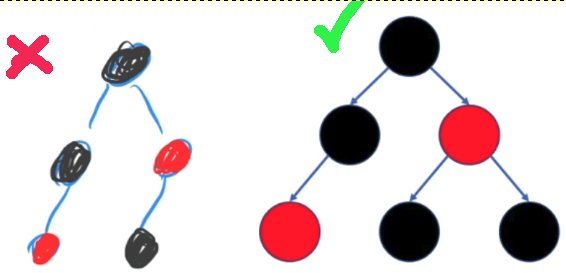
======================= **基础知识** =======================
红黑树的基本性质:(红黑树是弱化版的AVL 树)
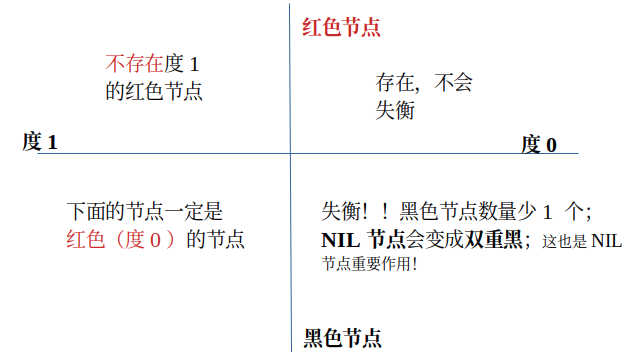
1. 每个节点非黑即红;
2. 根节点是黑色;
3. 叶节点(NIL(Null-pointer to objective))是黑色的; 在示意图中没有画出来的NIL!! 在删除操作中很重要,删除操作中主要就是处理双重黑失衡;
4. 如果一个节点是红色,则它的两个子结点都是黑色的;
5. 从根节点出发到所有叶节点路径上,黑色节点数量相同;
 ==添加上NIL 节点后的=>
==添加上NIL 节点后的=> 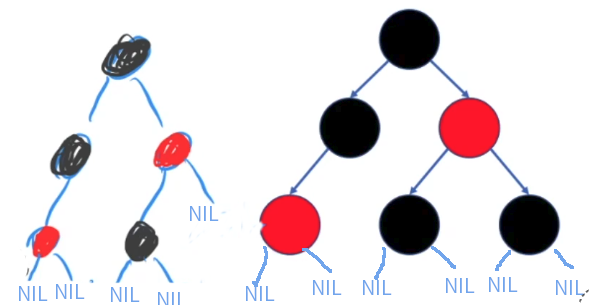
平衡调整法门:(前置知识点:AVL 树中的左旋/右旋 都是完美保证AVL 树性质的;)
1. 插入调整站在 祖父节点 看
2. 删除调整站在 父节点 看;
3. 调整前后都要保证所站的节点(包含)向下看时候,黑色节点的数量是相等的;
4. 根据当前情况中确定颜色的节点,以及满足条件3的前提下,进行调整;
红黑树操作调整过程:
插入调整:结构化思维!!
前置问题 Q:插入新节点是什么颜色? 黑色? 红色?
A:黑色一定会导致当前红黑树失衡,因为当前插入路径的黑色节点数量一定 > 其他叶子根节点到根节点中黑节点数目;
红色:不一定会引起失衡;只有当插入节点的上一节点是红色节点时,会导致失衡;
调整原则: (从祖父节点(包含)向下看)调整之前路径上黑节点数量 要等于 调整后黑节点数量!!!=
(结构化思维,当前子树只是大树中一部分,改变当前子树黑节点数目,有可能会导致整个大树失衡);
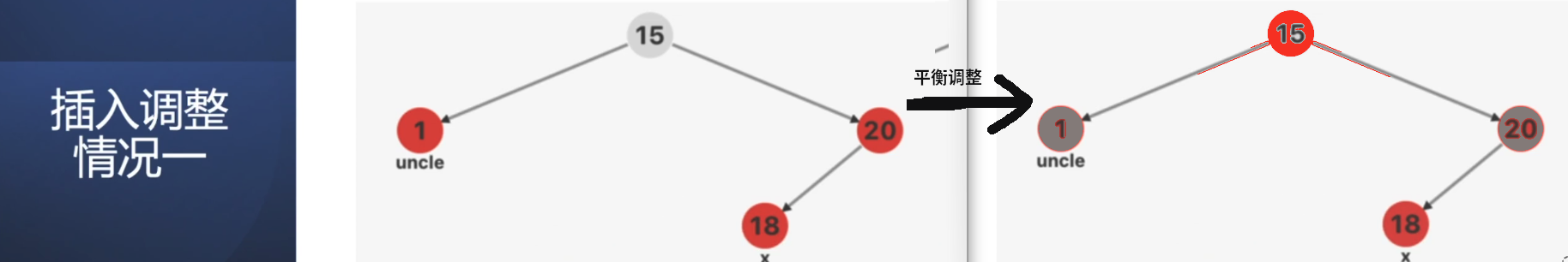
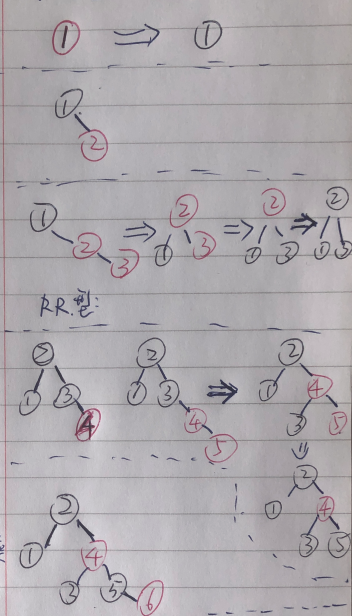
情况1:叔叔节点是红色;
从祖父节点15往下看,父节点20/叔叔节点1为红色,当前节点x = 18为红色(这里其实有4种小情况,x 可以在 叔叔节点1 的左右子结点;父节点20 的左右子结点);
平衡调整方案:祖父节点15 变成红色,父节点/叔叔节点变黑;
如果祖父节点是根节点,那就直接把根节点变黑;不是根节点,就让下一组调整;
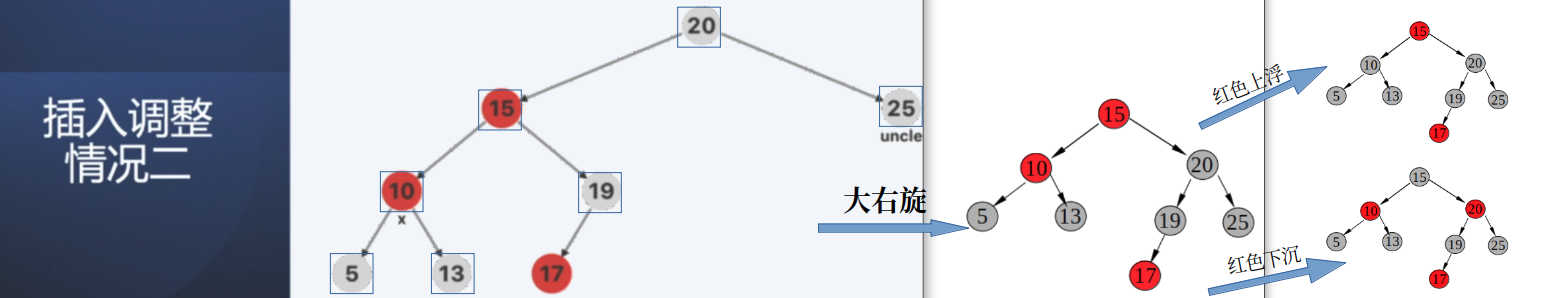
情况2: 叔叔节点25是黑色节点;
对于这种情况下,20/15/25/10/19/5/13 的颜色是确定的;17 是不确定;其中还分为4 种小情况: LL/LR/RL/RR不同类型;
平衡调整方案: 对于这四种情况,采用AVL树中的类似的处理方式;
旋转处理后,对于两个红色节点,可以采用的操作: 红色上浮/红色下沉;
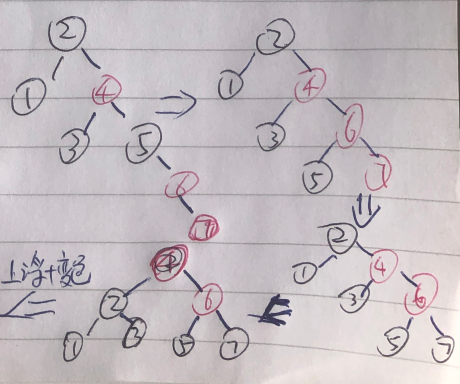
利用上面的规则,做一次顺序插入1,2 ... 7 的操作,使用上浮方式;
 ===>
===> 
删除调整:结构化思维;
前置问题Q:删除什么样的节点,会引发红黑树的失衡;
A: 删除度为0 的黑色节点的时候,会引发红黑树的失衡;被删除黑节点,导致该路径少了一个黑色;此时将NIL 节点作为双重黑节点。
度为1 红色,不存在, 度为0 红色,直接上来,变黑色; 度为1 的黑色,下面只有可能是红色节点;
删除发生时候,失衡的情况(这里主要考虑度0/1 的节点;对于度2 的红/黑色节点,都是找到该树中对应的前驱/后置节点,然后将问题转化为删除前驱/后置节点,这些节点一定是度0/1);
调整重点在于:处理双重黑的节点;保证从父节点(包含)向下看,调整前后的黑色节点数量相同;
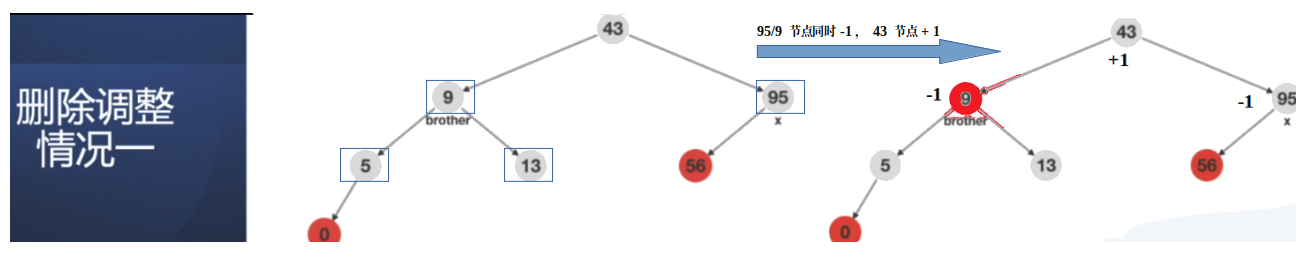
情况1:从父节点43向下看, 双重黑节点x(95),其兄弟节点9是黑色节点,并且兄弟节点的子结点5/13都是黑色节点;(造成这种情况:95 黑色,下面是2个黑色子结点,然后删除了右边黑色子结点后,右边成了双重黑,然后平衡调整成这样的;这也是情况1);
根据上面的条件,蓝框中的点都是确定颜色的点;
平衡调整方案:95/9 节点同时-1, 43 节点+ 1;此时43节点的下面两个节点满足RBT 的要求;
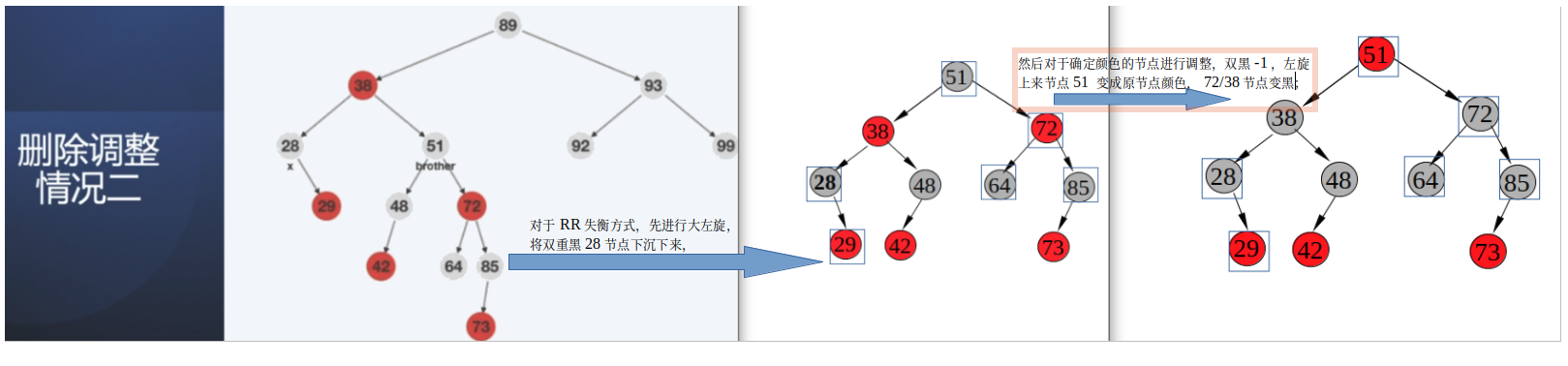
情况2:从父节点38向下看,双重黑节点28,兄弟节点51 为黑色,其子结点有红色节点72,并且红色节点72与其兄弟节点在同一侧;此时48节点是有可能为红色节点;(造成这种情况,最直接就是度2的28节点下面,是两个黑色节点(度0),然后删除了左节点,做了一次平衡调整);
此时是RR 类型;与此类似的还有LL 类型;
根据上面条件,蓝框中是确定颜色的节点;
平衡调整方案: RR 失衡,先进行大左旋,51改成原根节点颜色,38/72 改成黑色, 28恢复成黑节点;
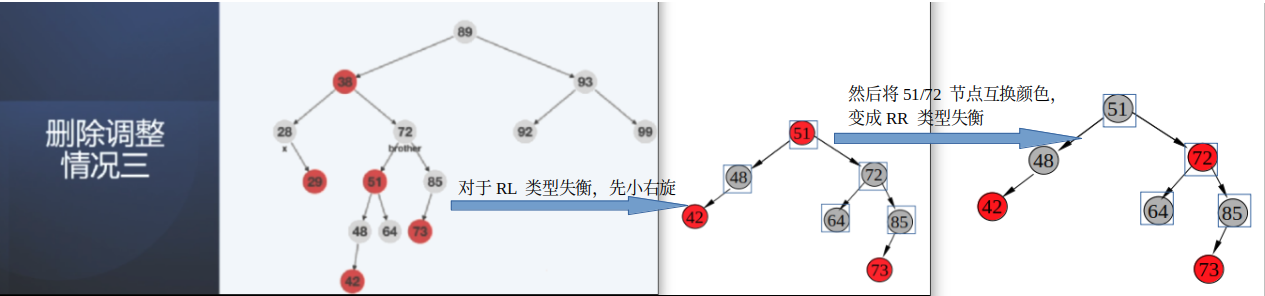
情况3:从父节点38向下看,节点28为双重黑,兄弟节点72 为黑色,其子结点51有红色,且红色与其兄弟节点不在一侧,即节点85一定是黑色节点。(产生这种失衡可能与情况2中类似);
此为RL类型;(与此类似的还有LR 类型)
根据上面条件,蓝框中是确定颜色的节点;
平衡调整方案:先小右旋,变成RR类型,然后51/72 互换颜色,变成RR 类型失衡,然后再按照RR方式调整;
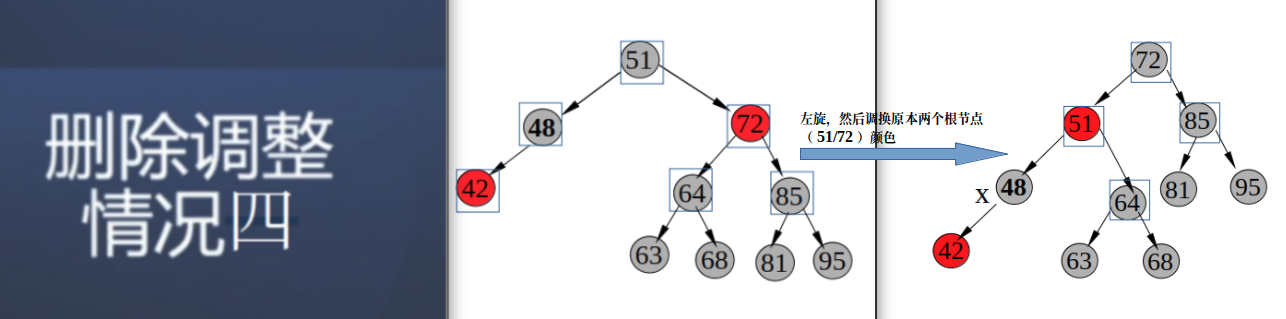
情况4: 上面讨论的都是叔叔节点是黑色,如果叔叔节点为红色的情况;
从父节点51向下看,双重黑48,兄弟节点72为红色;
蓝色框内为确定颜色节点;
平衡调整方案:将树左旋,然后互换当前72与原来51 根节点颜色;
此时失衡类型变成从红色节点51向下看,双重黑48, 兄弟节点64为黑色;有可能为上面3种情况中任意一种可能;
对于失衡的调整总结:几个调整中用到的技巧: 保证调整前后黑色节点数量不变;(重要原则)
一个根节点同时影响左右两个树,所以根变红,左右子树中分别有一个节点翻黑;根变黑,左右子树中各有一个翻红;(插入中用)
左旋时候,左子树树高+1,右子树树高-1;右旋反之;但是对于黑色节点数,有可能使一边不变,另一边-1,差1这个树的这个正好给双重黑去重(删除),或者红变黑(插入);
插入调整中,能将两个子树红色同时往根节点移动,就直接移(插入情况1);叔叔结点为黑的,就把叔叔节点旋转下去(黑节点树不变),父节点子树黑节点差一个,可以变黑;(插入情况2);
删除调整中,对于可以直接左右子树一起-1 方式,根节点+1, 就直接操作,将失衡问题向上移;(删除情况1)
因为子树中有红色节点,不能左右子树直接-1 操作的(删除情况3/4),通过左右旋,然后变换节点颜色,变成RR/LL类型;再通过旋转,将某边子树中黑节点数都-1,然后都需要一个红变黑(删除情况2);
======================= **代码演示** =======================

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define NIL &(Node::__NIL) 4 5 6 struct Node { 7 int key; 8 int color; //0 red, 1 blank, 2 double blank; 9 Node *lchild, *rchild; 10 static Node __NIL; 11 12 Node(int key = 0, int color = 0, Node *left = NIL, Node *right = NIL): 13 key(key), color(color), lchild(left), rchild(right) {} 14 }; 15 16 Node Node::__NIL(0, 1); //NIL 叶子节点为黑色 17 18 Node *getNewNode(int key) { 19 return new Node(key); //默认插入红色节点,黑色必失衡 20 } 21 bool has_red_child(Node *root) { 22 return root->lchild->color == 0 || root->rchild->color == 0; 23 } 24 25 Node *left_rotate(Node *root) { 26 Node *temp = root->rchild; 27 root->rchild= temp->lchild; 28 temp->lchild = root; 29 return temp; 30 } 31 32 Node *right_rotate(Node *root) { 33 Node *temp = root->lchild; 34 root->lchild = temp->rchild; 35 temp->rchild = root; 36 return temp; 37 } 38 39 Node *insert_maintain(Node *root) { //从祖父节点向下看,判断失衡 40 int flag = 0; //1: left , 2 right 41 if(root->lchild->color == 0 && has_red_child(root->lchild)) flag = 1; 42 if(root->rchild->color == 0 && has_red_child(root->rchild)) flag = 2; 43 if(flag == 0) return root; 44 45 //case 1 : 46 if(root->lchild->color == 0 && root->rchild->color == 0) { 47 root->color = 0; 48 root->lchild->color = root->rchild->color = 1; 49 return root; 50 } 51 52 if(flag == 1) { 53 //LR 54 if(root->lchild->rchild->color == 0) root->lchild = left_rotate(root->lchild); 55 //LL 56 root = right_rotate(root); 57 } else { 58 //RL 59 if(root->rchild->lchild->color == 0) root->rchild = right_rotate(root->rchild); 60 //RR 61 root = left_rotate(root); 62 } 63 64 //红色上浮(或下沉) 65 root->color = 0; 66 root->lchild->color = root->rchild->color = 1; 67 return root; 68 } 69 70 Node *__insert(Node *root, int key) { 71 if(root == NIL) return getNewNode(key); 72 if(root->key == key) return root; 73 if(key < root->key) root->lchild = __insert(root->lchild, key); 74 else root->rchild = __insert(root->rchild, key); 75 76 root = insert_maintain(root); 77 return root; 78 } 79 80 Node *insert(Node *root, int key) { 81 root = __insert(root, key); 82 root->color = 1; //为了保证根节点为黑色 83 return root; 84 } 85 86 Node *predecessor(Node *root) { 87 Node *lp = root->lchild; //只有度2调用,一定有左右子孩子 88 while(lp->rchild != NIL) lp = lp->rchild; 89 return lp; 90 } 91 92 Node *erase_maintain(Node *root) { 93 //不需要下面特判,是因为该节点在函数被调用前已经被特判过了 94 //if(root == NIL) return root; 95 //没有失衡 96 if(root->lchild->color != 2 && root->rchild->color != 2) return root; 97 98 //失衡,兄弟节点为红色: 99 if(has_red_child(root)) { 100 int flag = 0; //1: 右失衡,左红色; 2 : 左失衡,右红色 101 root->color = 0; 102 if(root->lchild->color == 0) root = right_rotate(root), flag = 1; 103 else root = left_rotate(root), flag = 2; 104 root->color = 1; 105 if(flag == 1) root->rchild= erase_maintain(root->rchild); 106 else root->lchild= erase_maintain(root->lchild); 107 return root; 108 } 109 110 // 失衡,但是兄弟节点为黑色,且子节点也都为黑色 111 if((root->lchild->color == 1 && !has_red_child(root->lchild)) || 112 (root->rchild->color == 1 && !has_red_child(root->rchild))){ 113 root->lchild->color -= 1; 114 root->rchild->color -= 1; 115 root->color += 1; 116 return root; 117 } 118 119 //失衡,兄弟节点为黑色,而且有一个红色子节点 120 if(root->lchild->color == 2) { //左节点失衡 121 root->lchild->color = 1; //先把失衡的恢复平衡 122 //RL 型 123 if(root->rchild->rchild->color != 0) { //重要点,必须是同一侧有个红色点,才能保证旋转以后,变色,保证这一侧黑色节点数量不变 124 root->rchild->color = 0; 125 root->rchild = right_rotate(root->rchild); 126 root->rchild->color = 1; //转换成RR 型 127 } 128 //RR 型处理 129 root->rchild->color = root->color; 130 root = left_rotate(root); 131 } else {//右节点失衡 132 root->rchild->color = 1; //先把节点恢复平衡 133 //LR 134 if(root->lchild->lchild->color != 0) { //重要点:将后面大右旋后左子树左边节点里,黑色节点数量保证不变 135 root->lchild->color = 0; 136 root->lchild = left_rotate(root->lchild); 137 root->lchild->color = 1; //转换成LL 138 } 139 root->lchild->color = root->color; 140 root = right_rotate(root); 141 } 142 root->lchild->color = root->rchild->color = 1; 143 return root; 144 145 } 146 147 Node *__erase(Node *root, int val){ 148 if(root == NIL) return root; 149 if(val < root-> key) root->lchild = __erase(root->lchild, val); 150 else if(val > root->key) root->rchild = __erase(root->rchild, val); 151 else { //当前节点 = val 152 //度为2 153 if(root->lchild != NIL && root->rchild != NIL) { 154 Node *pd = predecessor(root); 155 root->key = pd->key; 156 root->lchild = __erase(root->lchild, pd->key); //上3行也可以是右子树找值替换 157 return root; 158 } else { //度为0, 1 159 Node *temp = (root->lchild == NIL ? root->rchild : root->lchild); 160 temp->color += root->color; 161 delete root; 162 return temp; 163 } 164 } 165 //调整只在父节点往下看,所以对于当前节点为删除节点不需要调整 166 return erase_maintain(root); 167 } 168 169 Node *erase(Node *root, int val) { 170 root = __erase(root, val); 171 root->color = 1; 172 return root; 173 } 174 175 176 177 void clear(Node *root) { 178 if(root == NIL) return; 179 clear(root->lchild); 180 clear(root->rchild); 181 printf("clear the node (%d | %d)", root->key, root->color); 182 delete root; 183 return; 184 } 185 186 void output(Node *root) { 187 if(root == NIL) return; 188 printf("(%d|%d, %d %d)\n", root->color, root->key, root->lchild->key, root->rchild->key); 189 output(root->lchild); 190 output(root->rchild); 191 return; 192 } 193 194 int main() 195 { 196 int op, val; 197 Node *root = NIL; 198 while(cin >> op >> val){ 199 switch(op) { 200 case 1:root = insert(root, val); break; 201 case 2: root = erase(root, val); break; 202 } 203 cout << "\n======== RB tree print start========\n"; 204 output(root); 205 cout << "======== RB tree print end========\n"; 206 } 207 return 0; 208 }
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1. map/set 底层实现使用了红黑树;所以对于需要按照一定顺序查找数值就很方便了;

1 class TimeMap { 2 public: 3 map<string, map<int, string> > infor; 4 TimeMap() {} 5 6 void set(string key, string value, int timestamp) { 7 infor[key].insert(make_pair(timestamp, value)); 8 return; 9 } 10 11 string get(string key, int timestamp) { 12 if(infor.find(key) == infor.end()) return ""; 13 map<int, string> &temp = infor[key]; 14 if(temp.find(timestamp) != temp.end()) return temp[timestamp]; 15 16 string ret = ""; 17 temp.insert(make_pair(timestamp, "")); 18 auto cur = temp.find(timestamp); 19 if(cur != temp.begin()) ret = (--cur)->second, ++cur; 20 temp.erase(cur); 21 return ret; 22 } 23 }; 24 25 /** 26 * Your TimeMap object will be instantiated and called as such: 27 * TimeMap* obj = new TimeMap(); 28 * obj->set(key,value,timestamp); 29 * string param_2 = obj->get(key,timestamp); 30 */
2. RB Tree 也处处体现了结构化思维;
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II : 善于利用当前结构的性质,以及递归中已经处理好的信息;

1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 public: 5 int val; 6 Node* left; 7 Node* right; 8 Node* next; 9 10 Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} 11 12 Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} 13 14 Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) 15 : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} 16 }; 17 */ 18 19 class Solution { 20 public: 21 Node *layer_connect(Node *r) { 22 if(!r) return nullptr; 23 Node pre, *nxt = ⪯ 24 while(r) { 25 if(r->left) nxt->next = r->left, nxt = nxt->next; 26 if(r->right) nxt->next = r->right, nxt = nxt->next; 27 r = r->next; 28 } 29 return pre.next; 30 } 31 32 Node* connect(Node* root) { 33 Node *p = root; 34 while(p = layer_connect(p)); 35 return root; 36 } 37 };
3. 利用RB Tree 排序的特性:
220. 存在重复元素 III :区间最小距离,双指针 + 排序;因为存在重复元素,对于STL 中map/set 必须要strict weak ordering;
用打包结构,要注意CMP 过程,避免重复元素被覆盖; 或者用map, key 记录元素,value 记录个数,注意erase 情况;

class Solution { public: void del_num(map<int,int> &m, int num) { m[num] -= 1; if(!m[num]) m.erase(num); return; } bool checkPass(map<int, int> &m, int num, int t) { map<int, int>::iterator it = m.find(num); if(it != m.begin()){ if((long long) num - (long long)((--it)->first) <= t) return true; ++it; } if(++it != m.end() && ((long long)(it->first) - (long long)(num) <= t)) return true; return false; } bool containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k, int t) { map<int, int> mark; for(int i = 0, len = nums.size(); i < len; ++i) { if(i - k > 0) del_num(mark, nums[i - k - 1]); mark[nums[i]] += 1; if(mark[nums[i]] > 1 || checkPass(mark, nums[i], t)) return true; } return false; //打包两个数据 // typedef pair<int,int> PII; // int l = 0, len = nums.size(); // bool(*f1)(PII,PII) = [](PII a, PII b) { // if(a.second != b.second) return a.second < b.second; // return a.first < b.first; // }; // set<PII, bool(*)(PII, PII)> arr(f1); // for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) { // if(i - l > k) { // arr.erase(make_pair(l, nums[l])); // l++; // } // arr.insert(make_pair(i, nums[i])); // auto iter = arr.find(make_pair(i, nums[i])); // if(iter != arr.begin()){ // iter--; // if((long long)nums[i] - (long long)(iter->second) <= t) return true; // iter++; // } // if(++iter != arr.end() && (long long)(iter->second) - (long long)nums[i] <= t) return true; // } // return false; } };
======================= **应用场景** =======================
STL 中 map/set 这类的容器的底层都是使用RB tree 来实现的;




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号