======================= **基础知识** =======================
1.二分算法:二分的是问题规模,减少无用范围;
a. 二分查找: 对顺序查找的优化, 二分的是区间范围;最终找到的结果是在区间范围内,满足条件的位置(隐藏的含义是,最终找到的可能是最左边/右边的位置,这也是对于代码处理过程要注意的边界条件);
基本过程:
min 是头指针; max 是尾指针; mid = (min + max) / 2;
调整: 如果arr[mid] < x, min = mid + 1;
如果arr[mid] > x, max = mid - 1;
如果arr[mid] == x, 找到结果;
进阶:泛型情况 01/10 查找,查找第一个 > x 位置;这里对于01/10 模型有不同的取值方式,满足条件的值,要保留在后续的查找区间;(下面代码演示中,有提供一种规避它 的操作方式,快排中partition也是采用的一样的方式,避免了死循环);
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 // index
1 2 3 3 5 5 7 8 8 9 //value;
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 // 查找第一个 >= 5 的值;1指代第一个满足条件的值; min = 0, max = 9, mid = 4; 第一次查找以后,max = mid,再进行下一轮查找;
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 //查找 最后一个 < 7 的位置 ; mid = (min + max + 1) >> 1 --> mid = 5, min = mid; 再进行下一轮查找;
2. Deep-First-Search(DFS 深搜) & (BFS 广搜) :常见优化方式有记忆化(当状态定义比较复杂,记忆化复杂度会增加,而重复性降低);搜索减枝: 要基于具体问题,减少一些可以预判不成立的情况;
问题求解树/问题状态树: 代表问题从某个状态 进入下一个状态的过程,如果一个问题有解,那么一定能从开始状态 达到最终的状态;
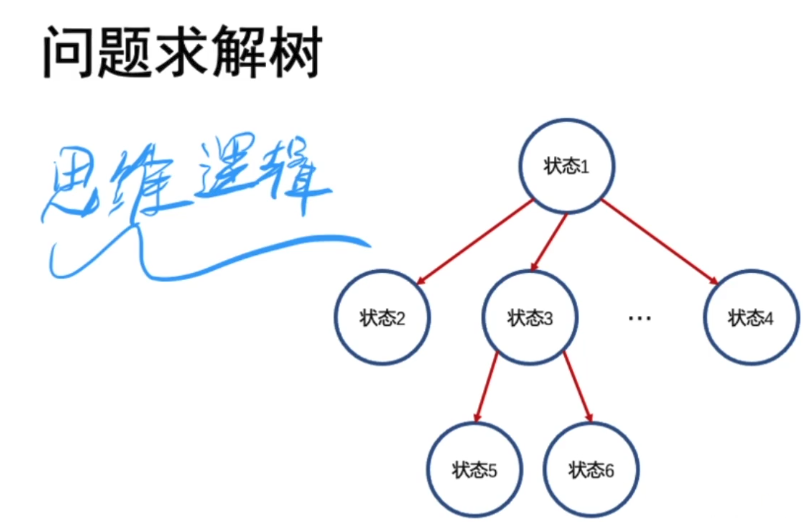 a. 什么是深搜与 广搜 : 这两种只是 对于问题求解树的不同遍历方式;
a. 什么是深搜与 广搜 : 这两种只是 对于问题求解树的不同遍历方式;
b. 什么是 搜索减枝 与 优化: 通过一些特定方式,排除某些问题求解树中的子树的遍历过程;
c. 设计搜索方法的核心关键点: 如何设计问题求解树的状态;
DFS : 基于递归方式实现遍历, 重点注意回溯过程!
BFS:基于队列方式实现遍历;方便对于最优化的求解,例如最少步数到达某个位置;
DP: 搜索 + 记忆化,对于问题状态树进行求解; 后续更新;
3. hashmap & RB tree & 布隆过滤器 : 常见的map/set/unordered_map/unordered_set 插入过程中进行排序,搜索实现O(1) ;
======================= **代码演示** =======================
1. 二分查找代码: 其中 binary_search_02 方式实现方式,可以有效的规避01/10 模型的不同mid 取值条件,对于最后小区间处理的过程,注意while/for 两种代码方式对于 最左/右 边界情况下的影响;

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 void output_bs(int *arr, int n, int head, int tail, int mid){ 5 int p1, p2, p3, len = 0; 6 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 7 len += printf("%5d", arr[i]); 8 if(i == head) p1 = len - 1; 9 if(i == tail) p2 = len - 1; 10 if(i == mid) p3 = len - 1; 11 } 12 printf("\n"); 13 14 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 15 if(i == p1 || i == p2 || i == p3) printf("^") ; 16 else printf(" "); 17 } 18 printf("\n"); 19 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { 20 if(i == p1 || i == p2 || i == p3) printf("|"); 21 else printf(" "); 22 } 23 printf("\n"); 24 return ; 25 } 26 27 int binary_search(int *arr, int n, int x) { 28 int head = 0, tail = n - 1, mid; 29 while(head <= tail) { 30 //mid = (head + tail) >> 1; 31 mid = (tail - head) / 2 + head; 32 output_bs( arr, n, head, tail, mid); 33 if(arr[mid] == x) return mid; 34 if(arr[mid] < x) head = mid + 1; 35 else tail = mid - 1; 36 } 37 return -1; 38 } 39 40 41 int binary_search_01(int *arr, int n, int x) { 42 int head = 0, tail = n - 1, mid; 43 while(head < tail) { 44 mid = (tail - head) / 2 + head; 45 output_bs( arr, n, head, tail, mid); 46 if(arr[mid] < x) head = mid + 1; 47 else tail = mid; 48 } 49 return head; 50 } 51 52 int binary_search_02(int *arr, int n, int x) { 53 int head = 0, tail = n - 1, mid; 54 while(tail - head > 3) { 55 mid = (tail - head) / 2 + head; 56 output_bs( arr, n, head, tail, mid); 57 if(arr[mid] < x) head = mid + 1; 58 else tail = mid; 59 } 60 for(int i = head; i <= tail; i++) { 61 if(arr[i] >= x) return i; 62 } 63 return head; 64 } 65 66 int* getRandData(int n){ 67 int *arr = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 68 memset(arr, 0, sizeof(int) * n); 69 arr[0] = rand() % 10; 70 for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { 71 arr[i] = arr[i - 1] + rand() % 5 + 1; 72 } 73 return arr; 74 } 75 76 void output(int *arr, int n) { 77 int len = 0; 78 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 79 len += printf("%5d", i); 80 } 81 printf("\n"); 82 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) printf("-"); 83 printf("\n"); 84 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 85 printf("%5d", arr[i]); 86 } 87 printf("\n"); 88 return; 89 } 90 int main() 91 { 92 srand(time(0)); 93 int n, x; 94 scanf("%d", &n); 95 int *arr = getRandData(n); 96 97 output(arr, n); 98 99 while(scanf("%d", &x)) { 100 printf("arr[%d] = %d\n", 101 binary_search_02(arr, n, x), x); 102 } 103 104 105 return 0; 106 }
2. DFS与BFS 重点在于状态的定义,以及随着遍历的进行状态变化的过程;
leetcode : 993. 二叉树的堂兄弟节点 : 对于BFS, 通常将状态放进队列中;

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 struct Node{ 15 TreeNode *now, *father; 16 int depth; 17 Node(TreeNode *now, TreeNode *prev, int depth): now(now), father(prev), depth(depth){} 18 }; 19 20 bool bfs_my(TreeNode *root, int x, int y) { 21 queue<Node*> que; 22 que.push(new Node(root, nullptr, 0)); 23 int ret = 0; //0: initial; 1; pass; 2: fail; 24 while(que.size()) { 25 int loop = que.size(); 26 TreeNode *findNode = nullptr; 27 while(loop--) { 28 Node* pN = que.front(); 29 que.pop(); 30 auto judge = [&](int val) { 31 if(pN->now->val == val) { 32 if(findNode) { 33 if(findNode != pN->father) ret = 1; 34 else ret = 2; 35 } else findNode = pN->father; 36 } 37 }; 38 judge(x); 39 judge(y); 40 if(pN->now->left) que.push(new Node(pN->now->left, pN->now, pN->depth + 1)); 41 if(pN->now->right) que.push(new Node(pN->now->right, pN->now, pN->depth + 1)); 42 delete pN; 43 if(ret) return ret == 1; 44 } 45 } 46 return false; 47 } 48 49 void __dfs(Node *r, int x, int y, Node* &fx, Node* &fy) { 50 51 if(fx && fy) return; 52 53 if(r->now->left) __dfs(new Node(r->now->left, r->now, r->depth + 1), x, y, fx, fy); 54 if(r->now->right) __dfs(new Node(r->now->right, r->now, r->depth + 1), x, y, fx, fy); 55 56 if(r->now->val == x) fx = r; 57 if(r->now->val == y) fy = r; 58 return; 59 } 60 61 bool dfs_my(TreeNode *root, int x, int y) { 62 Node *fx = nullptr, *fy = nullptr, *r = new Node(root, nullptr, 0); 63 __dfs(r, x, y, fx, fy); 64 if(fx && fy) return (fx->depth == fy->depth) && (fx->father != fy->father); 65 return false; 66 } 67 68 int dfs(TreeNode *r, int x, TreeNode *&father) { 69 if(!r) return -1; 70 if(r->val == x) return 0; 71 72 father = r; //这一步是该递归过程中容易出错的一点; 73 int depth = dfs(r->left, x, father); 74 if(depth != -1) return depth + 1; 75 76 father = r; 77 depth = dfs(r->right, x, father); 78 if(depth != -1) return depth + 1; 79 80 return -1; 81 } 82 83 bool isCousins(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) { 84 //bfs 85 // return bfs_my(root, x, y); 86 //dfs 87 // return dfs_my(root, x, y); 88 TreeNode *father_x = nullptr, *father_y = nullptr; 89 int depth_x = dfs(root, x, father_x), 90 depth_y = dfs(root, y, father_y); 91 92 return (depth_x == depth_y) && (father_x != father_y); 93 } 94 };
77. 组合 : 对于DFS 过程,使用循环,使用二进制优化;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 void dfs(int i, int n, int k, vector<int> &buff, vector<vector<int>> &ans) { 4 if(buff.size() == k) { 5 ans.push_back(buff); 6 return; 7 } 8 if(i == n) return; 9 buff.push_back(i); 10 dfs(i + 1, n, k, buff, ans); 11 buff.pop_back(); 12 dfs(i + 1, n, k, buff, ans); 13 return; 14 } 15 16 int get1(int n) { 17 int cnt = 0; 18 while(n) { 19 cnt += 1; 20 n &= (n - 1); 21 } 22 return cnt; 23 } 24 25 unordered_map<int,int> mark; 26 vector<int> getRet(int n) { 27 vector<int> ret; 28 while(n) { 29 ret.push_back(mark[(n & (-n))]); 30 n &= (n - 1); 31 } 32 return ret; 33 } 34 35 vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) { 36 // dfs 37 // vector<int> buff; 38 // vector<vector<int>> ans; 39 // dfs(1, n + 1, k, buff, ans); 40 // return ans; 41 //循环 42 // vector<vector<int>> buff(1), ans; 43 // for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { 44 // for(int j = 0, J = buff.size(); j < J; ++j) { 45 // vector<int> temp = buff[j]; 46 // temp.push_back(i); 47 // if(temp.size() == k) ans.push_back(temp); 48 // else buff.push_back(temp); 49 // } 50 // } 51 // return ans; 52 //二进制 53 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) mark[1 << i] = i + 1; 54 vector<vector<int>> ans; 55 for(int i = 1, I = (1 << n); i < I; ++i) { 56 if(get1(i) != k) continue; 57 ans.push_back(getRet(i)); 58 } 59 return ans; 60 } 61 };
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1. 使用二分算法 计算 函数结果;
数组 与 函数 之间 没有本质差别,都是映射;其中数组 就是展开的 函数,使用储存资源 ; 函数 是 压缩的 数组,使用计算资源;
数组 : 下标 --> 值 的映射;
函数: 参数 --> 值 的映射;
所以才有 时间 换 空间 ; 空间 换 时间 的两种做法;
所以对于树组,可以是对应一个函数,可以是对应 二叉树, 重点在于如何解析这些数据;
leetcode : 69. x 的平方根 ;这里引申下 float/double 这些计算机中对于小数的储存形式,以及精确度;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 #define LIMIT 1e-5 4 int mySqrt(int x) { 5 // //牛顿迭代法 6 // int cnt = 100; 7 // double cur = x; 8 // while(cur * cur - x > LIMIT) { 9 // cur = (cur + x / cur) / 2.0; 10 // } 11 // return cur; 12 13 double left = 0, right = x, mid; 14 int cnt = 100; 15 while(cnt--) { 16 mid = (left + right) / 2; 17 if(mid * mid > x) right = mid; 18 else left = mid; 19 } 20 return left; 21 22 } 23 };
2. leetcode : 81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II : 对于每次mid 的位置,要分为两种情况,然后针对这两种情况,再分别做判断时候,对结果处理再分为两种情况(变成常规的有序数组; 还是与当前数组结构一致);

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool search(vector<int>& nums, int target) { 4 int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1; 5 // [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2,1,1,1,1,1] 6 // 2 7 //这就是为了解决上面特殊情况,因为l/mid/r 都是一样的值,无法判断到底选择哪部分; 8 //而且这种情况,只有开始可能出现,后续处理中l / r 一定是不等的; 9 while(l < r && nums[l] == nums[r]) l++; 10 // 11 while(l <= r) { 12 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 13 if(nums[mid] == target) return true; 14 if(nums[mid] <= nums[r]) { 15 if(target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[r]) l = mid + 1; 16 else r = mid - 1; 17 } else { 18 if(target < nums[mid] && target >= nums[l]) r = mid - 1; 19 else l = mid + 1; 20 } 21 } 22 return false; 23 } 24 };
3. leetcode 4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 : 利用二分,不断减少答案的范围,最终求得结果;
重要一点是;如何将求中位数问题转换成 求 第k 个元素; 开始想法是不断将两个数组对半分,比较中间位置的值,然后剔除较小值对应数组的左边,较大值对应数组右边,然后求剩下来数的中位数;但是对于奇数/偶数 个数数组,如何取舍保证中位数不变,没有想好;
但是这里通过求第K 值方式,解决上面问题;
这里code 中几个注意点:
1. 任何 涉及到位置变化的 计算部分,都要考虑 越界可能;
k = 0时,k / 2 = 0, i + k / 2 - 1存在越界可能
2. 对于可能两个数组需要分别选择指定数量数值,但是有可能指定数量大于 数组总数 情况下,如何取值做法;
int cnt1 = min(k / 2, (int)nums1.size() - i), cnt2 = min(k - cnt1, (int)nums2.size() - j);
cnt1 = k - cnt2;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 4 double findKnum(vector<int> &nums1, vector<int> &nums2, int i, int j, int k) { 5 6 //先判断是否存在越界情况; 7 if(i == nums1.size()) return nums2[j + k - 1]; 8 if(j == nums2.size()) return nums1[i + k - 1]; 9 //在判断特殊情况, k = 0时,k / 2 = 0, i + k / 2 - 1存在越界可能; 10 //必须要特判 11 if(k == 1) return (nums1[i] > nums2[j] ? nums2[j] : nums1[i]); 12 //对于可能存在越界情况下,如何取值做法; 很好的例子 13 int cnt1 = min(k / 2, (int)nums1.size() - i), 14 cnt2 = min(k - cnt1, (int)nums2.size() - j); 15 cnt1 = k - cnt2; 16 17 int index1 = i + cnt1 - 1, index2 = j + cnt2 - 1; 18 if(nums1[index1] == nums2[index2]) return nums1[index1]; 19 else if(nums1[index1] < nums2[index2]) return findKnum(nums1, nums2, index1 + 1, j, k - cnt1); 20 return findKnum(nums1, nums2, i, index2 + 1, k - cnt2); 21 } 22 23 double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { 24 // int I1 = nums1.size(), I2 = nums2.size(); 25 // int mid = (I1 + I2 - 1) >> 1; 26 // //set STL 使用,然后寻找中位数 27 // multiset<int> arr; 28 // for(int i = 0; i < I1; i++) arr.insert(nums1[i]); 29 // for(int i = 0; i < I2; i++) arr.insert(nums2[i]); 30 // int temp = mid; 31 // multiset<int>::iterator iter = arr.begin(); 32 // while(temp--) iter++; 33 // 34 // if(mid * 2 == arr.size() - 1) return *(iter); 35 // else return 1.0 * (*iter + *(++iter)) / 2; 36 // 37 //二分方式,找到第k个数据 38 int a = nums1.size(), b = nums2.size(), k = (a + b + 1) / 2; 39 double ret = findKnum(nums1, nums2, 0, 0, k); 40 if((a + b) % 2) return ret; 41 int ret1 = findKnum(nums1, nums2, 0, 0, k + 1); 42 return (ret + ret1) / 2.0; 43 } 44 };
4. 对于通过不断枚举(尝试)的操作,可以通过 二分方法,将时间复杂度O(n) 变成O(logN) : leetcode : 1011. 在 D 天内送达包裹的能力

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int getDays(vector<int>& weights, int num) { 4 int cnt = 0, load = 0; 5 for(auto &x : weights) { 6 if((load += x) > num) { 7 cnt += 1; 8 load = x; 9 } 10 } 11 return cnt + 1; 12 } 13 14 int binarySearch_01(vector<int> &weights,int l, int r, int days) { 15 if(l > r) return -1; 16 17 while(l < r) { 18 int mid = (l + r) / 2; 19 if(getDays(weights, mid) > days) l = mid + 1; 20 else r = mid; 21 } 22 return l; 23 } 24 25 int shipWithinDays(vector<int>& weights, int days) { 26 int total_weight = 0, most_weight = 0; 27 for(int i = 0, I = weights.size(); i < I; ++i) { 28 most_weight = max(most_weight , weights[i]); 29 total_weight += weights[i]; 30 } 31 32 int min_load = max(most_weight, total_weight / days); 33 34 return binarySearch_01(weights, min_load, total_weight, days); 35 } 36 };
类似的题目,直接算怎么拆分最大数量袋子,不好判断;但是反过来,拆分成某个数量需要的操作比较容易求得;然后二分就可以了;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 4 int check(vector<int> &nums, int val){ 5 int ans = 0; 6 for(auto x : nums) ans += (x / val + !!(x % val) - 1); //这里操作类似 ceil, 算是比较有意思的变种, ceil 形参是double /float 7 return ans; 8 } 9 10 int binary_search(vector<int>& nums, int l, int r, int op){ 11 int mid; 12 while(l < r) { 13 mid = (l + r) >> 1; 14 if(check(nums, mid) > op) l = mid + 1; 15 else r = mid; 16 } 17 return l; 18 } 19 20 int minimumSize(vector<int>& nums, int maxOperations) { 21 int max_val = 0; 22 23 for(auto x : nums) max_val = max(max_val, x); 24 return binary_search(nums, 1, max_val, maxOperations); 25 } 26 };

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 long long bs_10(vector<int>& candies, int mid) { 4 if(!mid) return INT64_MAX; 5 long long ans = 0; 6 for(auto &x : candies) ans = ans + x / mid; 7 return ans; 8 } 9 10 int maximumCandies(vector<int>& candies, long long k) { 11 int l = 0, r = 0; 12 for(auto &x : candies) r = max(r, x); 13 14 while(l < r) { 15 int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1; 16 if(bs_10(candies, mid) >= k) l = mid; 17 else r = mid - 1; 18 } 19 20 return l; 21 } 22 };
//DFS & BFS:
BFS: 将每个状态作为一个数据存进队列中,然后将队列中元素按顺序取出,进行每条边(方向数组)的遍历过程;
DFS: 将每个状态作为参数传进递归过程中,然后通过这些参数,进行每条边(方向数组)的遍历过程;重点要注意回溯过程!

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 //DFS 13 //class Solution { 14 //public: 15 // int ans, depth; 16 // void dfs(TreeNode *root, int cur_dep) { 17 // if(!root) return; 18 // if(cur_dep > depth) ans = root->val, depth = cur_dep; 19 // dfs(root->left, cur_dep + 1); 20 // dfs(root->right, cur_dep + 1); 21 // return; 22 // } 23 // 24 // int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) { 25 // ans = root->val, depth = 0; 26 // dfs(root, 1); 27 // return ans; 28 // } 29 //}; 30 //BFS 31 class Solution { 32 public: 33 int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) { 34 int ans = 0; 35 queue<TreeNode*> que; 36 que.push(root); 37 while(que.size()) { 38 int cnt = que.size(); 39 ans = que.front()->val; 40 while(cnt--) { 41 TreeNode *temp = que.front(); 42 que.pop(); 43 if(temp->left) que.push(temp->left); 44 if(temp->right) que.push(temp->right); 45 } 46 } 47 return ans; 48 } 49 };
5. 寻找grid 中的最短路径; 一般来讲BFS 最合适,因为BFS 是从初始状态往外扩展,第一次到达终点,就是最小值;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int dir[8][2] = { 4 1, 0, 1, -1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 5 -1, 0, -1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}; 6 7 struct DATA { 8 DATA(int x, int y, int d) : x(x), y(y), dis(d) {} 9 int x, y, dis; 10 }; 11 int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { 12 int n = grid.size() - 1; 13 if(grid[0][0] || grid[n][n]) return -1; 14 vector<vector<int>> vis(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, -1)); 15 16 queue<DATA> que; 17 que.push(DATA(0, 0, 1)); 18 vis[0][0] = 1; 19 20 while(que.size()) { 21 DATA temp = que.front(); 22 23 for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++) { 24 int x_nxt = temp.x + dir[k][0], 25 y_nxt = temp.y + dir[k][1]; 26 if(x_nxt < 0 || x_nxt > n || y_nxt < 0 || y_nxt > n) continue; 27 if(-1 != vis[x_nxt][y_nxt] || grid[x_nxt][y_nxt]) continue; 28 vis[x_nxt][y_nxt] = temp.dis + 1; 29 if(x_nxt == n && y_nxt == n) return vis[x_nxt][y_nxt]; 30 que.push(DATA(x_nxt, y_nxt,vis[x_nxt][y_nxt])); 31 } 32 que.pop(); 33 } 34 return vis[n][n]; 35 } 36 };
130. 被围绕的区域 : 逆向思维去找不会被填充的点,算是一个解题技巧;

1 //dfs: 2 class Solution { 3 public: 4 int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0}; 5 void dfs(int x, int y, vector<vector<char>> &board) { 6 int mx = board.size(), my = board[0].size(); 7 if(board[x][y] == 'O') board[x][y] = 'o'; 8 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 9 int nx = x + dir[i][0]; 10 int ny = y + dir[i][1]; 11 if(nx < 0 || nx >= mx) continue; 12 if(ny < 0 || ny >= my) continue; 13 if(board[nx][ny] != 'O') continue; 14 dfs(nx, ny, board); 15 } 16 return; 17 } 18 19 void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) { 20 int mx = board.size(), my = board[0].size(); 21 for(int i = 0; i < my; i++) { 22 if(board[0][i] == 'O') dfs(0, i, board); 23 if(board[mx - 1][i] == 'O') dfs(mx - 1, i, board); 24 } 25 26 for(int i = 0; i < mx; i++) { 27 if(board[i][0] == 'O') dfs(i, 0, board); 28 if(board[i][my - 1] == 'O') dfs(i, my - 1, board); 29 } 30 31 for(int i = 0; i < mx; i++) { 32 for(int j = 0; j < my; j++) { 33 if(board[i][j] != 'o') board[i][j] = 'X'; 34 else board[i][j] = 'O'; 35 } 36 } 37 38 return; 39 } 40 }; 41 42 //bfs: class Solution { 43 //bfs: public: 44 //bfs: int dir[4][2] = {1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1}; 45 //bfs: struct Node { 46 //bfs: Node(int x = 0, int y = 0): x(x), y(y){} 47 //bfs: int x, y; 48 //bfs: }; 49 //bfs: 50 //bfs: void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) { 51 //bfs: int mx = board.size(), my = board[0].size(); 52 //bfs: queue<Node> que; 53 //bfs: for(int i = 0, xx = mx - 1; i < my; i++) { 54 //bfs: if(board[0][i] == 'O') que.push(Node(0, i)); 55 //bfs: if(xx > 0 && board[xx][i] == 'O') que.push(Node(xx, i)); 56 //bfs: } 57 //bfs: 58 //bfs: for(int i = 1, yy = my - 1, I = mx - 1; i < I; i++) { 59 //bfs: if(board[i][0] == 'O') que.push(Node(i, 0)); 60 //bfs: if(yy > 0 && board[i][yy] == 'O') que.push(Node(i, yy)); 61 //bfs: } 62 //bfs: while(!que.empty()){ 63 //bfs: Node item= que.front(); 64 //bfs: que.pop(); 65 //bfs: board[item.x][item.y] = 'Z'; 66 //bfs: for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 67 //bfs: int nx = item.x + dir[i][0]; 68 //bfs: int ny = item.y + dir[i][1]; 69 //bfs: if(nx < 0 || nx >= mx || ny < 0 || ny >= my) continue; 70 //bfs: if(board[nx][ny] == 'O') que.push(Node(nx,ny)); 71 //bfs: } 72 //bfs: } 73 //bfs: for(int i = 0; i < mx; i++) { 74 //bfs: for(int j = 0; j < my; j++) { 75 //bfs: if(board[i][j] != 'Z') board[i][j] = 'X'; 76 //bfs: else board[i][j] = 'O'; 77 //bfs: } 78 //bfs: } 79 //bfs: } 80 //bfs: };
6. 记忆化方式优化 BFS/DFS 效率:函数 与 数组之间的转化,函数是压缩的数组,数组是展开的函数;
494. 目标和 : 记忆化方式, 注意对于容器的使用;

1 //纯粹的DFS 2 class Solution { 3 public: 4 int dfs(vector<int> &nums, int i, int target) { 5 if(i == nums.size()) return 0 == target; 6 int ret = 0; 7 ret += dfs(nums, i + 1, target - nums[i]); 8 ret += dfs(nums, i + 1, target + nums[i]); 9 return ret; 10 } 11 12 int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) { 13 return dfs(nums, 0, target); 14 } 15 }; 16 17 18 //记忆化搜索 19 class Solution { 20 public: 21 typedef pair<int,int> PII; 22 struct CMP { 23 int operator() (const PII& a) const { 24 return a.first ^ a.second; 25 } 26 }; 27 unordered_map<PII,int, CMP> record; 28 29 int dfs(int i, vector<int> &nums, int target) { 30 if(i == nums.size()) return 0 == target; 31 32 if(record.find(PII(i, target)) != record.end()) return record[PII(i, target)]; 33 int cnt = 0; 34 cnt += dfs(i + 1, nums, target - nums[i]); 35 cnt += dfs(i + 1, nums, target + nums[i]); 36 record[PII(i, target)] = cnt; 37 return cnt; 38 } 39 40 int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) { 41 return dfs(0, nums, target); 42 } 43 };
但是当状态定义较为复杂时候,会导致记忆化数值复杂度 及 重复性降低,这时候就要考虑搜索减枝的方式减少DFS 的深度;
473. 火柴拼正方形 : 利用减枝优化查找效率,但是减枝的具体方法都要基于具体情况进行处理;

1 //没有任何减枝优化,很容易超时 2 class Solution { 3 public: 4 bool dfs(vector<int> &matchsticks, int index, array<int, 4> &sticks) { 5 if(index == matchsticks.size()) return true; 6 7 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { 8 int temp = sticks[i] - matchsticks[index]; 9 if(temp < 0) continue; 10 sticks[i] = temp; 11 if(dfs(matchsticks, index + 1, sticks)) return true; 12 sticks[i] = temp + matchsticks[index]; 13 } 14 15 return false; 16 } 17 18 bool makesquare(vector<int>& matchsticks) { 19 int total = 0; 20 for(auto &x : matchsticks) total += x; 21 if(total % 4) return false; 22 total /= 4; 23 24 array<int, 4> sticks = {total, total, total, total}; 25 return dfs(matchsticks, 0, sticks); 26 27 } 28 }; 29 30 31 32 //rev1:有效利用搜索减枝改善查找效率 33 class Solution { 34 public: 35 bool dfs(vector<int> &ms, vector<int> &arr, int ind) { 36 //状态定义比较复杂,增加记忆化数据的复杂度,重复性降低,使用搜索减枝的情况会更好; 37 //1.最长的火柴比当前边长要长,所以这个树节点的其中一个分支不可能找到结果了 38 //2. 当前边基于当前火柴处理后,还有剩余的话,如果比 最短的火柴还要短,那也不可能拼出来了 39 40 if(ind < 0) return true; 41 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 42 if(arr[i] < ms[ind]) continue; 43 if(arr[i] == ms[ind] || arr[i] >= ms[ind]+ ms[0]) { 44 arr[i] -= ms[ind]; 45 if(dfs(ms, arr, ind - 1)) return true; 46 arr[i] += ms[ind]; 47 } 48 } 49 return false; 50 } 51 52 bool makesquare(vector<int>& matchsticks) { 53 int all_sum = 0; 54 for(auto x : matchsticks) all_sum += x; 55 if(all_sum % 4) return false; 56 vector<int> arr(4, all_sum / 4); 57 //一个很好想法,排序以后从大到小查找,减少不必要继续查找; 58 sort(matchsticks.begin(), matchsticks.end()); 59 60 return dfs(matchsticks, arr, matchsticks.size() - 1); 61 } 62 };
39. 组合总和 : 一类比较典型的状态定义 及 DFS 过程;状态只有 选 / 不选; ->应该可以扩展到3 种状态?

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 unordered_map<int, set<vector<int>> > record; 4 bool __candidates(vector<int> &cand, int target, set<vector<int>> &prev) { 5 if(!target) return true; 6 7 if(record.find(target) != record.end()) prev = record[target]; 8 9 for(auto &x : cand) { 10 int left = target - x; 11 if(left < 0) break; 12 if(left == 0) { 13 prev.insert(vector<int> {x}); 14 break; 15 } 16 set<vector<int>> temp; 17 if(!__candidates(cand, left, temp)) continue; 18 for(auto y : temp) { //这里使用&, 推断出来的是const vector<int> & 19 y.push_back(x); 20 sort(y.begin(), y.end()); 21 prev.insert(y); 22 } 23 } 24 record[target] = prev; 25 return prev.size(); 26 } 27 28 void dfs(vector<int> &candidates, int target, vector<vector<int>> &ans, 29 vector<int> &buf, int index) { 30 if(target < 0) return; 31 if(0 == target) { 32 ans.push_back(buf); 33 return; 34 } 35 36 if(index == candidates.size()) return; 37 38 buf.push_back(candidates[index]); 39 dfs(candidates, target - candidates[index], ans, buf, index); 40 buf.pop_back(); 41 42 dfs(candidates, target, ans, buf, index + 1); 43 return; 44 } 45 46 vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) { 47 //状态定义简单:两种选择,选当前数字;不选当前数字。 48 //根据最终的target == 0, 决定是否压入结果; 49 //注意点就是:注意buf 在选/不选 对应的状态; 50 vector<vector<int>> ans; 51 vector<int> buf; 52 dfs(candidates, target, ans, buf, 0); 53 return ans; 54 //这种方式定义的状态,没有顺序关系,后续需要去重整理,导致时间过长 55 // sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end()); 56 // vector<vector<int>> ans; 57 // set<vector<int>> ret; 58 // __candidates(candidates, target, ret); 59 // 60 // for(auto &x : ret) ans.push_back(x); 61 // return ans; 62 } 63 };
51. N 皇后 : 再来个与上面39 类似题目,以及搜索减枝的优化;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int dir[8][2] = { 1, 0, -1, 1, -1, 0, -1, -1, 4 -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; 5 void transform(vector<string> &buf, int x, int y) { 6 int n = buf.size(); 7 for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++) { 8 int x_nxt = x + dir[k][0], y_nxt = y + dir[k][1]; 9 while(x_nxt >= 0 && x_nxt < n && y_nxt >= 0 && y_nxt < n) { 10 buf[x_nxt][y_nxt] += 1; 11 x_nxt += dir[k][0]; 12 y_nxt += dir[k][1]; 13 } 14 } 15 return; 16 } 17 18 void revert(vector<string> &buf, int x, int y) { 19 int n = buf.size(); 20 for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++) { 21 int x_nxt = x + dir[k][0], y_nxt = y + dir[k][1]; 22 while(x_nxt >= 0 && x_nxt < n && y_nxt >= 0 && y_nxt < n) { 23 buf[x_nxt][y_nxt] -= 1; 24 x_nxt += dir[k][0]; 25 y_nxt += dir[k][1]; 26 } 27 } 28 return; 29 } 30 31 void dfs(vector<vector<string>> &ans, vector<string> &buf, int n, int x, int y) { 32 if(0 == n) { 33 ans.push_back(buf); 34 return; 35 } 36 int len = buf.size(); 37 // for(int i = x; i < len; i++) { //搜索减枝,每行必须要有个Q 38 for(int i = x; i <= x; i++) { //搜索减枝,每行必须要有个Q 39 for(int j = y; j < len; j++) { 40 if(buf[i][j] != '0') continue; 41 transform(buf, i, j); 42 buf[i][j] = 'Q'; 43 dfs(ans, buf, n - 1, i + 1, 0); 44 revert(buf, i, j); 45 buf[i][j] = '0'; 46 } 47 } 48 return; 49 } 50 51 vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { 52 vector<vector<string>> ans; 53 vector<string> buf(n,string(n, '0')); 54 dfs(ans, buf, n, 0, 0); 55 56 for(auto &x : ans) { 57 for(auto &y : x) { 58 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 59 if('Q' == y[i] ) continue; 60 y[i] = '.'; 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 return ans; 65 } 66 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号