======================= **基础知识** =======================
前置知识:
母串S/文本串:被查找源字符串;
模式串T: 目标字符串;
单模匹配问题:只有一个模式串问题;
字符串匹配算法需要极强观察能力;
常见的算法:
1. 暴力匹配(brute force):保证不重不漏的进行每一次匹配,实现查找的目的;O(n * m);
2. KMP算法 : 模式串T 匹配 母串S 问题 ==>模式串 匹配 模式串过程; 在处理与匹配过程中,都是寻找到重复部分,减少重复过程;
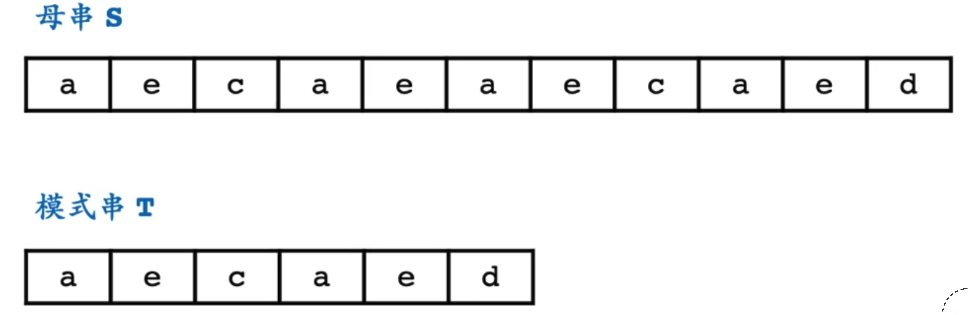
针对已经匹配好的部分在母串与模式串一致特性,后移模式串的失配位置前一位在模式串中匹配位置,减少重复匹配过程,继续匹配母串中失配位置,直到找到一个匹配,然后后移母串匹配位i = i + 1;
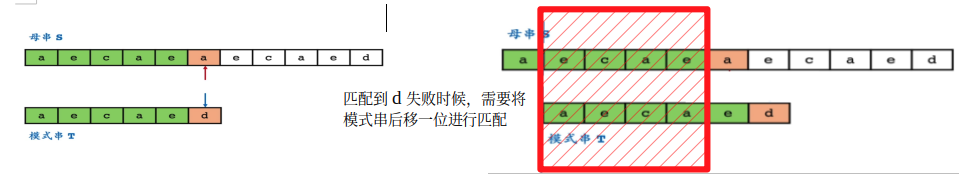
但是后移一位,明显并不能匹配;换个说法如果想要后移一位后,母串(a) 失配位置继续能够匹配,那么右边红色阴影部分必须匹配;
那么如何实现红色阴影部分的匹配? 首先母串中红色阴影部分是已经与模式串匹配成功的部分,也就意味着这部分在模式串中有一模一样的(也就是模式串中绿色部分);
那上面问题就变成了,在模式串绿色部分找到模式串失配位置前一位(e),在模式串中的最长匹配位置(保证不漏);将模式串移动至该位置,就可以继续匹配母串(a);这里就变成了模式串 匹配 模式串问题;而模式串的数据是可以预处理的,找出其中的关键信息;
关于上面所说的最长匹配位置,因为上面红色阴影部分为了保证不漏,要保证最长匹配;也就是说,假设绿色匹配部分的长度为n(0 ~ (n - 1), 示例中为5),那么先要看模式串中从头长度为(n - 1) (idx = 0 ~ (n - 2), (前缀)) 是否与 失配位置往前长度为(n - 1) (idx = 1 ~ (n - 1), (后缀)) 匹配; 如果不匹配,那么下一个长度为 n - 2 的前缀 与 后缀 之间是否匹配... ;从而保证不漏;
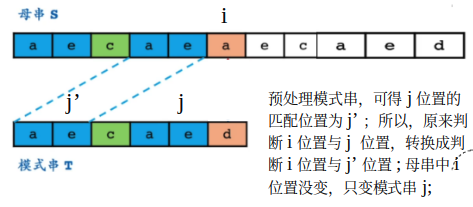
对上面过程总结,如果对模式串进行预处理,找到其中每个字符在模式串中匹配位置(Ta = Tb);当位置i 与 j 发生失配时( j之前是匹配好的数据部分),就将模式串后移(Ta与 Sb 重合), 将 i 与 j' 比较;不断重复这个过程,直到在模式串中找到匹配 i 位置(可以在模式串-1位置设立万能匹配位,保证一定能找到匹配);然后将i = i + 1 继续匹配;
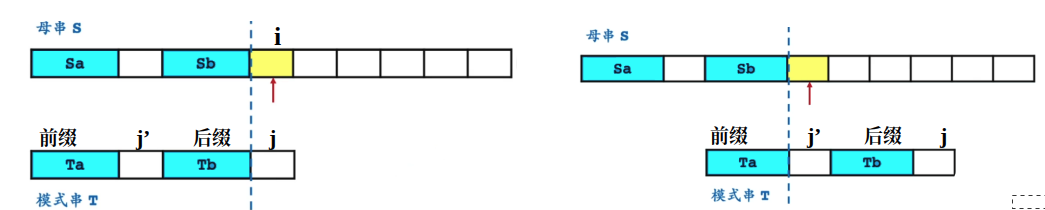
3. Sunday:通过黄金对齐点位,保证不重不漏,同时减少不必要的位置匹配;

其中对模式串的黄金点位求取过程,必须要保证是该字符在模式串中的最后一位;保证不漏;
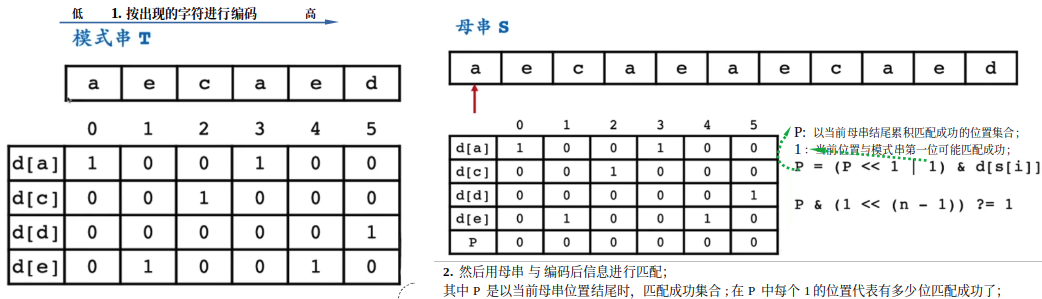
4. ShiftAnd:将模式串转换成信息编码,然后比较母串与信息串
这里有点类似拿一个打卡条,然后对着一位位去比较,match就为1,否则为0, 然后不断向后移动;
对于大于32 位的数据,可以使用bitmap;
5. 马拉车(Manacher)算法: 针对回文子串判断;
a). 预处理:避免回文串长度为偶数;
aba -> #a#b#a#
abab-> #a#b#a#b#
b). 针对字符串进行回文串匹配操作,记录每个点对应的最大回文字节半径,然后根据最大半径的长度可以根据对称性,减少这个对称位置的判断过程;
对于当前位置是否有对应已判断过的点有以下3中情况:其中 i / j 为 当前最远回文位置对应的P 的对称点,P 点半径为len[p];
1). i / j 位置没有在已匹配过的回文串内,只能使用暴力;
2). i / j 在已判断的回文串范围内,并且j 对应回文半径小于等于P 的回文范围内;
3). i / j 在已判断的回文串范围内,并且j 对应回文半径大于等于P 的回文范围内;

5. 最长回文子串 : 标准Manacher 题目:

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 string preprocess(string s) { 4 string ret = "#"; 5 for(int i = 0; s[i]; ++i) ret = ret + s[i] + "#"; 6 return ret; 7 } 8 9 string longestPalindrome(string s) { 10 string ns = preprocess(s), ans = ""; 11 int len = ns.size(), l = 0, r = 0; 12 vector<int> radius(len, 0); 13 14 int ret = 0; 15 for(int i = 0; ns[i]; ++i) { 16 //判断当前点是否可以使用之前的判断结果;min 过程是为处理2/3 中情况 17 if(i < r) radius[i] = min(radius[l + r - i], r - i); 18 //对当前位置进行判断; 19 while(i - radius[i] > 0 && ns[i - radius[i] - 1] == ns[i + radius[i] + 1]) radius[i]++; 20 //判断是否更新 l / r; 21 if(i + radius[i] > r) r = i + radius[i], l = i - radius[i]; 22 //判断结果; 23 if(radius[ret] < radius[i]) ret = i; 24 } 25 26 for(int i = ret - radius[ret], I = ret + radius[ret]; i <= I; ++i) { 27 if(ns[i] == '#') continue; 28 ans += ns[i]; 29 } 30 return ans; 31 } 32 };
6. 字典树(Trie) 与 双数组字典树(double Array Trie):
======================= **代码演示** =======================
1. 上面bruteForce/KMP/Sunday/shiftAnd 基本代码过程:

1 //#include "string_match.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 #define MAX_N 1000 7 #define CHAR_LEN 256 8 #define TESTFUNC(func, s1, s2) printf("func:%15s, idx:%3d\n", #func, func(s1,s2)) 9 int brute_force(const char* text, const char* pattern) { 10 for(int i = 0; text[i]; ++i) { 11 bool flag = 1; 12 for(int j = 0; pattern[j]; ++j) { 13 if(text[i + j] == pattern[j]) continue; 14 flag = 0; 15 break; 16 } 17 if(flag) return i; 18 } 19 return -1; 20 } 21 22 void getPre(const char* text, int *pre) { 23 pre[0] = -1; 24 for(int i = 1, j = -1; text[i]; ++i) { 25 while(j != -1 && text[i] - text[j + 1]) j = pre[j]; //这以前j 都是前一个匹配位置 26 if(text[i] == text[j + 1]) ++j; //这里才将j 设置为与当前i 匹配的位置 ,如果没有匹配则为-1 27 pre[i] = j; 28 } 29 return; 30 } 31 int getNextj(const char ch, const char* pattern, int *preMatch, int j) { 32 while(j != -1 && ch - pattern[j + 1]) j = preMatch[j]; 33 if(ch == pattern[j + 1]) j++; 34 return j; 35 } 36 37 //算法核心:在于对于模式串进行分析,找出模式串中每个index 中前面匹配的位置(以当前位置为结尾时,模式串前n位 与 当前结尾处前n位一致) 38 // 这样当某个位置不匹配时候,只要找模式串当前失配位置前一个值对应前置匹配的index 继续比较; 39 //编程技巧: 定义一个前置节点,作为一个万能匹配位置 40 // 对于母串匹配中的节点位置,不会倒回去 41 // 模式串前置匹配数组初始化:这里重点在于j 表示的是当前位置i 为结尾时,前缀n == 后缀n 对应的index 位置 42 int KMP(const char *text, const char *pattern) { 43 int n = strlen(pattern); 44 int *preMatch = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 45 getPre(pattern, preMatch); 46 47 for(int i = 0, j = -1; text[i]; i++) { 48 // while(j != -1 && text[i] - pattern[j + 1]) j = preMatch[j]; //这之前的j 都是表示i - 1 位置对应匹配patter 中的位置 49 // if(text[i] == pattern[j + 1]) j++; //这里才更新了当前text[i] 对应到pattern 中 j 的值 50 //将上面过程变成getNextj, 相当于每次输入一个值,就会更新一次状态,类似状态机的过程; 51 j = getNextj(text[i], pattern, preMatch, j); 52 if(pattern[j + 1] == '\0') return i - j; 53 } 54 return -1; 55 } 56 57 int SUNDAY(const char* text, const char* pattern) { 58 //所有可能字符串对应last position,即使模式串只包含26字母,但是字符串结尾是'\0',所以last_pos也必须保证有'\0'; 59 int *last_pos = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * CHAR_LEN), 60 n = strlen(text), m = strlen(pattern); 61 for(int i = 0; i < CHAR_LEN; ++i) last_pos[i] = -1; 62 for(int i = 0; pattern[i]; ++i) last_pos[pattern[i]] = i; 63 bool flag = 1; 64 for(int i = 0; i + m <= n; i += (m - last_pos[text[i + m]])) { 65 flag = 1; 66 for(int j = 0; pattern[j]; ++j) { 67 if(text[i + j] == pattern[j]) continue; 68 flag = 0; 69 break; 70 } 71 if(flag) return i; 72 } 73 return -1; 74 } 75 76 77 int ShiftAnd(const char *text, const char *pattern) { 78 //模式串长度小于32; 79 unsigned int P = 0, code[CHAR_LEN] = {0}; 80 int n = 0; 81 for(; pattern[n]; ++n) code[pattern[n]] |= (1 << n); 82 83 for(int i = 0; text[i]; ++i) { 84 P = (P << 1| 1) & code[text[i]]; //这里就是getNextP 过程; 85 if(P & (1 << (n- 1))) return (i - n + 1); 86 } 87 return -1; 88 } 89 90 91 int main() 92 { 93 char text[MAX_N], pattern[MAX_N]; 94 while(~scanf("%s %s", text, pattern)) { 95 TESTFUNC(brute_force, text, pattern); 96 TESTFUNC(KMP, text, pattern); 97 TESTFUNC(SUNDAY, text, pattern); 98 TESTFUNC(ShiftAnd, text, pattern); 99 } 100 return 0; 101 }
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1.KMP 中主要分为求模式串预处理过程,预处理后使用过程;很多时候是对于这两点分别考察的;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) { 4 5 vector<int> pre(s.size(), -1); 6 for(int i = 1, j = -1; s[i]; ++i) { 7 while(j != -1 && s[i] - s[j + 1]) j = pre[j]; 8 if(s[j + 1] == s[i]) pre[i] = ++j; 9 } 10 11 //这里隐藏着前缀 与 后缀之间差值,如果可以被字符长度除尽,那么字符一定是以这部分差重复的;可以自己证明下 12 return pre.back() != -1 && !(s.size() % (s.size() - 1 - pre.back())); 13 //brute force 14 // int pos = 0; 15 // while((pos = s.find(s[0], pos + 1)) != s.npos) { 16 // if(s.size() % pos) continue; 17 // int flag = 1; 18 // for(int i = pos; s[i];) { 19 // for(int j = 0; j < pos; ++j) { 20 // if(s[i] == s[j]) { 21 // i++; 22 // continue; 23 // } 24 // flag = 0; 25 // break; 26 // } 27 // if(!flag) break; 28 // } 29 // if(flag) return true; 30 // } 31 // return false; 32 } 33 };

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 string longestPrefix(string s) { 4 vector<int> pre(s.size(), -1); 5 for(int i = 1, j = -1; s[i]; ++i) { 6 while(j != -1 && s[i] - s[j + 1]) j = pre[j]; 7 if(s[j + 1] == s[i]) j++; 8 pre[i] = j; 9 } 10 return s.substr(0, pre.back() + 1); 11 } 12 };
214. 最短回文串 : 对于回文串,从前向后 与 从后向前都是一样,利用这一性质去掉满足回文的部分(也就是去掉重复的过程);

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 string shortestPalindrome(string s) { 4 if(!s.size()) return s; 5 string reverse_s = s, temp_s = ""; 6 reverse(reverse_s.begin(), reverse_s.end()); 7 //下面操作是解题的精髓,利用了下面几个特性; 8 //1.回文串自身性质是正着读/反着读都是一样的信息; 9 //2.将s 取反后,回文串部分顺序没有变化,那么回文串部分是能找到重复的; 10 //即可利用KMP 中对模式串的预处理过程; 11 //3. 编程技巧,中间'#'; Exam: aaaaaa 12 temp_s = s + '#' + reverse_s; 13 14 vector<int> pre(temp_s.size(), -1); 15 for(int i = 1, j = -1; temp_s[i]; ++i) { 16 while(j != -1 && temp_s[j + 1] - temp_s[i]) j = pre[j]; 17 if(temp_s[i] == temp_s[j + 1]) j++; 18 pre[i] = j; 19 } 20 21 int pos = pre.back() + 1; 22 s = temp_s.substr(pos, s.size() - pos); 23 return reverse_s + s; 24 } 25 };
2. 标准求匹配字符串题:

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 void getNext(string pat, vector<int>& next){ 4 for(int i = 1, j = -1, I = next.size(); i < I; ++i) { 5 while(j != -1 && pat[i] - pat[j + 1]) j = next[j]; 6 if(pat[i] == pat[j + 1]) ++j; 7 next[i] = j; 8 } 9 return; 10 } 11 12 int KMP(string src, string pat) { 13 int m = pat.size(); 14 vector<int> next(m, -1); 15 getNext(pat, next); 16 for(int i = 0, j = -1, I = src.size(); i < I; ++i){ 17 while(j != -1 && src[i] - pat[j + 1]) j = next[j]; 18 if(src[i] == pat[j + 1]) ++j; 19 if(j == m - 1) return i - j; 20 } 21 return -1; 22 } 23 24 int Sunday(string src, string pat) { 25 #define MAX_CHAR 256 26 int m = pat.size(); 27 vector<int> last_pos(MAX_CHAR, -1); 28 for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) last_pos[pat[i]] = i; 29 30 for(int i = 0, I = src.size() - m; i <= I; i += (m - last_pos[src[i + m]])) { 31 int flag = 1; 32 for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) { 33 if(src[i + j] == pat[j]) continue; 34 flag = 0; 35 break; 36 } 37 if(flag) return i; 38 } 39 return -1; 40 } 41 42 void leftShift(vector<unsigned int>& P, int val) { 43 int size = P.size(); 44 P[size - 1] = P[size - 1] << 1; 45 for(int i = size - 2; i >= 0; --i) { 46 if(P[i] & 0x80000000) P[i + 1] |= 1; 47 P[i] = P[i] << 1; 48 } 49 P[0] |= 1; 50 return; 51 } 52 53 int shiftAnd(string src, string pat) { 54 int m = pat.size(), granularity = sizeof(int) * 8; 55 int cnt = ceil(m / double(granularity)), last_shift = (m % granularity ? m % granularity - 1: granularity - 1); 56 #define BASE 256 57 vector<vector<unsigned int>> code(BASE, vector<unsigned int>(cnt, 0)); 58 for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { 59 int ind = i / granularity, shift = i % granularity; 60 code[pat[i]][ind] |= 1 << shift; 61 } 62 #undef BASE 63 vector<unsigned int> P(cnt, 0); 64 for(int i = 0, I = src.size(); i < I; ++i) { 65 leftShift(P, 1); 66 for(int j = 0; j < cnt; ++j) P[j] = P[j] & code[src[i]][j]; 67 if(P[cnt - 1] & (1 << last_shift)) return i - m + 1; 68 } 69 return -1; 70 } 71 72 int strStr(string haystack, string needle) { 73 if(!needle.size()) return 0; 74 return KMP(haystack, needle); 75 //return Sunday(haystack, needle); 76 //return shiftAnd(haystack, needle); 77 } 78 };
3. sunday 算法中对于字符串黄金对齐点的应用;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) { 4 if(!s.size()) return 0; 5 int pre = -1, ans = 0, n = s.size(); 6 vector<int> index(256, -1); 7 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 8 //当前字符在当前计算范围内出现了,就要更新pre节点 与 ans; 9 if(index[s[i]] > pre) { 10 ans = max(ans, i - 1 - pre); 11 pre = index[s[i]]; 12 } 13 index[s[i]] = i; 14 } 15 ans = max(ans, n - 1 - pre); 16 return ans; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 class Solution { 21 public: 22 int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) { 23 int ret = 0, before = -1; 24 vector<int> last(256, -1); 25 for(int i = 0, I = s.size(); i < I; ++i) { 26 //优化,每次算下当前字符是否重复过,如果重复就要更新 before 27 //减少if 判断过程,时间有减少 28 before = max(before, last[s[i]]); 29 last[s[i]] = i; 30 ret = max(ret, i - before); 31 } 32 return ret; 33 } 34 };
4. 面试题 17.17. 多次搜索 : 多次匹配问题;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 //KMP : 4 vector<int> KMP(string src, string pat) { 5 int len_p = pat.size(); 6 if(!len_p) return vector<int>(); 7 vector<int> pre(len_p, -1), ret; 8 for(int i = 1, j = -1; i < len_p; ++i) { 9 while(j != -1 && pat[j + 1] != pat[i]) j = pre[j]; 10 if(pat[j + 1] == pat[i]) j += 1; 11 pre[i] = j; 12 } 13 14 for(int i = 0, j = -1; i < src.size(); ++i) { 15 while(j != -1 && src[i] != pat[j + 1]) j = pre[j]; 16 if(src[i] == pat[j + 1]) j += 1; 17 if(j == len_p - 1) { 18 ret.push_back(i - j); 19 j = pre[j]; 20 } 21 } 22 return ret; 23 } 24 25 //Sunday: 26 vector<int> Sunday(string& src, string& pat) { 27 int len_p = pat.size(), len_s = src.size(); 28 if(!len_p) return vector<int>(); 29 #define BASE 128 30 vector<int> last(BASE, -1), ret; 31 for(int i = 0; i < len_p; ++i) last[(pat[i])] = i; 32 for(int i = 0, I = len_s - len_p; i <= I; i += (len_p - last[(src[i + len_p])])) { 33 int j = 0; 34 while(j < len_p && src[i + j] == pat[j]) j += 1; 35 if(j == len_p) ret.push_back(i); 36 } 37 #undef BASE 38 return ret; 39 } 40 41 //Shift-And: 这个长度1000,比较麻烦 42 vector<vector<int>> multiSearch(string big, vector<string>& smalls) { 43 vector<vector<int>> ret; 44 for(auto x : smalls) { 45 ret.push_back(KMP(big, x)); 46 // ret.push_back(Sunday(big, x)); 47 } 48 return ret; 49 } 50 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================
KMP:本质是一个状态机,它的状态就是每次匹配后得到的子串对应位置(j 值);根据每次输入的一个母串字符,得到更新后的状态;
在KMP 算法中,对于母串匹配过程,不会有回退过程(就是程序中getNextj部分);
针对这一特点,KMP可以用于流文件以及一些大文件的单模式匹配,比较适合。因为每次只需要匹配当前字符,不用存储所有的母串;
时间复杂度位 n + m(极限情况位n * m);
SUNDAY:
在文章中查找单词,最优情况下,时间复杂度O(n / m) (n:母串长度, m:模式串长度),远优于bruteForce, KMP;
但是没有办法处理流数据,因为需要存储相当一部分母串信息;
ShiftAnd:
时间复杂度O(n), 支持流数据处理,类比KMP 算法, shiftAnd 更高效,天生支持正则的多模式匹配;每行可以存在多种匹配;
同样也诠释了自动机思想,每次进入一个字符,更新状态;
EXAM: 正则表达式:(a|b|c) & (c|d) & e & (f|a|b), 用shiftAnd 方法很方便,编码后的信息如下;
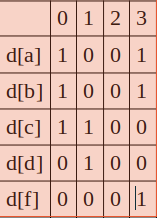
题外话:关于自动机,主要用于编译原理;但是自动机本质就是图灵机,也就是当代计算机的基础;




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号