$ZSH' if you want to reinstall. EOF exit 1 fi setup_ohmyzsh setup_zshrc setup_shell printf "$GREEN" cat <<-'EOF' __ __ ____ / /_ ____ ___ __ __ ____ _____ / /_ / __ \ / __ \ / __ `__ \ / / / / /_ / / ___ / __ \ / /_ / / / / / / / / / / / /_ / / / /_(__ ) / / / \____/_ / /_ / /_ / /_ / /_/\__, / /___/____/_ / /_/ /____ / ....is now installed! Please look over the ~/.zshrc file to select plugins, themes, and options. p.s. Follow us on https://twitter.com/ohmyzsh p.p.s. Get stickers, shirts, and coffee mugs at https://shop.planetargon.com/collections/oh-my-zsh EOF printf "$RESET" if [ $RUNZSH = no ]; then echo "${YELLOW}Run zsh to try it out.${RESET}" exit fi if [[ ${#args} -eq 1 ]];then exec zsh -l fi } main "$@"

4. 安装==zsh-syntax-highlighting== ```bash git clone https://gitee.com/suyelu/zsh-syntax-highlighting.git ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-~/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/plugins/zsh-syntax-highlighting ``` 5. 使用命令`vim ~/.zshrc`打开.zshrc文件,找到`plugins=()`这一行,将zsh-syntax-highlighting添加进去 ```bash plugins=(git zsh-syntax-highlighting) ``` 6. 安装其他插件 ```bash ##命令自动补全插件 mkdir ~/.oh-my-zsh/plugins/incr wget http://mimosa-pudica.net/src/incr-0.2.zsh -O ~/.oh-my-zsh/plugins/incr/incr.plugin.zsh ##目录自动跳转插件 sudo apt install autojump ``` 7. 使用命令`vim ~/.zshrc`,打开后在最后插入以下内容: ```bash #设置终端颜色,提示符,及上一条指令返回码提示 autoload -U colors && colors PROMPT="%{$fg[red]%}%n%{$reset_color%}@%{$fg[blue]%}%m %{$fg[yellow]%}%1~ %{$reset_color%}%# " RPROMPT="[%{$fg[yellow]%}%?%{$reset_color%}]" # Useful support for interacting with Terminal.app or other terminal programs [ -r "/etc/zshrc_$TERM_PROGRAM" ] && . "/etc/zshrc_$TERM_PROGRAM" source /usr/share/autojump/autojump.sh source ~/.oh-my-zsh/plugins/incr/incr*.zsh ``` > 注意,复制后可能会因为Vim的配置导致以上内容被注释,也就是在前面加上了`#`,如果有的话,删掉就行。 #### ctags安装与配置 1. 使用以下命令安装**ctags** ```bash sudo apt install ctags ``` 2. 执行以下命令 ```bash ctags -I __THROW -I __attribute_pure__ -I __nonnull -I __attribute__ --file-scope=yes --langmap=c:+.h --languages=c,c++ --links=yes --c-kinds=+p --c++-kinds=+p --fields=+iaS --extra=+q -f ~/.vim/systags /usr/include/* /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/* /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/* /usr/include/arpa/* ``` 3. 使用命令`vim ~/.vimrc`编辑.vimrc,在最后添加以下内容 ```bash set tags+=~/.vim/systags ``` #### 安装glibc-doc 1. 使用以下命令安装 ```bash sudo apt install glibc-doc ```
zsh 各种配置文件:
~/.zshrc /etc/zshrc ~/.zlogin /etc/zlogin ~/.zlogout /etc/zlogout ~/.zprofile /etc/zprofile 配置文件装载顺序,先是全局/etc/zsh,后是用户~/.zshenv Global Order: zshenv, zprofile, zshrc, zlogin 命令行快捷键: Ctrl+a/e/f/b/d/w/k/u: 头/尾/前进一个字符/后退一个字符/删除一个字符/向前删除一个单词/删除至行尾/清空整行 Alt+/f/b/d :前进一个单词/后退一个单词/删除一个单词
安装vim 及配置文件(使用vundle):
配置推荐:https://github.com/ma6174/vim

#!/bin/bash echo "This script will install and configure vim and zsh automatic." echo "The time this takes is related to the network conditions, please wait patiently." if [[ `whoami` == "root" ]];then echo -e "\033[31mYou are running this script with Root\033[0m" echo -e "\033[31mGenerally, we do not recommend using root for programming or directly controlling your Linux OS, especially when you are a beginner \033[0m" echo -e "\033[31mSo, There is no necessary for you to configure with root." read -p "Do you really want to do this?[N/y]" choice if [[ ${choice} != y ]];then echo "Bye." exit 1 fi fi if which apt-get >/dev/null; then sudo apt-get install -y vim vim-gnome ctags xclip astyle python-setuptools python-dev git wget elif which yum >/dev/null; then sudo yum install -y gcc vim git ctags xclip astyle python-setuptools python-devel wget fi ##Add HomeBrew support on Mac OS if which brew >/dev/null;then echo "You are using HomeBrew tool" brew install vim ctags git astyle fi sudo easy_install -ZU autopep8 sudo ln -s /usr/bin/ctags /usr/local/bin/ctags rm -rf ~/vim* 2>&1 >/dev/null rm -rf ~/.vim* 2>&1 >/dev/null mv -f ~/vim ~/vim_old cd ~/ && git clone https://gitee.com/suyelu/vim.git mv -f ~/.vim ~/.vim_old 2>&1 >/dev/null mv -f ~/vim ~/.vim 2>&1 >/dev/null mv -f ~/.vimrc ~/.vimrc_old 2>&1 >/dev/null mv -f ~/.vim/.vimrc ~/ git clone https://gitee.com/suyelu/vundle.git ~/.vim/bundle/vundle echo "程序正在自动安装相应插件" > process echo "command-t插件需要等待时间较长,不要担心" >> process echo "切勿强制退出该界面,否则会导致错误,需重新配置" >> process echo "安装完毕将自动退出" >> process echo "请耐心等待" >> process vim process -c "BundleInstall" -c "q" -c "q" rm process echo "安装完成"
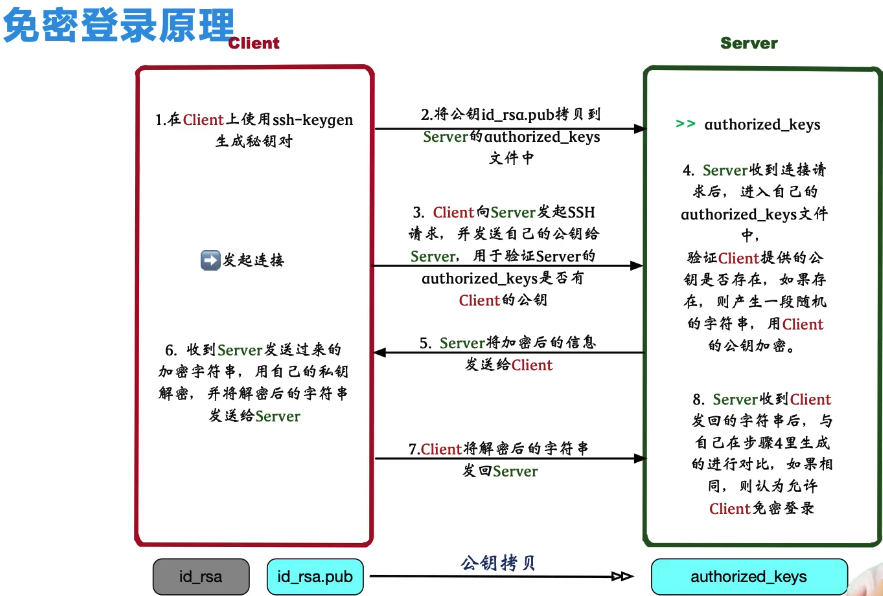
免密登陆:
ssh-keygen #生成密钥对 ssh-copy-id username@host #公钥复制到远程云主机 scp 文件名 用户名@主机名:目标位置 #从本地拷贝到远程主机 scp 用户名@主机名:文件名 目的位置 #从远程位置拷贝文件到本地




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号