======================= **基础知识** =======================
二叉排序树(二叉搜索树):思维结构中可以是有序数组,树;
性质: 左子树 < 根节点 ; 右子树 > 根节点;
中序遍历结果:就是递增排序的有序序列;(3,17, 20, 28, 28, 29, 30, 32)
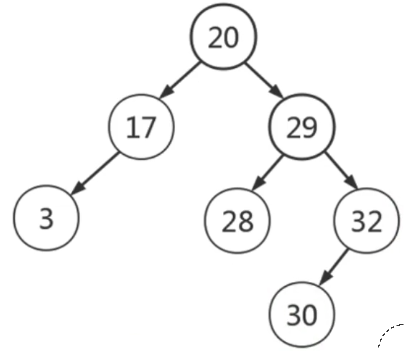
操作:
增(插入): 与根结点比较:小于:进入左子树;大于:进入右子树;重复操作,直到找到一个空节点插入该数;
查:与根节点比较,小于进入左子树,大于进入右子树,直到找到该数;
删:对应多种情况,分类处理;
1.删除叶子节点:直接删除;
2.删除度为1 的节点: 只要存在上一个根节点,直接将孩子顶替当前被删除的节点;
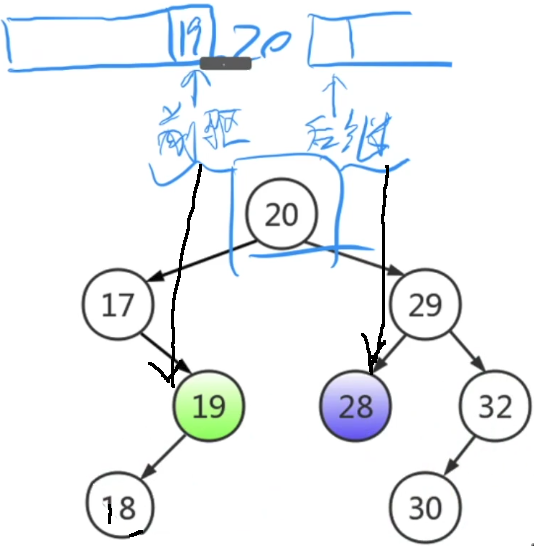
3. 删除度为2 的节点: 前驱节点 :相对删除节点,左子树中离他最近的节点(左子树一直往右),左子树中最大值;
后置节点: 相对删除节点,右子树中离他最近的节点(右子树一直往左),右子树中最小值;
对于前驱/后置节点:它们最多为度为1 的节点;如果度为2 ,一定存在左右子树,那就不会是当前子树中最值;
所以就可以把前驱(后置)节点替换删除节点,然后将问题转换为删除度为1/0 的操作;
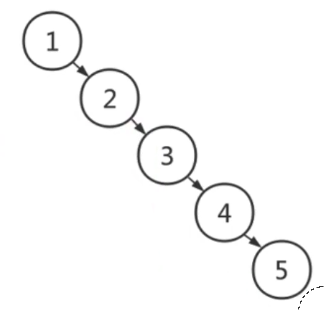
缺点: 二叉排序树,有可能退化成如下的链表,使得所有的操作时间复杂度变成O(n);
用途: 用于解决排名相关的检索需求;
AVL 树:平衡二叉排序树:重点在于平衡条件!!
AVL树得名于它的发明者G. M. Adelson-Velsky和E. M. Landis,他们在1962年的论文《An algorithm for the organization of information》中发表了它。
性质:除了上面的二叉排序树的性质以外: | H(left) - H(right) | <= 1; 左右子树的高度差不超过1;
优点:对于每个节点的左右子树的树高做了限制,所以整个树不会退化成链表;
特点:对于AVL 树的旋转操作,它使得一部分树高 - 1, 一部分树高 + 1, 还有一部分树高不变;这一特点使得平衡调整有可能成功;
基本操作:
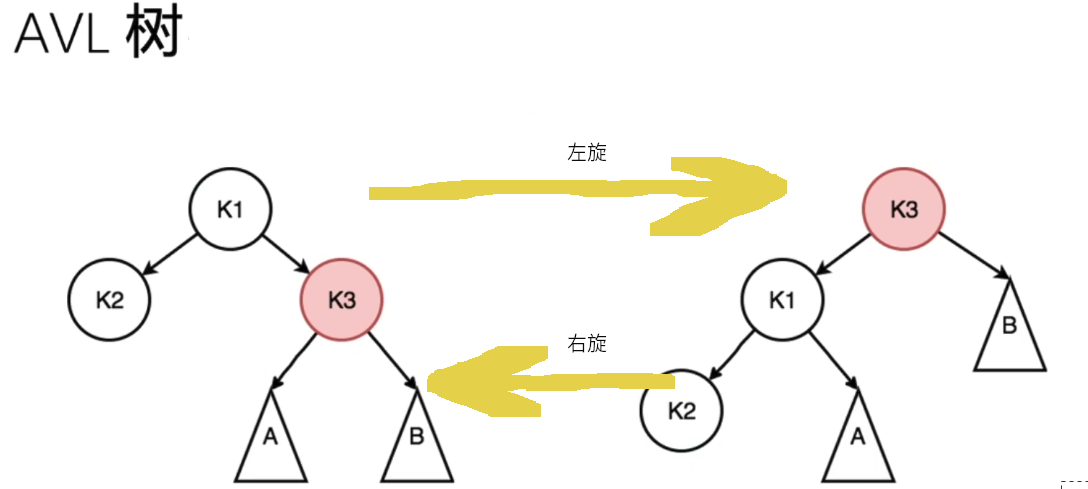
左旋: 以k1 为基点,将k3 点左旋上来;A 节点变成K1 的右子树;
右旋: 左旋的反向操作:
左/右旋操作后,仍然保证了二叉排序的性质;
在增删改查操作中,只有增/删 会有可能引起AVL 树失衡;
在增/删 以后的递归回溯过程中,在当前节点向下看,如果AVL 树失衡,为了维护AVL 树的性质,就需要进行调整;调整可能会进行多次;
经典的AVL 树 -失衡类型: 主要3大类: LL/RR型,LR型,RL 型;注意:删除/插入操作,每次只会增加(减少)一个节点,而原树也是AVL 树,这也是下面公式推导中要注意的点;
LL/RR 型: 在K1节点向下看, 左子树K2节点高(L); 在K2节点中,左子树A节点高(L);
解决方案:LL : 抓住K1 大右旋,将K2 旋转上来; RR: 直接抓住K1 大左旋;
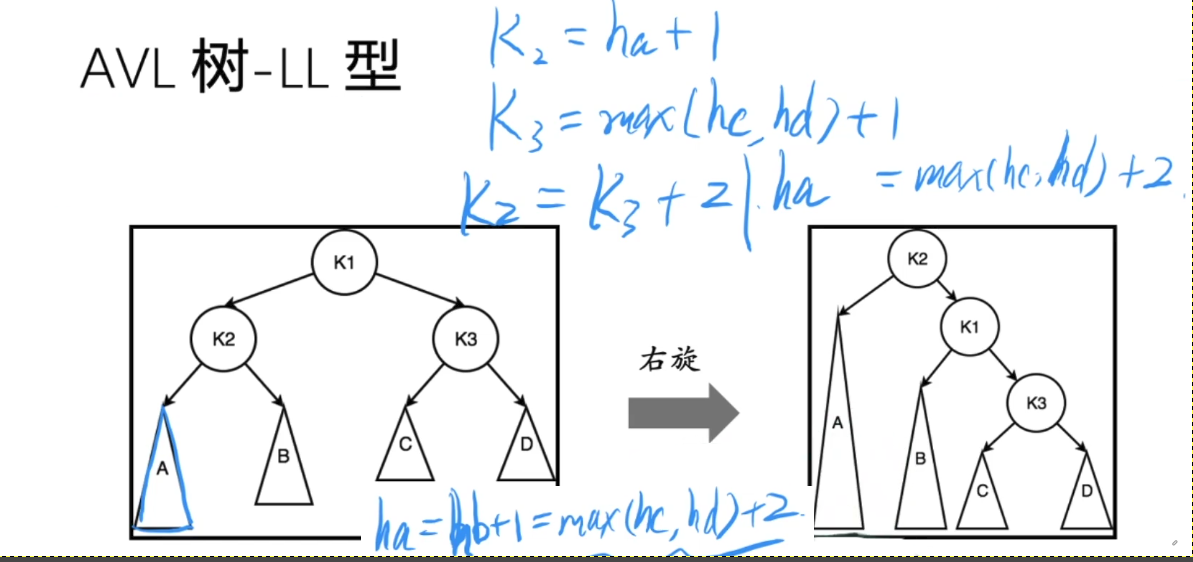 LL型:
LL型: 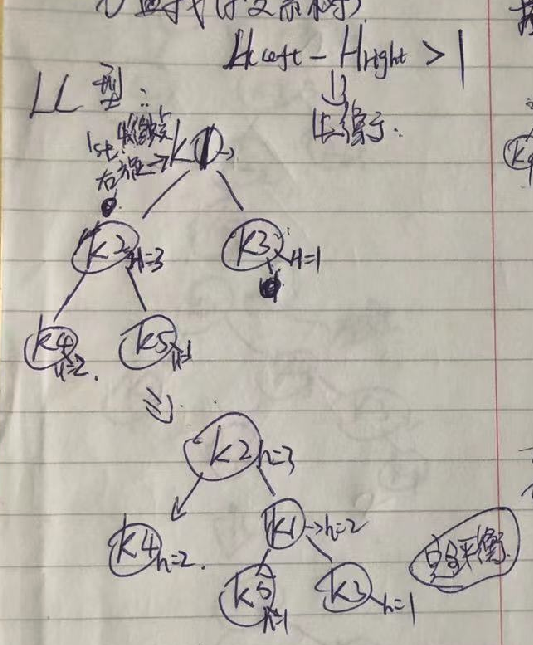 RR型
RR型 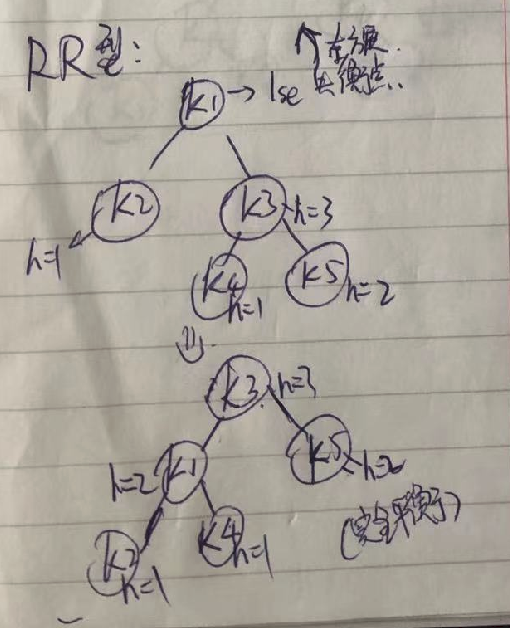
LR 型: 在K1节点向下看, 左子树K2节点高(L); 在K2节点中,左子树K3节点高(R);
解决方案: 先抓K2左旋,变成LL 型; 然后再抓K1 右旋;
RL 型: 与LR 型相反;
解决方案: 与LR 型相反,先小右旋,变成RR型; 再大左旋;
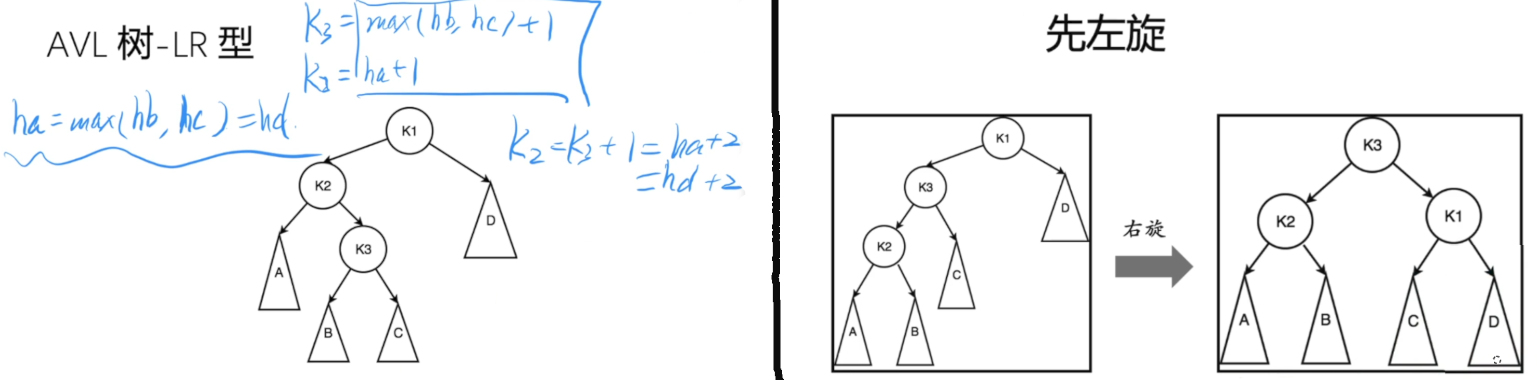
对于LR/RL 类型旋转的过程:
LR型: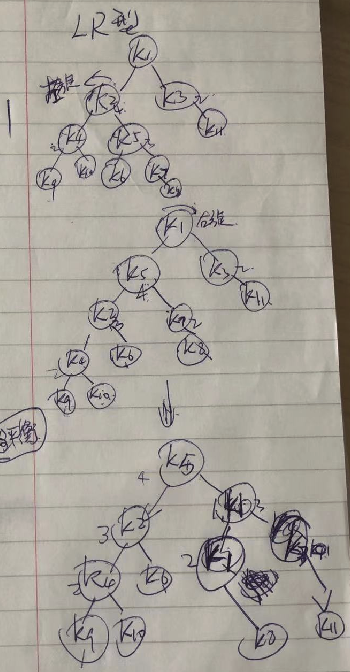 RL型:
RL型: 
======================= **代码演示** =======================
数据结构是定义一种性质,并维护这种性质;
1. 实现二叉排序树:代码中注意对于erase 的删除部分的处理,尤其是对于度为2 节点的删除;插入/删除过程返回更新后的节点;

1 //#include "binaryTree.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 struct Node{ 6 Node(int key = 0, Node *left = nullptr, Node *right = nullptr) 7 : key(key), left(left), right(right) {} 8 int key; 9 Node *left, *right; 10 11 }; 12 13 Node *getNewnode(int key) { 14 return new Node(key); 15 } 16 17 Node *insert(Node *root, int key){ //返回插入新节点以后的root 地址 18 if(root == nullptr) return getNewnode(key); 19 if(root->key == key) return root; 20 21 if(key < root->key) root->left = insert(root->left,key); //这里就用到返回值,减少操作,多体会 22 if(key > root->key) root->right = insert(root->right,key); 23 return root; 24 } 25 26 Node *predeccessor(Node *root) { //左子树最大值 27 Node *temp = root->left; 28 while(temp->right) temp = temp->right; 29 return temp; 30 } 31 32 Node *erase(Node *root, int key) { 33 if(root == nullptr) return root; 34 if(key < root->key) root->left = erase(root->left, key); 35 else if(key > root->key) root->right = erase(root->right, key); 36 else { 37 // if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr){ //度为0 38 // delete root; 39 // return nullptr; 40 if( root->left == nullptr || root->right == nullptr){//度为1 41 Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; 42 delete root; 43 return temp; 44 } else { 45 Node *temp = predeccessor(root); 46 root->key = temp->key; 47 root->left = erase(root->left, temp->key); 48 } 49 } 50 return root; 51 } 52 53 void clear(Node *root) { 54 if(root == nullptr) return; 55 clear(root->left); 56 clear(root->right); 57 delete root; 58 return; 59 } 60 61 void output(Node *root) { 62 if(!root) return; 63 output(root->left); 64 cout << root->key << " "; 65 output(root->right); 66 return; 67 } 68 69 int main() 70 { 71 int op, val; 72 Node *root = nullptr; 73 while(cin >> op >> val) { 74 switch (op) { 75 case 0 : root = insert(root, val); break; 76 case 1 : root = erase(root, val); break; 77 } 78 output(root); 79 cout << endl; 80 } 81 return 0; 82 }

1 //input : 2 //0 3 3 //0 2 4 //0 1 5 //0 5 6 //0 4 7 //1 3 8 //1 4 9 10 #include <iostream> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 struct Node { 14 Node(int v = -1, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr) : val(v), left(l), right(r){} 15 Node *left, *right; 16 int val; 17 }; 18 19 class BinaryTree{ 20 private: 21 Node *root; 22 void clear(Node *root){ 23 if(!root) return; 24 if(root->left) clear(root->left); 25 if(root->right) clear(root->right); 26 delete root; 27 return; 28 } 29 30 Node *__insert(Node* r, int key) { 31 if(!r) return new Node(key); 32 if(key < r->val) r->left = __insert(r->left, key); 33 else if(key > r->val) r->right = __insert(r->right, key); 34 return r; 35 } 36 37 Node *__find(Node *r, int key) { 38 if(!r) return nullptr; 39 if(key < r->val) return __find(r->left, key); 40 else if(key > r->val) return __find(r->right, key); 41 return r; 42 } 43 44 Node *predeccessor(Node *r) { //后驱节点 45 Node *temp = r->right; 46 while(temp->left) temp = temp->left; 47 return temp; 48 } 49 50 Node *__erase(Node *r, int key) { 51 if(!r) return nullptr; 52 53 if(key < r->val) r->left = __erase(r->left , key); 54 else if(key > r->val) r->right = __erase(r->right, key); 55 else { 56 if(!r->left || !r->right) { 57 Node *son = r->left ? r->left : r->right; 58 delete r; 59 return son; 60 } else { 61 Node *__predec = predeccessor(r); 62 r->val = __predec->val; 63 r->right = __erase(r->right, __predec->val); 64 } 65 } 66 return r; 67 } 68 69 void __output(Node *r) { 70 if(!r) return; 71 __output(r->left); 72 cout << r->val << " "; 73 __output(r->right); 74 return; 75 } 76 77 78 public: 79 BinaryTree(Node *pn) = delete; 80 BinaryTree(int key) { 81 root = new Node(key); 82 } 83 //copy/move ... 84 ~BinaryTree() { 85 clear(root); 86 } 87 88 void insert(int key) { 89 root = __insert(root, key); 90 return; 91 } 92 93 void erase(int key){ 94 root = __erase(root, key); 95 return; 96 } 97 98 Node *find(int key){ 99 return __find(root, key); 100 } 101 102 void output() { 103 __output(root); 104 return; 105 } 106 107 }; 108 109 int main() 110 { 111 int op, val; 112 BinaryTree *pbt = nullptr; 113 while(cin >> op >> val) { 114 switch(op) { 115 case 0: { 116 if(!pbt) pbt = new BinaryTree(val); 117 else pbt->insert(val); 118 break; 119 } 120 case 1: { 121 if(pbt) pbt->erase(val); 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 pbt->output(); 126 cout << endl; 127 } 128 return 0; 129 }
2. AVL树 代码实现:代码中注意点:虚拟空节点的引入,优化程序(虚拟空节点的 代码技巧);
对于每个变化的节点都要重新更新深度;左旋/右旋/插入/删除
以及上面二叉排序树中的注意点;

1 //input 2 //0 5 3 //0 9 4 //0 8 5 //0 3 6 //0 2 7 //0 4 8 //0 1 9 //0 7 10 //1 8 11 //1 1 12 //1 5 13 14 15 #include <iostream> 16 using namespace std; 17 18 #define NIL (&Node::__NIL) 19 20 struct Node { 21 Node(int k = 0, int h = 0, Node *l = NIL, Node *r = NIL) 22 : key(k), h(h), left(l), right(r) {} 23 int key, h; 24 Node *left, *right; 25 static Node __NIL; //这里只是声明 26 }; 27 28 Node Node::__NIL; //对于静态变量的使用,这里才是定义 29 30 Node *getNewNode(int key) { 31 return new Node(key,1); 32 } 33 34 void clear(Node *root) { 35 if(root == NIL) return; 36 clear(root->left); 37 clear(root->right); 38 cout << "del root key: " << root->key << endl; 39 delete root; 40 return; 41 } 42 43 void update_height(Node *root) { 44 //NIL if(root->left = nullptr && root->right == nullptr) return; 45 //NIL if(root->left == nullptr) root->h = root->right->h + 1; 46 //NIL else if(root->right == nullptr) root->h = root->left->h + 1; 47 root->h = max(root->left->h, root->right->h) + 1; 48 return; 49 } 50 51 Node *left_rotate(Node *root){ 52 Node *new_root = root->right; 53 root->right = new_root->left; 54 new_root->left = root; 55 update_height(root); 56 update_height(new_root); 57 return new_root; 58 } 59 60 Node *right_rotate(Node *root){ 61 Node *new_root = root->left; 62 root->left= new_root->right; 63 new_root->right= root; 64 update_height(root); 65 update_height(new_root); 66 return new_root; 67 } 68 69 const char *Type[5] = {"", "LL", "RR", "LR", "RL"}; 70 71 Node *maintain(Node *root) { 72 if(abs(root->left->h - root->right->h) < 2) return root; 73 int type = 0; 74 if(root->left->h > root->right->h) { 75 if(root->left->right->h > root->left->left->h) { 76 //lr 77 printf("%d : left rotate\n", root->left->key); 78 type = 3; 79 root->left = left_rotate(root->left); 80 } 81 //ll 82 if(!type) type = 1; 83 printf("%d : right rotate\n", root->key); 84 root = right_rotate(root); 85 }else { 86 if(root->right->left->h > root->right->right->h) { 87 //rl 88 type = 4; 89 printf("%d : right rotate\n", root->right->key); 90 root->right = right_rotate(root->right); 91 } 92 //rr 93 printf("%d : left rotate\n", root->key); 94 if(!type) type = 2; 95 root = left_rotate(root); 96 } 97 printf("maintian the type = %s;\n", Type[type]); 98 return root; 99 } 100 101 Node *insert(Node *root, int key) { 102 if(root == NIL) return getNewNode(key); 103 if(root->key == key) return root; 104 105 if(key < root->key) root->left = insert(root->left, key); 106 else root->right = insert(root->right, key); 107 update_height(root); 108 return maintain(root); 109 } 110 111 Node* predeccesor(Node *root) { 112 Node *temp = root->left; 113 while(temp->right != NIL) temp = temp->right; 114 return temp; 115 } 116 117 Node *erase(Node *root, int key){ 118 if(root == NIL) return root; 119 if(key < root->key) root->left = erase(root->left, key); 120 else if(key > root->key) root->right = erase(root->right, key); 121 else { 122 //删除节点数为0 或 1 的节点 123 if(root->left == NIL || root->right == NIL) { 124 Node *temp = root->left == NIL ? root->right : root->left; 125 delete root; 126 return temp; 127 }else { //删除节点数为2 , 这里使用左子树最右边的值替补被删除的数(也可以通过右子树最左边的值替补被删除的值) 128 Node *temp = predeccesor(root); 129 root->key = temp->key; 130 root->left = erase(root->left, temp->key); 131 } 132 } 133 update_height(root); 134 return maintain(root); 135 } 136 137 void print(Node *root) { 138 printf("(%d[%d] | %d, %d)\n", root->key, root->h, root->left->key, root->right->key); 139 return; 140 } 141 142 void output(Node *root) { 143 if(root == NIL) return; 144 print(root); 145 output(root->left); 146 output(root->right); 147 return; 148 } 149 150 int main() 151 { 152 int op, val; 153 Node *root = NIL; 154 while(cin >> op >> val) { 155 cout << endl << "====AVL tree print ====" << endl; 156 switch (op) { 157 case 0 : { 158 printf("insert %d\n", val); 159 root = insert(root, val); break; 160 } 161 case 1 : { 162 printf("erase the %d\n", val); 163 root = erase(root, val); break; 164 } 165 } 166 output(root); 167 cout << "====tree print end====" << endl; 168 } 169 170 clear(root); 171 172 return 0; 173 }
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1. 前驱/后继的求取: 面试题 04.06. 后继者 : 非常好的锻炼结构化思维的例题!; 使用pre 记录前一个节点值,代码技巧;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode* pre; 13 TreeNode *inOrder(TreeNode *r, TreeNode *p) { 14 if(!r) return nullptr; 15 TreeNode *ans = nullptr; 16 if(ans = inOrder(r->left, p)) return ans; 17 if(pre && pre == p) return r; 18 pre = r; //精髓 19 return inOrder(r->right, p); 20 } 21 22 TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p) { 23 //利用二叉树结构化思维方式求解 24 pre = nullptr; 25 return inOrder(root, p); 26 // 利用二叉排序树性质求解 27 // TreeNode *ans = nullptr; 28 // 29 // if(p->val < root->val) ans = inorderSuccessor(root->left, p); 30 // else if(p->val > root->val) return inorderSuccessor(root->right, p); 31 // else { 32 // if(!root->right) return nullptr; 33 // TreeNode *next = root->right; 34 // while(next->left) next= next->left; 35 // return next; 36 // } 37 // if(!ans) ans = root; 38 // return ans; 39 } 40 };
2. 450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 : BST 删除节点的裸题:对于不同度的节点处理;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode *predecessor(TreeNode *root){ 15 TreeNode *temp = root->left; 16 while(temp->right) temp = temp->right; 17 return temp; 18 } 19 20 //这题目就是BST 中删除指定节点操作 21 TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) { 22 if(!root) return nullptr; 23 24 if(key < root->val) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); 25 else if(key > root->val) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); 26 else { 27 //出度为0 或 1 28 if(root->left == nullptr || root->right == nullptr) { 29 TreeNode *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; 30 delete root; 31 return temp; 32 } else { 33 //出度为2 34 TreeNode *temp = predecessor(root); 35 root->val = temp->val; 36 root->left = deleteNode(root->left, temp->val); 37 } 38 } 39 return root; 40 } 41 };
3.对于树类型数据,结构化思维是很重要的一种手段;上面的AVL 树的代码实现中也利用了结构化思维来实现;
结构化思维训练:
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数 : 结构化思维;这里对于最后节点需要判断情况下,避免重复代码有很好示范;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 //这里对于减少最后节点判断过程,做了一个不错的示范; 13 class Solution { 14 public: 15 int max_cnt, cnt, pre_val; 16 vector<int> ans; 17 18 void __inorder(TreeNode* root) { 19 if(!root) return; 20 __inorder(root->left); 21 22 if(pre_val == root->val) cnt++; 23 else { 24 cnt = 1; 25 pre_val = root->val; 26 } 27 28 //这里是为了解决最后一个节点,不用单独写一份判断过程; 29 if(cnt == max_cnt) { 30 ans.push_back(pre_val); 31 } else if(cnt > max_cnt) { 32 max_cnt = cnt; 33 ans.clear(); 34 ans.push_back(pre_val); 35 } 36 37 __inorder(root->right); 38 return; 39 } 40 41 vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) { 42 pre_val = root->val, //体会这样做的好处 43 max_cnt = 0, cnt = 0; 44 ans.clear(); 45 46 __inorder(root); 47 return ans; 48 } 49 }; 50 51 52 //original 53 /** 54 * Definition for a binary tree node. 55 * struct TreeNode { 56 * int val; 57 * TreeNode *left; 58 * TreeNode *right; 59 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 60 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 61 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 62 * }; 63 */ 64 class Solution { 65 public: 66 int cnt, max_cnt; 67 TreeNode *pre; 68 69 void findMax(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &ans){ 70 if(!root) return; 71 72 findMax(root->left, ans); 73 if(!pre) cnt = 1; 74 else { 75 if(pre->val == root->val) cnt++; 76 else{ 77 if(cnt >= max_cnt) { 78 if(cnt > max_cnt) ans.clear(), max_cnt = cnt; 79 ans.push_back(pre->val); 80 } 81 cnt = 1; 82 } 83 } 84 pre = root; 85 86 findMax(root->right, ans); 87 return; 88 } 89 90 vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) { 91 cnt = max_cnt = 0; 92 pre = nullptr; 93 vector<int> ans; 94 findMax(root, ans); 95 if(cnt < max_cnt) return ans; 96 if(cnt > max_cnt) ans.clear(); 97 ans.push_back(pre->val); 98 return ans; 99 } 100 };
1382. 将二叉搜索树变平衡 : 二叉排序树的实现方式也有很多,在树结构中,很多时候使用结构性思维;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 void inorder(TreeNode *root, vector<TreeNode*> &nums) { 15 if(!root) return; 16 inorder(root->left, nums); 17 nums.push_back(root); 18 inorder(root->right, nums); 19 return; 20 } 21 22 TreeNode *buildTree(vector<TreeNode*> &nums, int l, int r) { 23 if(l > r) return nullptr; 24 int ind = (l + r) >> 1; 25 TreeNode *node = nums[ind]; 26 node->left = buildTree(nums, l, ind - 1); 27 node->right = buildTree(nums, ind + 1, r); 28 return node; 29 } 30 31 TreeNode* balanceBST(TreeNode* root) { 32 vector<TreeNode*> nums; 33 inorder(root, nums); 34 return buildTree(nums,0, nums.size() - 1); 35 } 36 };
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 : 结构化思维

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r) { 15 if(l > r) return nullptr; 16 int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1; 17 TreeNode *new_node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]); 18 new_node->left = buildTree(nums, l , mid - 1); 19 new_node->right = buildTree(nums, mid + 1, r); 20 return new_node; 21 } 22 23 TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) { 24 return buildTree(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1); 25 } 26 };
98. 验证二叉搜索树 : 结构化思维, 甚至可以理解为就是for 循环遍历有序数组;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode *pre; 15 bool __isValidVBST(TreeNode *root) { 16 if(!root) return true; 17 if(!__isValidVBST(root->left)) return false; 18 if(pre && pre->val >= root->val) return false; 19 pre = root; 20 if(!__isValidVBST(root->right)) return false; 21 return true; 22 } 23 bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) { 24 pre = nullptr; 25 return __isValidVBST(root); 26 } 27 };
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列 : pre的使用在于它的定义,以及在结构化中的使用方式;与前/中/后 序都没任何关系;前/中/后序都可以用pre实现按顺序循环;

1 //结构化思维方式: 这里是为了表达pre对于结构化思维意义; 2 //当然这里pre初始值设定有缺陷(要取一个不在范围内值); leetcode 23 个test case 可以过; 3 //fail case: [-6, -3, 9, -5, -1] 4 class Solution { 5 public: 6 int pre; 7 bool __postorder(vector<int>& nums, int l, int r) { 8 if(l >= r) return true; 9 int ind = l; 10 while(nums[ind] < nums[r]) ind++; 11 if(!__postorder(nums, l, ind - 1)) return false; 12 if(pre != -1 && nums[r] < pre) return false; 13 pre = nums[r]; 14 if(!__postorder(nums, ind, r - 1)) return false; 15 return true; 16 } 17 18 bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) { 19 pre = -1; 20 return __postorder(postorder, 0, postorder.size() - 1); 21 } 22 }; 23 24 //orignial 25 class Solution { 26 public: 27 28 bool checkPostorder(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r) { 29 if(l >= r) return true; 30 int ind = l; 31 while(nums[ind] < nums[r]) ind++; 32 if(!checkPostorder(nums, l, ind - 1) || !checkPostorder(nums, ind, r - 1)) return false; 33 while(nums[ind] > nums[r]) ind++; 34 return ind == r; 35 } 36 37 38 bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) { 39 return checkPostorder(postorder, 0, postorder.size() - 1); 40 } 41 };

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeNode *buildTree(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r) { 15 if(l > r) return nullptr; 16 int ind = l + 1; 17 while(ind <= r && nums[ind] <= nums[l]) ind++; 18 TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(nums[l]); 19 node->left = buildTree(nums, l + 1, ind - 1); 20 node->right = buildTree(nums, ind, r); 21 return node; 22 } 23 24 TreeNode* bstFromPreorder(vector<int>& preorder) { 25 return buildTree(preorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1); 26 } 27 };
思维锻炼结果检验:
面试题 04.09. 二叉搜索树序列: 对于vector<vector<int>> 套娃式结构中,对于空节点的返回值为vector<vector<int>>{vector<int>()};

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 void mergeSequence(vector<int>&l, int idx_l, vector<int>&r, int idx_r, vector<int> cur, vector<vector<int>> &ans) { 13 if(idx_l == l.size() || idx_r == r.size()) { 14 if(idx_l == l.size()) while(idx_r < r.size()) cur.push_back(r[idx_r++]); 15 else while(idx_l < l.size()) cur.push_back(l[idx_l++]); 16 ans.push_back(cur); 17 return; 18 } 19 20 cur.push_back(l[idx_l]); 21 mergeSequence(l, idx_l + 1, r, idx_r, cur, ans); 22 cur.pop_back(); 23 cur.push_back(r[idx_r]); 24 mergeSequence(l, idx_l, r, idx_r + 1, cur, ans); 25 return; 26 } 27 28 29 vector<vector<int>> BSTSequences(TreeNode* root) { 30 vector<vector<int>> ans; 31 if(!root) { 32 ans.push_back(vector<int>()); //对于vector<vector<int>>这类套圈的返回值对于nullptr 处理方案; 33 return ans; 34 } 35 vector<vector<int>> pre = BSTSequences(root->left), 36 next = BSTSequences(root->right); 37 38 vector<int> cur{root->val}; 39 for(int i = 0, I = pre.size(); i < I; ++i) { 40 for(int j = 0, J = next.size(); j < J; ++j) { 41 mergeSequence(pre[i], 0, next[j], 0, cur, ans); 42 } 43 } 44 return ans; 45 } 46 }; 47 48 //original 49 /** 50 * Definition for a binary tree node. 51 * struct TreeNode { 52 * int val; 53 * TreeNode *left; 54 * TreeNode *right; 55 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 56 * }; 57 */ 58 class Solution { 59 public: 60 void merge(vector<vector<int>> &ans, vector<int>&now, 61 vector<int> &l, int li, vector<int> &r, int ri) { 62 63 if(li == l.size() && ri == r.size()) { 64 ans.push_back(now); 65 return; 66 } 67 68 if(li < l.size()) { 69 now.push_back(l[li]); 70 merge(ans, now, l, li + 1, r, ri); 71 now.pop_back(); 72 } 73 if(ri < r.size()) { 74 now.push_back(r[ri]); 75 merge(ans, now, l, li, r, ri + 1); 76 now.pop_back(); 77 } 78 return; 79 } 80 81 82 vector<vector<int>> BSTSequences(TreeNode* root) { 83 vector<vector<int>> ans; 84 if(!root) { 85 ans.push_back(vector<int>()); 86 return ans; 87 } 88 89 vector<vector<int>> left = BSTSequences(root->left); 90 vector<vector<int>> right = BSTSequences(root->right); 91 92 vector<int> temp; 93 temp.push_back(root->val); 94 95 if(!left.size() && !right.size()) ans.push_back(temp); 96 for(int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++) { 97 for(int j = 0; j < right.size(); j++) { 98 merge(ans, temp, left[i], 0, right[j], 0); 99 } 100 } 101 102 return ans; 103 } 104 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================
1. 单从数据类型来讲,AVL 是可以用来实现map/set 的功能的,但是因为AVL 是一种高度平衡二叉树,左右树高差不超过1;所以在不断插入/删除过程中,为了保证数据性质,需要不断进行旋转;在大量数据插入/删除,这一操作有可能会降低速度;
所以使用RB Tree(这是一种弱平衡二叉树,只要保证没有一条路径会是其他路径的2倍以上),旋转的次数会更少,所以在STL种使用了RB tree 作为其底层数据结构;
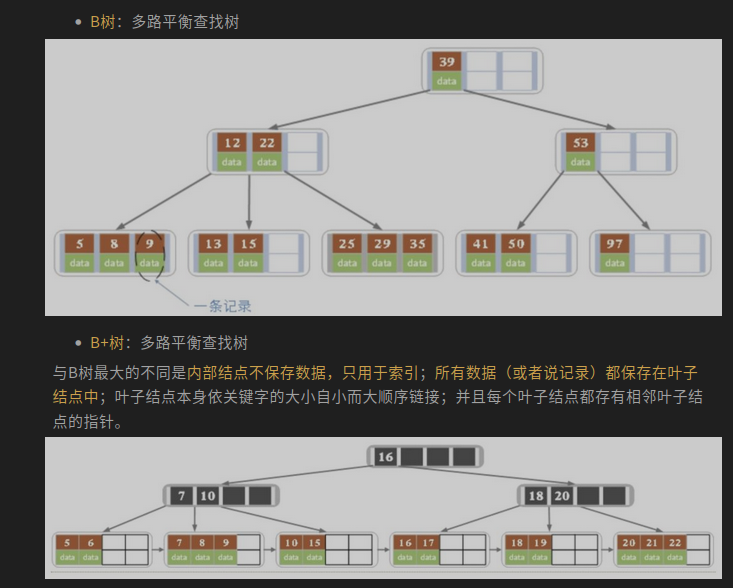
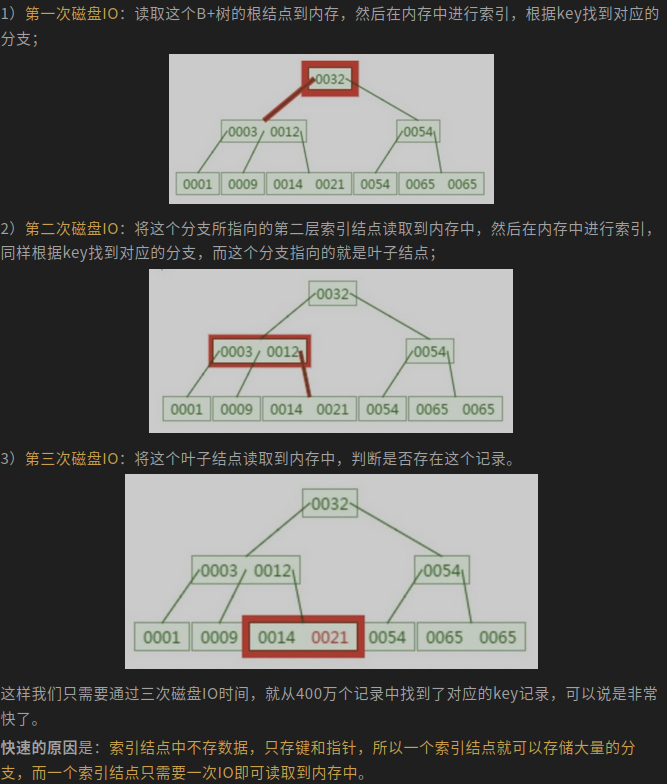
2. 类似的数据结构有: B树,B+树;都是针对具体的应用场景,对数据结构进行优化;
在实际存储引擎中一般都是使用B+ 树,这其中的原因与好处,下面文章写的很好,摘录部分信息;
数据存储技术:单机篇





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号