======================= **基础知识** =======================
前缀和数组:
初始化:O(n);
查询区间和: O(1) 度,S[j] - S[i] 即为原数组( i, j ] 的区间和, 前开后闭;
单点修改: O(n) ,需要修改S[i] ~ S[n] 所有值;
缺点:频繁修改原数组中值,前缀和数组就不适合了。
负数的补码 = 反码 + 1
lowbit(i) = x & (-x) ; 代表i 这个数字,二进制表示中最后一位1 的位权;
树状数组:为了弱化前缀和数组中修改元素值关联性。

前缀和查询: S[i] = S[i - lowbit(i)] + C[i], 时间复杂度 O(lgN);
单点修改:所有需要修改的C 数组下标 i 集合,while( i + lowbit(i) ) i = i + lowbit(i), 时间复杂度O(lgN);
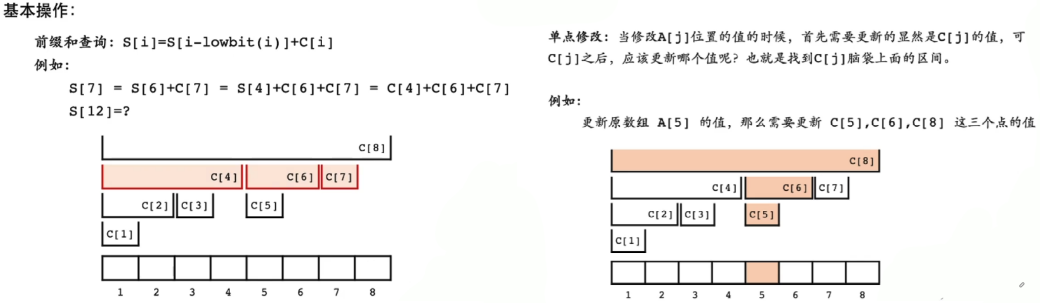
S[12] = S[8] + C[12] = C[8] + C[12]
======================= **代码演示** =======================
前缀和数组 与 差分数组 互为逆运算, 差分数组的 前缀和 就是 原数组。
对于区间范围统一增/减 一个值时候,差分数组最方便,只用操作同为两个数。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 #define lowbit(x) (x & (-x)) 6 7 class FenwickTree { 8 public: 9 FenwickTree(int cnt): n(cnt + 1), size(0) { 10 pC = new vector<int>(n, 0); 11 } 12 ~FenwickTree() { 13 delete pC; 14 } 15 16 void add(int ind, int val) { 17 while(ind <= n) (*pC)[ind] += val, ind += lowbit(ind); 18 return; 19 } 20 21 int queryS(int ind) { 22 int ret = 0; 23 while(ind) ret += (*pC)[ind], ind -= lowbit(ind); 24 return ret; 25 } 26 27 int queryA(int ind) { 28 return queryS(ind) - queryS(ind - 1); 29 } 30 31 void output() { 32 int len = 0; 33 len = printf("%5s:", "ind"); 34 for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { 35 len += printf("%5d", i); 36 } 37 printf("\n"); 38 39 for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) printf("="); 40 printf("\n"); 41 42 printf("%5s:", "s[i]"); 43 for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) printf("%5d", queryS(i)); 44 printf(" 前缀和数组\n"); 45 46 47 for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) printf("="); 48 printf("\n"); 49 50 printf("%5s:", "c[i]"); 51 for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) printf("%5d", (*pC)[i]); 52 printf(" 树状数组\n"); 53 54 for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) printf("="); 55 printf("\n"); 56 57 printf("%5s:", "a[i]"); 58 for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) printf("%5d", queryA(i)); 59 printf(" 原数组\n"); 60 61 for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) printf("="); 62 printf("\n"); 63 64 printf("%5s:", "x[i]"); 65 printf("%5d", queryA(1)); 66 for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i) printf("%5d", queryA(i) - queryA(i - 1)); 67 printf(" 差分数组\n"); 68 69 return; 70 } 71 72 private: 73 int n; 74 int size; 75 vector<int> *pC; 76 }; 77 78 79 80 int main() 81 { 82 int n, val; 83 cin >> n; 84 FenwickTree c(n); 85 86 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { 87 cin >> val; 88 c.add(i, val - c.queryA(i)); 89 } 90 91 c.output(); 92 93 return 0; 94 } 95 96 ///////////////////////////////////////input///////////////////// 97 10 98 1 99 1 100 1 101 1 102 1 103 1 104 1 105 1 106 1 107 1
tips: 单点修改都是基于原数组a[i] 基础上做修改;
对于树状数组来讲,下标是要注意的。类似与前缀和数组,数组元素的个数都要比原数组多一个,下标都是从 1 开始算的。
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1. 树状数组: 307. 区域和检索 - 数组可修改

1 #define lowbit(x) (x &(-x)) 2 class FenwickTree { 3 public: 4 FenwickTree(int n) : size(n), c(n + 1) {} 5 void add(int ind, int val) { 6 while(ind <= size) c[ind] += val, ind += lowbit(ind); 7 return; 8 } 9 10 int query(int ind) { 11 int ans = 0; 12 while(ind) ans += c[ind], ind -= lowbit(ind); 13 return ans; 14 } 15 16 int at(int ind) { 17 return query(ind) - query(ind - 1); 18 } 19 20 private: 21 int size; 22 vector<int> c; 23 }; 24 25 26 class NumArray { 27 public: 28 FenwickTree tree; 29 NumArray(vector<int>& nums) : tree(nums.size()) { 30 for(int i = 0, I = nums.size(); i < I; ++i) tree.add(i + 1, nums[i]); 31 } 32 33 void update(int index, int val) { 34 tree.add(index + 1, val - tree.at(index + 1)); 35 return; 36 37 } 38 39 int sumRange(int left, int right) { 40 return tree.query(right + 1) - tree.query(left); 41 } 42 }; 43 44 /** 45 * Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such: 46 * NumArray* obj = new NumArray(nums); 47 * obj->update(index,val); 48 * int param_2 = obj->sumRange(left,right); 49 */
2. 树状数组应用:

1 #define MAX_N 50005 2 #define lowbit(x) (x & (-x)) 3 class FenwickTree{ 4 public: 5 FenwickTree(int n = MAX_N): n(n) { 6 pc = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 7 memset(pc, 0, sizeof(int) * n); 8 } 9 10 void update(int index, int val) { 11 while(index < n) { 12 pc[index] += val; 13 index += lowbit(index); 14 } 15 return; 16 } 17 18 int queryS(int index) { 19 int ret = 0; 20 while(index) { 21 ret += pc[index]; 22 index -= lowbit(index); 23 } 24 return ret; 25 } 26 27 private: 28 int *pc; 29 int n; 30 }; 31 class StreamRank { 32 private: 33 FenwickTree *pft; 34 35 public: 36 StreamRank() { 37 pft = new FenwickTree(); 38 } 39 40 void track(int x) { 41 pft->update(x + 1, 1); 42 return; 43 } 44 45 int getRankOfNumber(int x) { 46 return pft->queryS(x + 1); 47 } 48 };

1 #define lowbit(x) x & (-x) 2 3 class FenwickTree{ 4 public: 5 FenwickTree(int n): size(n), c(n + 1) {} 6 void add(int ind, int val) { 7 while(ind <= size) c[ind] ^= val, ind += lowbit(ind); 8 return; 9 } 10 11 int query(int ind) { 12 int ans = 0; 13 while(ind) ans ^= c[ind], ind -= lowbit(ind); 14 return ans; 15 } 16 17 private: 18 int size; 19 vector<int> c; 20 }; 21 22 class Solution { 23 public: 24 vector<int> xorQueries(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { 25 26 FenwickTree tree(arr.size()); 27 for(int i = 0, I = arr.size(); i < I; ++i) tree.add(i + 1, arr[i]); 28 29 vector<int> ans; 30 for(int i = 0, I = queries.size(); i < I; ++i) { 31 ans.push_back(tree.query(queries[i][1] + 1) ^ tree.query(queries[i][0])); 32 } 33 return ans; 34 35 //default: 36 // for(int i = 1, I = arr.size(); i < I; ++i) arr[i] ^= arr[i - 1]; 37 // vector<int> ans; 38 // for(int i = 0, I = queries.size(); i < I; ++i) { 39 // ans.push_back(arr[queries[i][1]] ^ (queries[i][0] ? arr[queries[i][0] - 1]: 0)); 40 // } 41 // 42 // return ans; 43 } 44 };
3. fenwickTree 进一步应用:
每次操作移动一位元素到某个位置上,怎么来表示当前每个元素所对应的新的位置关系? 下面2道题,分别展示了不同做法;
1409. 查询带键的排列 : 专门建立一个下标数组来记录每个元素在线段树中的位置,然后再通过线段树作为计数数组得到新的位置关系; 值 与 计数数组的关系。

1 class Solution { 2 #define lowbit(x) (x & (-x)) 3 class FenwickTree{ 4 vector<int> c; 5 public: 6 FenwickTree(int n) : c(vector<int>(n + 1, 0)){} 7 8 void add(int index, int val) { 9 int n = c.size(); 10 while(index < n) { 11 c[index] += val; 12 index+= lowbit(index); 13 } 14 return; 15 } 16 int query(int idx) { 17 int ans = 0; 18 while(idx) { 19 ans += c[idx]; 20 idx -= lowbit(idx); 21 } 22 return ans; 23 } 24 }; 25 public: 26 vector<int> processQueries(vector<int>& queries, int m) { 27 int n = queries.size(); 28 FenwickTree tree(n + m); 29 vector<int> pos(m + 1, 0), ans(n, 0); 30 for(int j = 1; j <= m ; ++j){ 31 pos[j] = n + j; 32 tree.add(n + j, 1); 33 } 34 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 35 int index = pos[queries[i]]; 36 ans[i] = tree.query(index) - 1; 37 pos[queries[i]] = n - i; 38 tree.add(index, -1); 39 tree.add(pos[queries[i]], 1); 40 } 41 return ans; 42 } 43 }; 44 45 //original 46 class Solution { 47 public: 48 vector<int> processQueries(vector<int>& queries, int m) { 49 50 #define lowbit(x) x &(-x) 51 52 class FenwickTree{ 53 public: 54 FenwickTree(int n):size(n), c(n + 1) {} 55 void add(int ind, int val) { 56 while(ind <= size) c[ind] += val, ind += lowbit(ind); 57 return; 58 } 59 60 int query(int ind) { 61 int ans = 0; 62 while(ind) ans += c[ind], ind -= lowbit(ind); 63 return ans; 64 } 65 66 private: 67 int size; 68 vector<int> c; 69 }; 70 71 class Solution { 72 public: 73 vector<int> processQueries(vector<int>& queries, int m) { 74 vector<int> ans; 75 unordered_map<int,int> ind; 76 77 int lenq = queries.size(); 78 FenwickTree tree(m + lenq); //lenq ~ 1 每次操作的存放位置,lenq + 1~ lenq + m 存放初始值,这里都是对应的ind 位置 79 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){ 80 int temp = lenq + i; 81 ind[i] = temp; //存储初始值对应的位置, 82 tree.add(temp, 1); //存储对应有值位置标为1,然后通过后面求前缀和得到对应的下标位置 83 } 84 85 for(int i = 0, I = queries.size(); i < I; ++i) { 86 int num = queries[i]; 87 ans.push_back(tree.query(ind[num]) - 1); //这里求下标,所以要把前缀和-1 88 tree.add(ind[num], -1); //原来位置把计数1 删除 89 tree.add(lenq - i, 1); //新的位置计数1 加入 90 ind[num] = lenq - i; 91 } 92 return ans; 93 //brute force 94 // unordered_map<int,int> ind(m + 1); //(num, ind) 95 // vector<int> num(m, 0), ans; 96 // 97 // for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { 98 // num[i] = i + 1; 99 // ind[i + 1] = i; 100 // } 101 // 102 // for(auto x : queries) { 103 // ans.push_back(ind[x]); 104 // for(int i = ind[x]; i > 0; --i) swap(num[i], num[i - 1]); 105 // for(int i = 0, I = ind[x]; i <= I; i++) ind[num[i]] = i; 106 // } 107 // 108 // return ans; 109 } 110 };
1505. 最多 K 次交换相邻数位后得到的最小整数 : 通过计算自己后面有多少元素移动到前面以及自己原始坐标位置来得到新的位置信息;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 string __minInteger(string num, int index, int k){ 4 if(k == 0 || index == num.size()) return num; 5 int pre = index, i = index + 1; 6 for(; num[i] && (i - index) <= k; ++i) { 7 if(num[i] >= num[i - 1]) continue; 8 if(num[pre] > num[i]) pre = i; 9 } 10 11 if(pre == index) return __minInteger(num, index + 1, k); 12 num.insert(index, 1, num[pre]); 13 num.erase(pre + 1, 1); 14 return __minInteger(num, index + 1, k - (pre - index)); 15 } 16 17 struct fenwickTree{ 18 public: 19 fenwickTree(int _n) : n(_n) { 20 pc = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 1)); 21 memset(pc, 0, sizeof(int) * (n + 1)); 22 } 23 24 void update(int pos, int val) { 25 while(pos <= n) { 26 pc[pos] += val; 27 pos += lowbit(pos); 28 } 29 return; 30 } 31 32 int queryS(int pos) { 33 int ret = 0; 34 while(pos) { 35 ret += pc[pos]; 36 pos -= lowbit(pos); 37 } 38 return ret; 39 } 40 41 int queryA(int p1, int p2) { 42 return queryS(p2) - queryS(p1); 43 } 44 45 private: 46 int n; 47 int *pc; 48 static int lowbit(int x) { 49 return x & (-x); 50 } 51 }; 52 string minInteger(string num, int k) { 53 //bruteForce 54 // return __minInteger(num, 0, k); 55 int len = num.size(); 56 vector<deque<int>> nums(10, deque<int>()); 57 fenwickTree pos(len + 1); 58 for(int i = 0; num[i]; ++i) nums[num[i] - '0'].push_back(i); 59 60 string ans = ""; 61 for(int i = 0; num[i]; ++i) { 62 for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) { 63 if(nums[j].empty()) continue; 64 int dis = nums[j].front() + pos.queryA(nums[j].front() + 1, len) - i; 65 if(k >= dis) { 66 ans += (j + '0'); 67 pos.update(nums[j].front() + 1, 1); 68 nums[j].pop_front(); 69 k -= dis; 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 return ans; 75 } 76 };
4. 差分数组: 1109. 航班预订统计

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<int> corpFlightBookings(vector<vector<int>>& bookings, int n) { 4 vector<int> arr(n, 0); 5 for(auto &x : bookings) { 6 arr[x[0] - 1] += x[2]; 7 if(x[1] == n) continue; 8 arr[x[1]] -= x[2]; 9 } 10 for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) arr[i] += arr[i - 1]; 11 return arr; 12 } 13 }; 14 15 ////////////////////////fenwickTree 16 #define lowbit(x) (x & (-x)) 17 class Solution { 18 public: 19 class FenwickTree { 20 public: 21 FenwickTree(int cnt):n(cnt), c(n + 1) {} 22 23 void add(int ind, int val) { 24 while(ind <= n) c[ind] += val, ind += lowbit(ind); 25 return; 26 } 27 28 int query(int ind) { 29 int ret = 0; 30 while(ind) ret += c[ind], ind -= lowbit(ind); 31 return ret; 32 } 33 34 int at(int ind) { 35 return query(ind) - query(ind - 1); 36 } 37 38 private: 39 int n; 40 vector<int> c; 41 }; 42 43 vector<int> corpFlightBookings(vector<vector<int>>& bookings, int n) { 44 45 //Fenwick Tree 存储机票订购的差分数组,减少求前缀和操作 46 vector<int> ans(n, 0); 47 FenwickTree c(n); 48 for(auto x : bookings) { 49 c.add(x[0], x[2]); 50 if(x[1] == n) continue; //其实这里不加判断条件也可以,因为fenwickTree 中不会对 > n 的值操作 51 c.add(x[1] + 1, -x[2]); 52 } 53 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans[i] = c.query(i + 1); 54 return ans; 55 } 56 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号